
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1833668
전기 건설기계 시장 기회, 성장 촉진요인, 산업 동향 분석, 예측(2025-2034년)Electric Construction Equipment Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
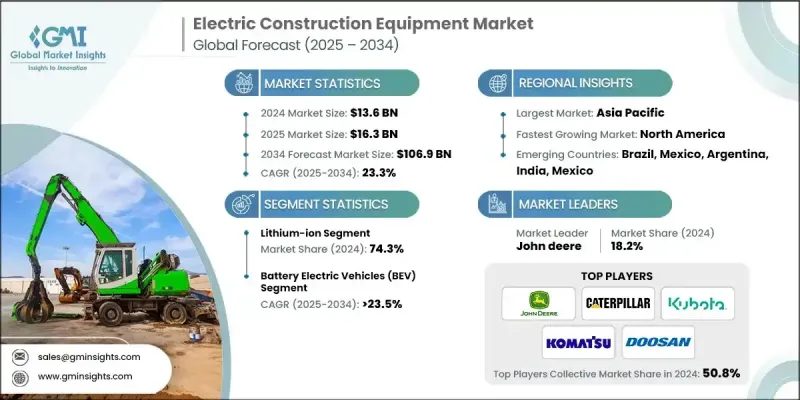
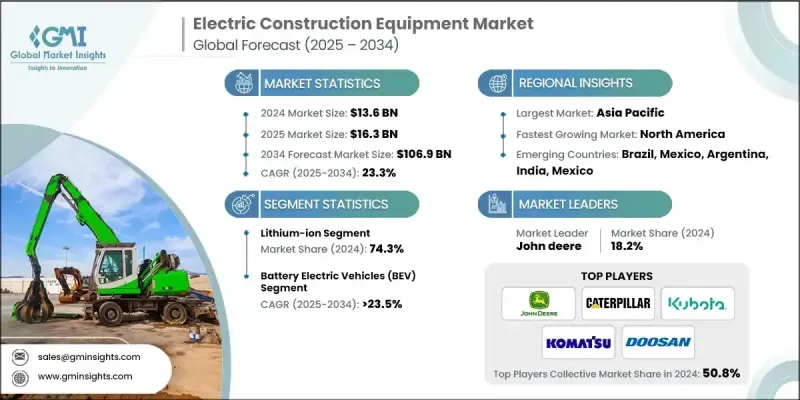
Global Market Insights Inc.가 발행한 최신 보고서에 따르면 세계의 전기 건설기계 시장은 2024년에 136억 달러로 추정되며, CAGR 23.3%로 2025년 163억 달러에서 2034년에는 1,069억 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다.
유럽, 북미, 아시아 일부 정부는 건설기계를 포함한 비도로 이동기계에 대한 배기가스 규제를 점점 더 강화하고 있습니다. 이러한 규제는 대기오염과 기후변화의 주요 원인인 질소산화물(NOx), 입자상 물질(PM), 이산화탄소(CO2) 등 유해한 오염물질을 억제하는 것을 목적으로 하고 있습니다.
| 시장 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 시작 연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 연도 | 2025-2034 |
| 시장 규모 | 136억 달러 |
| 예측 금액 | 1,069억 달러 |
| CAGR | 23.3% |
리튬 이온 채택 증가
리튬이온 배터리는 높은 에너지 밀도, 긴 수명 주기, 빠른 충전이 가능하여 2024년 큰 점유율을 차지했습니다. 기업들이 리튬이온 기술을 중시하는 이유는 까다로운 건설 작업에 필요한 안정적인 전력을 공급하는 동시에 전체 장비의 무게를 줄일 수 있기 때문입니다. 기술 혁신과 규모의 경제로 인해 배터리 비용이 지속적으로 하락함에 따라 리튬이온 배터리는 제조업체와 최종사용자 모두에게 선호되는 선택이 되고 있습니다.
