
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1858531
고고도 의사 위성 시장(2025-2035년)Global High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
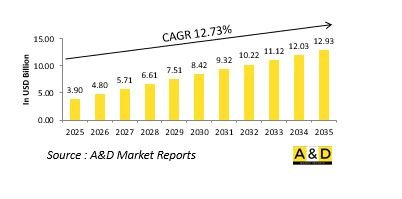
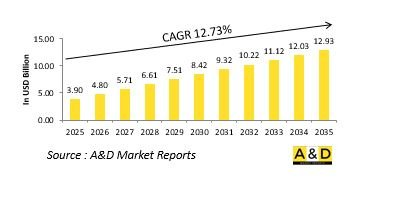
세계의 고고도 의사 위성 시장 규모는 2025년에 39억 달러로 추정되며, 2035년까지 129억 3,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측되고 있으며, 예측 기간인 2025-2035년 연평균 성장률(CAGR)은 12.73%로 전망되고 있습니다.
세계 고고도 의사 위성 시장 소개
국방용 고고도 의사 위성(HAPS) 시장은 지속적인 공중 감시, 통신 및 정보 수집 시스템 분야에서 새롭게 부상하는 영역입니다. 드론과 인공위성의 중간에 위치한 HAPS 플랫폼은 성층권에서 운영되며, 궤도위성처럼 고비용을 들이지 않고도 전략지역을 장기간 지속적으로 감시할 수 있습니다. 국방 기관은 네트워크 중심 전쟁과 멀티 도메인 작전의 중요한 요소로서 이 시스템을 점점 더 많이 연구하고 있습니다. 유연한 배치, 빠른 이동성, 기존 우주 기반 자산에 비해 낮은 유지보수 비용을 제공합니다. 실시간 상황 인식, 국경 감시, 탄력적인 통신 인프라에 대한 수요가 증가함에 따라 HAPS 플랫폼은 현대의 국방 생태계에 필수적인 요소로 자리 잡고 있습니다. HAPS의 안정적인 비행 프로파일을 유지하면서 기상 시스템 상공에서 운용할 수 있는 능력은 평시 감시 및 전투 지원 활동 모두에 전략적인 자산이 되고 있습니다.
고고도 의사 위성 시장에서 기술의 영향:
기술의 발전은 HAPS 시스템의 가능성을 재정의하고, 멀티미션 방어 자산으로 변모시키고 있습니다. 경량 복합재료, 태양전지 추진, 자율비행 제어, 에너지 저장 등의 기술 혁신으로 비행 내구시간을 연장하고 운영비용을 절감할 수 있게 되었습니다. 전기 광학, 적외선, 레이더 시스템을 포함한 첨단 센서 페이로드를 통합하여 정찰 능력과 정보 수집 능력을 강화했습니다. AI를 활용한 탑재 데이터 분석을 통해 실시간 위협 감지 및 적응형 임무 계획이 가능하며, 보안 통신 링크를 통해 방어 네트워크 간 원활한 데이터 전송을 보장합니다. 5G와 위성통신 기술의 융합은 분쟁 환경에서 공중 중계 노드로서의 역할을 더욱 강화할 것입니다. 기술의 발전에 따라 HAPS는 우주 자산과 전술 무인 항공기 시스템 간의 격차를 해소하는 고내구성 플랫폼으로 점점 더 자리매김하고 있습니다.
고고도 의사 위성 시장의 주요 촉진요인:
몇 가지 전략적 요인이 국방 활동에서 HAPS의 채택을 촉진하고 있습니다. 특히 국경 보안과 해상 감시의 경우, 광범위한 지역에 대한 지속적인 정보, 감시, 정찰의 필요성이 증가하고 있는 것이 주요 동기입니다. 방위군은 기존 위성을 대체할 수 있는 비용 효율적인 대안을 찾고 있으며, 신속한 배치와 임무의 유연성을 제공할 수 있는 대안을 찾고 있습니다. 도메인 간 원활한 데이터 연결이 중요한 네트워크 중심 전략의 비중이 높아지고 있는 것도 HAPS 기반 통신 중계에 대한 관심을 높이고 있습니다. 또한 저배출 및 태양전지를 동력원으로 하는 플랫폼으로의 전환은 지속가능성 목표에 부합하는 동시에 운영 내구성을 연장하는 것이기도 합니다. 지정학적 긴장이 고조되고 전자전 시나리오에서 탄력적인 통신 인프라에 대한 요구가 증가함에 따라 국방 기관이 이러한 시스템에 투자하는 것을 더욱 촉진하고 있습니다. 이러한 요소들이 결합되어 HAPS는 차세대 국방 전략에 필수적인 존재가 되었습니다.
