
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1812630
자동차 시험 장비 시장(-2032년)Automotive Test Equipment Market by Equipment (Dynamometer, Vehicle Emission Test, Wheel Alignment, Battery Test System), Propulsion (ICE, EV), Vehicle Type (PC, CV), End Market, Application, Advanced Technology, and Region - Global Forecast to 2032 |
||||||
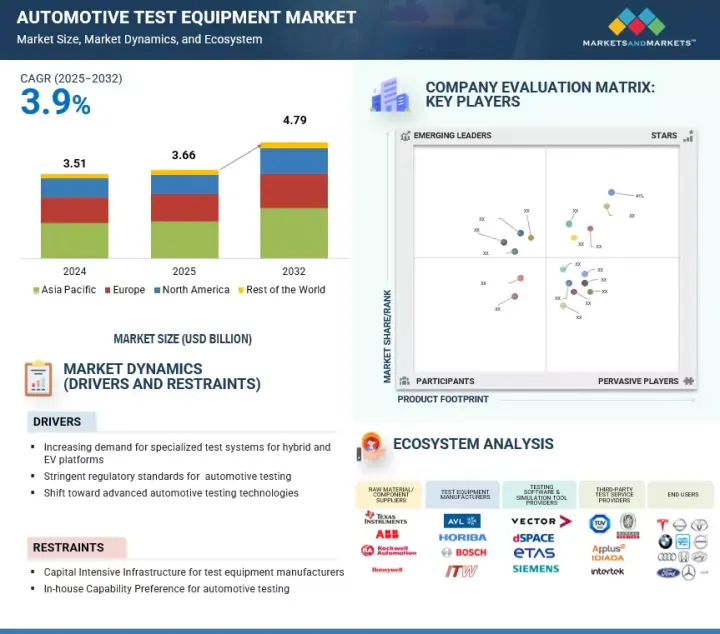
자동차 시험장비 시장 규모는 2025년 36억 6,000만 달러에서 예측기간 동안 3.9%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 성장을 지속하여 2023년까지 47억 9,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.
차량 일렉트로닉스와 소프트웨어의 복잡화는 통합형 HiL(Hardware-in-the-Loop) 및 SiL(Software-in-the-Loop) 테스트 솔루션에 대한 강한 수요를 창출하고 있으며, 세계적인 배출 규제 강화가 첨단 연료 분사 및 배출 가스 테스트 시스템의 도입을 가속화하고 있습니다. Horiba Ltd., AVL, National Instruments, Siemens AG, ATS Korea와 같은 주요 시험 장비 제공업체는 신흥 시장을 위한 비용 효율적이고 휴대 가능한 솔루션을 제공하고 ECU, 배터리, ADAS 시험을 포괄하는 종합적인 플랫폼을 구축함과 동시에 차세대 자동차 기술을 검증하기 위해 산학 연계를 강화함으로써 이러한 동향에 대응하고 있습니다.
| 조사 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 조사 대상 연도 | 2021-2032년 |
| 기준연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 기간 | 2025-2032년 |
| 단위 | 달러 |
| 부문 | 용도, 장비, 차량 유형, 엔드 시장, 추진 구분, 첨단 기술, 지역 |
| 대상 지역 | 아시아태평양, 유럽, 북미 및 기타 지역 |
National Instruments는 2024년 7월에 EV 파워트레인의 검증을 보다 신속하게 수행하기 위해 LabVIEW 기반 테스트 소프트웨어를 고급 PC 기반 시뮬레이션으로 강화했습니다. 또한 Keysight는 2025년 3월 ADAS 및 EV 시스템의 고장 감지를 개선하기 위해 AI 구동 분석을 PathWave 플랫폼에 통합했습니다. 첨단 시험 시스템의 고비용과 급속한 진부화는 특히 다양하고 진화하는 규제에 대응하기 위해 빈번한 업그레이드를 강요하는 중소규모 공급업체에게 장벽이 되고 있습니다. 그러나 같은 동향이 모듈형으로 AI 구동, 클라우드 대응의 시험장비에 기회를 만들어내고 있습니다. 이를 통해 자동 진단, 예측 분석 및 국제 규제 조화를 지원하고 OEM과 공급업체 간에 보다 빠르고 비용 효율적인 검증이 가능합니다.
"변속기 다이나모미터는 예측 기간 동안 가장 빠르게 성장하는 테스트 장비 유형"
다단 EV 기어 박스, 하이브리드 e 액슬, 고급 듀얼 클러치 변속기(DCT)의 보급에 따라 효율성, 내구성, NVH(소음, 진동 및 불쾌감) 시험에 대한 수요가 급증하고 있습니다. 엔진 및 섀시 다이나모미터와 달리 변속기 다이나모미터는 보다 높은 토크 밀도와 다양한 부하 프로파일 하에서의 검증을 가능하게 하며 EV 작동의 중심인 회생 브레이크 부하의 시뮬레이션 기능도 갖추고 있습니다. 또한 차세대 변속기는 모터, 파워 일렉트로닉스 및 냉각 시스템을 통합하지만 복잡한 전기 기계적 상호작용을 정확하게 재현할 수 있는 변속기 다이나모미터만 있습니다. 또한 연비 및 CO2 규제를 강화함으로써 OEM은 변속기 손실을 1% 미만으로 줄이는 것을 목표로 하므로, 보다 고도이고 빈도가 높은 효율 시험이 필수적입니다. 예를 들어 AVL은 2024년 9월 대형 트럭을 위한 고도로 통합된 다단 e-액슬을 발표했습니다. 이 시스템은 연속 400kW, 피크 540kW의 출력을 가지며, 토크로스가 없는 시프트를 가능하게 하고, 변속기 다이나모미터가 실제 작동 조건 하에서 검증해야 하는 시스템의 전형적인 예를 보여줍니다. 이러한 요인들이 결합되어 변속기 다이나모미터는 EV와 하이브리드 파워트레인에서 혁신의 중요한 추진 요소가 되어 시장에서 가장 역동적인 성장 부문이 되고 있습니다.
