
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1904991
방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장(2026-2036년)Global Defense Multirotor Drone Market 2026-2036 |
||||||
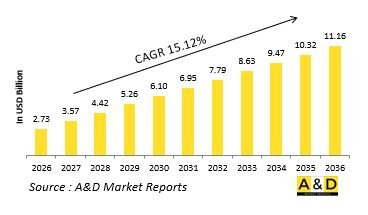
세계의 방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장 규모는 2026년 27억 3,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 2026-2036년의 예측 기간 동안 CAGR은 15.12%를 나타낼것으로 보이며, 2036년에는 111억 6,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 전망됩니다.

방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장 개요 :
세계의 방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장은 다중 로터로 특징지어지는 수직 이착륙(VTOL) 무인 항공 시스템을 포괄하며, 제한된 공간에서 탁월한 호버링 안정성, 기동성 및 운영 유연성을 제공합니다. 이러한 플랫폼은 소규모 부대 수준에서 즉각적이고 지역화된 정보, 감시 및 정찰(ISR) 능력을 제공함으로써 전술적 군사 작전을 혁신했습니다. 고정익 드론과 달리 멀티로터 시스템은 도시 환경, 건물 내부, 발사 인프라 없이도 사실상 모든 배치 지점에서 효과적으로 운용될 수 있습니다. 그 적용 범위는 기본 정찰에서 표적 지정, 통신 중계, 전자전, 물자 보급, 부대 보호 등으로 확대되었습니다. 점점 더 고도화되는 상업용 드론 기술의 확산은 군사적 채택을 가속화하는 동시에 새로운 비대칭적 위협을 창출하여, 향상된 성능, 보안성, 내구성을 갖춘 군용 등급 멀티로터 시스템의 개발을 촉진하고 있습니다.
방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장의 기술적 영향 :
멀티로터 드론 기술의 진화는 자율성, 지속 비행 능력, 탑재체 통합을 중심으로 이루어집니다. 고급 비행 제어 알고리즘은 열악한 시각 환경과 강풍 조건에서도 안정적인 작동을 가능하게 합니다. 인공지능 기반 장애물 회피 및 항법 시스템은 지속적인 조종사 개입 없이도 복잡한 도시 지형에서 작전을 수행할 수 있게 합니다. 배터리와 소형 내연 기관 또는 연료 전지를 결합한 하이브리드 동력 시스템은 일반적인 전기 전용 시스템의 한계를 크게 뛰어넘는 비행 시간을 제공합니다. 센서 패키지의 소형화로 고해상도 전기광학 장비, 열화상 카메라, 레이저 표적 지시기, 신호 정보 수집 장비를 소형 플랫폼에 통합할 수 있게 되었습니다. 군집 협동 기술은 여러 드론이 공동 임무를 수행하도록 합니다. 방해 방지 기능을 갖춘 안전한 디지털 데이터 링크는 명령 및 영상 전송이 가로채거나 방해받는 것을 방지합니다. 이러한 발전은 멀티로터 드론을 원격 조종 카메라에서 지능적이고 지속적이며 다목적 전술 자산으로 변화시키고 있습니다.
방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장의 주요 촉진요인 :
전술 수준에서 항공 감시의 대중화는 근본적인 시장 촉진요인으로 작용하며, 기존 플랫폼 기반 능력을 보병 분대에게 직접 제공합니다. 비대칭 전쟁 및 반군 진압 작전은 대형 항공기에 의존하지 않고 즉각적인 상공 관측을 지속적으로 요구합니다. 도시전 확산은 고정익 플랫폼이 효과적이지 않은 복잡한 3차원 환경에서 운용 가능한 시스템을 필요로 합니다. 부대 보호 요구사항은 인원의 위협 노출을 줄이는 경계 감시 및 정찰 드론 도입을 촉진합니다. 대(對)드론 임무 필요성은 적대적 드론을 무력화할 수 있는 요격용 멀티로터 시스템 개발을 촉진합니다. 또한 상업 기술 발전은 유능한 시스템 개발 장벽을 지속적으로 낮추는 동시에, 경쟁 환경을 위한 강화된 보안 및 견고성을 갖춘 군용 특화 솔루션에 대한 시급성을 창출합니다.
