
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1479768
파워 반도체 시장, 재료, 기술Power Semiconductors: Markets, Materials and Technologies |
||||||
서론
자동차 및 산업에서 CE(Consumer Electronics) 및 재생 에너지 시스템에 이르기까지 다양한 분야에서 에너지 효율이 높은 솔루션에 대한 수요가 증가함에 따라 파워 반도체의 환경은 큰 변화를 겪고 있습니다. 세계가 보다 지속가능하고 전기화된 미래로 나아가는 가운데, 효율적인 에너지 관리, 전력 변환 및 제어를 가능하게 하는 파워 반도체의 역할이 점점 더 중요해지고 있습니다.
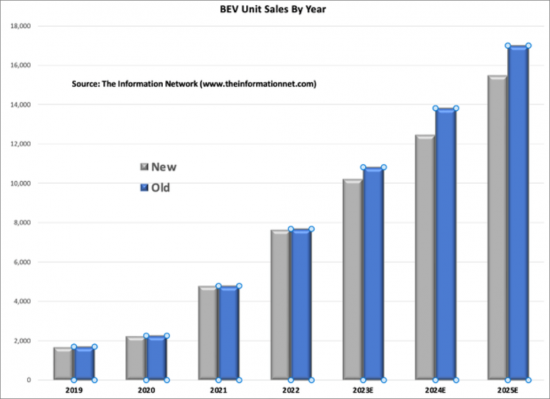
동향
광대역갭 재료, 특히 SiC와 GaN의 등장은 파워 반도체 산업에서 큰 패러다임의 전환을 의미합니다. 이들 재료는 기존 실리콘 기반 반도체에 비해 높은 내전압, 고속 스위칭, 열전도율 향상 등 뚜렷한 장점을 가지고 있으며, 고성능, 에너지 효율이 높은 전력 전자기기에 이상적인 후보로 떠오르고 있습니다.
실리콘 카바이드(SiC)는 실리콘에 비해 넓은 밴드 갭과 높은 임계 전계 강도 등 뛰어난 전기적 특성을 가지고 있습니다. 이러한 특성으로 인해 SiC 기반 기기는 효율적인 성능을 유지하면서 더 높은 온도와 전압에서 작동할 수 있으며, SiC 기기는 낮은 온 상태 손실과 스위칭 손실로 인해 전기자동차, 재생 에너지 시스템, 산업용 전력 변환기 등 다양한 용도에서 효율을 높이고 에너지 소비를 줄일 수 있습니다.
마찬가지로 질화갈륨(GaN)은 넓은 밴드갭과 높은 전자 이동도를 포함한 뛰어난 전기적 특성으로 주목을 받고 있으며, 전력 밀도, 스위칭 속도 및 효율 측면에서 큰 장점을 가지고 있으며, 고주파 및 고전력 용도에 적합하며, 스위칭 손실이 낮기 때문에 스위칭 주파수를 높이고 전력 전자 시스템의 소형화 및 경량화를 가능하게 합니다. 스위칭 손실이 낮기 때문에 스위칭 주파수의 향상과 전력 전자 시스템의 소형화 및 경량화가 가능하며, 특히 자동차 및 항공우주 용도에서 소형 및 경량 설계에 유리합니다.
SiC/GaN 소재의 파워 반도체 소자 채택은 재료 성장 방법, 제조 공정 및 소자 아키텍처의 발전으로 인해 가속화되고 있습니다. 생산량이 증가하고 제조 비용이 감소함에 따라 SiC/GaN 장비는 보다 광범위한 용도에서 실리콘 기반 제품과 경쟁력이 강화되고 있습니다.
또한 SiC/GaN 기술의 채택을 더욱 가속화하기 위해 장비 성능 최적화, 신뢰성 향상 및 비용 절감에 초점을 맞춘 연구개발이 진행되고 있습니다. 여기에는 광대역 갭 재료와 관련된 고유한 문제를 해결하기 위한 장비 설계, 포장 기술 및 열 관리 솔루션의 혁신이 포함됩니다.
전체적으로, SiC/GaN 소재의 광범위한 채택은 에너지 효율이 높은 파워 일렉트로닉스의 새로운 시대를 열며, 효율을 높이고, 배출을 줄이고, 지속가능한 에너지 솔루션을 추진하고자 하는 산업계에 변화의 기회를 제공합니다. 이러한 소재가 시장에서 성숙하고 성장함에 따라 파워 반도체 산업에 미치는 영향은 매우 광범위하고 광범위할 것으로 예상됩니다.