"배터리 시험 장비는 예측 기간 동안 최대 부문이 될 전망"
이 시스템은 배터리 셀, 모듈 및 팩을 광범위한 작동 범위에서 평가하도록 설계되었으며, 일반적으로 5 - 1,000V, 최대 1,200A의 전류를 지원하며 전압 ±0.02%, 전류 ±0.05%의 고정밀도를 제공합니다. 첨단 구성은 채널당 최대 300kW의 양방향 전력 흐름을 지원하고 멀티 메가와트 규모로 확장 가능하며 256채널 이상의 동시 테스트 능력을 갖추고 있으며 연구 개발 처리량을 크게 향상시킵니다. 온도 챔버와의 통합으로 -40℃에서 80℃까지의 극단적인 환경 조건을 시뮬레이션할 수 있으며, 과전압, 단락, 열폭주에 대한 안전 시스템도 내장되어 있습니다.
배터리 시험장비 시장은 급속한 EV 보급, 보다 엄격한 안전 및 성능 규제, 장거리 주행과 내구성이 뛰어난 배터리에 대한 수요 증가에 의해 세계적으로 강한 성장을 보이고 있습니다. UNECE R100 및 ISO 12405와 같은 표준 준수를 보장하고 안전성, 수명주기 내구성 및 실제 주행 조건에서 성능을 인증하는 것이 중요한 추진 요인입니다. 이러한 시스템은 화학적 혁신과 드라이브 사이클 시뮬레이션을 지원하는 R&D 실험실부터 대량 생산 라인에서 엔드 오브 라인 검증 및 진단을 수행하는 서비스 센터에 이르기까지 밸류체인 전반에 걸쳐 필수적인 존재입니다.
본 보고서에서는 세계 자동차 시험 장비 시장을 조사했으며, 시장 개요, 시장 성장 영향요인 분석, 기술 및 특허 동향, 법규제 환경, 사례연구, 시장 규모 추이와 예측, 각종 구분 및 지역/주요 국가별 상세 분석, 경쟁 구도, 주요기업 프로파일 등을 정리했습니다.
목차
제1장 서론
제2장 주요 요약
제3장 중요 인사이트
제4장 시장 개요
- 시장 역학
- 성장 촉진요인
- 성장 억제요인
- 기회
- 과제
제5장 업계 동향
- 공급망 분석
- 생태계 분석
- 가격 분석
- 무역 분석
- 고객의 사업에 영향을 미치는 동향/혼란
- 사례 연구 분석
- 2025-2026년 주요 회의 및 이벤트
- 투자 및 자금조달 시나리오
제6장 기술, 특허, 디지털, AI 채용에 의한 전략적 혁신
- 기술 분석
- 특허 분석
- AI/생성형 AI가 자동차 시험 장비 시장에 미치는 영향
- OEM이 채용하는 자동차 시험 전략
- 자동차 시험에서의 스타트업과 중소기업의 혁신
- 지역별 투자 핫스팟 : 현지화된 시험 능력과 비용 우위
- OEM 및 Tier 1 공급업체를 위한 설비 투자(CAPEX) 최적화 : 자사 내 vs 외부 위탁
- 경쟁 비교 매트릭스 : 자동차 시험의 OEM 전략
제7장 지속가능성과 규제상황
- 규제 상황
- 세계의 배출가스 규제와 안전규제가 자동차 시험 장비에 미치는 영향
- 규제시험 요건
제8장 고객정세와 구매행동
- 주요 이해관계자와 구매 기준
제9장 자동차 시험 장비 시장 : 장비별
- 엔진 다이나모미터
- 섀시 다이나모미터
- 차량 배출 가스 시험 시스템
- 휠 얼라인먼트 테스터
- 변속기 다이나모미터
- 연료 분사 펌프 테스터
- 배터리 시험 장비
- E모터 시험장비
- E 액슬 시험
- EV 드라이브 트레인 시험
- 하드웨어 인 더 루프 시험
- 차량 충전 및 고전압 시험 시스템
- 기타
- 주요 인사이트
제10장 자동차 시험 장비 시장 : 용도별
- 모바일/태블릿 기반 기기
- PC/랩탑 기반 기기
- 주요 인사이트
제11장 자동차 시험 장비 시장 : 차량 유형별
- 승용차
- 상용차
- 소형 상용차
- 대형 상용차
- 주요 인사이트
제12장 자동차 시험 장비 시장 : 추진 구분별
- ICE
- EV
- 주요 인사이트
제13장 자동차 시험 장비 시장 : 엔드 시장별
- 인증 서비스 센터
- OEM 조립 공장
- 연구개발/기술센터
- 주요 인사이트
제14장 자동차 시험 장비 시장 : 첨단 기술별
- ADAS 시험
- ECU 시험
- 데이터 로거
- 시뮬레이션 시험
- 충돌 충격 시뮬레이션
- 자율주행 시뮬레이터
- 센서 시험
- 인식 시스템 시험
- 엣지 컴퓨팅
- V2X 시험
제15장 자동차 시험 장비 시장 : 지역별
- 아시아태평양
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 거시경제 전망
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 기타
- 유럽
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 거시경제 전망
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 영국
- 기타
- 북미
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 거시경제 전망
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 미국
- 세계 기타 지역
- 거시경제 전망
- 브라질
- 러시아
- 기타
제16장 경쟁 구도
- 주요 진입기업의 전략/강점
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 수익 분석
- 기업평가와 재무지표
- 브랜드/제품 비교
- 자동차 시험 장비 제조업체의 생산 능력
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 주요 기업
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 스타트업/중소기업
- 경쟁 시나리오
제17장 기업 프로파일
- 주요 기업
- PHINIA INC.
- ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
- HORIBA GROUP
- AVL
- ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC.
