
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1783245
패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장 예측(-2030년) : 용도별, 규격별, 유형별, 전압별, 지역별Pad-Mounted Switchgear Market by Type (Air, Gas, Solid Dielectric, Others), Voltage (Up to 15 kV, 15-25 kV, 25-38 kV), Application (Industrial, Commercial, Residential), Standard (IEC, IEEE), and Region - Global Forecast to 2030 |
||||||
세계의 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장 규모는 5.4%의 CAGR로 확대하며, 2025년 61억 3,000만 달러에서 2030년에는 79억 7,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다.
| 조사 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 조사 대상연도 | 2021-2030년 |
| 기준연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 기간 | 2025-2030년 |
| 검토 단위 | 금액(10억 달러) |
| 부문 | 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장 : 용도별, 규격별, 유형별, 전압별, 지역별 |
| 대상 지역 | 북미, 유럽, 아시아태평양, 중동 및 아프리카, 남미 |
세계 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장은 현대적이고 탄력적이며 유지보수가 용이한 배전 인프라에 대한 수요 증가로 인해 견고한 성장이 예상됩니다. 전력회사가 스마트 그리드와 분산형 에너지 시스템으로 전환하는 가운데, 첨단 모니터링 및 예지보전 기능을 통합한 지능형 스위치기어 솔루션에 대한 신뢰가 높아지고 있습니다. 주거, 상업, 산업 분야의 지하 배전 시스템에 널리 사용되는 패드 마운트 스위치기어는 실시간 진단, 고장 감지, 원격 상태 모니터링을 가능하게 하는 기능을 갖추고 진화하고 있습니다.
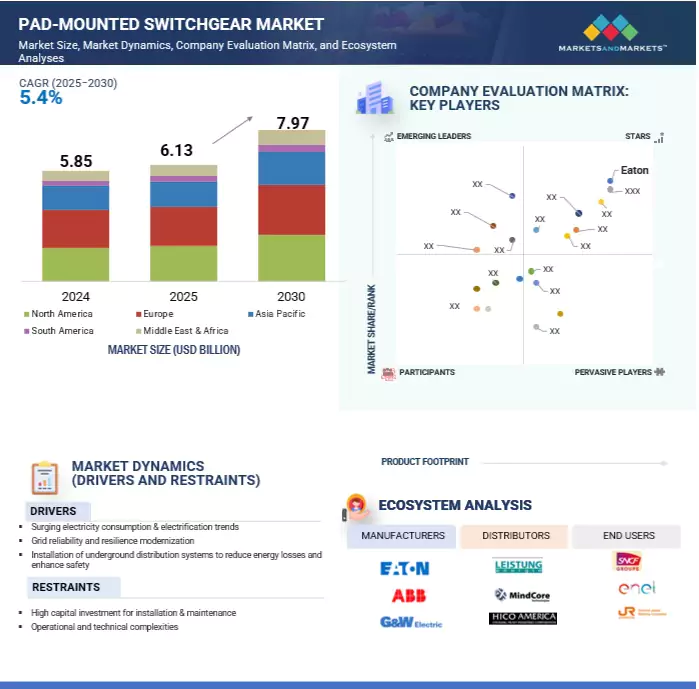
예지보전 기술은 절연체 노화를 모니터링하고, 스위치기어의 마모를 추적하고, 잠재적 고장의 초기 징후를 파악하여 유틸리티 기업이 비용이 많이 드는 정전을 방지하고 운영 효율성을 높일 수 있도록 돕습니다. 시간 기반 유지보수에서 상태 기반 유지보수로의 전환은 데이터센터, 헬스케어, EV 충전 네트워크 등 다운타임이 큰 손실로 이어질 수 있는 중요한 용도에서 특히 가치가 있습니다. 또한 재생에너지의 통합과 양방향 전력 흐름이 증가함에 따라 최신 패드 마운트 스위치기어는 동적 조건에서 작동해야합니다. 온도 센서, 아크 고장 감지, 통신 지원 모듈을 갖춘 지능형 솔루션은 신속한 절연 및 서비스 복구를 가능하게 하여 그리드 신뢰성을 향상시킵니다. 전력회사가 자산의 수명을 연장하고 작업자의 안전을 보장하기 위해 노력하는 가운데, 예지보전이 중요한 실현 요소가 되고 있으며, 수명주기 비용을 절감하고 서비스 연속성을 향상시키면서 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장의 지속적인 성장을 지원하고 있습니다.