배터리 전기자동차 수요 증가
배터리 전기자동차(BEV)는 전 세계적으로 무공해 솔루션에 대한 관심이 높아지면서 2025년부터 2034년까지 큰 폭의 성장을 이룰 것으로 예상됩니다. 이 차량은 소음 공해를 최소화하고 테일 파이프 배출을 없애는 두 가지 장점을 가지고 있어 도시 지역과 실내 건설 현장에 이상적입니다. BEV를 개발하는 기업들은 가동 시간을 늘리고 충전 중단 시간을 줄이기 위해 배터리 기술의 발전을 우선시하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양이 유망한 지역이 될 것입니다.
아시아태평양 전기 건설기계 시장은 급속한 도시화, 인프라 개발, 청정에너지 도입을 촉진하는 정부 지원 정책에 힘입어 2024년 큰 점유율을 차지했습니다. 중국, 일본, 한국 등의 국가들이 조사개발과 전기자동차 보급에 많은 투자를 하며 주도권을 쥐고 있습니다. 이 지역의 건설 산업이 확대되고 환경 인식이 높아짐에 따라 성능과 지속가능성 기준을 모두 충족하는 전기 기계에 대한 수요가 가속화되고 있습니다.
전기 건설기계 산업에서 사업을 전개하고 있는 주요 기업은 Liebherr, Kubota, Doosan Infracore, Mecalac, John Deere, LiuGong Machinery, Caterpillar, Komatsu, Manitou, Hitachi Construction입니다.
진화하는 전기 건설기계 시장에서 발판을 마련하고 강화하기 위해 기업들은 다각적인 전략을 채택하고 있습니다. 제품 혁신은 여전히 핵심 초점이며, 더 오래 지속되는 배터리, 개선된 에너지 관리 시스템, 다양한 장비 카테고리를 포괄하는 다용도 전기 모델 개발에 투자하고 있습니다. 배터리 제조업체 및 기술 기업과의 전략적 제휴 및 합작투자는 기업이 혁신을 가속화하고 시장 출시 시간을 단축하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 또한, 애프터 서비스 네트워크를 확장하고 고객 교육 이니셔티브에 투자하는 것은 신뢰를 구축하고 디젤에서 전기 기계로의 전환을 용이하게 하기 위해 필수적입니다.
목차
제1장 조사 방법과 범위
제2장 주요 요약
제3장 업계 인사이트
- 생태계 분석
- 원재료 공급업체
- 부품 제조업체
- 기기 제조업체
- 판매대리점 및 딜러
- 애프터마켓 공급업체
- 업계에 대한 영향요인
- 성장 촉진요인
- 엄격한 배출 규제
- 도시화와 스마트 시티 프로젝트
- 비용 절감과 효율화
- OEM과 렌탈 채용
- 업계의 잠재적 리스크와 과제
- 높은 초기 비용
- 충전 인프라 격차
- 시장 기회
- 정부 인센티브와 보조금
- 배터리 기술의 진보
- 스마트한 현장 통합
- 그린 인프라 프로젝트
- 성장 촉진요인
- 성장 가능성 분석
- 특허 분석
- 규제 상황
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
- Porters 분석
- PESTEL 분석
- 기술 통합과 표준화 과제
- 충전 인프라 호환성과 표준
- 커넥터 표준과 상호운용성 문제
- 통신 프로토콜과 데이터 교환
- 제조업체간 호환성 과제
- 레거시 시스템의 통합과 전환 비용
- 플릿 관리 시스템의 통합
- 복수 브랜드 플릿 관리의 복잡성
- 데이터 통합 및 분석 플랫폼
- 텔레매틱스 및 원격 모니터링 시스템
- 유지보수 스케줄과 최적화
- 디지털 전환과 IoT 통합
- 접속 규격과 프로토콜
- 3데이터 보안과 프라이버시 요건
- 엣지 컴퓨팅과 실시간 분석
- 디지털 트윈 기술과 시뮬레이션
- 복수 벤더의 통합의 복잡성
- 브랜드 간의 충전 커넥터 호환성 문제
- 플릿 관리 시스템 통합 과제(15개 이상 플랫폼)
- 데이터 형식 표준화와 상호운용성 격차
- 서비스 진단 툴 요건과 트레이닝
- 충전 인프라 호환성과 표준
- 3에너지 관리와 그리드 통합
- 스마트 충전 및 부하 관리 시스템
- 동적 부하 분산과 피크 쉐이빙
- 시간대별 최적화와 비용 절감
- 그리드 안정성과 수요 반응의 통합
- AI와 머신러닝 애플리케이션
- 재생에너지의 통합
- 태양광과 풍력발전의 통합에 의한 이점
- 에너지 저장 및 배터리 시스템
- 마이크로그리드 개발과 아일랜드화 기능
- 탄소발자국 절감과 지속가능성
- 차량에서 전력망에의(V2G)와 양방향 충전
- 그리드 서비스와 수익 기회
- 기술 요건과 표준
- 비즈니스 모델 개발과 구현
- 규제 프레임워크와 시장 장벽
- 스마트 충전 및 부하 관리 시스템
- 서비스 네트워크 준비 상황 평가