- SIEMENS
- DURR GROUP
- CONTINENTAL AG
- VECTOR INFORMATIK GMBH
- SOFTING AG
- MUSTANG ADVANCED ENGINEERING
- SCHAEFFLER AG
- MAHA MASCHINENBAU HALDENWANG GMBH & CO. KG
- MULLER AUTOMOTIVE
- 기타 기업
- INTERTEK GROUP PLC
- TUV SUD
- ROHDE & SCHWARZ
- SINFONIA TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.
- AMPRO TESTING MACHINES
- AMETEK CTS
- AUTEL INTELLIGENT TECHNOLOGY CORP., LTD.
- NSM INDUSTRIAL SOLUTIONS PVT LTD
- DSA DATEN-UND SYSTEMTECHNIK GMBH
- IPETRONIK GMBH & CO.KG
- HUFF TECHNOLOGIES
- DYNO ONE INC.
- DRIVE SYSTEM DESIGN
- ANTHONY BEST DYNAMICS LIMITED
- SAJ TEST PLANT PVT. LTD.
- MAXEYE TECHNOLOGIES
- NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS CORP.
제18장 MARKETSANDMARKETS의 권고
- 아시아태평양이 자동차 시험 장비의 주요 성장 거점으로
- OEM은 모듈형 배터리 시험으로 안전성과 효율성 향상에 주력
- 시험장비 제조업체는 서비스 네트워크의 근대화에 주력
- EV 및 자율주행차의 시험 능력 개발을 위한 전략적 투자
- 결론
제19장 부록
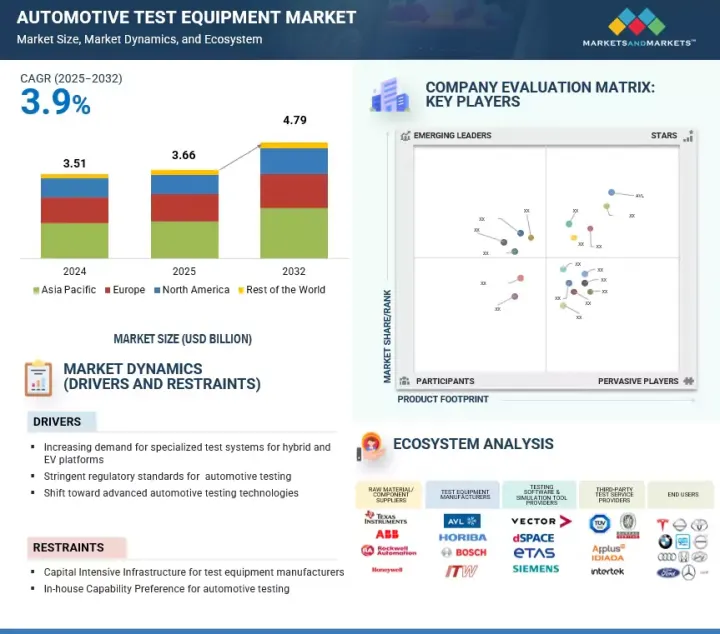
JHS 25.09.26The automotive test equipment market is projected to reach USD 4.79 billion by 2032 from USD 3.66 billion in 2025 at a CAGR of 3.9%. Rising vehicle electronics and software complexity have driven strong demand for integrated HiL and SiL testing solutions, while stricter global emission norms have accelerated the adoption of advanced fuel injection and emission testing systems. Leading test equipment providers, including Horiba Ltd., AVL, National Instruments, Siemens AG, and ATS Korea, are addressing these trends by delivering cost-efficient, portable solutions for emerging markets, building comprehensive platforms spanning ECU, battery, and ADAS testing, and strengthening industry-academia collaborations to validate next-generation automotive technologies.
| Scope of the Report | |
|---|---|
| Years Considered for the Study | 2021-2032 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2032 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Million/Billion) |
| Segments | Application, Equipment, Vehicle Type, End Market, Propulsion, Advanced Technology, and Region |
| Regions covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, and Rest of the World |
National Instruments, in July 2024, enhanced its LabVIEW-based testing software with advanced PC-based simulation for faster EV powertrain validation, and Keysight, in March 2025, integrated AI-driven analytics into its PathWave platform to improve ADAS and EV system fault detection. The high cost and rapid obsolescence of advanced test systems pose barriers, particularly for smaller suppliers having to upgrade often to align with diverse and evolving regulatory frameworks. However, these same trends create opportunities for modular, AI-driven, and cloud-enabled test equipment that supports automated diagnostics, predictive analytics, and global harmonization, which enables a faster and more cost-effective validation across OEMs and suppliers.
"Transmission dynamometer is the fastest-growing test equipment type during the forecast period."
With the rise of multi-speed EV gearboxes, hybrid e-axles, and advanced dual-clutch transmissions (DCTs), the demand for precise efficiency, durability, and NVH (noise, vibration, harshness) testing is increasing sharply. Unlike engine or chassis dynamometers, transmission dynamometers enable validation under higher torque densities and varying load profiles, including the ability to simulate regenerative braking loads central to EV operation. Moreover, next-generation transmissions integrate motors, power electronics, and cooling systems, creating complex electro-mechanical interactions that only transmission dynamometers can accurately replicate. At the same time, tightening fuel economy and CO2 regulations are compelling OEMs to target transmission losses below 1%, which in turn requires more advanced and frequent efficiency testing. For instance, in September 2024, AVL introduced a highly integrated multi-speed e-axle for heavy-duty trucks-delivering 400 kW continuous and 540 kW peak power with shifting capability that avoids torque loss-demonstrating the type of system that transmission dynamometers must now validate under real operating conditions. Together, these factors position transmission dynamometers as a critical enabler of innovation in EV and hybrid powertrains, making them the most dynamic growth segment within the automotive test equipment market.
"Battery test equipment is expected to be the largest segment of the market during the forecast period."