15-25kV는 범용성이 높고 다양한 유틸리티 및 인프라 용도에서 사용이 증가함에 따라 예측 기간 중 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장에서 가장 빠르게 성장하는 전압 부문이 될 것으로 예측됩니다. 이 전압 범위는 일반적으로 피더 자동화, 변전소 업그레이드, 2 차 배전 시스템, 고장 격리, 부하 전환, 서비스 복구를 용이하게하기 위해 일반적으로 사용됩니다. 스마트 그리드 인프라로의 전환에 따라 유틸리티 기업은 원격 모니터링, 고장 감지, 자동 스위칭 등의 스마트 기능을 갖춘 15-25kV의 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시스템을 점점 더 많이 채택하고 있습니다. 이러한 시스템은 특히 안정적이고 고품질의 전력에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있는 도시, 반도시 및 급성장하는 도시 주변 지역에서 정전 시간을 단축하고 그리드의 신뢰성을 높이는 데 도움이 됩니다. 또한이 전압 범위는 비용과 용량의 균형이 잘 맞으며 재생에너지 통합, 전기자동차 충전소, 중간 규모의 산업 프로젝트에 인기가 있습니다. 전 세계 각국의 정부와 전력회사들은 노후화된 인프라 교체와 배전망 자동화에 많은 투자를 하고 있으며, 이는 15-25kV 부문의 성장을 지속적으로 촉진하고 있습니다. 그 결과, 이 부문은 선진국과 신흥 국가 모두에서 전기화 진전, 스마트 시티 구상, 전력 품질에 대한 수요 증가로 인해 강력한 모멘텀을 보일 것으로 예측됩니다.
패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장의 고체 유전체 부문은 환경 친화적이고 컴팩트하며 유지보수가 필요 없는 스위치기어 솔루션에 대한 세계 수요 증가에 힘입어 예측 기간 중 가장 높은 CAGR을 보일 것으로 예측됩니다. 기존의 석유 절연 및 SF6 기반 스위치기어와 달리 고체 유전체 스위치기어는 에폭시 또는 폴리머 기반 절연을 사용하므로 누전, 가연성 및 유해한 온실 가스 배출의 위험이 없습니다. 이 때문에 안전, 지속가능성, 설치 면적 감소가 우선시되는 도시 지역, 인구 밀집 지역, 환경적으로 민감한 지역에서는 특히 매력적인 제품입니다. 이 부문은 특히 이상기후에 취약한 지역에서 지하 배전망의 채택이 증가하고 있으며, 고체 유전체 스위치기어가 신뢰성과 운영 연속성을 향상시키는 이점을 누리고 있습니다. 또한 유틸리티 및 인프라 개발에서는 총소유비용을 낮추고 유지보수가 적고 오래 지속되는 솔루션을 선호하고 있습니다. 자동화, 원격 제어, 상태 모니터링 기술과 고체 유전체 스위치기어의 호환성은 최신 스마트 그리드 용도의 사용 확대를 지원하고 있습니다. 지구 온난화 가능성으로 인해 SF6를 제한하는 규제 압력이 증가하고 친환경 그리드 솔루션에 대한 전 세계적인 추진으로 인해 고체 유전체 부문은 선진국과 신흥 경제국 모두에서 급속한 성장과 시장 침투가 예상됩니다.
유럽은 강력한 규제 프레임워크, 노후화된 전력망 인프라 업그레이드, 재생에너지 도입 가속화 등으로 인해 예측 기간 중 패드 마운트 스위치기어의 가장 큰 시장이 될 것으로 예측됩니다. 유럽의 많은 국가에서는 신뢰성과 미관을 개선하기 위해 가공 배전에서 지중 배전으로 전환하고 있으며, 특히 도시와 교외 지역에서는 패드 마운트 스위치기어가 중전압 전력망의 중요한 부분으로 자리 잡았습니다. 또한 EU의 엄격한 환경 정책과 SF6 단계 감축 구상은 전력 회사 및 산업 사업자에게 고체 유전체 및 건식 공기 절연 옵션과 같은 환경 친화적이고 자동화 가능한 스위치기어 시스템에 대한 투자를 장려하고 있습니다. 스마트 그리드 인프라, 에너지 시스템의 탈탄소화, 분산형 에너지 자원(DER) 통합에 대한 대규모 지출도 수요 증가에 기여하고 있습니다. 독일, 프랑스, 영국, 이탈리아 등의 국가들은 전력망 현대화, EV 충전 인프라, 분산형 재생에너지 프로젝트에 많은 투자를 하고 있으며, 이 모든 것은 패드 마운트 스위치기어와 같은 컴팩트하고 신뢰할 수 있는 안전한 스위칭 장치를 필요로 합니다. 필요합니다. 그 결과, 유럽은 향후 수년간 수요와 기술 발전 측면에서 세계 시장을 선도할 것으로 예측됩니다.
패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장은 지역적으로 광범위하게 존재감을 드러내는 소수의 주요 진입업체가 지배적입니다. 주요 진출 기업은 Eaton(아일랜드), Hubbell(미국), ABB(스위스), G&W Electric(미국), S&C Electric(미국) 등이 있습니다.
이 보고서에서는 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장을 용도별(산업용, 상업용, 주거용), 유형별(공기 절연, 가스 절연, 고체 유전체, 기타), 전압별(15kV까지 15-25kV, 25-38kV), 표준별(IEC, IEEE), 지역별로 정의, 설명, 예측했습니다. 또한 시장의 상세한 질적, 양적 분석을 실시했습니다. 이 보고서에서는 주요 시장 성장 촉진요인, 억제요인, 기회 및 과제를 철저히 검증하고 있습니다. 또한 시장의 여러 가지 중요한 측면에 대해서도 논의했습니다. 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장의 주요 기업을 종합적으로 분석합니다. 이 분석은 각 회사의 사업 개요, 솔루션 및 서비스, 주요 전략에 대한 인사이트를 제공합니다. 또한 신제품 출시, 합병, 인수, 인수, 기타 최근 동향과 함께 관련 계약, 파트너십, 협정 등도 제공합니다. 또한 패드마운트 스위치기어 시장 생태계의 신생 기업 경쟁 분석도 함께 수록되어 있습니다.
