
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1740757
상업 우주 발사 시장 기회, 성장 촉진 요인, 산업 동향 분석, 예측(2025-2034년)Commercial Space Launch Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
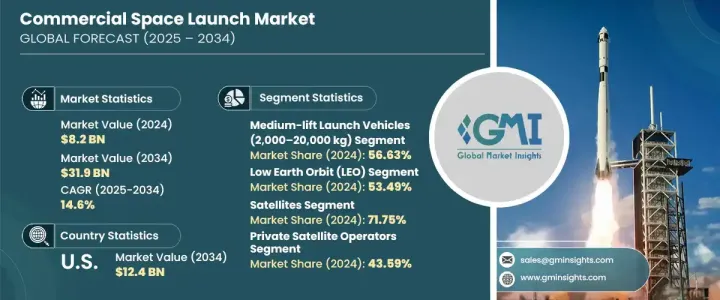
세계 상업 우주 발사 시장은 2024년에는 82억 달러로 평가되었으며, CAGR 14.6%로, 2034년에는 319억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.
이 폭발적인 성장은 우주 기술의 급속한 진보, 발사 서비스의 저가격화, 연결성, 지구관측, 과학 연구에 대한 수요 증가에 힘입어지고 있습니다. 부주도의 분야였던 것이 경쟁력 있는 혁신 주도의 산업으로 변모를 이루고 근본적인 변화를 이루고 있습니다.
저궤도 위성 별자리, 기상 모니터링, 실시간 이미징, 차세대 통신에 대한 관심이 높아지는 가운데, 상업 우주 발사 부문은 보다 광범위한 항공우주 생태계의 중요한 기둥으로 발전하고 있습니다. 세계 각국은 발사 인프라, 규제 개혁, 연구 개발에 많은 투자를 하고 있으며, 신흥 국가 시장은 자본과 인재 모두에게 매력적인 시장이 되고 있습니다.
| 시장 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 시작 연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 연도 | 2025-2034년 |
| 시작 금액 | 82억 달러 |
| 예측 금액 | 319억 달러 |
| CAGR | 14.6% |
소형 위성 발사 수요는 통신, 지구 이미지, 기후 추적, 과학 실험 등 광범위한 기능에 대응하는 소형 페이로드의 배치 가능성이 높아짐에 따라 급증하고 있습니다. 합리적인 가격으로 발사하는 능력은 민간 기업과 정부 기관 모두에게 획기적인 것입니다.
그 결과 기업은 궤도 플랫폼에 대한 액세스가 확대되어 혁신적인 위성 서비스의 신속한 전개가 가능해졌습니다. 상승 에코시스템을 재구성하고 있습니다. 증가하는 상업 미션의 양과 유형을 지원하기 위해 전용 발사장과 지역 우주항의 개발이 진행되고 있습니다.
그러나 지정 학적 무역 마찰과 변동하는 국제 정책은 업계의 비용 구조에 복잡성을 추가하고 있습니다. 국내에서 조달하는 방향으로 움직이고 있습니다.이 전략적 전환은 국가의 우주 정책에 따라뿐만 아니라 국제 공급업체에 대한 의존도를 줄임으로써 운영의 안정성을 높입니다.
2024년에는 중형 로켓이 56.63%의 점유율로 시장을 장악했습니다. 이 로켓은 페이로드 용량과 운영 효율성의 이상적인 조합을 제공하여 폭넓은 발사 미션에 인기 있는 선택이 되었습니다. 이 로드와 라이드 쉐어 미션 모두에 대응할 수 있기 때문에 민간 사업자나 정부 기관에 있어서도 매우 매력적입니다.
낮은 궤도는 궤도 유형별로 리드를 유지하며, 2024년에는 시장의 53.49%를 차지했습니다. 따라서 확장 가능하고 비용 효율적인 방식으로 고밀도 위성 별자리를 구축 할 수 있습니다. 저지연 통신 서비스 및 실시간 데이터 솔루션을 제공하는 기업은 LEO를 점점 더 목표로하고 있으며 상업 우주 활동의 전략적 핫스팟이되었습니다.
미국의 상업 우주 발사 시장은 강력한 관민 협력에 힘입어 2034년까지 124억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다. 간기업과의 파트너십, 연구개발 이니셔티브는 재사용 가능한 발사 시스템과 모듈식 위성 페이로드의 획기적인 진보를 가속화하고 있습니다.