The battery test equipment segment is projected to showcase significant growth of all EV test equipment during the forecast period. These systems are designed to evaluate battery cells, modules, and packs across wide operating ranges, typically spanning 5V to 1,000V and currents up to 1,200A, with high precision levels of +-0.02% for voltage and +-0.05% for current. Advanced configurations support bi-directional power flow up to 300 kW per channel, are scalable to multi-megawatt levels, and offer multi-channel capacity that often exceeds 256 channels for simultaneous testing, thereby enhancing R&D throughput. Integration with thermal chambers enables simulation of extreme environmental conditions (-40°C to +80°C), while built-in safety systems guard against overvoltage, short circuits, and thermal runaway. Battery testing equipment is witnessing strong global growth, primarily driven by rapid EV adoption, stricter safety and performance regulations, and rising demand for longer-range and durable batteries. Regulatory compliance is a key driver, as equipment ensures adherence to standards like UNECE R100 and ISO 12405, certifying safety, lifecycle durability, and performance under real-world driving conditions. These systems are critical across the value chain from R&D labs supporting chemistry innovation and drive cycle simulations, to production lines enabling end-of-line validation, and service centers performing diagnostics. Leading providers in this space include Intertek and AVL, who deliver advanced solutions for both OEMs and suppliers. Stringent global regulations and extended warranty obligations are compelling OEMs and suppliers to invest in advanced lifecycle, durability, and abuse testing systems to ensure long-term battery reliability. The advent of next-generation chemistries, including solid-state batteries, is further accelerating demand for specialized testing equipment such as impedance spectroscopy analyzers and dendrite detection systems, which are critical for validating safety and scalability. In parallel, growing emphasis on end-of-life and second-life applications is driving adoption of automated grading and rapid diagnostic tools, enabling efficient battery repurposing and recycling. Leading providers of battery testing equipment and services include Intertek, AVL, TUV Rheinland, Keysight, Dewesoft, HORIBA, SGS, National Instruments, Softing, Durr Group, and Arbin Instruments. These companies offer comprehensive testing solutions such as cell/module/pack-level testing, charge/discharge cycles, and battery lifecycle simulations.
"The Rest of the World is expected to be the second fastest-growing market during the forecast period."
The Rest of the World is the second fastest-growing region during the forecast period. Among the Rest of the World countries, Brazil has established itself as the leading mobility hub, advancing faster than its peers through a dual push of OEM assembly plant expansion and testing facility growth. BYD accelerated localization with three factories in Bahia, including EV, battery, and bus chassis plants, alongside a new Flex 1.5L plug-in engine facility at the Camacari complex in March 2025. GWM began hybrid SUV production in Iracemapolis, while Stellantis introduced Bio-Hybrid technology in Pernambuco, integrating ethanol with electrification for cost-effective solutions. OEMs are investing in testing the hybrid and alternative fuel vehicles in the country. For instance, Volkswagen and Toyota strengthened hybrid flex-fuel programs, and Hyundai advanced ethanol-hybrid R&D at Piracicaba, positioning Brazil as a global testbed for renewable energy vehicles. In commercial transport, Scania rolled out ethanol-hybrid trucks aligned with Brazil's low-carbon policies. Additionally, in June 2025, Marelli inaugurated an INMETRO-accredited EV lab in Hortolandia, enhancing local validation and homologation capacity. This convergence of industrial scale-up and advanced testing positioned Brazil as the fastest-growing market outside the global triad, anchoring its leadership in the evolving mobility landscape.
In Russia, the government and industry players are intensifying efforts to build a domestic automotive ecosystem, with a strong emphasis on testing and R&D. In February 2025, the Ministry of Industry and Trade, the Government of Tatarstan, and RUSNANO Group signed a trilateral agreement to establish an automotive component development center at the Idea Technopark in Kazan, focused on body and chassis components, power electronics, and traction batteries for passenger cars and trucks. The initiative also includes a modern testing laboratory and a training hub for engineering and technical specialists, reinforcing Russia's push for technological self-reliance. Complementing this, Atom announced in December 2024 that its upcoming EV will undergo 48 crash tests, along with aerodynamic, torsional rigidity, climatic, and corrosion durability evaluations, ahead of serial production in 2025. Together, these developments underscore Russia's accelerated push to strengthen its domestic testing infrastructure, enhance EV readiness, and reduce reliance on imports.
In-depth interviews were conducted with CEOs, marketing directors, other innovation and technology directors, and executives from various key organizations operating in this market.
- By Company Type: OEMs - 30%, Tier I & Tier II - 50%, and Others - 20%,
- By Designation: CXOs - 35%, Managers - 25%, and Executives - 40%
- By Region: North America - 30%, Europe - 20%, Asia Pacific - 50%, and Rest of the World - 15%
The automotive test equipment market is dominated by established players such as AVL (Austria), Horiba, Ltd.(Japan), Robert Bosch GmbH (Germany), Phinia Inc.(US), and Illinois Tool Works Inc. (US). These companies actively manufacture and develop new and advanced connectors. They have set up R&D facilities and offer best-in-class products to their customers.
Research Coverage:
The market study covers the automotive test equipment market by product type (engine dynamometer, chassis dynamometer, vehicle emission test system, wheel alignment tester, Fuel injection pump tester, transmission dynamometer), application (mobile/tablet-based equipment, PC/Laptop-based equipment), equipment type (inverter test, electric propulsion test, e-axle test, battery test equipment, on-board charger ATS, motor test equipment, EV drivetrain test), end market (OEM assembly plant, R&D/Technical center, authorized service center), vehicle type (commercial vehicle, passenger car), EV type (battery electric vehicle, plug-in hybrid electric vehicle, and hybrid electric vehicle), advanced technology, and region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Rest of the World). It also covers the competitive landscape and company profiles of the major players in the automotive test equipment market.
Key Benefits of Purchasing this Report
The study offers a detailed competitive analysis of the key players in the market, including their company profiles, important insights into product and business offerings, recent developments, and main market strategies. The report will assist market leaders and new entrants with estimates of revenue figures for the overall automotive test equipment market and its subsegments. It helps stakeholders understand the competitive landscape and gain additional insights to better position their businesses and develop effective go-to-market strategies. Additionally, the report provides information on key market drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities, helping stakeholders keep track of market dynamics.