- 지리적 서비스 커버리지 분석
- 서비스 커버리지 격차 특정(40%의 시장이 서비스 부족)
- 지역 서비스 밀도와 응답 시간 분석
- 농촌과 도시 서비스 이용 가능성 격차
- 긴급 서비스 대응 능력
- 기술자 인증 및 트레이닝 인프라
- 고전압 인증 프로그램 가용성
- 트레이닝 능력과 보틀넥 분석
- 스킬 개발 타임라인과 요건
- 인증 비용과 투자 분석
- 진단 기기 및 툴 요건
- 특수 진단 툴에 대한 투자
- 소프트웨어 플랫폼의 통합과 업데이트
- 복수 브랜드 호환성과 표준화
- 기술 업그레이드와 진부화 관리
- 지리적 서비스 커버리지 분석
- 부품 입수 가능성과 공급망 서포트
- 전기 부품 공급망 성숙도
- 배터리 교환과 서비스 인프라
- 긴급 부품 입수 가능성과 리드타임
- 지역 공급망 개발과 로컬라이제이션
- 서비스 모델 혁신과 디지털 통합
- 원격 진단과 예측 유지보수
- 증강현실과 디지털 서비스 툴
- SaaS(Service-as-a-Service) 모델과 구독
- 고객 셀프서비스와 디지털 플랫폼
- 특허 분석
- 지속가능성과 환경 측면
- 지속가능한 관행
- 폐기물 절감 전략
- 생산의 에너지 효율
- 친환경 대처
- 탄소발자국 고려
- 이용 사례
- 최선 시나리오
제4장 경쟁 구도
- 소개
- 기업의 시장 점유율 분석
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 주요 시장 기업 경쟁 분석
- 경쟁 포지셔닝 매트릭스
- 전략적 전망 매트릭스
- 주요 발전
- 인수합병
- 파트너십과 협업
- 신제품 발매
- 확장 계획과 자금 조달
제5장 시장 추정과 예측 : 장비별, 2021-2034
- 주요 동향
- 굴착기
- 로더
- 불도저
- 크레인
- 덤프트럭
- 롤러
- 기타
제6장 시장 추정과 예측 : 배터리 용량별, 2021-2034
- 주요 동향
- 50kWh 미만
- 50kWh-200kWh
- 200kWh 이상
제7장 시장 추정과 예측 : 배터리 기술, 2021-2034
- 주요 동향
- 납축배터리
- 리튬이온
- 니켈수소
제8장 시장 추정과 예측 : 전원별, 2021-2034
- 주요 동향
- 배터리 전기자동차(BEV)
- 플러그인 하이브리드 전기자동차(PHEV)
제9장 시장 추정과 예측 : 최종 용도별, 2021-2034
- 주요 동향
- 건설
- 광업
- 자재관리
- 농업
- 기타
제10장 시장 추정과 예측 : 지역별, 2021-2034
- 주요 동향
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 유럽
- 영국
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 러시아
- 북유럽 국가
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 호주
- 한국
- 동남아시아
- 라틴아메리카
- 브라질
- 멕시코
- 아르헨티나
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 남아프리카공화국
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트
제11장 기업 개요
- 세계 기업
- Caterpillar
- CNH Industrial
- Hitachi Construction Machinery
- JCB
- John Deere
- Komatsu
- Komatsu
- Liebherr
- 지역 기업
- Develon
- Doosan Infracore
- Hyundai Construction Equipment
- LiuGong Machinery
- Manitou
- Mecalac
- SDLG
- 신흥 기업
- Avant Tecno
- Elematic
- Kramer-Werke
- Sunward Intelligent Equipment
- Zoomlion Heavy Industry Science &Technology
The global electric construction equipment market was estimated at USD 13.6 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow from USD 16.3 billion in 2025 to USD 106.9 billion by 2034 at a CAGR of 23.3%, according to the latest report published by Global Market Insights Inc.