세계의 파워 반도체 시장에 대해 조사했으며, 시장, 재료, 기술에 관한 상세 분석과 인사이트를 제공하고 있습니다.
목차
제1장 서론
- IGBT 칩 구조의 진화
- IGBT 칩 소형화의 영향
- DMOSFET와 비교한 트렌치형 SiC MOSFET 저항 저감
- 평면형과 수직형(트렌치형) MOSFET
- FinFET 회로도
- MOSFET와 초접합 MOSFET 회로도
- SiC U MOSFET
제2장 파워 반도체의 용도
- 태양광발전의 예측
- 풀 브릿지 IGBT 토폴로지
- 마이크로컨트롤러 기반 인버터 블럭도
- 세계의 풍력 터빈 출하량
- 주요 풍력발전 발전력 : 국가별
- 일반적인 30-50kW 인버터 부품표
- HEV 트랙션 드라이브 시스템 약도
- 플러그인 하이브리드 전기자동차(PHEV) PEEM의 복잡한 그림
- 인버터의 전도와 스위칭 손실
- 파워 반도체 단가 동향
- 와이드 밴드갭 반도체 시스템과 컴포넌트의 비용
- 종형/횡형 HEMT
- EV에서 GaN 횡형/GaN 종형 HEMT
- LED 비즈니스와 용도의 시장 촉진요인
- SSL vs. 기존 기술
- LED의 성능과 기존 광원의 비교
- 에너지 생산과 사용의 비교
- 일반적인 LED 구동 회로
- TSV를 사용한 LED와 LED 드라이버의 통합
- 심플 파워 MOSFET 모터 컨트롤러
- 인버터의 기본 동작 원리
- 태양광발전의 예측
- 풀 브릿지 IGBT 토폴로지
- 마이크로컨트롤러 기반 인버터 블럭도
- 세계의 풍력 터빈 출하량
- 주요 풍력발전 발전력 : 국가별
- 일반적인 30-50kW 인버터 부품표
- HEV 트랙션 드라이브 시스템 약도
- 플러그인 하이브리드 전기자동차(PHEV) PEEM의 복잡한 그림
- 인버터의 전도와 스위칭 손실
- 파워 반도체의 단가 동향
- 와이드 밴드갭 반도체 시스템과 컴포넌트의 비용
제3장 시장 분석
- 반도체 시장에서 파워 반도체의 포지션
- IGBT와 파워 MOSFET의 성장 가능성
- IGBT 시장
- IGBT 기술의 동향
- IGBT TAM
- IGBT 시장의 성장 : 용도별
- IGBT의 경쟁 구도
- MOSFET TAM
- MOSFET TAM 조사 방법
- MOSFET 시장의 성장 : 용도별
- MOSFET의 경쟁 구도
- 새로운 최종 용도 시장
- 전기자동차
- 5G인프라
- 와이드 밴드갭 파워 반도체 시장
제4장 차세대 파워 반도체
- 실리콘의 한계 극복에 대한 기대
- 차세대 기판으로서의 SiC와 GaN에 대한 기대
- 와이드 밴드갭 반도체의 이점
- SiC와 GaN
- SiC 기기의 제조
- GaN 기기의 제조
- 포장
제5장 기업 개요
- 파워 반도체 기업
- Infineon
- Mitsubishi
- Toshiba
- STMicroelectronics
- Vishay
- Fuji Electric
- Renesas
- Semikron
- NXP Semiconductors
- Hitachi Power Semiconductor Device
- X-Rel Semiconductor
- Advanced Linear Devices
- Nexperia
- Rohm
- Sanken Electric
- Shindengen Electric 5+
- Microchip Technology
- GeneSiC Semiconductor
- Semisouth Laboratories
- United Silicon Carbide
- MicroGaN
- Powerex
- Nitronix
- Transform
- Allegro Microsystems
- GaN Systems
- Navitas Semiconductor
- Alpha and Omega Semiconductor
- ON Semiconductor
- Jilin Sino-Microelectronics
- BYD Microelectronics
- Yangzhou Yangjie Electronic Technology
- StarPower
- Sino Micro
- Yangjie
- Jiejie
- GoodArk
- NCE Power
Introduction
The landscape of power semiconductors is undergoing a profound transformation driven by the escalating demand for energy-efficient solutions across various sectors, ranging from automotive and industrial to consumer electronics and renewable energy systems. As the world transitions towards a more sustainable and electrified future, the role of power semiconductors becomes increasingly pivotal in enabling efficient energy management, power conversion, and control.