The report provides insights into the following points:
- Analysis of key drivers (Increasing demand for specialized test systems for hybrid and EV platforms, stringent regulatory standards for automotive testing, shift toward advanced automotive testing technologies), restraints (capital-intensive infrastructure for test equipment manufacturers, in-house capability preference for automotive testing), opportunities (Test-as-a-Service and cloud-integrated virtual labs, convergence toward X-in-the-Loop (XiL) technology, localized, compact test benches for Tier-2 and mid-sized suppliers), and challenges (heterogeneous validation needs across OEMs, high complexity in ADAS and ECU co-validation, lack of standardization in battery testing protocols) influencing the growth of the automotive test equipment market
- Product Development/Innovation: Detailed insights into upcoming technologies, R&D activities, and product launches in the automotive test equipment market
- Market Development: Comprehensive information about lucrative markets (the report analyzes the automotive test equipment across various regions)
- Market Diversification: Exhaustive information about new products, untapped geographies, recent developments, and investments in the automotive test equipment market
- Competitive Assessment: In-depth assessment of market shares, growth strategies, and service offerings of leading players like AVL (Austria), Horiba, Ltd. (Japan), Robert Bosch GmbH (Germany), Phinia Inc. (US), and Illinois Tool Works Inc. (US) in the automotive test equipment market
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES
- 1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
- 1.3 STUDY SCOPE
- 1.3.1 MARKET SEGMENTATION AND REGIONAL SCOPE
- 1.3.2 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- 1.4 YEARS CONSIDERED
- 1.5 CURRENCY CONSIDERED
- 1.6 STAKEHOLDERS
- 1.7 SUMMARY OF CHANGES
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
- 3.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET
- 3.2 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY EQUIPMENT
- 3.3 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY PROPULSION
- 3.4 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE
- 3.5 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY END MARKET
- 3.6 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY APPLICATION
- 3.7 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY REGION
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 INTRODUCTION
- 4.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.2.1 DRIVERS
- 4.2.1.1 Increasing demand for specialized test systems for hybrid and EV platforms
- 4.2.1.2 Stringent regulatory standards for automotive testing
- 4.2.1.3 Shift toward advanced automotive testing technologies
- 4.2.2 RESTRAINTS
- 4.2.2.1 Capital-intensive infrastructure for test equipment manufacturers
- 4.2.2.2 In-house capability preference for automotive testing
- 4.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
- 4.2.3.1 Popularity of test-as-a-service and cloud-integrated virtual labs
- 4.2.3.2 Convergence toward X-in-the-Loop (XiL) technology
- 4.2.3.3 Localized, compact test benches for tier-2 and mid-sized suppliers
- 4.2.4 CHALLENGES
- 4.2.4.1 Heterogeneous validation needs across OEMs
- 4.2.4.2 High complexity in ADAS and ECU co-validation
- 4.2.4.3 Lack of standardization in battery testing protocols
- 4.2.1 DRIVERS
5 INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 5.1 SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 5.2 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
- 5.2.1 RAW MATERIAL/COMPONENT SUPPLIERS
- 5.2.2 TEST EQUIPMENT MANUFACTURERS
- 5.2.3 TESTING SOFTWARE & SIMULATION TOOL PROVIDERS
- 5.2.4 THIRD-PARTY TESTING SERVICE PROVIDERS
- 5.2.5 END USERS
- 5.3 PRICING ANALYSIS
- 5.3.1 BY VEHICLE TYPE
- 5.3.2 BY EQUIPMENT & REGION
- 5.4 TRADE ANALYSIS
- 5.4.1 EXPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 90318000)
- 5.4.2 IMPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 90318000)
- 5.5 TRENDS & DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
- 5.6 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
- 5.6.1 NOVELIC DEVELOPED HIGHLY PROGRAMMABLE AND CONFIGURABLE HIGH-SPEED DATA LOGGER PLATFORM TO ENABLE LOW-LATENCY DATA STREAMING
- 5.6.2 BRIGGS & STRATTON UTILIZED SIEMENS' FLEXIBLE AND INTUITIVE SIMCENTER TESTLAB SOFTWARE TO INTEGRATE SOFTWARE AND HARDWARE TESTING INTO SEAMLESS WORKFLOW
- 5.6.3 MAN TRUCK & BUS DEPLOYED VECTOR INDIGO TO OPTIMIZE DIAGNOSTIC VALIDATION AND TESTING PROCESSES
- 5.7 KEY CONFERENCES & EVENTS, 2025-2026
- 5.8 INVESTMENT & FUNDING SCENARIO
6 STRATEGIC DISRUPTION THROUGH TECHNOLOGY, PATENTS, DIGITAL, AND AI ADOPTIONS
- 6.1 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS
- 6.1.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.1.1.1 E-motor test benches
- 6.1.1.2 Battery test systems
- 6.1.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.1.2.1 Simulation and modeling software
- 6.1.2.2 Data acquisition and analytics (DAQ & analytics)
- 6.1.3 ADJACENT TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.1.3.1 Cybersecurity testing tools
- 6.1.3.2 Autonomous driving test ecosystem