Governments across Europe, North America, and parts of Asia are increasingly tightening emission standards for non-road mobile machinery, including construction equipment. These regulations aim to curb harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon dioxide (CO2), which are major contributors to air pollution and climate change.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $13.6 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $106.9 billion |
| CAGR | 23.3% |
Rising Adoption of Lithium-Ion
The lithium-ion battery segment held a significant share in 2024, owing to its high energy density, longer lifecycle, and rapid charging capabilities. Companies emphasize lithium-ion technology because it provides the reliable power needed for demanding construction tasks while reducing overall equipment weight. As battery costs continue to decline, driven by technological innovation and economies of scale, lithium-ion batteries are becoming the preferred choice for both manufacturers and end-users.
Increasing Demand for Battery Electric Vehicles
The battery electric vehicles (BEVs) are witnessing significant growth from 2025 to 2034, fueled by a global push toward zero-emission solutions. These vehicles offer the dual benefits of minimizing noise pollution and eliminating tailpipe emissions, making them ideal for urban and indoor construction sites. Companies developing BEVs are prioritizing advancements in battery technology to extend operational hours and reduce charging downtime.
Asia Pacific to Emerge as a Lucrative Region
Asia Pacific electric construction equipment market held a sizeable share in 2024, driven by rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and supportive government policies promoting clean energy adoption. Countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea are leading the charge with substantial investments in research and development and the deployment of electric fleets. The region's expanding construction industry, coupled with rising environmental awareness, is accelerating demand for electric machinery that meets both performance and sustainability criteria.
Major players operating in the electric construction equipment industry are Liebherr, Kubota, Doosan Infracore, Mecalac, John Deere, LiuGong Machinery, Caterpillar, Komatsu, Manitou, and Hitachi Construction.
To secure and strengthen their foothold in the evolving electric construction equipment market, companies are adopting multifaceted strategies. Product innovation remains a core focus, with investments funneled into developing longer-lasting batteries, improved energy management systems, and versatile electric models that cover various equipment categories. Strategic collaborations and joint ventures with battery manufacturers and technology firms help companies accelerate innovation and reduce time-to-market. Furthermore, expanding after-sales service networks and investing in customer education initiatives are critical to building trust and easing the transition from diesel to electric machinery.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology & Scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast model
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 3600 synopsis, 2021 - 2034
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Regional
- 2.2.2 Equipment
- 2.2.3 Battery Capacity
- 2.2.4 Battery Technology
- 2.2.5 Power Source
- 2.2.6 End Use
- 2.3 TAM Analysis, 2025-2034
- 2.4 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 Critical success factors
- 2.5 Future outlook and strategic recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Raw material suppliers