The "Power Semiconductors: Markets, Materials, Technologies" report provides a comprehensive analysis of the dynamic power semiconductor market, delving into key trends, emerging materials, and cutting-edge technologies shaping the industry's trajectory. With a focus on market dynamics, material innovations, and technological advancements, the report offers valuable insights into the evolving landscape of power semiconductor devices and their applications across diverse sectors.
Amidst the evolving energy landscape and the imperative for energy conservation, the demand for power semiconductors continues to soar, driven by the need for high-performance, energyefficient solutions. From advanced silicon-based devices to emerging wide-bandgap materials such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), the report explores the evolving material landscape and its impact on the performance and efficiency of power semiconductor devices.
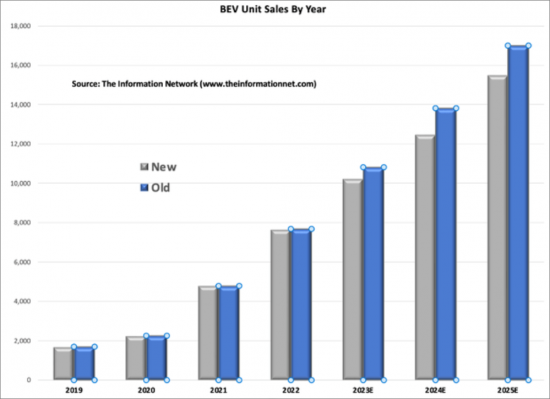
Moreover, the report examines the latest technological developments and innovations in power semiconductor design, packaging, and integration techniques. From discrete circuits to integrated modules and advanced packaging solutions, the report elucidates the technological trends driving efficiency enhancements, miniaturization, and reliability improvements in power semiconductor devices.
In addition to analyzing market trends and technological advancements, the report also provides insights into the competitive landscape of the power semiconductor industry, profiling key players, their strategies, and market positioning. Furthermore, it assesses regional dynamics, regulatory frameworks, and emerging market opportunities, offering stakeholders a comprehensive understanding of the global power semiconductor ecosystem.
Trends
The emergence of wide-bandgap materials, particularly SiC and GaN, represents a significant paradigm shift in the power semiconductor industry. These materials offer distinct advantages over traditional silicon-based semiconductors, including higher breakdown voltages, faster switching speeds, and improved thermal conductivity, making them ideal candidates for highperformance and energy-efficient power electronic devices.
Silicon carbide (SiC) stands out for its superior electrical properties, including a wider bandgap and higher critical electric field strength compared to silicon. These properties enable SiC-based devices to operate at higher temperatures and voltages while maintaining efficient performance. SiC devices exhibit lower on-state losses and switching losses, translating into higher efficiency and reduced energy consumption in various applications, such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial power converters.
Similarly, gallium nitride (GaN) has garnered attention for its exceptional electrical characteristics, including a wide bandgap and high electron mobility. GaN-based devices offer significant advantages in terms of power density, switching speed, and efficiency, making them well-suited for high-frequency and high-power applications. GaN devices exhibit lower switching losses, enabling higher switching frequencies and reduced size and weight of power electronic systems, which is particularly beneficial for compact and lightweight designs in automotive and aerospace applications.
The adoption of SiC and GaN materials in power semiconductor devices is accelerating, driven by advancements in material growth techniques, manufacturing processes, and device architectures. As production volumes increase and manufacturing costs decline, SiC and GaN devices are becoming increasingly competitive with silicon-based counterparts across a wide range of applications.
Furthermore, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on optimizing device performance, enhancing reliability, and reducing costs to further accelerate the adoption of SiC and GaN technology. This includes innovations in device design, packaging technologies, and thermal management solutions to address the unique challenges associated with wide-bandgap materials.
Overall, the widespread adoption of SiC and GaN materials heralds a new era of energyefficient power electronics, offering transformative opportunities for industries seeking to improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and advance sustainable energy solutions. As these materials continue to mature and gain traction in the market, their impact on the power semiconductor industry is poised to be profound and far-reaching.
About This Report
This comprehensive report delves into various aspects of the power semiconductor industry, providing in-depth analysis and insights into markets, materials, and technologies shaping the landscape. Here's an expanded overview of what the report covers:
Market Analysis: The report offers a detailed examination of the global power semiconductor market, including historical trends, current market dynamics, and future growth prospects. It assesses market size, revenue forecasts, and key drivers and challenges influencing market growth. Additionally, the report provides insights into market segmentation by product type, end-user industry, and geographic region.
Material Trends: It explores the latest advancements and trends in semiconductor materials, with a particular focus on wide-bandgap materials such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN). The report discusses the properties and benefits of these materials, their applications across various industries, and their impact on the performance and efficiency of power semiconductor devices.