- 6.1.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.2 PATENT ANALYSIS
- 6.3 IMPACT OF AI/GEN AI ON AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET
- 6.4 AUTOMOTIVE TESTING STRATEGIES ADOPTED BY OEMS
- 6.4.1 IN-HOUSE VS. OUTSOURCED TESTING
- 6.4.2 TESTING INFRASTRUCTURE DIGITIZATION
- 6.4.3 END-OF-LINE (EOL) AUTOMATION
- 6.4.4 MODULAR AND SCALABLE TEST PLATFORMS
- 6.4.5 SOFTWARE-DEFINED VEHICLE (SDV) AND CYBERSECURITY TESTING
- 6.4.6 GLOBAL R&D-MANUFACTURING NETWORK INTEGRATION
- 6.4.7 STANDARDIZATION AND REGULATORY READINESS
- 6.4.8 PARTNERSHIP WITH TEST EQUIPMENT SUPPLIERS
- 6.4.9 SUSTAINABILITY AND ENERGY-EFFICIENT TESTING
- 6.4.10 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) AND PREDICTIVE TESTING MODELS
- 6.5 STARTUP AND SME INNOVATIONS IN AUTOMOTIVE TESTING
- 6.6 REGIONAL INVESTMENT HOTSPOTS: LOCALIZED TESTING CAPABILITIES & COST ADVANTAGES
- 6.7 CAPEX OPTIMIZATION FOR OEMS AND TIER-1 SUPPLIERS ( IN-HOUSE VS. OUTSOURCED)
- 6.8 COMPETITIVE COMPARISON MATRIX: OEM STRATEGIES IN AUTOMOTIVE TESTING
7 SUSTAINABILITY AND REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 7.1.1 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- 7.1.2 KEY REGULATIONS, BY REGION
- 7.2 IMPACT OF GLOBAL EMISSION AND SAFETY REGULATIONS ON AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT
- 7.2.1 EU7, US EPA, CHINA 6: INFLUENCE ON CHASSIS DYNOS, EMISSION TESTERS, AND HOMOLOGATION EQUIPMENT
- 7.2.2 ISO 26262, UNECE R155/R156 COMPLIANCE VIA TEST EQUIPMENT
- 7.3 REQUIREMENTS FOR REGULATORY TESTING
8 CUSTOMER LANDSCAPE & BUYER BEHAVIOR
- 8.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA
- 8.1.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS
- 8.1.2 BUYING CRITERIA
9 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY EQUIPMENT
- 9.1 INTRODUCTION
- 9.2 ENGINE DYNAMOMETER
- 9.2.1 RISING DEMAND FOR HIGH-PERFORMANCE ENGINES, FUEL-EFFICIENCY REGULATIONS, AND TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCEMENTS IN HYBRID POWERTRAINS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.3 CHASSIS DYNAMOMETER
- 9.3.1 EXPANSION OF AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY IN DEVELOPING ECONOMIES TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.4 VEHICLE EMISSION TEST SYSTEM
- 9.4.1 STRINGENT REGULATIONS, AIR QUALITY FOCUS, AND HYBRID VEHICLE ADOPTION TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.5 WHEEL ALIGNMENT TESTER
- 9.5.1 INCREASING ADOPTION OF AUTOMATED VEHICLES AND PRECISION DRIVETRAIN TESTING TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.6 TRANSMISSION DYNAMOMETER
- 9.6.1 HIGH VEHICLE PARC, OEM SERVICE EXPANSION, AND POWERTRAIN SHIFT TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.7 FUEL INJECTION PUMP TESTER
- 9.7.1 ALTERNATIVE FUELS AND DIAGNOSTIC INFRASTRUCTURE IN ICE-DOMINANT REGIONS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.8 BATTERY TEST EQUIPMENT
- 9.8.1 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGIES AND HIGH-VOLTAGE VALIDATION TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.9 E-MOTOR TEST EQUIPMENT
- 9.9.1 EV ADOPTION AND HIGH-VOLTAGE MOTOR ARCHITECTURES TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.10 E-AXLE TESTING
- 9.10.1 GROWING DEMAND FOR LIFECYCLE TESTING OF E-AXLES IN FLEET AND SHARED MOBILITY EVS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.11 EV DRIVETRAIN TESTING
- 9.11.1 NEXT-GEN VALIDATION IN EV DRIVETRAINS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.12 HARDWARE-IN-THE-LOOP TESTING
- 9.12.1 FOCUS ON REAL-TIME INTERACTION BETWEEN PHYSICAL ECUS AND SIMULATED VEHICLE ENVIRONMENTS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.13 VEHICLE CHARGING & HIGH-VOLTAGE TEST SYSTEMS
- 9.13.1 HIGH-VOLTAGE BATTERY PACKS AND V2G CAPABILITIES IN EVS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 9.14 OTHERS
- 9.15 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
10 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY APPLICATION
- 10.1 INTRODUCTION
- 10.2 MOBILE/TABLET-BASED EQUIPMENT
- 10.2.1 INCREASING DEMAND FOR CONNECTED VEHICLES AND EV ADOPTION IN MOBILE/TABLET-BASED TESTING TO DRIVE MARKET
- 10.3 PC/LAPTOP-BASED EQUIPMENT
- 10.3.1 HIGH COMPUTATIONAL POWER AND MULTI-SYSTEM INTEGRATION TO DRIVE MARKET
- 10.4 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
11 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE
- 11.1 INTRODUCTION
- 11.1.1 COMPARISON OF TEST EQUIPMENT SPECIFICATIONS IN PASSENGER CAR AND COMMERCIAL VEHICLE
- 11.2 PASSENGER CAR
- 11.2.1 ADVANCEMENTS IN ADAS AND AUTONOMOUS DRIVING TECHNOLOGIES TO DRIVE MARKET
- 11.3 COMMERCIAL VEHICLE
- 11.3.1 INCREASING DEMAND FOR HEAVY-DUTY CHASSIS AND ENGINE DYNAMOMETERS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 11.3.2 LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE
- 11.3.3 HEAVY COMMERCIAL VEHICLE
- 11.4 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
12 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY PROPULSION
- 12.1 INTRODUCTION
- 12.2 ICE
- 12.2.1 ADVANCEMENTS IN ENGINE TECHNOLOGIES AND STRICT EMISSION REGULATIONS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 12.3 EV
- 12.3.1 INCREASING DEMAND FOR ADVANCED BATTERY TESTING TO DRIVE MARKET