이 보고서는 업계 리더와 신규 시장 진출기업에게 시장과 그 하위 부문에 대한 종합적인 분석을 제공하는 전략적 자원이 될 것입니다. 경쟁 구도에 대한 깊은 이해를 통해 이해관계자들이 비즈니스 포지셔닝을 개선하고 효과적인 시장 진출 전략을 수립할 수 있도록 돕습니다. 또한 현재 시장 역학을 밝히고, 전략적 의사결정의 지침이 되는 주요 촉진요인, 제약요인, 과제, 기회를 강조하고 있습니다.
목차
제1장 서론
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 개요
제4장 주요 인사이트
제5장 시장 개요
- 서론
- 시장 역학
- 고객 비즈니스에 영향을 미치는 동향/혼란
- 에코시스템 분석
- 공급망 분석
- 기술 분석
- 2025-2026년의 주요 컨퍼런스와 이벤트
- 관세와 규제 상황
- 가격 분석
- 특허 분석
- 무역 분석
- 사례 연구 분석
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 주요 이해관계자와 구입 기준
- 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장에서 생성형 AI/AI의 영향
- 2025년 미국 관세의 영향 - 개요
- 주요 관세율
- 가격 영향 분석
- 국가/지역에 대한 영향
- 최종 용도 산업에 대한 영향
제6장 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장(용도별)
- 서론
- 산업용
- 상업용
- 주택용
제7장 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장(규격별)
- 서론
- IEC(INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL COMMISSION)
- IEEE(INSTITUTE OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERS)
- 기타
제8장 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장(유형별)
- 서론
- 공기 단열
- 가스 단열
- 고체 유전체
- 기타
제9장 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장(전압별)
- 서론
- 15KV 미만
- 15-25KV
- 25-38KV
제10장 패드 마운트 스위치기어 시장(지역별)
- 서론
- 유럽
- 영국
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 기타
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 호주
- 한국
- 기타
- 중동 및 아프리카
- GCC 국가
- 남아프리카공화국
- 이집트
- 기타
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타
제11장 경쟁 구도
- 주요 참여 기업이 채택한 전략의 개요
- 2024년에서 TOP 5시장 점유율 분석
- 매출 분석, 2020-2024년
- 기업 평가 매트릭스/상한, 2024년
- 스타트업/중소기업 평가 쿼드런트
- 경쟁 시나리오
제12장 기업 개요
- 주요 참여 기업
- EATON
- HUBBELL
- ABB
- G&W ELECTRIC
- S&C ELECTRIC
- POWELL
- FEDERAL PACIFIC
- ENTEC ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC
- NOJA POWER
- TIEPCO GROUP
- GHORIT ELECTRICALS
- NINGBO TIANAN GROUP
- TRAYER SWITCHGEAR
- KDM STEEL
- SWITCHGEAR POWER SYSTEMS LLC
- PARK DETROIT
- 기타 기업
- BEIJING KYLIN POWER & TECHNOLOGY
- TELAWNE POWER EQUIPMENTS PVT. LTD.
- ORMAZABAL
- ACTOM
제13장 부록
KSA 25.08.12The global Pad-mounted switchgear market is projected to grow from USD 6.13 billion in 2025 to USD 7.97 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.4%.
| Scope of the Report | |
|---|---|
| Years Considered for the Study | 2021-2030 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2030 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Billion) |
| Segments | Pad-mounted switchgear market by application, standard, voltage, type, and region |
| Regions covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America |
The global pad-mounted switchgear market is expected to grow steadily, driven by increasing demand for modern, resilient, and low-maintenance power distribution infrastructure. As utilities continue transitioning toward smart grids and decentralized energy systems, there is a growing reliance on intelligent switchgear solutions embedded with advanced monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. Pad-mounted switchgear, widely used in underground distribution systems across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, is evolving with features that enable real-time diagnostics, fault detection, and remote condition monitoring.
