
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1777939
전해 산화 시장 : 전극 재료별, 유형별, 전극 재료별, 최종 이용 산업별, 용도별, 지역별 - 예측(-2030년)Electro-Oxidation Market by Type, Electrode Material (Boron-Doped Diamond, Lead Dioxide, Stannic Oxide, Titanium Suboxides, Graphite, and Platinum), Application, End-Use Industry & Region - Forecast to 2030 |
||||||
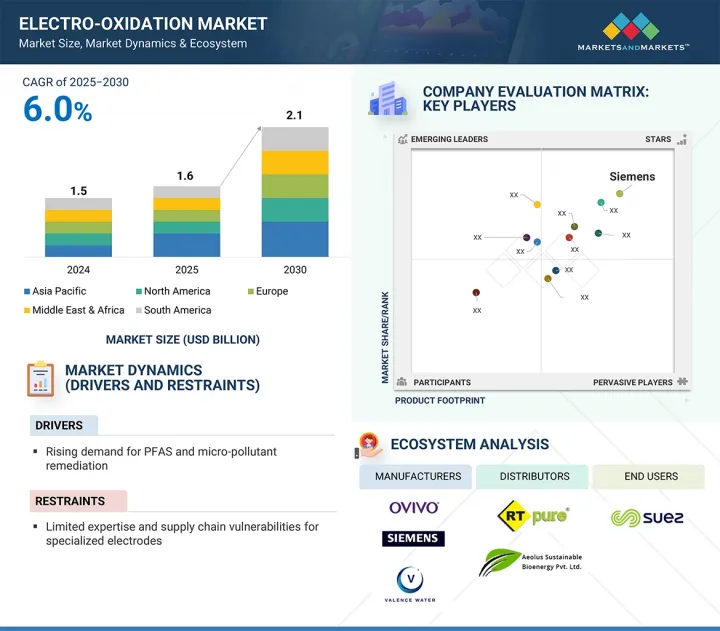
전해 산화 시장 규모는 2025년 16억 달러에서 2030년에는 21억 달러로 성장하고, 예측 기간 중 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)은 6.0%를 기록할 것으로 예측됩니다.
| 조사 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 조사 대상 연도 | 2021-2030년 |
| 기준연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 기간 | 2025-2030년 |
| 검토 단위 | 금액( 100만 달러/10억 달러) |
| 부문 | 전극 재료별, 유형별, 전극 재료별, 최종 이용 산업별, 용도별, 지역별 |
| 대상 지역 | 북미, 유럽, 중동 및 아프리카, 남미 |
수질 오염과 물 부족이라는 지속적이고 광범위한 문제에 대응하기 위해 친환경 수처리 솔루션에 대한 수요가 증가함에 따라 전해 산화 시장이 확대되고 있습니다. 전 세계적으로 환경 규제가 강화됨에 따라 산업계는 폐수 기준을 충족하기 위해 새로운 처리 기술을 채택해야 하며, 전해 산화는 외부 투입을 최소화하면서 특히 까다로운 오염 물질을 변환할 수 있는 방법으로 각광받고 있습니다. 의료시설이나 공공 급수 시스템 등 물 안전이 특히 중요한 분야에서는 공중보건에 대한 관심이 높아지면서 수계 전염병과 신종 오염물질(CECs)에 대한 우려가 커지고 있습니다. 또한, 산업의 탈탄소화와 스마트 물 관리 시스템의 성장에 따라, 전해산화는 지속가능성에 기반한 차세대 수처리 접근법으로 확대될 수 있는 큰 잠재력을 가지고 있습니다.

직접 전해산화는 조작이 간단하고 처리 효율이 높으며 시약과 촉매에 대한 추가 수요가 적기 때문에 전해산화 시장에서 가장 빠르게 성장하는 유형이 될 것으로 예측됩니다. 오염물질은 양극 표면에서 직접 산화되며, 중간 단계나 2차 산화제의 생성은 없습니다. 직접 전기분해 산화를 통해 효율적이고 일관성 있고 신뢰할 수 있는 폐수 처리 솔루션을 원하는 산업 및 유틸리티 고객들은 시스템 설계, 유지보수 및 모니터링을 간소화할 수 있습니다. 직접 전기분해 산화가 급성장하는 주된 이유는 유기 오염물질을 효과적으로 분해하고 난분해성 비생분해성 물질을 무기화할 수 있는 능력에 있습니다. 직접 전기분해 산화는 전극 표면에서 강력한 산화 조건을 만들어 극성 및 비극성 오염물질을 무해한 최종 제품으로 완전히 무기화할 수 있습니다. 이는 화학, 제약, 염료, 석유화학 등 산업에서 고강도 폐수를 배출하는 고객에게 특히 매력적이며, 특히 생물학적 처리 한계에 도달했거나 염소나 오존과 같은 화학적 처리로 오염물질을 효과적으로 제거하거나 전환할 수 없는 경우에 특히 효과적입니다.