Technology Insights: The report delves into emerging technologies and innovations in power semiconductor devices, including silicon-based and wide-bandgap devices. It covers developments in device architectures, manufacturing processes, packaging technologies, and thermal management solutions aimed at enhancing device performance, reliability, and costeffectiveness.
Market Segmentation: An in-depth analysis of the power semiconductor market segmentation is provided, highlighting key product categories such as discrete circuits, module circuits, and power integrated circuits (ICs). The report examines market trends and growth opportunities across different end-user industries, including automotive, consumer electronics, industrial, and power distribution.
Regional Analysis: It offers a comprehensive assessment of the power semiconductor market across major geographic regions, including North America, Europe, and Asia including China. The report analyzes regional market trends, competitive landscapes, and regulatory frameworks shaping the industry landscape in each region.
Competitive Landscape: The report profiles leading companies and key players in the power semiconductor industry, providing insights into their market share, product portfolios, strategic initiatives, and competitive strategies. It assesses the competitive intensity and market positioning of major players, along with their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Market Opportunities and Challenges: The report identifies and analyzes emerging market opportunities, growth prospects, and challenges facing the power semiconductor industry. It explores factors such as technological advancements, regulatory trends, investment opportunities, and competitive dynamics shaping the market landscape.
Regional Analysis: It offers a comprehensive assessment of the power semiconductor market across major geographic regions, including North America, Europe, and Asia including China. The report analyzes regional market trends, competitive landscapes, and regulatory frameworks shaping the industry landscape in each region.
Competitive Landscape: The report profiles leading companies and key players in the power semiconductor industry, providing insights into their market share, product portfolios, strategic initiatives, and competitive strategies. It assesses the competitive intensity and market positioning of major players, along with their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Market Opportunities and Challenges: The report identifies and analyzes emerging market opportunities, growth prospects, and challenges facing the power semiconductor industry. It explores factors such as technological advancements, regulatory trends, investment opportunities, and competitive dynamics shaping the market landscape.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction
- 1.1. Evolution Of IGBT Chip Structure
- 1.2. Effects Of Miniaturization Of IGBT Chip
- 1.3. SiC Trench-Type MOSFET And Resistance Reduction As Compared With DMOSFET
- 1.4. Planar And Vertical (Trench) MOSFET
- 1.5. Schematic Of A FinFET
- 1.6. Schematic Of A MOSFET And Super Junction MOSFET
- 1.7. SiC U MOSFET
Chapter 2. Applications of Power Semiconductors
- 2.1. Forecast Of Solar Power
- 2.2. Full Bridge IGBT Topology
- 2.3. Block Diagram Of Microcontroller-Based Inverter
- 2.4. Worldwide Wind Turbine Shipments
- 2.5. Top Wind Power Capacity by Country
- 2.6. Bill Of Materials For A Typical 30-50kw Inverter
- 2.7. A Simple Diagram Of A HEV Traction Drive System.
- 2.8. A More Complex Diagram Of PEEM In A Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- 2.9. Conducting And Switching Loses For Inverter
- 2.10. Unit Pricing Trends In Power Semiconductors
- 2.11. System And Component Costs For Wide Bandgap Semiconductors
- 2.12. Vertical And Lateral HEMT
- 2.13. GaN Lateral And GaN Vertical HEMTs In EVs
- 2.14. Market Drivers For LED Biz And Applications
- 2.15. SSL Vs. Classical Technologies