- 3.1.2 Component manufacturers
- 3.1.3 Equipment manufacturers
- 3.1.4 Distributors and dealers
- 3.1.5 Aftermarket suppliers
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.1.1 Stringent emission regulations
- 3.2.1.2 Urbanization & smart city projects
- 3.2.1.3 Cost savings & efficiency
- 3.2.1.4 OEM and rental adoption
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.2.1 High upfront costs
- 3.2.2.2 Charging infrastructure gaps
- 3.2.3 Market opportunities
- 3.2.3.1 Government incentives & subsidies
- 3.2.3.2 Advancements in battery tech
- 3.2.3.3 Smart jobsite integration
- 3.2.3.4 Green infrastructure projects
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Patent analysis
- 3.5 Regulatory landscape
- 3.5.1 North America
- 3.5.2 Europe
- 3.5.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.5.4 Latin America
- 3.5.5 Middle East & Africa
- 3.6 Porter's analysis
- 3.7 PESTEL analysis
- 3.8 Technology Integration and Standardization Challenges
- 3.8.1 Charging Infrastructure Compatibility and Standards
- 3.8.1.1 Connector Standards and Interoperability Issues
- 3.8.1.2 Communication Protocols and Data Exchange
- 3.8.1.3 Cross-Manufacturer Compatibility Challenges
- 3.8.1.4 Legacy System Integration and Migration Costs
- 3.8.2 Fleet Management System Integration
- 3.8.2.1 Multi-Brand Fleet Management Complexity
- 3.8.2.2 Data Integration and Analytics Platforms
- 3.8.2.3 Telematics and Remote Monitoring Systems
- 3.8.2.4 Maintenance Scheduling and Optimization
- 3.8.3 Digital Transformation and IoT Integration
- 3.8.3.1 Connectivity Standards and Protocols
- 3.8.3.2 3Data Security and Privacy Requirements
- 3.8.3.3 Edge Computing and Real-Time Analytics
- 3.8.3.4 Digital Twin Technology and Simulation
- 3.8.4 Multi-Vendor Integration Complexity
- 3.8.4.1 Charging Connector Compatibility Issues Across Brands
- 3.8.4.2 Fleet Management System Integration Challenges (15+ Platforms)
- 3.8.4.3 Data Format Standardization and Interoperability Gaps
- 3.8.4.4 Service Diagnostic Tool Requirements and Training
- 3.8.1 Charging Infrastructure Compatibility and Standards
- 3.9 3 Energy Management and Grid Integration
- 3.9.1 Smart Charging and Load Management Systems
- 3.9.1.1 Dynamic Load Balancing and Peak Shaving
- 3.9.1.2 Time-of-Use Optimization and Cost Reduction
- 3.9.1.3 Grid Stability and Demand Response Integration
- 3.9.1.4 AI and Machine Learning Applications
- 3.9.2 Renewable Energy Integration
- 3.9.2.1 Solar and Wind Power Integration Benefits
- 3.9.2.2 Energy Storage and Battery Systems
- 3.9.2.3 Microgrid Development and Islanding Capabilities
- 3.9.2.4 Carbon Footprint Reduction and Sustainability
- 3.9.3 Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) and Bidirectional Charging
- 3.9.3.1 Grid Services and Revenue Opportunities
- 3.9.3.2 Technology Requirements and Standards
- 3.9.3.3 Business Model Development and Implementation
- 3.9.3.4 Regulatory Framework and Market Barriers
- 3.9.1 Smart Charging and Load Management Systems
- 3.10 Service Network Readiness Assessment
- 3.10.1 Geographic Service Coverage Analysis
- 3.10.1.1 Service Coverage Gap Identification (40% Markets Underserved)
- 3.10.1.2 Regional Service Density and Response Time Analysis
- 3.10.1.3 Rural vs Urban Service Availability Disparities
- 3.10.1.4 Emergency Service Response Capabilities
- 3.10.2 Technician Certification and Training Infrastructure
- 3.10.2.1 High-Voltage Certification Program Availability
- 3.10.2.2 Training Capacity and Bottleneck Analysis
- 3.10.2.3 Skill Development Timeline and Requirements
- 3.10.2.4 Certification Cost and Investment Analysis
