
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1716502
고전압 변전소 시장 기회, 성장 촉진 요인, 산업 동향 분석, 예측(2025-2034년)High Voltage Substation Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
고전압 변전소 세계 시장은 2024년에 357억 달러로 평가되었고 2025년부터 2034년에 걸쳐 CAGR 2.1%로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다.
도시 인구의 확대와 신흥 경제 국가의 급속한 산업화를 배경으로 전력 수요 증가가 이 시장의 성장을 견인하고 있습니다. 전송을 확보하기 위해 고전압 변전소를 포함한 효율적인 전력 인프라가 시급해지고 있습니다. 이에 대응하기 위해 전력 인프라에 대한 투자를 우선하고 있습니다. 뿐만 아니라 원격지에서의 재생 가능 에너지 프로젝트 증가로 견고한 송전 시스템이 필요해 고전압 변전소에 대한 수요가 높아지고 있습니다.

송전망의 근대화와 회복력이 중시되게 됨으로써, 고도의 변전소 기술 도입이 더욱 가속화되고 있습니다. 변동하는 에너지의 흐름을 처리하고 효율적인 배전을 확보할 수 있는 변전소의 업그레이드가 필요합니다. 그리드 자동화, 모니터링 및 제어 기능을 향상시키기 위한 스마트 그리드 이니셔티브가 부상하면서 첨단 디지털 변전소의 도입이 촉진되었습니다. 그러나 기존 변전소는 여전히 지배적인 부문이며, 2034년까지 412억 달러의 매출이 전망되고 있습니다. 이를 통해 예산에 제약이 있는 지역에서는 선호되는 옵션이 되고 있습니다. 이 변전소는 조작 및 유지 보수가 쉽고 전문적인 인력과 복잡한 인프라의 필요성을 줄이고, 이것이 더욱 보급에 기여하고 있습니다.
| 시장 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 시작 연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 연도 | 2025-2034년 |
| 시작 금액 | 357억 달러 |
| 예측 금액 | 447억 달러 |
| CAGR | 2.1% |
고전압 변전소 시장의 전기 시스템 부문은 신흥 경제 국가의 인프라 노후화에 견인되어 2034년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 1.7%로 성장할 것으로 예상되고 있습니다. 변압기, 개폐기, 차단기, 보호 시스템 등의 중요한 부품은 고전압 변전소의 효율과 안정성을 유지하는 데 필수적입니다. 따라서 효율적으로 전송하는 데 필수적입니다. 또한 재생 가능 에너지 프로젝트는 지리적으로 고립된 지역에 위치하는 경우가 많기 때문에 주요 송전망과 연결하기위한 효율적인 송전 솔루션이 필요하며 전기 시스템의 업그레이드 수요가 더욱 높아지고 있습니다.
미국의 고전압 변전소 시장은 2024년에 37억 달러를 창출했지만, 이것은 주로 시대 지연의 송전 인프라를 현대화하기 위한 지속적인 투자에 의한 것입니다. 업그레이드 및 장비 교환에 투자하고 있습니다. 현대화 이니셔티브는 전력망의 전반적인 효율성을 높이면서 전력 수요 증가에 대응하기 위해 전력 전송의 흐름을 강화하고 전력망의 신뢰성을 향상시키고 최첨단 기술을 도입하는 것을 목표로 하고 있습니다.
목차
제1장 조사 방법과 조사 범위
제2장 주요 요약
제3장 업계 인사이트
- 생태계 분석
- 규제 상황
- 업계에 미치는 영향요인
- 성장 촉진요인
- 업계의 잠재적 위험 및 과제
- 성장 가능성 분석
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- PESTEL 분석
제4장 경쟁 구도
- 전략 대시보드
- 혁신과 지속가능성의 전망
제5장 시장 규모와 예측 : 기술별, 2021년-2034년
- 주요 동향
- 기존
- 디지털
제6장 시장 규모와 예측 : 컴포넌트별, 2021년-2034년
- 주요 동향
- 변전소 자동화 시스템
- 통신 네트워크
- 전기 시스템
- 감시·제어 시스템
- 기타
제7장 시장 규모와 예측 : 카테고리별, 2021년-2034년
- 주요 동향
- 신품
- 리퍼 비쉬
제8장 시장 규모와 예측 : 지역별, 2021년-2034년
- 주요 동향
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 영국
- 러시아
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 호주
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 카타르
- 오만
- 남아프리카
- 라틴아메리카
- 브라질
- 칠레
제9장 기업 프로파일
- ABB
- Alstom
- Belden
- Cisco Systems
- Eaton
- Efacec
- General Electric
- Grid to Great
- Hitachi Energy
- L&T Electrical and Automation
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Netcontrol Group
- Open System International
- Rockwell Automation
- Schneider Electric
- Siemens
- SIFANG
- Tesco Automation
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
- Toshiba
The Global High Voltage Substation Market generated USD 35.7 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 2.1% between 2025 and 2034. The rising demand for electricity, fueled by expanding urban populations and the rapid industrialization of developing economies, is driving the growth of this market. Increasing energy consumption has led to a pressing need for efficient power infrastructure, including high voltage substations, to maintain grid stability and ensure seamless energy transmission. Governments and utilities worldwide are prioritizing investments in power infrastructure to minimize transmission losses, boost power reliability, and accommodate the growing integration of renewable energy sources. Substations play a critical role in converting high-voltage electricity from power plants into lower voltages suitable for residential and industrial use, making them indispensable for sustaining a stable energy supply. Additionally, the rising number of renewable energy projects in remote locations necessitates robust transmission systems, adding to the demand for high voltage substations.