- 12.4 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
13 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY END MARKET
- 13.1 INTRODUCTION
- 13.2 AUTHORIZED SERVICE CENTER
- 13.2.1 RISING DEMAND FOR WHEEL ALIGNMENT TESTERS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 13.3 OEM ASSEMBLY PLANT
- 13.3.1 END-OF-LINE TESTING AND OPTIMIZATION OF FACILITIES BY OEMS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 13.4 R&D/TECHNICAL CENTER
- 13.4.1 DEMAND FOR ADVANCED ADAS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEM TESTING TECHNOLOGIES TO DRIVE MARKET
- 13.5 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
14 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY
- 14.1 INTRODUCTION
- 14.2 ADAS TESTING
- 14.3 ECU TESTING
- 14.4 DATA LOGGER
- 14.5 SIMULATION TESTING
- 14.5.1 CRASH IMPACT SIMULATION
- 14.5.2 AUTONOMOUS DRIVING SIMULATOR
- 14.6 SENSOR TESTING
- 14.7 PERCEPTION SYSTEM TESTING
- 14.8 EDGE COMPUTING
- 14.9 V2X TESTING
15 AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET, BY REGION
- 15.1 INTRODUCTION
- 15.2 ASIA PACIFIC
- 15.2.1 ASIA PACIFIC: AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET DRIVERS
- 15.2.2 ASIA PACIFIC: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 15.2.3 CHINA
- 15.2.3.1 Adoption of expansion strategy by OEMs to drive market
- 15.2.4 INDIA
- 15.2.4.1 Rapid expansion of authorized service centers to foster growth
- 15.2.5 JAPAN
- 15.2.5.1 Assembly plant growth and rise in R&D investments to drive market
- 15.2.6 SOUTH KOREA
- 15.2.6.1 Heavy investments in advanced battery test equipment to boost market
- 15.2.7 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC
- 15.3 EUROPE
- 15.3.1 EUROPE: AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET DRIVERS
- 15.3.2 EUROPE: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 15.3.3 FRANCE
- 15.3.3.1 EV adoption, regulatory compliance, and strategic R&D investments to drive market
- 15.3.4 GERMANY
- 15.3.4.1 Investment and collaborative R&D in autonomous driving and ADAS technologies to spur demand
- 15.3.5 ITALY
- 15.3.5.1 Hybridization and export-oriented production to drive market
- 15.3.6 SPAIN
- 15.3.6.1 Emphasis on developing robust testing and quality assurance infrastructure to boost market
- 15.3.7 UK
- 15.3.7.1 Demand for electrification and R&D-driven EV testing to drive market
- 15.3.8 REST OF EUROPE
- 15.4 NORTH AMERICA
- 15.4.1 NORTH AMERICA: AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MARKET DRIVERS
- 15.4.2 NORTH AMERICA: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 15.4.3 CANADA
- 15.4.3.1 Rise in investments for connected and autonomous vehicle development to drive market
- 15.4.4 MEXICO
- 15.4.4.1 Expansion of EV manufacturing to drive market
- 15.4.5 US
- 15.4.5.1 Focus on innovation, technology, and development of high-performance, fuel-efficient vehicles to drive market
- 15.5 REST OF THE WORLD
- 15.5.1 REST OF THE WORLD: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 15.5.2 BRAZIL
- 15.5.2.1 Heavy investments by OEMs to drive market
- 15.5.3 RUSSIA
- 15.5.3.1 Focus on developing local manufacturing centers to drive market
- 15.5.4 OTHERS
16 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 16.1 INTRODUCTION
- 16.2 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN, 2021-2025
- 16.3 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2024
- 16.4 REVENUE ANALYSIS, 2020-2024
- 16.5 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS
- 16.6 BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- 16.7 PRODUCTION CAPABILITIES OF AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT MANUFACTURERS
- 16.7.1 PHINIA INC.
- 16.7.1.1 PHINIA Inc.: Upcoming centers
- 16.7.2 SOFTING AG
- 16.7.2.1 Softing AG: Upcoming centers
- 16.7.3 ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
- 16.7.3.1 Robert Bosch GmbH: Upcoming centers
- 16.7.4 HORIBA, LTD.
- 16.7.4.1 HORIBA, Ltd.: Upcoming centers
- 16.7.5 AVL
- 16.7.5.1 AVL: Upcoming centers
- 16.7.6 SIEMENS AG
- 16.7.6.1 Siemens AG: Upcoming centers
- 16.7.7 SCHAEFFLER AG
- 16.7.7.1 Schaeffler AG: Upcoming centers
- 16.7.1 PHINIA INC.
- 16.8 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 16.8.1 STARS
- 16.8.2 EMERGING LEADERS
- 16.8.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
- 16.8.4 PARTICIPANTS
- 16.8.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT
- 16.8.5.1 Company footprint
- 16.8.5.2 Region footprint
- 16.8.5.3 Equipment footprint
- 16.8.5.4 Vehicle type footprint
- 16.9 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 16.9.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
- 16.9.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
- 16.9.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
- 16.9.4 STARTING BLOCKS
- 16.9.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING
- 16.9.5.1 List of startups/SMEs
- 16.9.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of startups/SMEs
- 16.10 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
- 16.10.1 PRODUCT LAUNCHES/DEVELOPMENTS
- 16.10.2 DEALS
- 16.10.3 EXPANSION
- 16.10.4 OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
17 COMPANY PROFILES
- 17.1 KEY PLAYERS
- 17.1.1 PHINIA INC.