- 3.10.3 Diagnostic Equipment and Tool Requirements
- 3.10.3.1 Specialized Diagnostic Tool Investment
- 3.10.3.2 Software Platform Integration and Updates
- 3.10.3.3 Multi-Brand Compatibility and Standardization
- 3.10.3.4 Technology Upgrade and Obsolescence Management
- 3.10.1 Geographic Service Coverage Analysis
- 3.11 Parts Availability and Supply Chain Support
- 3.11.1 Electric Component Supply Chain Maturity
- 3.11.2 Battery Replacement and Service Infrastructure
- 3.11.3 Emergency Parts Availability and Lead Times
- 3.11.4 Regional Supply Chain Development and Localization
- 3.12 Service Model Innovation and Digital Integration
- 3.12.1 Remote Diagnostics and Predictive Maintenance
- 3.12.2 Augmented Reality and Digital Service Tools
- 3.12.3 Service-as-a-Service Models and Subscriptions
- 3.12.4 Customer Self-Service and Digital Platforms
- 3.13 Patent analysis
- 3.14 Sustainability and environmental aspects
- 3.14.1 Sustainable practices
- 3.14.2 Waste reduction strategies
- 3.14.3 Energy efficiency in production
- 3.14.4 Eco-friendly Initiatives
- 3.14.5 Carbon footprint considerations
- 3.15 Use cases
- 3.16 Best-case scenario
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 North America
- 4.2.2 Europe
- 4.2.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.4 LATAM
- 4.2.5 MEA
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategic outlook matrix
- 4.6 Key developments
- 4.6.1 Mergers & acquisitions
- 4.6.2 Partnerships & collaborations
- 4.6.3 New product launches
- 4.6.4 Expansion plans and funding
Chapter 5 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Equipment, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Excavators
- 5.3 Loaders
- 5.4 Bulldozers
- 5.5 Cranes
- 5.6 Dump Trucks
- 5.7 Roller
- 5.8 Others
Chapter 6 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Battery Capacity, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Less than 50 kWh
- 6.3 50 kWh to 200 kWh
- 6.4 More than 200 kWh
Chapter 7 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Battery Technology, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Lead-acid
- 7.3 Lithium-ion
- 7.4 Nickel-metal hydride
Chapter 8 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Power Source, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV)
- 8.3 Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV)
Chapter 9 Market Estimates & Forecast, By End Use, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 Construction
- 9.3 Mining
- 9.4 Material Handling
- 9.5 Agriculture
- 9.6 Others
Chapter 10 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 North America
- 10.2.1 US
- 10.2.2 Canada
- 10.3 Europe
- 10.3.1 UK
- 10.3.2 Germany
- 10.3.3 France
- 10.3.4 Italy
- 10.3.5 Spain
- 10.3.6 Russia
- 10.3.7 Nordics
- 10.4 Asia Pacific
- 10.4.1 China
- 10.4.2 India
- 10.4.3 Japan
- 10.4.4 Australia
- 10.4.5 South Korea
- 10.4.6 Southeast Asia
- 10.5 Latin America
- 10.5.1 Brazil
- 10.5.2 Mexico
- 10.5.3 Argentina
- 10.6 MEA
- 10.6.1 South Africa
- 10.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 10.6.3 UAE
Chapter 11 Company Profiles
- 11.1 Global Players
- 11.1.1 Caterpillar
- 11.1.2 CNH Industrial
- 11.1.3 Hitachi Construction Machinery
- 11.1.4 JCB
- 11.1.5 John Deere
- 11.1.6 Komatsu
- 11.1.7 Komatsu
- 11.1.8 Liebherr
- 11.2 Regional Players
- 11.2.1 Develon
- 11.2.2 Doosan Infracore
- 11.2.3 Hyundai Construction Equipment
- 11.2.4 LiuGong Machinery
- 11.2.5 Manitou
- 11.2.6 Mecalac
- 11.2.7 SDLG
- 11.3 Emerging Players
- 11.3.1 Avant Tecno
- 11.3.2 Elematic
- 11.3.3 Kramer-Werke
- 11.3.4 Sunward Intelligent Equipment
- 11.3.5 Zoomlion Heavy Industry Science & Technology



