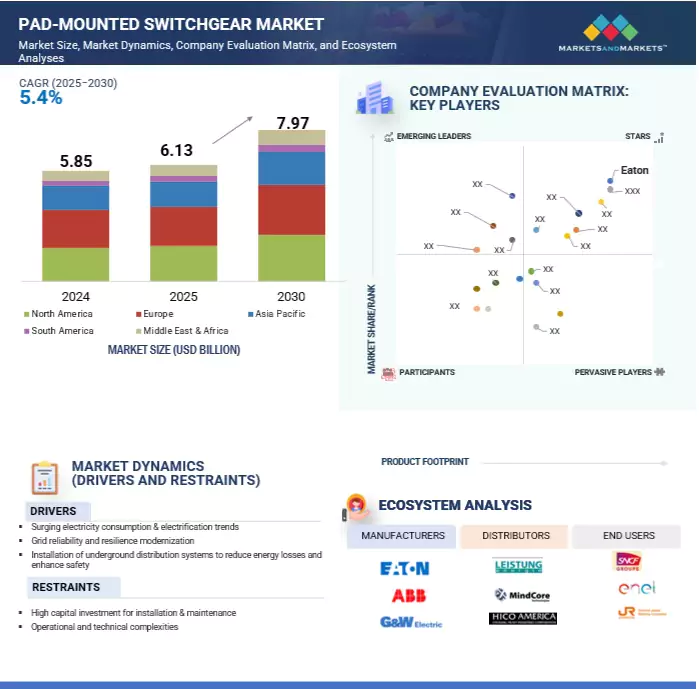
Predictive maintenance technologies assist utilities in monitoring insulation aging, tracking switchgear wear and tear, and identifying early signs of potential failures-thus preventing costly outages and boosting operational efficiency. This move from time-based to condition-based maintenance is especially valuable in critical applications such as data centers, healthcare, and EV charging networks, where downtime can lead to significant losses. Additionally, with the increasing integration of renewable energy and bidirectional power flows, modern pad-mounted switchgear must operate under dynamic conditions. Intelligent solutions with thermal sensors, arc-fault detection, and communication-enabled modules allow for quick isolation and service restoration, thereby improving grid reliability. As utilities seek to extend asset life and ensure workforce safety, predictive maintenance is becoming a key enabler, supporting sustained growth in the pad-mounted switchgear market while reducing lifecycle costs and enhancing service continuity.
15-25 kV to be the fastest-growing voltage segment during the forecast period
The 15-25 kV segment is expected to be the fastest-growing voltage category in the pad-mounted switchgear market during the forecast period, due to its versatility and increasing use across various utility and infrastructure applications. This voltage range is commonly used in feeder automation, substation upgrades, and secondary distribution systems, where it facilitates fault isolation, load switching, and service restoration. As the world moves toward smart grid infrastructure, utilities are increasingly adopting 15-25 kV pad-mounted switchgear systems with smart features like remote monitoring, fault detection, and automated switching. These systems help reduce outage times and enhance grid reliability, especially in urban, semi-urban, and growing peri-urban areas where demand for stable, high-quality power is rising. Additionally, this voltage range provides a good balance between cost and capacity, making it popular for renewable energy integration, electric vehicle charging stations, and medium-scale industrial projects. Governments and utilities globally are heavily investing in replacing aging infrastructure and automating distribution networks, which continues to fuel growth in the 15-25 kV segment. Consequently, this segment is expected to gain strong momentum in both developed and emerging economies, driven by rising electrification, smart city initiatives, and increasing power quality demand.
Solid dielectric segment to exhibit highest CAGR during forecast period
The solid dielectric segment of the pad-mounted switchgear market is expected to have the highest CAGR during the forecast period, driven by the global move toward environmentally friendly, compact, and maintenance-free switchgear solutions. Unlike traditional oil-insulated or SF6-based switchgear, solid dielectric switchgear uses epoxy or polymer-based insulation, which removes the risk of leakage, flammability, or harmful greenhouse gas emissions. This makes it especially appealing in urban, densely populated, or environmentally sensitive areas where safety, sustainability, and footprint reduction are priorities. The segment is also benefiting from the increasing adoption of underground distribution networks, particularly in regions prone to extreme weather events, where solid dielectric switchgear provides improved reliability and operational continuity. Moreover, utilities and infrastructure developers are increasingly favoring low-maintenance, long-lasting solutions that lower the total cost of ownership. The compatibility of solid dielectric switchgear with automation, remote control, and condition monitoring technologies also supports its expanding use in modern smart grid applications. With growing regulatory pressure to limit SF6 due to its high global warming potential, and a worldwide push toward greener grid solutions, the solid dielectric segment is set for rapid growth and market penetration in both developed and emerging economies.
Europe to be largest market during forecast period
Europe is expected to be the largest market for pad-mounted switchgear during the forecast period, driven by strong regulatory frameworks, aging grid infrastructure upgrades, and the continent's accelerated efforts to adopt renewable energy. Many European countries are shifting from overhead to underground distribution systems for better reliability and aesthetics-especially in urban and suburban areas-making pad-mounted switchgear a vital part of medium-voltage power networks. Additionally, strict EU environmental policies and SF6 phase-down initiatives are encouraging utilities and industrial operators to invest in environmentally friendly and automation-ready switchgear systems, including solid dielectric and dry-air insulated options. Major spending on smart grid infrastructure, decarbonizing energy systems, and integrating distributed energy resources (DER) also contribute to the increased demand. Countries like Germany, France, the UK, and Italy are heavily investing in grid modernization, EV charging infrastructure, and distributed renewable projects, all of which need compact, reliable, and safe switching equipment like pad-mounted switchgear. Consequently, Europe is poised to lead the global market in both demand and technological progress in the coming years.
In-depth interviews have been conducted with chief executive officers (CEOs), directors, and other executives from various key organizations operating in the pad-mounted switchgear market.