세계 시장을 형성하는 주요 기업은 SpaceX, United Launch Alliance, Rocket Lab USA, Blue Origin, Safran SA 등이 있습니다. 이러한 기업은 미션 코스트의 삭감과 발사 빈도 증가를 목표로 재사용 가능한 발사 시스템을 적극적으로 개발하고 있습니다. 민간 발사 인프라에 투자하고 제조 공정를 수직 통합하고 세계적인 파트너십을 맺음으로써 이러한 기업은 공급망의 강인성을 강화하고 운영 유연성을 높이고 국제적인 도달범위를 넓히고 있습니다.
목차
제1장 조사 방법과 범위
제2장 주요 요약
제3장 업계 인사이트
- 생태계 분석
- 트럼프 정권에 의한 관세에 대한 영향
- 무역에 미치는 영향
- 무역량의 혼란
- 보복 조치
- 업계에 미치는 영향
- 공급측의 영향(서비스 제공업체)
- 주요 서비스의 가격 변동
- 공급망 재구성
- 생산 비용에 미치는 영향
- 수요측의 영향(가격 설정)
- 최종 시장에의 가격 전달
- 시장 점유율 동향
- 소비자의 반응 패턴
- 공급측의 영향(서비스 제공업체)
- 영향을 받는 주요 기업
- 전략적인 업계 대응
- 서버 프로바이더의 재구성
- 가격 설정 및 서비스 전략
- 정책관여
- 전망과 향후 검토 사항
- 무역에 미치는 영향
- 업계에 미치는 영향요인
- 성장 촉진요인
- 소형 위성 발사 수요 증가
- 재사용형 발사 로켓에 대한 주목의 고조
- 민간 발사업자와 우주항의 출현
- 관민 연계의 강화
- 우주 관광과 탄도 비행 확대
- 업계의 잠재적 위험 및 과제
- 높은 출시 비용과 자본 집약도
- 규제와 안전 컴플라이언스의 복잡성
- 성장 촉진요인
- 성장 가능성 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 상황
- 장래 시장 동향
- 갭 분석
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- PESTEL 분석
제4장 경쟁 구도
- 소개
- 기업의 시장 점유율 분석
- 주요 시장 기업의 경쟁 분석
- 경쟁 포지셔닝 매트릭스
- 전략 대시보드
제5장 시장 추정 및 예측 : 페이로드 유형별, 2021-2034
- 주요 동향
- 위성
- 화물 및 물류
- 유인 우주 비행
- 행성간 미션
제6장 시장 추정 및 예측 : 로켓유형별, 2021-2034
- 주요 동향
- 소형 로켓(2,000 kg 미만)
- 중형 로켓(2,000-20,000 kg)
- 대형 발사 로켓(20,000 kg 이상)
제7장 시장 추정 및 예측 : 궤도 유형별, 2021-2034
- 주요 동향
- 저지구 궤도(LEO)
- 정지궤도(GEO)
- 중궤도(MEO)
- 극궤도 및 태양동기궤도(SSO)
- 깊은 우주
제8장 시장 추정 및 예측 : 최종 용도별, 2021-2034
- 민간 위성 사업자
- 정부와 민간의 파트너십
- 우주 관광 기업
- 조사 및 학술 기관
- 방어와 군사
제9장 시장 추정 및 예측 : 지역별, 2021 –2034
- 주요 동향
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 스페인
- 이탈리아
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 호주 및 뉴질랜드
- 한국
- 라틴아메리카
- 브라질
- 멕시코
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 사우디아라비아
- 남아프리카
제10장 기업 프로파일
- Agnikul Cosmos
- Astra
- Blue Origin
- Firefly Aerospace
- GALACTIC ENERGY
- Isar Aerospace SE
- ispace
- LandSpace
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Northrop Grumman
- PLD Space
- Relativity Space
- Rocket Lab USA
- Safran SA
- SpaceX
- United Launch Alliance, LLC.
