
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1706587
마이크로드론 시장(2025-2035년)Global Microdrones Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
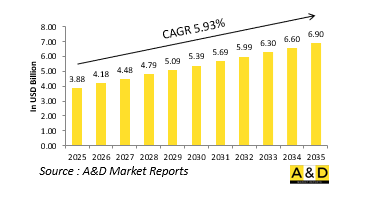
세계의 마이크로드론 시장 규모는 2025년 38억 8,000만 달러로 추정됩니다. 2035년까지 69억 달러로 성장할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간의 2025-2035년 연간 평균 성장률(CAGR)은 5.93%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

마이크로드론 시장 서론
군용 마이크로드론은 무인 항공기 시스템 중에서 가장 작은 계층으로 분류되는 경우가 많으며, 방위 기술의 틈새 분야에서 급속히 성장하고 있습니다. 혹은 포켓 사이즈로 설계된 이러한 드론은 기존의 UAV나 소형 드론에서도 너무 크거나 검출할 수 없는 환경에서의 근거리 정찰, 전술적 감시, 상황 인식용으로 조조 정돈되어 있습니다. 컴팩트한 크기, 눈에 띄지 않는 조작, 배치의 용이함에 의해 시가전, 특수 작전, 대반란, 국경 경비의 임무에 독자적으로 적합합니다. 마음은 실내 환경, 밀림, 터널 네트워크 또는 복잡한 도시 지형과 같은 시선이 제한되고 기동성이 중요한, 매우 다툼하거나 지저분한 공간에서의 운영 능력에서 유래합니다. 작음에도 불구하고 고해상도 카메라, 열 센서, 심지어 경량의 전자전 페이로드를 탑재할 수 있게 되어 있습니다. 로드론은 군인의 감각을 연장하고 위협에 노출을 최소화하면서 작전 인식을 강화합니다. 현대 전장이 더욱 분산되고 다차원화됨에 따라 마이크로드론은 전술적 지 오퍼레이션에 불가결한 것이 되고 있습니다.마이크로드론은 인간의 한계와 전장 인텔리전스와의 갭을 메우고, 대원을 위험에 노출시키지 않고, 구석, 옥상, 잠재적인 매복 포인트를 스캔하는 것을 가능하게 합니다.
마이크로드론 시장 기술의 영향
기술은 군용 마이크로드론의 설계, 능력, 배치에 큰 변화를 촉진하고 있습니다. 소형화된 구성 요소의 개발이 가장 중요한 요인 중 하나가 되고 있습니다. 큰 진보의 하나는 센서 기술입니다.최신의 마이크로드론에는 이전에는 이러한 소형 플랫폼에는 너무 크거나, 전력 소비가 너무 많았던 멀티 스펙트럼 센서, 나이트 비전, 적외선 화상 시스템이 탑재되게 되었습니다.
인공지능과 온보드 프로세싱은 마이크로드론의 자율성을 재정의합니다. 위험한 복잡한 지형에서는 특히 가치가 있습니다. 또한 통신과 데이터의 암호화도 대폭 개선되었습니다.
스웜밍 알고리즘의 통합은 마이크로드론의 능력에서 최첨단 도약을 의미합니다. 리어 거부 전략을 위해 연구되었습니다.마지막으로 재료 과학은 이러한 플랫폼의 탄력성과 경량화에 기여합니다.
마이크로드론 시장 주요 성장 촉진요인 :
세계의 군용 마이크로드론 상승을 뒷받침하고 있는 주요 요인은 우선, 분대 레벨에서의 상황 인식 강화의 필요성입니다. 알타임의 데이터가 필요합니다.마이크로드론은 복잡한 인프라나 전문적인 훈련을 필요로 하지 않고, 그 능력을 제공합니다.시가전과 근접 전투도 강력한 추진력입니다., 효과적인 조종을 할 수 없는 경우가 있습니다. 한편, 마이크로드론은 건물에 들어가, 방을 스캔해, 병사가 들어가기 전에 위협을 평가할 수가 있습니다. 위협이 점점 더 확산되고 있습니다. 마이크로드론은 부대를 불필요한 위험에 노출시키지 않고 정확한 정찰을 수행함으로써 이러한 위협을 무력화하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
저비용으로 신속한 전개가 가능한 ISR 솔루션에 대한 수요도 또 하나의 중요한 요인입니다. 이 비용 효율성은 중간 규모 또는 예산에 억제요인이 있는 군라도 광범위한 채용을 가능하게 합니다. 게다가 전 세계의 국방 근대화 이니셔티브는 디지털화, 부대의 기동성, 네트워크 중심 전쟁에 중점을 두고 있습니다.