이산화납(PbO2)은 전해 산화 시장에서 가장 인기 있는 전극 재료로 빠르게 부상하고 있습니다. 이러한 추세는 알칼리 고도 산화 공정에서 고성능, 화학적 안정성 및 비용 효율성의 탁월한 조합으로 인해 발생했습니다. 이산화납이 빠르게 채택된 주된 이유는 표준 치료법으로 제거할 수 없는 미량 오염물질과 비생분해성 오염물질을 포함한 광범위한 유기 오염물질을 산화적으로 분해할 수 있기 때문입니다. 또한, 이산화납 전극은 높은 산소 발생 오버 가능성을 특징으로 하며, 부반응에 의해 빠르게 소모되지 않고 하이드록시라디칼과 같은 강력한 산화 종을 형성할 수 있어 치료 효율을 향상시킵니다. 산화력 외에도 PbO2는 전기 화학적 조건에서 우수한 안정성을 보여줍니다. 따라서 다른 전극은 시간이 지남에 따라 열화되거나 효과가 떨어질 수 있는 유기물이 많이 함유된 고농도 오염 산업폐수 처리에 적합한 전극 재료입니다. 이산화납 전극의 내구성은 가혹한 부식 환경에서도 산화 능력을 잃지 않고 장기간 사용할 수 있어 성능과 신뢰성이 향상됩니다. 이러한 특성으로 인해 이산화납 전극은 지자체 및 산업 응용 분야에서 자주 사용되는 연속 흐름 처리 시스템에서 우위를 점하고 있습니다.
중금속, 질산염 및 기타 무기 오염물질을 처리할 필요가 있기 때문에 무기 오염물질은 전해 산화 시장에서 가장 빠르게 성장하는 응용 분야입니다. 전해산화는 직접 전자 이동 또는 반응종 생성에 의한 산화 또는 환원에 의해 무기물을 제거하며, 무기물 처리는 기존의 방법으로 제거 니즈를 충족시킬 수 없는 경우에 매우 효과적입니다. 산업 관행의 변화와 규제 강화로 인해 전해 산화는 주로 아시아태평양에서 선호되는 처리 기술로 부상하고 있습니다. 이 지역에서는 광업, 화학, 전자 산업이 오염물질, 특히 중금속의 엄격한 배출 기준을 충족해야 합니다. 북미에서는 질산염 오염에 대한 농업 규제가 농업 폐수 및 지하수를 대상으로 변경됨에 따라 효과적이고 효율적인 질산염 처리를 위해 이산화 납과 티타늄 전극을 사용한 전기분해 산화 파일럿의 사용이 증가하고 있습니다. 유럽에서는 도시 폐수 처리 지침과 산업 폐수 중 무기 오염 물질을 포함한 오염 방지에 대한 요구 사항으로 인해 화학 공장에서 전해 산화에 대한 관심이 높아지고 있습니다. 아프리카, 남미, 라틴아메리카 국가들의 광산 활동의 성장도 세계은행의 지원을 받아 중금속을 포함한 산성 광산 폐수를 처리할 수 있는 전해 산화 처리에 대한 수요를 촉진하고 있습니다.
산업 제조 산업은 폐수 배출 환경 기준을 준수하고 지속가능성 목표를 지원하기 위한 고도의 폐수 처리에 대한 수요가 매우 높기 때문에 전기분해 산화(EO) 시장에서 가장 빠르게 성장하는 최종 사용 분야가 되고 있습니다. 제조 부문(화학물질 및 의약품 포함)은 중금속, 과불화알킬물질 및 폴리불화알킬물질(PFAS로 그룹화됨)과 같은 미량 오염물질과 함께 난치성 유기오염물질을 포함한 복잡한 폐수를 생성하며, 기존의 수처리로는 지속 가능한 처리에 어려움을 겪고 있습니다. 전해 산화는 직접 또는 간접 산화를 통해 오염물질을 분해할 수 있으며, 붕소 다이아몬드나 이산화 납과 같은 강력한 전극을 유지할 수 있습니다. 전기화학적 폐수처리 상한은 재투입을 목적으로 한 폐수의 재이용을 주 목적으로 하여 열악한 배출기준을 달성하는 경우에 발생합니다. 제조업의 폐수 무방류(ZLD) 목표는 전해 산화 방식을 채택하도록 장려하고, 순환 경제를 실천하고 모든 폐기물을 없애기 위해 폐기물을 줄이도록 강요합니다. 전해산화는 폐수 처리 공정을 발전시키는 전해산화의 예에서 볼 때, 전해산화가 폐수의 복잡한 기존 배출 기준을 충족시키기 위한 일부 산업체의 노력에 대응하는 개별적인 처리 솔루션이 될 가능성은 매우 낮습니다. 전해산화는 광범위한 유기 및 무기 오염물질을 처리할 수 있는 능력이 있기 때문에 고농도 폐수를 생성할 수 있으며, 제약회사 및 복잡한 산업 폐수 기준을 준수하려는 화학회사에서 발생하는 고COD, 고독성 폐수와도 잘 작동합니다.