방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장의 지역별 동향 :
지역별 도입 패턴은 서로 다른 작전 우선순위, 위협 환경 및 산업적 접근 방식을 반영합니다. 북미 개발은 기존 전장 관리 인프라와 통합된 안전한 네트워크 시스템을 중시합니다. 유럽 프로그램은 데이터 보호 및 규제 준수에 강한 중점을 둔 모듈식, 임무 구성 가능 드론에 초점을 맞춥니다. 아시아-태평양 지역은 특히 빠른 도입 속도를 보이며, 첨단 군사 시스템과 상업용 파생 드론의 대규모 조달을 통한 광범위한 배치가 이루어지고 있습니다. 중동 분쟁 지역은 다회전 전투 응용 부문의 시험장이 되어 공격 및 방어 시스템 모두에서 혁신을 주도하고 있습니다. 아프리카 국가들은 인프라 제약으로 수직 이착륙(VTOL) 시스템이 유리한 국경 감시 및 평화 유지 임무에 다회전 드론을 점점 더 많이 활용하고 있습니다. 전 세계적으로 상업용과 군용 드론 기술의 경계는 계속 모호해지고 있으며, 이중용도 시스템이 분쟁 및 보안 응용 부문 전반에 걸쳐 확산되고 있습니다.
본 보고서에서는 세계의 방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장을 조사했으며, 시장 배경, 시장 영향요인 분석, 시장 규모 추이와 예측, 각종 구분, 지역별 상세 분석 등을 정리했습니다.
목차
방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장 : 보고서 정의
방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장 : 세분화
지역별
용도별
범위별
향후 10년간 방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장 분석
시장 성장, 변화하는 동향, 기술 채택 개요, 전반적인 시장 매력
방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장 : 기술
상위 10 기술과 시장 전체에 미치는 영향
세계의 방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장 : 예측
방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장 : 지역별 동향 및 예측
지역별 시장 동향, 촉진요인, 억제요인, 과제, PEST 분석, 지역별 시장 예측, 시나리오 분석, 주요 기업 프로파일링, 공급자 상황, 기업 벤치마킹
북미
촉진요인, 억제요인, 과제
PEST
시장 예측 및 시나리오 분석
주요 기업
공급자 계층 구조 상태
기업 벤치마킹
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장 : 국가별 분석
주요 방위 프로그램, 최신 뉴스, 특허, 국가 수준의 10개년 예측, 시나리오 분석
미국
방위 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
이 시장의 현재 기술 성숙도
시장 예측 및 시나리오 분석
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장 : 기회 매트릭스
방위용 멀티로터 드론 시장 : 보고서에 대한 전문가 의견
결론
항공 및 방위 시장 보고서에 대해서
HBR 26.01.20The Global Defense Multirotor Drone market is estimated at USD 2.73 billion in 2026, projected to grow to USD 11.16 billion by 2036 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 15.12% over the forecast period 2026-2036.
Introduction to Defense Multirotor Drone Market:
The Global Defense Multirotor Drone Market encompasses vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) unmanned aerial systems characterized by multiple rotors, offering exceptional hover stability, maneuverability, and operational flexibility in confined spaces. These platforms have transformed tactical military operations by providing immediate, localized intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities at the small unit level. Unlike fixed-wing drones, multirotor systems can operate effectively in urban environments, inside structures, and from virtually any deployment point without launch infrastructure. Their applications have expanded from basic reconnaissance to include target designation, communications relay, electronic warfare, logistics resupply, and force protection. The proliferation of increasingly capable commercial drone technology has both accelerated military adoption and created new asymmetric threats, driving corresponding development of military-grade multirotor systems with enhanced performance, security, and durability.