By Company Type: Tier 1 - 35%, Tier 2 - 45%, and Tier 3 - 20%
By Designation: C-level Executives - 35%, Directors - 25%, and Others - 40%
By Region: Asia Pacific - 30%, North America - 40%, Europe - 20%, Middle East & Africa - 5%, and South America - 5%
Note: Other designations include engineers and sales & regional managers.
The tiers of the companies are defined based on their total revenue as of 2024: Tier 1: >USD 1 billion, Tier 2: USD 500 million-1 billion, and Tier 3: <USD 500 million.
A few major players with extensive geographical presence dominate the pad-mounted switchgear market. The leading players are Eaton (Ireland), Hubbell (US), ABB (Switzerland), G&W Electric (US), and S&C Electric (US)
Research Coverage:
The report defines, describes, and forecasts the pad-mounted switchgear market applications (industrial, commercial, residential), types (Air-insulated, Gas-insulated, Solid dielectric, others), voltages (Up to 15 kV, 15-25 kV, 25-38 kV), standards (IEC, IEEE), and regions. It also provides a detailed qualitative and quantitative analysis of the market. The report thoroughly reviews the main market drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges. It also discusses various important aspects of the market. A comprehensive analysis of key players in the pad-mounted switchgear market has been performed. This analysis offers insights into their business overview, solutions and services, and key strategies. It also includes relevant contracts, partnerships, and agreements, along with new product launches, mergers, acquisitions, and other recent developments. Additionally, the report features a competitive analysis of emerging startups within the pad-mounted switchgear market ecosystem.
Reasons to Buy This Report:
This report serves as a strategic resource for industry leaders and newcomers, providing a comprehensive analysis of the market and its subsegments. It gives stakeholders a deep understanding of the competitive landscape, helping them improve their business positioning and develop effective go-to-market strategies. Additionally, the report clarifies current market dynamics, emphasizing key drivers, constraints, challenges, and opportunities that guide strategic decision-making.
The report provides insights on the following points:
- Analysis of key drivers (surging electricity consumption & electrification trends, grid reliability and resilience modernization), restraints (high capital investment for installation & maintenance, operational and technical complexities), opportunities (investments in upgrading and expanding power distribution infrastructure, automation and reduction of AT&C losses), and challenges (synchronization of SF6 phase-out in hybrid networks, retrofit difficulties in legacy systems) influencing the growth
- Product Development/Innovation: Innovation in pad-mounted switchgear focuses on solid dielectric insulation, dry air alternatives to SF6, and digital automation technologies. Leading companies are enhancing their products with self-powered relays, arc-resistant designs, thermal and arc-flash sensors, and SCADA integration, boosting the switchgear's responsiveness, diagnostics, and safety. New models feature modular compartments, low carbon footprints, and touch-safe interfaces, which improve safety and shorten installation time. Advanced sealing, corrosion-resistant materials, and vandal-proof enclosures are utilized to endure tough environmental conditions, particularly for urban and industrial applications.
- Market Development: Emerging economies in Asia Pacific, Africa, and South America are experiencing strong growth in pad-mounted switchgear deployment due to rapid urbanization, smart city initiatives, and expansion of distribution networks. Government-funded projects, such as India's Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS), Kenya's Last Mile Connectivity Project, and Brazil's DER integration plans, are consistently driving demand for pad-mounted switchgear in low-to-medium voltage applications. These systems are essential for reliable secondary distribution, particularly where aesthetics, safety, and compactness matter.
- Market Diversification: Pad-mounted switchgear is increasingly used in diverse applications beyond traditional utilities, including EV charging stations, solar parks, commercial complexes, underground metro systems, data centers, and hospitals. Each application requires specific configurations-from smart automation-ready units to compact, solid-insulated gear suitable for tight spaces. Manufacturers are meeting this demand by offering plug-and-play modular systems, low-maintenance designs, and arc-flash mitigation features that minimize downtime while boosting safety and resilience.