세계의 전해산화 시장에 대해 조사했으며, 전극 재료별/유형별/전극 재료별/최종 이용 산업별/용도별/지역별 동향, 시장 진출 기업 프로파일 등의 정보를 정리하여 전해드립니다.
목차
제1장 서론
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 프리미엄 인사이트
제5장 시장 개요
- 서론
- 시장 역학
- 생성형 AI가 전해 산화 시장에 미치는 영향
제6장 업계 동향
- 서론
- 고객의 비즈니스에 영향을 미치는 동향/혼란
- 밸류체인 분석
- 2025년 미국 관세의 영향-전해 산화 시장
- 지표 가격 분석
- 투자 및 자금조달 시나리오
- 생태계 분석
- 기술 분석
- 특허 분석
- 무역 분석
- 2025-2026년 주요 컨퍼런스 및 이벤트
- 관세 및 규제 상황
- Porter의 Five Forces 분석
- 주요 이해관계자와 구입 기준
- 거시경제 전망
- 사례 연구 분석
제7장 전해 산화 시장(전극 재료별)
- 서론
- 붕소 도핑 다이아몬드
- 이산화 납
- 산화 주석
- 티타늄 서브 옥사이드
- 흑연
- 백금
제8장 전해 산화 시장(유형별)
- 서론
- 직접 전해 산화
- 간접 전해 산화
제9장 전해 산화 시장(최종 이용 산업별)
- 서론
- 도시 상하수도 및 폐수
- 산업 제조업
- 섬유
- 식품 및 음료
- 광업
- 기타
제10장 전해 산화 시장(용도별)
- 서론
- 유기 및 미량 처리 부문
- 무기 처리
- 소독 및 특수 처리
제11장 전해 산화 시장(지역별)
- 서론
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 기타
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 이탈리아
- 프랑스
- 영국
- 스페인
- 기타
- 중동 및 아프리카
- GCC 국가
- 남아프리카공화국
- 기타
- 남미
- 아르헨티나
- 브라질
- 기타
제12장 경쟁 구도
- 서론
- 주요 시장 진출기업의 전략/강점
- 시장 점유율 분석, 2024년
- 매출 분석
- 브랜드/제품 비교
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 주요 시장 진출기업, 2024년
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 스타트업/중소기업, 2024년
- 기업 평가와 재무 지표, 2024년
- 경쟁 시나리오
제13장 기업 개요
- 주요 시장 진출기업
- LUMMUS TECHNOLOGY
- OVIVO USA LLC
- VALENCE WATER INC
- HYDROLEAP
- JIANGSU JINGYUAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION CO., LTD
- GROUND EFFECTS ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES INC
- E-FLOC WASTEWATER SOLUTIONS
- YASA ET(SHANGHAI) CO., LTD.
- AQUA PULSAR
- AXINE WATER TECHNOLOGIES
- 기타 기업
- AEOLUS SUSTAINABLE BIOENERGY PVT. LTD
- MAGNELI MATERIALS
- HUNAN BOROMOND EPT CO. LTD.
- VENTILAQUA
- RT SAFEBALLAST PVT LTD.
- MAGNETO SPECIAL ANODES(SUZHOU) CO., LTD.
- AQUACARE SOLUTION ENVIRO ENGINEERS
- GREEN ECOWATER SYSTEMS
- BLUE EDEN CLEAN TECHNOLOGY
- PPU UMWELTTECHNIK
제14장 부록
LSH 25.08.01The electro-oxidation market size is projected to grow from USD 1.6 billion in 2025 to USD 2.1 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 6.0% during the forecast period.
| Scope of the Report | |
|---|---|
| Years Considered for the Study | 2021-2030 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2030 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Million/Billion) |
| Segments | Type, Electrode Material, Application, End-Use Industry, and Region |
| Regions covered | North America, Europe, Middle East & Africa, South America |
The market for electro-oxidation is expanding as it meets the rising demand for green water treatment solutions in response to ongoing and widespread issues of water pollution and scarcity. Stricter environmental regulations worldwide are encouraging industries to adopt new treatment technologies to meet effluent standards, and electro-oxidation stands out as a method capable of transforming pollutants that are particularly challenging with minimal external inputs. In sectors where water safety is especially critical, such as healthcare facilities and public water systems, there is increased focus on public health and concerns over waterborne diseases and emerging contaminants (CECs). Additionally, with the growth of industrial decarbonization and smart water management systems, electro-oxidation has significant potential for expansion as a next-generation water treatment approach rooted in sustainability.