Technology Impact in Defense Multirotor Drone Market:
Technological evolution in multirotor drones centers on autonomy, endurance, and payload integration. Advanced flight control algorithms enable stable operation in degraded visual environments and high wind conditions. Artificial intelligence-powered obstacle avoidance and navigation systems allow operation in complex urban terrain without continuous pilot intervention. Hybrid power systems combining batteries with miniature internal combustion engines or fuel cells significantly extend flight durations beyond typical electric-only limitations. Miniaturization of sensor packages enables integration of high-resolution electro-optics, thermal imagers, laser designators, and signal intelligence collectors on small platforms. Swarm coordination technology allows multiple drones to operate collaboratively on shared missions. Secure digital data links with anti-jamming features protect command and video feeds from interception or disruption. These advancements are transforming multirotor drones from remotely piloted cameras into intelligent, persistent, multi-role tactical assets.
Key Drivers in Defense Multirotor Drone Market:
The democratization of aerial surveillance at the tactical level represents the fundamental market driver, putting previously platform-based capabilities directly in infantry squads' hands. Asymmetric warfare and counter-insurgency operations create persistent demand for immediate overhead observation without relying on larger, less responsive aircraft. Urban warfare proliferation necessitates systems capable of operating in complex three-dimensional environments where fixed-wing platforms are ineffective. Force protection requirements drive adoption of perimeter surveillance and inspection drones that reduce personnel exposure to threats. Counter-drone mission needs spur development of interceptor multirotor systems capable of neutralizing hostile drones. Additionally, commercial technology advancement continuously lowers barriers to capable system development while creating urgency for military-specific solutions with enhanced security and robustness for contested environments.
Regional Trends in Defense Multirotor Drone Market:
Regional adoption patterns reflect differing operational priorities, threat environments, and industrial approaches. North American development emphasizes secure, networked systems integrated with existing battlefield management infrastructure. European programs focus on modular, mission-configurable drones with strong emphasis on data protection and regulatory compliance. The Asia-Pacific region shows particularly rapid adoption, with both advanced military systems and large-scale procurement of commercial-derived drones for widespread deployment. Middle Eastern conflict zones have become proving grounds for multirotor combat applications, driving innovation in both offensive and defensive systems. African nations increasingly employ multirotor drones for border surveillance and peacekeeping missions where infrastructure limitations favor VTOL systems. Globally, the line between commercial and military drone technology continues to blur, with dual-use systems proliferating across conflict and security applications.
Key Defense Multirotor Drone Program:
India-based unmanned systems manufacturer ideaForge Technology Ltd has received a supply order valued at approximately ₹100 crore from the Indian Army for its next-generation tactical unmanned platforms, including the Zolt unmanned aerial vehicle and the all-terrain vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) drone, SWITCH 2. The order represents a significant endorsement of indigenous drone capabilities developed for military applications. The procurement includes a capital emergency acquisition for the Zolt platform, estimated at around ₹75 crore, following a comprehensive evaluation process. The system underwent rigorous field trials in electronic warfare environments and was subjected to strict country-of-origin verification requirements before approval. In addition, the SWITCH 2 system has been ordered under a separate contract valued at approximately ₹30 crore. Both platforms were officially unveiled by ideaForge at the Aero India exhibition held earlier this year in Bengaluru. The Zolt UAV is designed as a multi-mission platform, offering extended-range intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance capabilities, along with precision payload delivery. It is optimized for contemporary military operations, emphasizing autonomy, endurance, and resilience in contested environments. The SWITCH 2 drone, already operational with the Indian Army, has been battle-tested and is currently deployed for ISR missions, reinforcing its reliability and operational maturity.
Table of Contents
Defense Multirotor Drone Market Report Definition
Defense Multirotor Drone Market Segmentation
By Region
By Application
By Range
Defense Multirotor Drone Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year Defense Multirotor Drone Market analysis would give a detailed overview of Defense Multirotor Drone Market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Defense Multirotor Drone Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Defense Multirotor Drone Market Forecast
The 10-year Defense Multirotor Drone Market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Defense Multirotor Drone Market Trends & Forecast
The regional Defense Multirotor Drone Market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Defense Multirotor Drone Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Defense Multirotor Drone Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Defense Multirotor Drone Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.


