마이크로드론 시장 지역 동향 :
세계의 군용 마이크로드론 상황은 특정 작전 요구, 기술 인프라, 전략적 우선순위에 따라 지역별로 독특한 진화를 이루고 있습니다.
북미에서는 미국 국방부가 분대 수준에서 정찰 능력을 강화하기 위해 FLIR Black Hornet과 같은 마이크로드론을 배치한 Solder Borne Sensor(SBS) initiative와 같은 프로그램을 통해 개발을 주도하고 있습니다. 수행에도 투자하고 있습니다.미국 특수 작전 사령부와 육군 미래 사령부는 멀티 도메인 작전에 있어서의 마이크로드론의 이용을 모색하고 있어, 특히 시가지의 분쟁 지역이나 전자전 환경에서의 이용을 검토하고 있습니다.
유럽은 원정 작전과 국토 안보에 중점을 두고 있으며, 마이크로드론의 능력을 도입하고 있습니다. FLIR(영국/노르웨이)과 같은 기업이 자체 솔루션을 제공하고 있으며, EU는 또한 드론의 혁신과 회원국 간의 상호 운용성을 위한 공유 표준을 지원하기 위해 국경을 넘는 연구 개발 프로그램에 자금을 제공합니다.
아시아태평양에서는 영토 분쟁과 국경의 긴장이 높아지고 있으며, 급속한 보급이 진행되고 있습니다. 한편, 인도는 「메이크 인 인디아」방위 제조 이니셔티브 아래, 특히 실력 통제선(LAC)을 따라 등 산악 지대나 반란 환경에서의 작전용으로, 마이크로드론의 조달을 가속시키고 있습니다.
주요 마이크로드론 프로그램
미국 특수 작전 사령부(SOCOM)는 복수의 도메인, 특히 공중과 수중의 양쪽 모두에서 동작할 수 있는 마이크로드론을 요구하고 있습니다. 수술 및 물류 부서가 발행한 특별 통지에서는 테스트에 적합한 그룹 1 무인 항공기 시스템(UAS)의 식별을 지원하기 위해 업계 피드백을 모집했습니다.
본 보고서에서는 세계의 마이크로드론 시장에 대해 조사했으며, 10년간의 부문별 시장 예측, 기술 동향, 기회 분석, 기업 프로파일, 국가별 데이터 등을 정리했습니다.
목차
마이크로드론 시장 보고서 정의
마이크로드론 시장 세분화
유형별
지역별
최종 사용자별
향후 10년간 마이크로드론 시장 분석
이 장에서는 10년간의 마이크로드론 시장 분석을 통해 마이크로드론 시장의 성장, 변화하는 추세, 기술 채택의 개요, 전체 시장의 매력에 대한 자세한 개요를 제공합니다.
마이크로드론 시장 기술
이 부문에서는 이 시장에 영향을 미칠 것으로 예상되는 상위 10개 기술과 이러한 기술이 시장 전체에 미칠 수 있는 영향에 대해 설명합니다.
세계의 마이크로드론 시장 예측
이 시장의 10년간의 마이크로드론 시장 예측은 위의 전체 부문에서 상세하게 다루어졌습니다.
지역별 마이크로드론 시장 동향과 예측
이 부문에서는 지역별 마이크로드론 시장 동향, 성장 촉진요인, 성장 억제요인, 과제, 그리고 정치, 경제, 사회, 기술 등의 측면을 망라하고 있습니다. 또한 지역별 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석도 상세 지역 분석의 마지막은 주요 기업프로파일 링, 공급업체의 상황, 기업 벤치 마크를 포함하고 있습니다.