고고도 인공위성 시장의 지역별 동향 :
국방 HAPS 시장의 지역 역학은 전략적 우선순위, 산업 역량, 국방 현대화 계획의 차이에 따라 형성됩니다. 북미에서는 상황 통제력을 높이기 위해 HAPS를 보다 광범위한 지휘통제 아키텍처에 통합하는 데 중점을 두고 개발이 진행되고 있습니다. 유럽 국가들은 기존 우주 시스템에 대한 의존도를 낮추기 위해 주권과 공동 연구 구상을 중시하고 있습니다. 아시아태평양에서는 국경 간 긴장이 고조되고 해양 안보 문제가 대두되면서 HAPS 개발에 대한 투자가 가속화되고 있습니다. 중동 국가들은 혹독한 기후 조건 하에서 지속적인 국경 감시 및 대테러 활동을 위해 이러한 시스템을 모색하고 있습니다. 한편, 라틴아메리카와 아프리카의 신흥 방위 산업은 제한된 위성 액세스를 보완할 수 있는 비용 효율적인 감시 솔루션으로 HAPS를 주목하고 있습니다. 전반적으로 지역 전략은 HAPS가 국방 정보 및 통신 인프라에 필수적인 계층이라는 인식이 높아진 것을 반영합니다.
주요 고고도 의사 위성 프로그램
인도 해군은 벵갈루루에 본사를 둔 NewSpace Research and Technologies(NRT)와 고고도 의사 위성(HAPS) 설계 및 개발 계약을 체결했습니다. 이번 계약은 iDEX(Innovations for Defence Excellence) 구상에 해당하며, 해군의 장거리 감시 능력을 향상시키는 것을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 지난해 12월, NRT는 태양전지를 동력원으로 하는 장기 내구형 HAPS가 21시간의 첫 비행에 성공했다고 발표했습니다. iDEX 프로그램에 따라 이 회사는 현재 48시간 이상의 태양전지 비행을 목표로 하는 개념증명 비행체 개발에 매진하고 있습니다. NRT의 CEO이자 전 공군 조종사 출신인 사미르 조시(Samir Joshi)는 X에서 프로토타입이 동짓날인 12월 22일에 시험 비행을 실시하여 이 이정표를 달성했다고 밝혔습니다.
목차
고고도 의사 위성 시장 - 목차
고고도 의사 위성 시장 보고서의 정의
고고도 의사 위성 시장 세분화
지역별
용도별
추진력별
향후 10년간 고고도 의사 위성 시장 분석
이 장에서는 10년간 고고도 의사 위성 시장 분석에 의해 고고도 의사 위성 시장의 성장, 변화하는 동향, 기술 채택의 개요 및 전체적인 시장의 매력에 대해 상세한 개요가 제공됩니다.
고고도 의사 위성 시장의 시장 기술
이 부문에서는 이 시장에 영향을 미칠 것으로 예상되는 상위 10개의 기술과 이러한 기술이 시장 전체에 미칠 가능성이 있는 영향에 대해 설명합니다.
세계의 고고도 의사 위성 시장 예측
이 시장의 10년간 고고도 의사 위성 시장 예측은 상기 부문에서 상세하게 다루어지고 있습니다.
지역별 고고도 의사 위성 시장 동향과 예측
이 부문에서는 지역별 고고도 의사 위성 시장의 동향, 촉진요인, 제약 요인, 과제, 그리고 정치, 경제, 사회, 기술이라는 측면을 다루고 있습니다. 또한 지역별 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석도 상세하게 다루고 있습니다. 지역 분석의 최종 단계에서는 주요 기업의 프로파일링, 공급업체의 상황, 기업 벤치마킹 등에 대해 분석하고 있습니다. 현재 시장 규모는 일반 시나리오에 기반하여 추정되고 있습니다.
북미
촉진요인, 억제요인, 과제
PEST
시장 예측과 시나리오 분석
주요 기업
공급업체 계층의 상황
기업 벤치마킹
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
고고도 의사 위성 시장의 국가별 분석
이 장에서는 이 시장의 주요 방위 프로그램을 다루며, 이 시장에서 신청된 최신 뉴스 및 특허에 대해서도 해설합니다. 또한 국가 레벨의 10년간 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석에 대해서도 해설합니다.
미국
방위 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
이 시장에서의 현재 기술 성숙도
시장 예측과 시나리오 분석
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카공화국
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
고고도 의사 위성 시장 기회 매트릭스
기회 매트릭스는 독자가 이 시장에서 기회가 높은 부문을 이해하는데 도움이 됩니다.