- Skyroot Aerospace
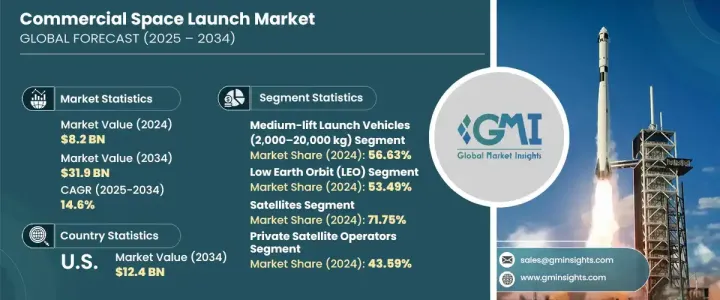
The Global Commercial Space Launch Market was valued at USD 8.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.6% to reach USD 31.9 billion by 2034. This explosive growth is fueled by rapid advancements in space technologies, increasing affordability of launch services, and rising demand for connectivity, Earth observation, and scientific research. The global space economy is undergoing a fundamental shift as commercial players become more active and influential, transforming what was once a government-dominated sector into a competitive, innovation-driven industry. Miniaturization of satellites and reduced manufacturing costs have made it easier for private and institutional customers to access space.
With growing interest in low Earth orbit satellite constellations, weather monitoring, real-time imaging, and next-generation communications, the commercial space launch sector has evolved into a key pillar of the broader aerospace ecosystem. As the space economy diversifies beyond traditional exploration, opportunities in data services, inter-satellite links, and space-based infrastructure continue to open new frontiers. Countries around the world are investing heavily in launch infrastructure, regulatory reform, and research and development, making the commercial space launch market a magnet for both capital and talent.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $8.2 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $31.9 Billion |
| CAGR | 14.6% |
Demand for small satellite launches has skyrocketed due to the rising feasibility of deploying compact payloads that serve a wide range of functions across communication, Earth imaging, climate tracking, and scientific experimentation. The ability to launch smaller satellites more frequently and affordably is a game-changer for both commercial enterprises and government agencies. This transformation has been accelerated by significant reductions in launch costs and the introduction of cost-effective miniaturization technologies.
As a result, companies now have greater access to orbital platforms, enabling the rapid deployment of innovative satellite services. Increased participation from the private sector in launch operations, combined with supportive government policies and streamlined licensing procedures, is reshaping the global space launch ecosystem. A growing number of dedicated launch sites and regional spaceports are being developed to support the increasing volume and variety of commercial missions. This expansion is drawing in a broader base of institutional and commercial clients, contributing to a sharp increase in launch frequency.
However, geopolitical trade tensions and fluctuating international policies have added complexity to the industry's cost structure. Import tariffs on aerospace components and propulsion systems have disrupted supply chains and increased production costs. To mitigate these risks, companies are moving toward localizing production and sourcing materials domestically. This strategic pivot not only aligns with national space policies but also enhances operational stability by reducing reliance on international suppliers. Domestic sourcing supports better cost control, improves delivery timelines, and ensures greater compliance with security regulations.
In 2024, medium-lift launch vehicles dominated the market with a 56.63% share. These rockets offer the ideal combination of payload capacity and operational efficiency, making them a popular choice for a broad spectrum of launch missions. Their flexibility allows them to accommodate both single-customer payloads and ride-share missions, which is highly attractive to commercial operators and government agencies alike. With capabilities to reach both low Earth orbit (LEO) and geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), medium-lift vehicles remain the workhorses of the launch industry.
Low Earth orbit maintained the lead by orbit type, capturing 53.49% of the market in 2024. Its popularity stems from advantages such as low latency, faster data transmission, and reduced deployment costs. These factors are critical for applications like broadband connectivity, surveillance, and environmental monitoring. LEO's proximity to Earth allows for the deployment of dense satellite constellations in a scalable, cost-efficient manner. Companies aiming to deliver low-latency communication services and real-time data solutions are increasingly targeting LEO, making it a strategic hotspot for commercial space activity.
The United States Commercial Space Launch Market is forecasted to reach USD 12.4 billion by 2034, underpinned by strong public-private collaboration. Streamlined regulations, innovation incentives, and investments in infrastructure are driving the U.S. forward as a global space leader. Public funding, partnerships with private firms, and R&D initiatives are fast-tracking breakthroughs in reusable launch systems and modular satellite payloads. Agencies continue to work hand-in-hand with commercial players to advance next-generation launch capabilities.