" Direct electro-oxidation is the fastest-growing type segment of the electro-oxidation market in terms of value."
Direct electro-oxidation is expected to be the fastest-growing type segment in the electro-oxidation market because it is simple to operate, efficient to treat, and has lower demands for additional reagents or catalysts. Pollutants are oxidized directly at the surface of the anode, with no intermediate steps and no secondary oxidants produced. This straightforward mechanism of direct electro-oxidation simplifies system design, maintenance, and monitoring for industrial or utility clients seeking an efficient, consistent, and reliable wastewater treatment solution. The primary reason for the rapid growth of direct electro-oxidation is its ability to effectively break down organic pollutants and help mineralize persistent, non-biodegradable substances. Direct electro-oxidation creates strong oxidizing conditions at the electrode surface, enabling the complete mineralization of polar and non-polar contaminants into harmless end products. This is particularly appealing to clients discharging high-strength effluents from industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, dyes, and petrochemicals, especially when biological treatment limits are met or chemical treatments such as chlorine and ozone are ineffective in removing or transforming contaminants effectively.
"Lead oxidation is the fastest-growing electrode material segment of the electro-oxidation market in terms of value."
Lead dioxide (PbO2) is rapidly becoming the most popular electrode material in the electro-oxidation market. This trend is driven by its unmatched combination of high performance, chemical stability, and cost-effectiveness in alkaline advanced oxidation processes. A key reason for its quick adoption is its ability to oxidatively break down a wide range of organic pollutants, including micropollutants and non-biodegradable pollutants that standard treatment methods cannot remove. Additionally, lead dioxide electrodes feature a high oxygen evolution overpotential, which enables the formation of strong oxidizing species like hydroxyl radicals without being quickly consumed by side reactions, thus improving treatment efficiency. Besides its oxidizing power, PbO2 shows excellent stability under electrochemical conditions. This makes it a suitable electrode material for treating heavily contaminated industrial wastewater containing high levels of organics, where other electrode options may degrade or lose effectiveness over time. The durability of lead dioxide electrodes means they can operate for a long period in harsh, corrosive environments without losing their oxidizing capability, thereby enhancing performance and reliability. This characteristic gives PbO2 electrodes an advantage in continuous-flow treatment systems, often used in municipal or industrial applications.
"Inorganic pollutant treatment for the fastest-growing electrode material segment of the electro-oxidation market in terms of value."
Inorganic pollutants are the fastest-growing application segment in the electro-oxidation market due to the need to treat heavy metals, nitrates, and other inorganic contaminants. Electro-oxidation removes inorganics through oxidation or reduction by direct electron transfer or reactive species generation, and treatment of inorganics can be very effective when traditional methods cannot meet removal needs. Due to changes in industrial practices and stricter regulations, electro-oxidation is mainly emerging as a preferred treatment technology in the Asia-Pacific region, where industries in mining, chemicals, and electronics must meet stringent discharge standards for pollutants, especially heavy metals-as seen in pilots in China's industrial wastewater and mining industries and in India, where mining operations have a zero-liquid discharge component in wastewater standards. Changes in North America's agricultural regulations for nitrate contamination, which now target agricultural runoff and groundwater, have increased the use of electro-oxidation pilots using lead dioxide or titanium electrodes for effective and efficient nitrate treatment. In Europe, the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive and its requirements for pollution prevention-including inorganic contaminants-in industrial discharges have generated interest in electro-oxidation applications in chemical plants. The growth of mining activities in countries across Africa, South America, and Latin America has also driven demand for electro-oxidation treatment, as it can treat acidic mine drainage with heavy metals, with support from the World Bank.
"Industrial manufacturing is expected to be the fastest-growing segment of the electro-oxidation market in terms of value."
Industrial manufacturing is becoming the fastest-growing end-use segment of the Electro-Oxidation (EO) market due to its highly intense demand for advanced wastewater treatment to comply with water discharge environmental standards and support sustainability goals. The manufacturing sectors (including chemicals and pharmaceuticals) produce complex effluents with recalcitrant organic contaminants along with heavy metals and micropollutants like per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (completed grouped as PFAS) that conventional water treatments struggle to sustainably treat. Electro-oxidation is able to degrade contaminants through either direct or indirect oxidation which can preserve strong electrodes such as boron-doped diamond or lead dioxide. The upper limits of electrochemical wastewater treatment occur when poor discharge standards are being achieved with the primary goal of reclaiming wastewater for the purpose of reinjection. The zero-liquid discharge (ZLD) goals in manufacturing industries encourage the adoption of electro-oxidation, forcing the reduction of wastes with the intention of implementing circular economy practices and the elimination of any waste. In the instance of electro-oxidation producing advanced wastewater treatment processes, it is highly unlikely electro-oxidation will become a discrete treatment solution catered to some industrial companies' efforts to meet complex existing discharge standards in their rejected water. Electro-oxidation has the potential to generate advanced wastewater as it has the ability to treat a wide range of organic and inorganic contaminants, and works well with high-COD, highly toxic effluents from a pharmaceutical manufacturer or a chemical manufacturer trying to comply with their complex industry water discharge standards.