- 2.16. LED Performance Vs. Traditional Light Sources
- 2.17. Energy Production And Use Comparison
- 2.18. Typical LED Drive Circuit
- 2.19. Integration Of LED And LED Driver Using TSV
- 2.20. Simple Power MOSFET Motor Controller
- 2.21. Basic Operating Principle Of Inverter
- 2.1. Forecast Of Solar Power
- 2.2. Full Bridge IGBT Topology
- 2.3. Block Diagram Of Microcontroller-Based Inverter
- 2.4. Worldwide Wind Turbine Shipments
- 2.5. Top Wind Power Capacity by Country
- 2.6. Bill Of Materials For A Typical 30-50kw Inverter
- 2.7. A Simple Diagram Of A HEV Traction Drive System
- 2.8. A More Complex Diagram Of PEEM In A Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- 2.9. Conducting And Switching Loses For Inverter
- 2.10. Unit Pricing Trends In Power Semiconductors
- 2.11. System And Component Costs For Wide Bandgap Semiconductors
Chapter 3. Market Analysis
- 3.1. Position of Power Semiconductors in Semiconductor Market
- 3.2. Growth Potential of IGBTs and Power MOSFETs
- 3.3. IGBT Market
- 3.3.1. IGBT Technology Trends
- 3.3.2. IGBT TAM
- 3.3.3. IGBT Market Growth By Applications
- 3.3.3.1. Automotive
- 3.3.3.2. Power Generation And Grid
- 3.3.3.3. Consumer Electronics
- 3.3.3.4. Industrial Controls
- 3.3.3.5. Railway/Train
- 3.3.3.6. EV Charging Systems
- 3.3.4. IGBT Competitive Landscape
- 3.3.4.1. Global And China Market Share
- 3.3.4.2. IGBT Business Model
- 3.3.4.3. Technology Gap Between China And Global Players
- 3.4. MOSFET TAM
- 3.4.1. MOSFET TAM Methodology
- 3.4.2. MOSFET Market Growth By Applications
- 3.4.2.1. Automotive
- 3.4.2.2. EV Charging
- 3.4.2.3. Industrial And Medical
- 3.4.2.4. Consumer
- 3.4.2.5. Telecom Network
- 3.4.3.6. Computing
- 3.4.4. MOSFET Competitive Landscape
- 3.4.4.1. Global And China Market Share
- 3.4.4.2. China Suppliers' Technology/Product Gaps Vs Global Peers
- 3.5. Emerging End Application Markets
- 3.5.1. Electric Vehicles
- 3.5.2 5G Infrastructure
- 3.4. Wide Bandgap Power Semiconductor Market
Chapter 4. Next-Generation Power Semiconductors
- 4.1. Expectations for Overcoming Silicon's Limitations
- 4.2. Expectations Of SiC and GaN as Next-Generation Substrates
- 4.3. Benefits of Wide Band Gap Semiconductors
- 4.4. SiC versus GaN
- 4.4.1. Material Properties
- 4.4.2. Material Quality
- 4.4.3. SiC Lateral Devices:
- 4.4.4. SiC Vertical Devices
- 4.4.5. GaN Lateral Devices
- 4.5. Fabrication of SiC devices
- 4.5.1. Bulk and Epitaxial Growth of SiC
- 4.5.1.1. Bulk Growth
- 4.5.1.2. Epitaxial Growth
- 4.5.1.3. Defects
- 4.5.2. Surface Preparation
- 4.5.3. Etching
- 4.5.4. Lithography
- 4.5.5. Ion Implantation
- 4.5.6. Surface Passivation
- 4.5.7. Metallization
- 4.5.1. Bulk and Epitaxial Growth of SiC
- 4.6. Fabrication of GaN devices
- 4.6.1. GaN Challenges
- 4.6.1.1. Costs
- 4.6.1.2. Reliability
- 4.6.1.3. Component Packaging and Thermal Reliability
- 4.6.1.4. Control
- 4.6.1.5. Device Modeling
- 4.6.1. GaN Challenges
- 4.7. Packaging
Chapter 5. Company Profiles
- 5.1. Power Semiconductor Companies
- 5.1.1. Infineon
- 5.1.2. Mitsubishi
- 5.1.3. Toshiba
- 5.1.4. STMicroelectronics
- 5.1.5. Vishay
- 5.1.6. Fuji Electric
- 5.1.7. Renesas
- 5.1.8. Semikron
- 5.1.9. NXP Semiconductors
- 5.1.10. Hitachi Power Semiconductor Device
- 5.1.11. X-Rel Semiconductor
- 5.1.12. Advanced Linear Devices
- 5.1.13. Nexperia
- 5.1.14. Rohm
- 5.1.15. Sanken Electric
- 5.1.16. Shindengen Electric 5+
- 5.1.17. Microchip Technology
- 5.1.18. GeneSiC Semiconductor
- 5.1.19. Semisouth Laboratories
- 5.1.20. United Silicon Carbide
- 5.1.21. MicroGaN
- 5.1.22. Powerex
- 5.1.23. Nitronix
- 5.1.24. Transform
- 5.1.25. Allegro Microsystems
- 5.1.26. GaN Systems
- 5.1.27. Navitas Semiconductor
- 5.1.28. Alpha and Omega Semiconductor
- 5.1.29. ON Semiconductor
- 5.1.30. Jilin Sino-Microelectronics
- 5.1.31. BYD Microelectronics
- 5.1.32. Yangzhou Yangjie Electronic Technology
- 5.1.33. StarPower
- 5.1.34. Sino Micro
- 5.1.35. Yangjie
- 5.1.36. Jiejie
- 5.1.37. GoodArk
- 5.1.38. NCE Power


