고고도 의사 위성 시장 보고서에 관한 전문가의 의견
이 시장의 가능성 있는 분석에 관한 당사 전문가의 의견을 전해드립니다.
결론
항공·방위 시장 보고서 소개
KSA 25.11.14The global High Altitude Pseudo Satellite market is estimated at USD 3.90 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 12.93 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.73% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
Introduction to Global High Altitude Pseudo Satellites market:
The defense High Altitude Pseudo Satellites (HAPS) market represents an evolving frontier in persistent aerial surveillance, communication, and intelligence-gathering systems. Positioned between drones and satellites, HAPS platforms operate in the stratosphere, enabling continuous monitoring over strategic regions for extended durations without the high costs of orbital satellites. Defense agencies are increasingly exploring these systems as a critical component of network-centric warfare and multi-domain operations. They offer flexible deployment, rapid mobility, and low maintenance compared to traditional space-based assets. With increasing demand for real-time situational awareness, border monitoring, and resilient communication infrastructure, HAPS platforms are becoming vital for modern defense ecosystems. Their ability to operate above weather systems while maintaining stable flight profiles makes them a strategic asset for both peacetime surveillance and combat support operations
Technology Impact in High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market:
Technological advancements are redefining the potential of HAPS systems, transforming them into multi-mission defense assets. Innovations in lightweight composite materials, solar propulsion, autonomous flight control, and energy storage have extended flight endurance and reduced operational costs. The integration of advanced sensor payloads, including electro-optical, infrared, and radar systems, has enhanced their reconnaissance and intelligence-gathering capabilities. AI-driven onboard data analytics enable real-time threat detection and adaptive mission planning, while secure communication links ensure seamless data transfer across defense networks. The convergence of 5G and satellite communication technologies further strengthens their role as aerial relay nodes in contested environments. As technology evolves, HAPS are increasingly positioned as high-resilience platforms bridging the gap between space assets and tactical unmanned aerial systems.
Key Drivers in High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market:
Several strategic factors are driving the adoption of HAPS in defense operations. The growing need for persistent intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance over wide areas is a primary motivator, particularly in border security and maritime monitoring. Defense forces seek cost-effective alternatives to traditional satellites that offer quicker deployment and greater mission flexibility. The rising emphasis on network-centric operations, where seamless data connectivity across domains is critical, also fuels interest in HAPS-based communication relays. Additionally, the shift toward low-emission and solar-powered platforms aligns with sustainability goals while offering extended operational endurance. Heightened geopolitical tensions and the demand for resilient communication infrastructure during electronic warfare scenarios further push defense agencies to invest in these systems. Collectively, these drivers are positioning HAPS as essential enablers of next-generation defense strategies.
Regional Trends in High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market:
Regional dynamics in the defense HAPS market are shaped by differing strategic priorities, industrial capabilities, and defense modernization programs. In North America, development is focused on integrating HAPS into broader command and control architectures to enhance situational dominance. European nations are emphasizing sovereignty and joint research initiatives to reduce reliance on traditional space systems. In the Asia-Pacific region, rising border tensions and maritime security challenges are accelerating investments in indigenous HAPS development. Middle Eastern countries are exploring these systems for persistent border surveillance and counterterrorism operations under harsh climatic conditions. Meanwhile, emerging defense industries in Latin America and Africa are viewing HAPS as cost-effective surveillance solutions that can compensate for limited satellite access. Overall, regional strategies reflect a growing recognition of HAPS as an indispensable layer in defense intelligence and communications infrastructure.
Key High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Program:
The Indian Navy has signed a contract with Bengaluru-based NewSpace Research and Technologies (NRT) for the design and development of a High Altitude Pseudo Satellite (HAPS). This agreement falls under the Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) initiative and aims to boost the Navy's long-range surveillance capabilities. In December last year, NRT announced that its solar-powered, long-endurance HAPS successfully completed its first 21-hour flight. Under the iDEX programme, the company is now working on a proof-of-concept demonstrator targeting solar-powered flights exceeding 48 hours. NRT's CEO and former Air Force pilot, Sameer Joshi, shared on X that the prototype achieved this milestone during a test flight on December 22, the Winter Solstice-the shortest day of the year-posing the toughest endurance conditions for a solar-powered UAV.
Table of Contents
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market - Table of Contents
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Report Definition
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Segmentation
By Region
By Application
By Propulsion
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year high altitude pseudo satellites market analysis would give a detailed overview of high altitude pseudo satellites market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Forecast
The 10-year high altitude pseudo satellites market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Trends & Forecast
The regional high altitude pseudo satellites market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.