In-depth interviews were conducted with chief executive officers (CEOs), marketing directors, other innovation and technology directors, and executives from various key organizations operating in the Electro-Oxidation market, and information was gathered from secondary research to determine and verify the market size of several segments.
- By Company Type: Tier 1 - 50%, Tier 2 - 30%, and Tier 3 - 20%
- By Designation: Managers- 15%, Directors - 20%, and Others - 65%
- By Region: North America - 25%, Europe - 15%, Asia Pacific - 45%, Middle East & Africa - 10%, South America - 5%.
Aqua Pulsar (US), Hydroleap (Singapore), Yasa ET (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (China), OVIVO USA LLC (US), E-FLOC (US), Siemens (Germany), Valence Water Inc. (Colombia), PPU Umwelttechnik (Germany), Inc. (Canada), and Jiangsu Jingyuan Environmental Protection Co., Ltd (China) are the major companies in this market. The study includes an in-depth competitive analysis of these key players in the electro-oxidation market, with their company profiles, recent developments, and key market strategies.
Research Coverage
This report segments the electro-oxidation market based on type, electrode material, application, end-use industry, and region and provides estimates for the overall market value across different regions. It has also conducted a detailed analysis of key industry players to offer insights into their business overviews, products and services, key strategies, and expansions related to the electro-oxidation market.
Key benefits of buying this report
This research report focuses on various levels of analysis - industry analysis (industry trends), market ranking analysis of top players, and company profiles, which together provide an overall view of the competitive landscape; emerging and high-growth segments of the electro-oxidation market; high-growth regions; and market drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges.
The report provides insights on the following pointers:
- Analysis of drivers (Rising Demand for PFAS and Micro-Pollutant Remediation), restraints (Limited Expertise and Supply Chain Vulnerabilities for Specialized Electrodes), opportunities (Integration of Renewable Energy Sources to Reduce Operational Costs), and challenges (Partial Oxidation of Ammonia and Ions Requiring Additional Processes).
- Market Penetration: Comprehensive information on the Electro-Oxidation market offered by top players in the electro-oxidation market.
- Product Development/Innovation: Detailed insights on upcoming technologies, research & development activities, partnership, agreement, joint venture, collaboration, announcement, awards, and expansion in the market.
- Market Development: The report provides comprehensive information about lucrative emerging markets and analyzes the electro-oxidation market across regions.
- Market Capacity: Production capacities of companies producing electro-oxidation are provided wherever available, with upcoming capacities for the electro-oxidation market.
- Competitive Assessment: In-depth assessment of market shares, strategies, products, and manufacturing capabilities of leading players in the electro-oxidation market.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES
- 1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
- 1.3 STUDY SCOPE
- 1.3.1 MARKETS COVERED AND REGIONAL SNAPSHOT
- 1.3.2 INCLUSIONS & EXCLUSIONS
- 1.3.3 YEARS CONSIDERED
- 1.3.4 CURRENCY CONSIDERED
- 1.4 LIMITATIONS
- 1.5 STAKEHOLDERS
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 RESEARCH DATA
- 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.1.1.1 Key data from secondary sources
- 2.1.2 PRIMARY DATA
- 2.1.2.1 Key data from primary sources
- 2.1.2.2 Key primary sources
- 2.1.2.3 Key participants for primary interviews
- 2.1.2.4 Breakdown of primary interviews
- 2.1.2.5 Key industry insights
- 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.2 BASE NUMBER CALCULATION
- 2.2.1 SUPPLY-SIDE ANALYSIS
- 2.2.2 DEMAND-SIDE ANALYSIS
- 2.3 GROWTH FORECAST
- 2.3.1 SUPPLY SIDE
- 2.3.2 DEMAND SIDE
- 2.4 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
- 2.4.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 2.4.2 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- 2.5 DATA TRIANGULATION
- 2.6 RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS
- 2.7 GROWTH FORECAST
- 2.8 RISK ASSESSMENT