- Competitive Assessment: Major players in the pad-mounted switchgear market include Eaton (Ireland), Hubbell (US), ABB (Switzerland), G&W Electric (US), and S&C Electric (US). These companies maintain global manufacturing networks and are actively involved in regional partnerships, utility collaborations, and EPC projects to localize production and better serve rapidly growing markets. Their competitive strategies involve investments in eco-friendly technologies, regional R&D facilities, and digital platforms that enable real-time monitoring and predictive diagnostics. By focusing on sustainability, compliance, and modularity, these firms are well-positioned to meet the changing demands of a modern, decarbonized grid infrastructure.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES
- 1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
- 1.3 MARKET SCOPE
- 1.3.1 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 1.3.2 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- 1.4 YEARS CONSIDERED
- 1.5 CURRENCY CONSIDERED
- 1.6 LIMITATIONS
- 1.7 STAKEHOLDERS
- 1.8 SUMMARY OF CHANGES
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 RESEARCH DATA
- 2.2 MARKET BREAKDOWN AND DATA TRIANGULATION
- 2.2.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.2.1.1 Key data from secondary sources
- 2.2.2 PRIMARY DATA
- 2.2.2.1 Key data from primary sources
- 2.2.2.2 Breakdown of primary interviews
- 2.2.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.3 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
- 2.3.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 2.3.2 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- 2.3.3 DEMAND-SIDE METRICS
- 2.3.3.1 Assumptions for demand-side analysis
- 2.3.3.2 Calculations for demand-side analysis
- 2.3.4 SUPPLY-SIDE ANALYSIS
- 2.3.4.1 Supply-side calculation
- 2.3.4.2 Assumptions for the supply side
- 2.3.4.3 Assumptions and calculations
- 2.4 FORECAST
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
- 4.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET
- 4.2 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET IN EUROPE, BY APPLICATION AND COUNTRY
- 4.3 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET, BY APPLICATION
- 4.4 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET, BY VOLTAGE
- 4.5 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET, BY TYPE
- 4.6 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET, BY STANDARD
- 4.7 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET, BY REGION
5 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 5.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.2.1.1 Surging electricity consumption & electrification trends
- 5.2.1.2 Grid reliability and resilience modernization
- 5.2.1.3 Installation of underground distribution systems to reduce energy losses and enhance safety
- 5.2.2 RESTRAINTS
- 5.2.2.1 High capital investment for installation & maintenance
- 5.2.2.2 Operational and technical complexities
- 5.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
- 5.2.3.1 Investments in upgrade and expansion of power distribution infrastructure
- 5.2.3.2 Automation and reduction of AT&C losses
- 5.2.4 CHALLENGES
- 5.2.4.1 Synchronization of SF6 phase-out in hybrid networks
- 5.2.4.2 Retrofitting in legacy systems
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.3 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
- 5.3.1 NEW REVENUE POCKETS FOR POWER GRID PROVIDERS
- 5.4 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
- 5.5 SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 5.5.1 RAW MATERIAL SUPPLIERS
- 5.5.2 COMPONENT MANUFACTURERS
- 5.5.3 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MANUFACTURERS/ASSEMBLERS
- 5.5.4 DISTRIBUTORS
- 5.5.5 END USER
- 5.6 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS
- 5.6.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.6.1.1 Vacuum interruption technology
- 5.6.1.2 Solid dielectric insulation
- 5.6.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.6.2.1 Remote terminal units
- 5.6.2.2 Sensor technology (thermal, arc flash, voltage/current)
- 5.6.3 ADJACENT TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.6.3.1 Underground distribution cabling
- 5.6.3.2 Distributed energy resources & microgrids
- 5.6.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.7 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2025-2026
- 5.8 TARIFF AND REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 5.8.1 TARIFFS RELATED TO SWITCHGEARS
- 5.8.2 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR: REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 5.8.3 CODES AND REGULATORY POLICIES RELATED TO PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR SYSTEMS
- 5.9 PRICING ANALYSIS
- 5.10 PATENT ANALYSIS
- 5.11 TRADE ANALYSIS
- 5.11.1 TRADE ANALYSIS FOR HS CODE 853590
- 5.11.2 IMPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 853590)