Key players shaping the global market landscape include SpaceX, United Launch Alliance, Rocket Lab USA, Blue Origin, and Safran S.A. These companies are actively developing reusable launch systems to lower mission costs and increase launch frequency. Strategic collaborations with defense organizations and telecom providers are enabling them to secure long-term contracts. By investing in private launch infrastructure, vertically integrating manufacturing processes, and entering global partnerships, these firms are strengthening supply chain resilience, increasing operational flexibility, and extending their international reach.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology and Scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definitions
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.3.1 Base year calculation
- 1.3.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.4 Forecast model
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.5.2 Data mining sources
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 360° synopsis
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.2 Trump administration tariffs
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.2.1.1 Trade volume disruptions
- 3.2.1.2 Retaliatory measures
- 3.2.2 Impact on the industry
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (service providers)
- 3.2.2.1.1 Price volatility in key services
- 3.2.2.1.2 Supply chain restructuring
- 3.2.2.1.3 Production cost implications
- 3.2.2.2 Demand-side impact (pricing)
- 3.2.2.2.1 Price transmission to end markets
- 3.2.2.2.2 Market share dynamics
- 3.2.2.2.3 Consumer response patterns
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (service providers)
- 3.2.3 Key companies impacted
- 3.2.4 Strategic industry responses
- 3.2.4.1 Server provider reconfiguration
- 3.2.4.2 Pricing and service strategies
- 3.2.4.3 Policy engagement
- 3.2.5 Outlook and future considerations
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.3 Industry impact forces
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3.1.1 Growth in small satellite launch demand
- 3.3.1.2 Rising focus on reusable launch vehicles
- 3.3.1.3 Emergence of private launch providers and spaceports
- 3.3.1.4 Increased government-private sector collaborations
- 3.3.1.5 Expansion of space tourism and suborbital flights
- 3.3.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.3.2.1 High launch costs and capital intensity
- 3.3.2.2 Regulatory and safety compliance complexities
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.4 Growth potential analysis
- 3.5 Regulatory landscape
- 3.6 Technology landscape
- 3.7 Future market trends
- 3.8 Gap analysis
- 3.9 Porter's analysis
- 3.10 PESTEL analysis
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategy dashboard
Chapter 5 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Payload Type, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Satellites
- 5.3 Cargo & logistics
- 5.4 Human spaceflight
- 5.5 Interplanetary missions
Chapter 6 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Launch Vehicle Type, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Small-lift launch vehicles (< 2,000 kg)
- 6.3 Medium-lift launch vehicles (2,000–20,000 kg)
- 6.4 Heavy-lift launch vehicles (> 20,000 kg)
Chapter 7 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Orbit Type, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Low earth orbit (LEO)
- 7.3 Geostationary orbit (GEO)
- 7.4 Medium earth orbit (MEO)
- 7.5 Polar & sun-synchronous orbit (SSO)
- 7.6 Deep space
Chapter 8 Market Estimates & Forecast, By End Use, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 8.1 Private satellite operators
- 8.2 Government-commercial partnerships
- 8.3 Space tourism companies
- 8.4 Research & academic institutions
- 8.5 Defense & military
Chapter 9 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Region, 2021 – 2034 (USD Billion)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 North America
- 9.2.1 U.S.
- 9.2.2 Canada
- 9.3 Europe
- 9.3.1 Germany
- 9.3.2 UK
- 9.3.3 France
- 9.3.4 Spain
- 9.3.5 Italy
- 9.4 Asia Pacific
- 9.4.1 China
- 9.4.2 India
- 9.4.3 Japan
- 9.4.4 ANZ
- 9.4.5 South Korea
- 9.5 Latin America
- 9.5.1 Brazil
- 9.5.2 Mexico
- 9.6 Middle East and Africa
- 9.6.1 UAE
- 9.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 9.6.3 South Africa
Chapter 10 Company Profiles
- 10.1 Agnikul Cosmos
- 10.2 Astra
- 10.3 Blue Origin
- 10.4 Firefly Aerospace
- 10.5 GALACTIC ENERGY
- 10.6 Isar Aerospace SE
- 10.7 ispace
- 10.8 LandSpace
- 10.9 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- 10.10 Northrop Grumman
- 10.11 PLD Space
- 10.12 Relativity Space
- 10.13 Rocket Lab USA
- 10.14 Safran S.A.
- 10.15 SpaceX
- 10.16 United Launch Alliance, LLC.
- 10.17 Skyroot Aerospace