- 2.9 FACTOR ANALYSIS
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
- 4.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET
- 4.2 ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET, BY TYPE
- 4.3 ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET, BY ELECTRODE MATERIAL
- 4.4 ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET, BY APPLICATION
- 4.5 ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET, BY END-USE INDUSTRY
- 4.6 ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET, BY COUNTRY
5 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 5.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.2.1.1 Rising demand for PFAS and micro-pollutant remediation
- 5.2.1.2 Adoption in decentralized and modular wastewater treatment
- 5.2.2 RESTRAINTS
- 5.2.2.1 Limited expertise and supply chain vulnerabilities for specialized electrodes
- 5.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
- 5.2.3.1 Integration of renewable energy sources to reduce operational costs
- 5.2.3.2 Treatment of non-biodegradable organic compounds and nitrogen organisms
- 5.2.4 CHALLENGES
- 5.2.4.1 Partial oxidation of ammonia and ions requiring additional processes
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.3 IMPACT OF GENERATIVE AI ON ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET
- 5.3.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.3.2 IMPACT ON ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET
6 INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 6.1 INTRODUCTION
- 6.2 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
- 6.3 VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 6.3.1 RAW MATERIAL PROCUREMENT
- 6.3.2 TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT & R&D
- 6.3.3 COMPONENT MANUFACTURING & ASSEMBLY
- 6.3.4 SYSTEM INTEGRATION & END-USE CUSTOMIZATION
- 6.3.5 DISTRIBUTION, INSTALLATION & AFTER-SALES SERVICE
- 6.4 IMPACT OF 2025 US TARIFFS-ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET
- 6.4.1 INTRODUCTION
- 6.4.2 KEY TARIFF RATES
- 6.4.3 PRICE IMPACT ANALYSIS
- 6.4.4 KEY IMPACT ON VARIOUS REGIONS
- 6.4.4.1 US
- 6.4.4.2 Europe
- 6.4.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 6.4.5 END-USE INDUSTRY IMPACT
- 6.5 INDICATIVE PRICING ANALYSIS
- 6.5.1 INTRODUCTION
- 6.5.2 INDICATIVE PRICING OF ELECTRO-OXIDATION AMONG KEY PLAYERS, BY TYPE, 2021-2024
- 6.5.3 INDICATIVE PRICE, BY TYPE, 2021-2024
- 6.6 INVESTMENT AND FUNDING SCENARIO
- 6.7 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
- 6.8 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS
- 6.8.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.8.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.9 PATENT ANALYSIS
- 6.9.1 METHODOLOGY
- 6.9.2 PATENTS GRANTED, 2015-2024
- 6.9.3 PATENT PUBLICATION TRENDS
- 6.9.4 INSIGHTS
- 6.9.5 LEGAL STATUS OF PATENTS
- 6.9.6 JURISDICTION ANALYSIS
- 6.9.7 TOP APPLICANTS
- 6.9.8 LIST OF MAJOR PATENTS
- 6.10 TRADE ANALYSIS
- 6.10.1 EXPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 842121)
- 6.10.2 IMPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 842121)
- 6.11 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2025-2026
- 6.12 TARIFF AND REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 6.12.1 TARIFF, 2024
- 6.12.2 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- 6.12.3 REGULATIONS RELATED TO ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET
- 6.13 PORTER'S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS
- 6.13.1 THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS
- 6.13.2 THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES
- 6.13.3 BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS
- 6.13.4 BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS
- 6.13.5 INTENSITY OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- 6.14 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA
- 6.14.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS
- 6.14.2 BUYING CRITERIA
- 6.15 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 6.15.1 GDP TRENDS AND FORECASTS, BY COUNTRY
- 6.16 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
- 6.16.1 APPLICATION OF ELECTRO-OXIDATION TECHNOLOGY FOR EFFECTIVE TREATMENT OF MUNICIPAL LANDFILL LEACHATE
- 6.16.2 OX TREATMENT OF MUNICIPAL WASTEWATER FOR DISCHARGE TO WATERSHED
7 ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET, BY ELECTRODE MATERIAL