- 5.11.3 EXPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 853590)
- 5.11.4 TRADE ANALYSIS FOR HS CODE 853690
- 5.11.5 IMPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 853690)
- 5.11.6 EXPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 853690)
- 5.12 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
- 5.12.1 S&C'S PAD-MOUNTED GEAR PROVIDED SUPERIOR QUALITY AND RELIABILITY REQUIRED BY MUNICIPAL UTILITY
- 5.12.2 ELASTIMOLD'S SOLID-DIELECTRIC SWITCHGEAR ADDRESSED CHALLENGES FACED BY FIRSTENERGY DUE TO AGING INFRASTRUCTURE
- 5.12.3 UK-BASED NORTHERN POWERGRID COMPANY DEPLOYED ABB'S SF6-FREE SWITCHGEAR TO DECARBONIZE ITS ELECTRICAL NETWORK
- 5.12.4 NATIONAL GRID EMPLOYED SF6-FREE HV SUBSTATIONS IN ITS SOUTHEAST ENGLAND NETWORK TO ENSURE A RELIABLE ELECTRICITY SUPPLY
- 5.13 PORTER'S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS
- 5.13.1 THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES
- 5.13.2 BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS
- 5.13.3 BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS
- 5.13.4 THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS
- 5.13.5 INTENSITY OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- 5.14 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA
- 5.14.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS
- 5.14.2 BUYING CRITERIA
- 5.15 IMPACT OF GEN AI/AI IN PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET
- 5.15.1 ADOPTION OF GEN AI/AI IN PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET
- 5.15.2 IMPACT OF GEN AI/AI ON PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET, BY REGION
- 5.16 IMPACT OF 2025 US TARIFF - OVERVIEW
- 5.16.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.17 KEY TARIFF RATES
- 5.18 PRICE IMPACT ANALYSIS
- 5.19 IMPACT ON COUNTRY/REGION
- 5.19.1 US
- 5.19.2 EUROPE
- 5.19.3 ASIA PACIFIC
- 5.20 IMPACT ON END-USE INDUSTRIES
6 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET, BY APPLICATION
- 6.1 INTRODUCTION
- 6.2 INDUSTRIAL
- 6.2.1 RISING DEMAND FOR RELIABLE AND RESILIENT POWER DISTRIBUTION SOLUTIONS TO DRIVE SEGMENT
- 6.3 COMMERCIAL
- 6.3.1 STRENGTHENING POWER RESILIENCE AMID EXPANDING COMMERCIAL INFRASTRUCTURE TO BOOST SEGMENT
- 6.4 RESIDENTIAL
- 6.4.1 ENHANCED URBAN AESTHETICS AND RELIABILITY WITH UNDERGROUND DISTRIBUTION TO FUEL SEGMENT
7 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET, BY STANDARD
- 7.1 INTRODUCTION
- 7.2 INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL COMMISSION (IEC)
- 7.3 INSTITUTE OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERS (IEEE)
- 7.4 OTHER STANDARDS
8 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET, BY TYPE
- 8.1 INTRODUCTION
- 8.2 AIR-INSULATED
- 8.2.1 ADOPTION TO GAIN MOMENTUM DUE TO ENVIRONMENTAL BENEFITS
- 8.3 GAS-INSULATED
- 8.3.1 HIGH GRID RESILIENCE WITH COMPACT GAS-INSULATED PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR - KEY DRIVER
- 8.4 SOLID-DIELECTRIC
- 8.4.1 OFFERS RELIABILITY FOR MISSION-CRITICAL POWER DISTRIBUTION
- 8.5 OTHER TYPES
9 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET, BY VOLTAGE
- 9.1 INTRODUCTION
- 9.2 UP TO 15 KV
- 9.2.1 RISING DEMAND IN RESIDENTIAL APPLICATIONS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.3 15-25 KV
- 9.3.1 INCREASING ADOPTION IN FEEDER AND SUBSTATION AUTOMATION APPLICATIONS TO PROPEL MARKET GROWTH
- 9.4 25-38 KV
- 9.4.1 RISING DEMAND FROM INDUSTRIAL AND COMMERCIAL EXPANSION TO DRIVE GLOBAL GROWTH
10 PAD-MOUNTED SWITCHGEAR MARKET, BY REGION
- 10.1 INTRODUCTION
- 10.2 EUROPE
- 10.2.1 UK
- 10.2.1.1 Renewable energy integration in power grids to drive market
- 10.2.2 GERMANY
- 10.2.2.1 Increasing focus on energy efficiency and grid expansion to fuel market growth
- 10.2.3 FRANCE
- 10.2.3.1 Improvement in power generation, transmission, and distribution infrastructure to propel market
- 10.2.4 REST OF EUROPE
- 10.2.1 UK
- 10.3 NORTH AMERICA
- 10.3.1 US
- 10.3.1.1 Strong need to modernize aging power infrastructure to drive demand
- 10.3.2 CANADA
- 10.3.2.1 Increasing investment in renewables to support market growth
- 10.3.3 MEXICO
- 10.3.3.1 Adoption of smart grid technology to fuel the need for pad-mounted switchgear systems
- 10.3.1 US
- 10.4 ASIA PACIFIC
- 10.4.1 CHINA
- 10.4.1.1 Increasing investments in clean energy projects to accelerate demand for pad-mounted switchgear
- 10.4.2 INDIA
- 10.4.2.1 Rising electrification to drive market
- 10.4.3 AUSTRALIA
- 10.4.3.1 Electrification of railroad network to boost demand
- 10.4.4 SOUTH KOREA
- 10.4.4.1 Rising consumption of natural gas, nuclear energy, and coal in power sector to boost demand
- 10.4.5 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC
- 10.4.1 CHINA
- 10.5 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
- 10.5.1 GCC COUNTRIES
- 10.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 10.5.1.1.1 Favorable government policies for use of renewables in power generation to drive market