북미
성장 촉진요인, 성장 억제요인, 과제
PEST
시장 예측 및 시나리오 분석
주요 기업
공급업체 계층의 상황
기업 벤치마킹
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
마이크로드론 시장의 국가별 분석
이 장에서는 이 시장에서 주요 방위 프로그램을 다루며 이 시장에서 신청된 최신 뉴스와 특허에 대해서도 설명하고, 국가 수준의 10년간 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석에 대해서도 설명합니다.
미국
방위 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
이 시장의 현재 기술 성숙도
시장 예측 및 시나리오 분석
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
마이크로드론 시장 기회 매트릭스
마이크로드론 시장 보고서에 대한 전문가의 의견
결론
항공 및 방위 시장 보고서에 대해서
KTH 25.04.28The Global Microdrones market is estimated at USD 3.88 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 6.90 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.93% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
Introduction to Microdrones Market:
Military microdrones, often classified as the smallest tier within unmanned aerial systems, represent a rapidly growing niche in defense technology. Generally weighing under 2 kg and designed to be man-portable or even pocket-sized, these drones are tailored for close-range reconnaissance, tactical surveillance, and situational awareness in environments where traditional UAVs or even small drones may be too large or detectable. Their compact size, discreet operation, and ease of deployment make them uniquely suited for urban warfare, special operations, counter-insurgency, and border security tasks. The global military interest in microdrones stems from their ability to operate in highly contested or cluttered spaces-indoor environments, dense forests, tunnel networks, or complex urban terrain-where line-of-sight is limited and maneuverability is crucial. Despite their small stature, microdrones are increasingly capable of carrying high-resolution cameras, thermal sensors, and even lightweight electronic warfare payloads. Used by infantry, SWAT teams, and reconnaissance units, they serve as an extension of the soldier's senses, offering enhanced operational awareness with minimal exposure to threat. As modern battlefields become more decentralized and multidimensional, microdrones are proving essential for tactical edge operations. They bridge the gap between human limitations and battlefield intelligence, enabling forces to scan corners, rooftops, and potential ambush points without endangering personnel. Their silent operation and real-time feedback make them invaluable for missions that demand speed, stealth, and precision.
Technology Impact in Microdrones Market:
Technology is driving a significant transformation in the design, capability, and deployment of military microdrones. One of the most crucial enablers has been the development of miniaturized components-from brushless motors and advanced lithium-polymer batteries to ultra-lightweight composite frames and compact sensors. These innovations allow for extended flight times, improved payload capacity, and enhanced durability in harsh conditions. One major advancement is in sensor technology. Modern microdrones are now equipped with multi-spectral sensors, night vision, and thermal imaging systems that were previously too large or power-hungry for such small platforms. These sensors offer 360-degree awareness and enable the drone to function effectively in complete darkness, smoke-filled areas, or during electronic interference.
Artificial intelligence and onboard processing are redefining autonomy in microdrone operations. Real-time object recognition, facial detection, threat classification, and autonomous navigation allow these drones to function with limited human input. AI enables microdrones to map environments, avoid obstacles, and even follow specific targets automatically. This is especially valuable in complex terrain where manual piloting is difficult or dangerous. Moreover, communications and data encryption have improved significantly. Microdrones now use secure, encrypted links to prevent interception and jamming. Some operate in mesh networks or relay mode, enabling multiple units to collaborate and share intelligence even in GPS-denied or signal-contested environments.
The integration of swarming algorithms marks a cutting-edge leap in microdrone capabilities. With swarm logic, groups of microdrones can autonomously coordinate movement, surround targets, or conduct simultaneous multi-angle surveillance. This is being explored for force multiplication, perimeter monitoring, and area denial strategies. Lastly, materials science has contributed to making these platforms more resilient and lightweight. Carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics and nano-coatings provide durability against environmental factors like sand, rain, and electromagnetic exposure-ensuring operational continuity in hostile conditions.