- 7.1 INTRODUCTION
- 7.2 BORON-DOPED DIAMOND
- 7.2.1 ENABLING HIGH-EFFICIENCY POLLUTANT MINERALIZATION
- 7.3 LEAD DIOXIDE
- 7.3.1 PROVIDING COST-EFFECTIVE OXIDATION OF CONTAMINANTS
- 7.4 STANNIC OXIDE
- 7.4.1 FACILITATING EFFICIENT DEGRADATION WITH STABLE PERFORMANCE
- 7.5 TITANIUM SUBOXIDE
- 7.5.1 DELIVERING CORROSION-RESISTANT OXIDATION SOLUTIONS
- 7.6 GRAPHITE
- 7.6.1 SUPPORTING ECONOMIC ELECTROCHEMICAL TREATMENT
- 7.7 PLATINUM
- 7.7.1 ENHANCING CATALYTIC OXIDATION WITH NOBLE METAL PRECISION
8 ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET, BY TYPE
- 8.1 INTRODUCTION
- 8.2 DIRECT ELECTRO-OXIDATION
- 8.2.1 OXIDIZING POLLUTANTS DIRECTLY AT ANODE
- 8.3 INDIRECT ELECTRO-OXIDATION
- 8.3.1 GENERATING INTERMEDIATE OXIDANTS FOR POLLUTANT DEGRADATION
9 ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET, BY END-USE INDUSTRY
- 9.1 INTRODUCTION
- 9.2 MUNICIPAL WATER & WASTEWATER
- 9.2.1 ENSURING PUBLIC WATER SAFETY AND COMPLIANCE
- 9.3 INDUSTRIAL MANUFACTURING
- 9.3.1 TREATING ORGANIC POLLUTANTS IN INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER
- 9.4 TEXTILES
- 9.4.1 REMOVING DYES FROM WASTEWATER FOR COMPLIANCE
- 9.5 FOOD & BEVERAGE
- 9.5.1 BALANCING ORGANIC WASTE TREATMENT AND HYGIENE STANDARDS
- 9.6 MINING
- 9.6.1 MITIGATING ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT OF INORGANIC POLLUTANTS
- 9.7 OTHERS
- 9.7.1 ELECTRONIC & SEMICONDUCTOR
- 9.7.2 AQUACULTURE
10 ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET, BY APPLICATION
- 10.1 INTRODUCTION
- 10.2 ORGANIC & MICROPOLLUTANT TREATMENT SEGMENT
- 10.2.1 DEGRADING ORGANIC POLLUTANTS AND EMERGING CONTAMINANTS
- 10.3 INORGANIC TREATMENT
- 10.3.1 REMOVING HEAVY METALS AND INORGANIC CONTAMINANTS
- 10.4 DISINFECTION & SPECIALIZED TREATMENT
- 10.4.1 ENSURING MICROBIAL SAFETY AND ENHANCING WATER QUALITY
11 ELECTRO-OXIDATION MARKET, BY REGION
- 11.1 INTRODUCTION
- 11.2 ASIA PACIFIC
- 11.2.1 CHINA
- 11.2.1.1 Stricter industrial effluent control driving electro-oxidation adoption in textile and chemical sectors
- 11.2.2 JAPAN
- 11.2.2.1 Focus on emerging contaminants in electronics and pharmaceutical industries
- 11.2.3 INDIA
- 11.2.3.1 Urban wastewater management driving electro-oxidation adoption in municipal and agricultural sectors
- 11.2.4 SOUTH KOREA
- 11.2.4.1 Water reuse mandates boosting electro-oxidation in semiconductor and municipal sectors
- 11.2.5 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC
- 11.2.1 CHINA
- 11.3 NORTH AMERICA
- 11.3.1 US
- 11.3.1.1 PFAS remediation to drive electro-oxidation adoption in municipal and chemical sectors
- 11.3.2 CANADA
- 11.3.2.1 Mining effluent management boosting electro-oxidation in mining and forestry sectors
- 11.3.3 MEXICO
- 11.3.3.1 Industrial water reuse to drive electro-oxidation in manufacturing and textile sectors
- 11.3.1 US
- 11.4 EUROPE
- 11.4.1 GERMANY
- 11.4.1.1 Industrial Compliance Driving Electro-Oxidation adoption in Chemical Sector
- 11.4.2 ITALY
- 11.4.2.1 Water Scarcity Mitigation Driving Electro-oxidation in Agricultural and Aquaculture Sectors
- 11.4.3 FRANCE
- 11.4.3.1 Pharmaceutical Residue Control Boosting Electro-oxidation in Healthcare and Biotech Sectors
- 11.4.4 UK
- 11.4.4.1 Decentralized Demand and Regulatory Shift Fueling Electro-oxidation Uptake
- 11.4.5 SPAIN
- 11.4.5.1 Drought and Industrial Agriculture Demanding Advanced Wastewater Solutions
- 11.4.6 REST OF EUROPE
- 11.4.1 GERMANY
- 11.5 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
- 11.5.1 GCC COUNTRIES
- 11.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 11.5.1.1.1 Industrial diversification and water sustainability mandates fueling market expansion
- 11.5.1.2 UAE
- 11.5.1.2.1 Water stress and smart infrastructure agenda driving electro-oxidation deployment
- 11.5.1.3 Rest of GCC countries
- 11.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 11.5.2 SOUTH AFRICA
- 11.5.2.1 Industrial contamination and urban infrastructure gaps propelling electro-oxidation adoption
- 11.5.3 REST OF MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
- 11.5.1 GCC COUNTRIES
- 11.6 SOUTH AMERICA
- 11.6.1 ARGENTINA
- 11.6.1.1 Aging infrastructure and food processing demand prompt electro-oxidation integration
- 11.6.2 BRAZIL
- 11.6.2.1 Industrial hubs and water scarcity driving electro-oxidation expansion in urban and semi-urban zones
- 11.6.3 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA
- 11.6.1 ARGENTINA
12 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 12.1 INTRODUCTION
- 12.2 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN
- 12.3 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2024
- 12.4 REVENUE ANALYSIS
- 12.5 BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- 12.6 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 12.6.1 STARS
- 12.6.2 EMERGING LEADERS
- 12.6.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
- 12.6.4 PARTICIPANTS
- 12.6.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 12.6.5.1 Company footprint
- 12.6.5.2 Region footprint
- 12.6.5.3 Product type footprint
- 12.6.5.4 Application footprint
- 12.6.5.5 End-use industry footprint
- 12.7 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 12.7.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
- 12.7.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
- 12.7.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
- 12.7.4 STARTING BLOCKS
- 12.7.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 12.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
- 12.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
- 12.8 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS, 2024
- 12.9 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
- 12.9.1 DEALS
- 12.9.2 OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
13 COMPANY PROFILES
- 13.1 KEY PLAYERS
- 13.1.1 LUMMUS TECHNOLOGY
- 13.1.1.1 Business overview
- 13.1.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 13.1.1.3 Recent developments
- 13.1.1.3.1 Deals
- 13.1.1.4 MnM view
- 13.1.1.4.1 Right to win
- 13.1.1.4.2 Strategic choices
- 13.1.1.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 13.1.2 OVIVO USA LLC
- 13.1.2.1 Business overview
- 13.1.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 13.1.2.3 Recent developments
- 13.1.2.3.1 Deals
- 13.1.2.3.2 Other developments
- 13.1.2.4 MnM view
- 13.1.2.4.1 Right to win
- 13.1.2.4.2 Strategic choices
- 13.1.2.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 13.1.3 VALENCE WATER INC
- 13.1.3.1 Business overview
- 13.1.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 13.1.3.3 Recent developments
- 13.1.3.3.1 Other developments
- 13.1.3.4 MnM view
- 13.1.3.4.1 Right to win
- 13.1.3.4.2 Strategic choices
- 13.1.3.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 13.1.4 HYDROLEAP
- 13.1.4.1 Business overview
- 13.1.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 13.1.4.3 Recent developments
- 13.1.4.3.1 Other developments
- 13.1.4.4 MnM view
- 13.1.4.4.1 Right to win
- 13.1.4.4.2 Strategic choices
- 13.1.4.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 13.1.5 JIANGSU JINGYUAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION CO., LTD
- 13.1.5.1 Business overview
- 13.1.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 13.1.5.3 MnM view
- 13.1.5.3.1 Right to win
- 13.1.5.3.2 Strategic choices
- 13.1.5.3.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 13.1.6 GROUND EFFECTS ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES INC
- 13.1.6.1 Business overview
- 13.1.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 13.1.7 E-FLOC WASTEWATER SOLUTIONS
- 13.1.7.1 Business overview
- 13.1.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 13.1.8 YASA ET (SHANGHAI) CO., LTD.
- 13.1.8.1 Business overview
- 13.1.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 13.1.9 AQUA PULSAR
- 13.1.9.1 Business overview
- 13.1.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 13.1.10 AXINE WATER TECHNOLOGIES
- 13.1.10.1 Business overview
- 13.1.10.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 13.1.10.3 Recent developments
- 13.1.10.3.1 Deals
- 13.1.10.3.2 Other developments
- 13.1.1 LUMMUS TECHNOLOGY
- 13.2 OTHER PLAYERS
- 13.2.1 AEOLUS SUSTAINABLE BIOENERGY PVT. LTD
- 13.2.2 MAGNELI MATERIALS
- 13.2.3 HUNAN BOROMOND EPT CO. LTD.
- 13.2.4 VENTILAQUA
- 13.2.5 RT SAFEBALLAST PVT LTD.
- 13.2.6 MAGNETO SPECIAL ANODES (SUZHOU) CO., LTD.
- 13.2.7 AQUACARE SOLUTION ENVIRO ENGINEERS
- 13.2.8 GREEN ECOWATER SYSTEMS
- 13.2.9 BLUE EDEN CLEAN TECHNOLOGY
- 13.2.10 PPU UMWELTTECHNIK
14 APPENDIX
- 14.1 DISCUSSION GUIDE
- 14.2 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS' SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL
- 14.3 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS
- 14.4 RELATED REPORTS
- 14.5 AUTHOR DETAILS