- 17.1.1.1 Business overview
- 17.1.1.2 Products offered
- 17.1.1.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.1.3.1 Product launches/developments
- 17.1.1.3.2 Deals
- 17.1.1.3.3 Other developments
- 17.1.1.4 MnM view
- 17.1.1.4.1 Key strengths
- 17.1.1.4.2 Strategic choices
- 17.1.1.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 17.1.2 ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
- 17.1.2.1 Business overview
- 17.1.2.2 Products offered
- 17.1.2.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.2.3.1 Product launches/developments
- 17.1.2.4 MnM view
- 17.1.2.4.1 Key strengths
- 17.1.2.4.2 Strategic choices
- 17.1.2.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 17.1.3 HORIBA GROUP
- 17.1.3.1 Business overview
- 17.1.3.2 Products offered
- 17.1.3.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.3.3.1 Product launches/developments
- 17.1.3.3.2 Deals
- 17.1.3.3.3 Expansion
- 17.1.3.4 MnM view
- 17.1.3.4.1 Key strengths
- 17.1.3.4.2 Strategic choices
- 17.1.3.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 17.1.4 AVL
- 17.1.4.1 Business overview
- 17.1.4.2 Products offered
- 17.1.4.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.4.3.1 Product launches/developments
- 17.1.4.3.2 Deals
- 17.1.4.3.3 Expansion
- 17.1.4.4 MnM view
- 17.1.4.4.1 Key strengths
- 17.1.4.4.2 Strategic choices
- 17.1.4.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 17.1.5 ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC.
- 17.1.5.1 Business overview
- 17.1.5.2 Products offered
- 17.1.5.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.5.3.1 Deals
- 17.1.5.3.2 Other developments
- 17.1.5.4 MnM view
- 17.1.5.4.1 Key strengths
- 17.1.5.4.2 Strategic choices
- 17.1.5.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 17.1.6 SIEMENS
- 17.1.6.1 Business overview
- 17.1.6.2 Products offered
- 17.1.6.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.6.3.1 Product launches/developments
- 17.1.6.3.2 Deals
- 17.1.7 DURR GROUP
- 17.1.7.1 Business overview
- 17.1.7.2 Products offered
- 17.1.7.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.7.3.1 Deals
- 17.1.7.3.2 Expansion
- 17.1.7.3.3 Other developments
- 17.1.8 CONTINENTAL AG
- 17.1.8.1 Business overview
- 17.1.8.2 Products offered
- 17.1.8.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.8.3.1 Product launches/developments
- 17.1.8.3.2 Deals
- 17.1.8.3.3 Expansion
- 17.1.8.3.4 Other developments
- 17.1.9 VECTOR INFORMATIK GMBH
- 17.1.9.1 Business overview
- 17.1.9.2 Products offered
- 17.1.9.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.9.3.1 Product launches/developments
- 17.1.9.3.2 Deals
- 17.1.10 SOFTING AG
- 17.1.10.1 Business overview
- 17.1.10.2 Products offered
- 17.1.10.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.10.3.1 Other developments
- 17.1.11 MUSTANG ADVANCED ENGINEERING
- 17.1.11.1 Business overview
- 17.1.11.2 Products offered
- 17.1.11.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.11.3.1 Product launches/developments
- 17.1.11.3.2 Deals
- 17.1.11.3.3 Expansion
- 17.1.11.3.4 Other developments
- 17.1.12 SCHAEFFLER AG
- 17.1.12.1 Business overview
- 17.1.12.2 Products offered
- 17.1.12.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.12.3.1 Other developments
- 17.1.13 MAHA MASCHINENBAU HALDENWANG GMBH & CO. KG
- 17.1.13.1 Business overview
- 17.1.13.2 Products offered
- 17.1.13.3 Recent developments
- 17.1.13.3.1 Deals
- 17.1.13.3.2 Other developments
- 17.1.14 MULLER AUTOMOTIVE
- 17.1.14.1 Business overview
- 17.1.14.2 Products offered
- 17.1.1 PHINIA INC.
- 17.2 OTHER PLAYERS
- 17.2.1 INTERTEK GROUP PLC
- 17.2.2 TUV SUD
- 17.2.3 ROHDE & SCHWARZ
- 17.2.4 SINFONIA TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.
- 17.2.5 AMPRO TESTING MACHINES
- 17.2.6 AMETEK CTS
- 17.2.7 AUTEL INTELLIGENT TECHNOLOGY CORP., LTD.
- 17.2.8 NSM INDUSTRIAL SOLUTIONS PVT LTD
- 17.2.9 DSA DATEN- UND SYSTEMTECHNIK GMBH
- 17.2.10 IPETRONIK GMBH & CO.KG
- 17.2.11 HUFF TECHNOLOGIES
- 17.2.12 DYNO ONE INC.
- 17.2.13 DRIVE SYSTEM DESIGN
- 17.2.14 ANTHONY BEST DYNAMICS LIMITED
- 17.2.15 SAJ TEST PLANT PVT. LTD.
- 17.2.16 MAXEYE TECHNOLOGIES
- 17.2.17 NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS CORP.
18 RECOMMENDATIONS BY MARKETSANDMARKETS
- 18.1 ASIA PACIFIC TO BE LEADING GROWTH HUB FOR AUTOMOTIVE TEST EQUIPMENT
- 18.2 OEMS TO FOCUS ON IMPROVING SAFETY AND EFFICIENCY WITH MODULAR BATTERY TESTING
- 18.3 TEST EQUIPMENT MANUFACTURERS TO FOCUS ON SERVICE NETWORK MODERNIZATION
- 18.4 STRATEGIC INVESTMENTS FOR DEVELOPING EV AND AUTONOMOUS VEHICLE TESTING CAPABILITIES
- 18.5 CONCLUSION
19 APPENDIX
- 19.1 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 19.1.1 RESEARCH DATA
- 19.1.2 SECONDARY DATA
- 19.1.2.1 List of secondary sources
- 19.1.2.2 Key data from secondary sources
- 19.1.3 PRIMARY DATA
- 19.1.3.1 List of primary participants
- 19.1.3.2 Primary interviewees from demand and supply sides
- 19.1.3.3 Breakdown of primary interviews
- 19.2 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
- 19.2.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 19.2.2 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- 19.3 DATA TRIANGULATION
- 19.4 FACTOR ANALYSIS
- 19.5 RISK & IMPACT ASSESSMENT
- 19.6 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS
- 19.7 DISCUSSION GUIDE
- 19.8 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS' SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL
- 19.9 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS
- 19.10 RELATED REPORTS
- 19.11 AUTHOR DETAILS



