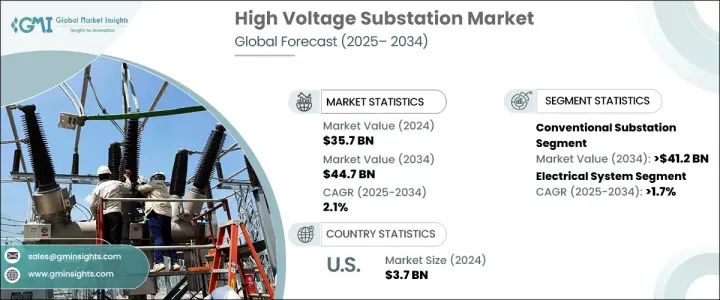
The growing emphasis on grid modernization and resilience has further fueled the deployment of advanced substation technologies. As global economies strive to meet net-zero targets, integrating renewable energy into existing grids requires upgraded substations that can handle variable energy flows and ensure efficient power distribution. Emerging smart grid initiatives, aimed at enhancing grid automation, monitoring, and control capabilities, have propelled the adoption of advanced digital substations. However, conventional substations remain a dominant segment, expected to generate USD 41.2 billion by 2034. Their cost-effectiveness and reliance on proven technologies make them the preferred choice for regions with budget constraints. These substations are easier to operate and maintain, reducing the need for specialized personnel and complex infrastructure, which further contributes to their widespread adoption.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $35.7 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $44.7 Billion |
| CAGR | 2.1% |
The electrical system segment within the high voltage substation market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 1.7% through 2034, driven by the aging infrastructure in developed economies. Critical components such as transformers, switchgear, circuit breakers, and protection systems are essential for maintaining the efficiency and stability of high voltage substations. As renewable energy generation increases, modernized electrical systems become crucial for managing power flow and transmitting energy effectively across long distances. Additionally, renewable energy projects, often located in geographically isolated regions, require efficient transmission solutions to link them with the main grid, further driving the demand for upgraded electrical systems.
The U.S. high voltage substation market generated USD 3.7 billion in 2024, largely fueled by ongoing investments to modernize outdated transmission infrastructure. Many existing substations operate beyond their intended lifespan, prompting utilities to invest in system upgrades and equipment replacement. Modernization initiatives aim to enhance power flow, improve grid reliability, and incorporate cutting-edge technologies that accommodate the growing demand for electricity while increasing the overall efficiency of power transmission networks.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology & Scope
- 1.1 Market definitions
- 1.2 Base estimates & calculations
- 1.3 Forecast calculation
- 1.4 Data sources
- 1.4.1 Primary
- 1.4.2 Secondary
- 1.4.2.1 Paid
- 1.4.2.2 Public
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry synopsis, 2021 - 2034
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.2 Regulatory landscape
- 3.3 Industry impact forces
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3.2 Industry pitfalls & challenges
- 3.4 Growth potential analysis
- 3.5 Porter's analysis
- 3.5.1 Bargaining power of suppliers
- 3.5.2 Bargaining power of buyers
- 3.5.3 Threat of new entrants
- 3.5.4 Threat of substitutes
- 3.6 PESTEL analysis
Chapter 4 Competitive landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Strategic dashboard
- 4.2 Innovation & sustainability landscape
Chapter 5 Market Size and Forecast, By Technology 2021 – 2034 (USD Million, Units)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Conventional
- 5.3 Digital
Chapter 6 Market Size and Forecast, By Component 2021 – 2034 (USD Million)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Substation automation system
- 6.3 Communication network
- 6.4 Electrical system
- 6.5 Monitoring & control system
- 6.6 Others
Chapter 7 Market Size and Forecast, By Category 2021 – 2034 (USD Million, Units)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 New
- 7.3 Refurbished
Chapter 8 Market Size and Forecast, By Region, 2021 – 2034 (USD Million, ‘000 Units)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 North America
- 8.2.1 U.S.
- 8.2.2 Canada
- 8.2.3 Mexico
- 8.3 Europe
- 8.3.1 Germany
- 8.3.2 France
- 8.3.3 Italy
- 8.3.4 UK
- 8.3.5 Russia
- 8.4 Asia Pacific
- 8.4.1 China
- 8.4.2 India
- 8.4.3 Japan
- 8.4.4 South Korea
- 8.4.5 Australia
- 8.5 Middle East & Africa
- 8.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 8.5.2 UAE
- 8.5.3 Qatar
- 8.5.4 Oman
- 8.5.5 South Africa
- 8.6 Latin America
- 8.6.1 Brazil
- 8.6.2 Chile
Chapter 9 Company Profiles
- 9.1 ABB
- 9.2 Alstom
- 9.3 Belden
- 9.4 Cisco Systems
- 9.5 Eaton
- 9.6 Efacec
- 9.7 General Electric
- 9.8 Grid to Great
- 9.9 Hitachi Energy
- 9.10 L&T Electrical and Automation
- 9.11 Mitsubishi Electric
- 9.12 Netcontrol Group
- 9.13 Open System International
- 9.14 Rockwell Automation
- 9.15 Schneider Electric
- 9.16 Siemens
- 9.17 SIFANG
- 9.18 Tesco Automation
- 9.19 Texas Instruments Incorporated
- 9.20 Toshiba