- 10.5.1.2 UAE
- 10.5.1.2.1 Government focus on increasing power generation capacity to boost demand
- 10.5.1.3 Qatar
- 10.5.1.3.1 Grid modernization and smart city projects to fuel demand
- 10.5.1.4 Rest of GCC
- 10.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 10.5.2 SOUTH AFRICA
- 10.5.2.1 Investment in power capacity addition and energy efficiency improvement to accelerate market growth
- 10.5.3 EGYPT
- 10.5.3.1 Refurbishment of power plant infrastructure to lead to high demand
- 10.5.4 REST OF MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
- 10.5.1 GCC COUNTRIES
- 10.6 SOUTH AMERICA
- 10.6.1 BRAZIL
- 10.6.1.1 Urban expansion and grid resilience to fuel demand
- 10.6.2 ARGENTINA
- 10.6.2.1 Need for uninterrupted power supply in oil & gas operations to fuel demand
- 10.6.3 REST OF SOUTH AMERICA
- 10.6.1 BRAZIL
11 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 11.1 OVERVIEW OF STRATEGIES ADOPTED BY KEY PLAYERS
- 11.2 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS OF TOP FIVE PLAYERS, 2024
- 11.3 REVENUE ANALYSIS, 2020-2024
- 11.4 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX/QUADRANT, 2024
- 11.4.1 STARS
- 11.4.2 EMERGING LEADERS
- 11.4.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
- 11.4.4 PARTICIPANTS
- 11.4.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 11.4.5.1 Company footprint
- 11.4.5.2 Region footprint
- 11.4.5.3 Standard footprint
- 11.4.5.4 Application footprint
- 11.5 STARTUPS/SMES EVALUATION QUADRANT
- 11.5.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
- 11.5.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
- 11.5.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
- 11.5.4 STARTING BLOCKS
- 11.5.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 11.5.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
- 11.5.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
- 11.6 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
12 COMPANY PROFILES
- 12.1 KEY PLAYERS
- 12.1.1 EATON
- 12.1.1.1 Business overview
- 12.1.1.2 Products offered
- 12.1.1.3 Recent developments
- 12.1.1.3.1 Deals
- 12.1.1.4 MnM view
- 12.1.1.4.1 Right to win
- 12.1.1.4.2 Strategic choices
- 12.1.1.4.3 Weaknesses & competitive threats
- 12.1.2 HUBBELL
- 12.1.2.1 Business overview
- 12.1.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 12.1.2.3 Recent developments
- 12.1.2.3.1 Deals
- 12.1.2.4 MnM view
- 12.1.2.4.1 Right to win
- 12.1.2.4.2 Strategic choices
- 12.1.2.4.3 Weaknesses & competitive threats
- 12.1.3 ABB
- 12.1.3.1 Business overview
- 12.1.3.2 Products offered
- 12.1.3.3 Recent developments
- 12.1.3.3.1 Deals
- 12.1.3.3.2 Expansions
- 12.1.3.3.3 Other developments
- 12.1.3.4 MnM view
- 12.1.3.4.1 Right to win
- 12.1.3.4.2 Strategic choices
- 12.1.3.4.3 Weaknesses & competitive threats
- 12.1.4 G&W ELECTRIC
- 12.1.4.1 Business overview
- 12.1.4.2 Products offered
- 12.1.4.3 Recent developments
- 12.1.4.3.1 Deals
- 12.1.4.3.2 Expansions
- 12.1.4.3.3 Others
- 12.1.4.4 MnM view
- 12.1.4.4.1 Right to win
- 12.1.4.4.2 Strategic choices
- 12.1.4.4.3 Weaknesses & competitive threats
- 12.1.5 S&C ELECTRIC
- 12.1.5.1 Business overview
- 12.1.5.2 Products offered
- 12.1.5.3 Recent developments
- 12.1.5.3.1 Expansions
- 12.1.5.3.2 Deals
- 12.1.5.4 MnM view
- 12.1.5.4.1 Right to win
- 12.1.5.4.2 Strategic choices
- 12.1.5.4.3 Weaknesses & competitive threats
- 12.1.6 POWELL
- 12.1.6.1 Business overview
- 12.1.6.2 Products offered
- 12.1.7 FEDERAL PACIFIC
- 12.1.7.1 Business overview
- 12.1.7.2 Products offered
- 12.1.7.3 Recent developments
- 12.1.7.3.1 Expansions
- 12.1.8 ENTEC ELECTRIC & ELECTRONIC
- 12.1.8.1 Business overview
- 12.1.8.2 Products offered
- 12.1.9 NOJA POWER
- 12.1.9.1 Business overview
- 12.1.9.2 Products offered
- 12.1.9.3 Recent developments
- 12.1.9.3.1 Deals
- 12.1.10 TIEPCO GROUP
- 12.1.10.1 Business overview
- 12.1.10.2 Products offered
- 12.1.11 GHORIT ELECTRICALS
- 12.1.11.1 Business overview
- 12.1.11.2 Products offered
- 12.1.12 NINGBO TIANAN GROUP
- 12.1.12.1 Business overview
- 12.1.12.2 Products offered
- 12.1.13 TRAYER SWITCHGEAR
- 12.1.13.1 Business overview
- 12.1.13.2 Products offered
- 12.1.13.3 Recent developments
- 12.1.13.3.1 Deals
- 12.1.14 KDM STEEL
- 12.1.14.1 Business overview
- 12.1.14.2 Products offered
- 12.1.15 SWITCHGEAR POWER SYSTEMS LLC
- 12.1.15.1 Business overview
- 12.1.15.2 Products offered
- 12.1.16 PARK DETROIT
- 12.1.16.1 Business overview
- 12.1.16.2 Products offered
- 12.1.1 EATON
- 12.2 OTHER PLAYERS
- 12.2.1 BEIJING KYLIN POWER & TECHNOLOGY
- 12.2.2 TELAWNE POWER EQUIPMENTS PVT. LTD.
- 12.2.3 ORMAZABAL
- 12.2.4 ACTOM
13 APPENDIX
- 13.1 INSIGHTS FROM INDUSTRY EXPERTS
- 13.2 DISCUSSION GUIDE
- 13.3 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS' SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL
- 13.4 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS
- 13.5 RELATED REPORTS
- 13.6 AUTHOR DETAILS