Key Drivers in Microdrones Market:
Several key factors are propelling the rise of military microdrones globally. First and foremost is the need for enhanced situational awareness at the squad level. Modern infantry operations require real-time data about immediate surroundings to avoid ambushes, navigate unfamiliar terrain, and detect hidden threats. Microdrones deliver that capability without requiring complex infrastructure or specialized training. Urban warfare and close-quarters combat are also strong drivers. In dense city environments or during counterterrorism operations, traditional UAVs are often too large or loud to maneuver effectively. Microdrones, on the other hand, can enter buildings, scan rooms, and assess threats before soldiers enter-effectively acting as remote eyes in tight spaces. Another major influence is the increasing prevalence of asymmetric threats, such as insurgent groups and non-state actors using guerrilla tactics or makeshift explosives. Microdrones help neutralize such threats by providing precise reconnaissance without exposing forces to unnecessary risk. In many cases, they are used to identify IED placements or hidden enemy positions in real time.
The demand for low-cost, rapidly deployable ISR solutions is another significant factor. Compared to larger drones or manned reconnaissance flights, microdrones are far more affordable and can be fielded in large numbers. This cost efficiency allows for wide-scale adoption, even by mid-sized or budget-constrained militaries. The ability to lose a drone without compromising mission success is critical in high-risk environments. Moreover, defense modernization initiatives across the globe are placing emphasis on digitization, force mobility, and network-centric warfare. Microdrones fit into this paradigm by serving as agile, data-generating platforms that can link seamlessly into command-and-control networks, mission planning software, and soldier systems.
Regional Trends in Microdrones Market:
The global military microdrone landscape is evolving uniquely across different regions based on specific operational needs, technological infrastructure, and strategic priorities.
In North America, the U.S. Department of Defense is leading development through programs like the Soldier Borne Sensor (SBS) initiative, which has deployed microdrones like the FLIR Black Hornet to enhance reconnaissance capabilities at the squad level. The Pentagon is also investing in swarm technologies and autonomous mission execution as part of the broader push for AI-enabled warfighting. U.S. Special Operations Command and the Army Futures Command are exploring microdrone use in multi-domain operations, particularly for contested urban zones and electronic warfare environments.
Europe is embracing microdrone capabilities in line with its focus on expeditionary operations and homeland security. NATO forces in the UK, France, and Norway have already integrated microdrones for tactical ISR, with companies like Parrot (France) and Teledyne FLIR (UK/Norway) offering indigenous solutions. The EU is also funding cross-border R&D programs to support drone innovation and shared standards for interoperability among member states.
In the Asia-Pacific region, rising territorial disputes and border tensions are pushing rapid adoption. China has heavily invested in microdrone swarms for reconnaissance and asymmetric attack purposes, often showcasing swarming drones in military exercises. Its strategy emphasizes overwhelming adversaries with low-cost, AI-coordinated assets. India, meanwhile, is accelerating its microdrone procurement under the "Make in India" defense manufacturing initiative, particularly for operations in mountainous and counterinsurgency environments such as along the Line of Actual Control (LAC). South Korea and Japan are also deploying microdrones as part of surveillance and homeland security modernization efforts.
Key Microdrones Program:
U.S. Special Operations Command (SOCOM) is seeking micro drones capable of operating across multiple domains, specifically in both aerial and underwater environments. The request comes from SOCOM's Program Management Office for Remote Capabilities, which is aiming to identify uncrewed systems for potential evaluation in the coming year. In a special notice issued , the acquisition, technology, and logistics division of SOCOM invited industry feedback to assist in identifying Group 1 uncrewed aerial systems (UAS) suitable for testing. Group 1 drones represent the smallest class of UAS currently utilized by the Department of Defense and are typically deployable from a variety of platforms.
Table of Contents
Microdrones Market Report Definition
Microdrones Market Segmentation
By Type
By Region
By End User
Microdrones Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year Microdrones Market analysis would give a detailed overview of Microdrones Market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Microdrones Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Microdrones Market Forecast
The 10-year Microdrones Market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Microdrones Market Trends & Forecast
The regional Microdrones Market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Microdrones Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Microdrones Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Microdrones Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.










