
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1923695
광(레이저) 위성 통신 시장(-2030년) : 레이저 유형(반도체 다이오드, 파이버 및 고체) 및 데이터 속도 등급(2.5Gbps 미만, 2.5-10Gbps, 10Gbps 초과), 플랫폼, 용도, 컴포넌트, 지역별Optical (laser) Satellite Communication Market by Laser Type (Semiconductor Diode, Fiber, Solid-state), Data Rate (< 2.5, 2.5-10, > 10 GBPs), Platform, Application, Component and Region - Global Forecast To 2030 |
||||||
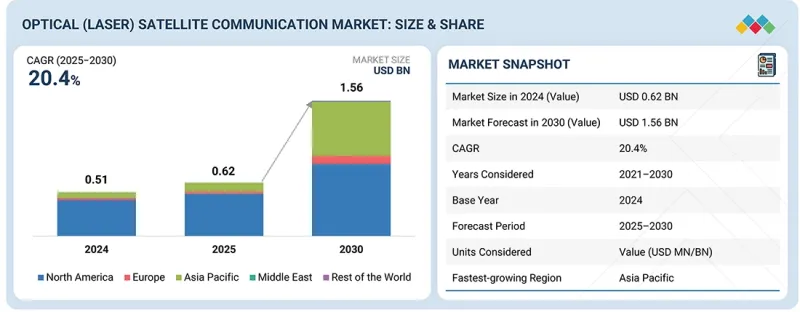
광(레이저) 위성 통신 시장 규모는 레이저 위성간 링크의 채택 확대와 저궤도(LEO) 및 다궤도 위성 네트워크 간의 대용량 및 안전한 데이터 전송에 대한 수요 증가를 배경으로 2025년의 6억 2,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 2030년까지 15억 6,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며 CAGR은 20.4%를 나타낼 전망입니다.
| 조사 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 조사 대상 기간 | 2021-2030년 |
| 기준 연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 기간 | 2025-2030년 |
| 대상 단위 | 금액(달러) |
| 부문 | 유형, 데이터 범위, 용도, 지역별 |
| 대상 지역 | 북미, 유럽, 아시아태평양 및 기타 지역 |
"플랫폼별로는 항공기 부문이 예측 기간 동안 가장 높은 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 기록할 것으로 전망"
플랫폼별로는 항공기 부문이 예측 기간 동안 가장 높은 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 기록할 것으로 예상되며, 이는 ISR 항공기, 무인항공기(UAV), 고고도 플랫폼에서 대용량 및 저탐지 가능성 통신 수요 증가에 힘입은 것입니다. 광학 링크는 실시간 정보 및 센서 데이터 공유를 위한 안전한 항공-위성 및 항공-항공 간 데이터 전송을 가능하게 합니다. 소형화되고 진동에 강한 레이저 단말기의 개선 또한 항공 플랫폼에의 통합을 용이하게 하고 있습니다.

"용도별로는 네트워크 백본 및 중계 통신 부문이 예측 기간 동안 가장 우세한 위치를 차지할 것으로 전망"
용도별로는 네트워크 백본 및 중계 통신 부문이 우주 기반 광학 메쉬 네트워크로의 전환에 힘입어 예측 기간 동안 가장 우세한 위치를 차지할 것으로 전망됩니다. 이러한 네트워크는 멀티 기가비트급 위성 간 데이터 라우팅을 지원하고 지상국 의존도를 낮추며 지속적인 글로벌 커버리지를 가능하게 합니다. 이는 광대역 위성군 및 시간 민감형 국방 통신에 매우 중요합니다.
"예측 기간 동안 아시아태평양이 가장 빠르게 성장하는 시장이 될 전망"
아시아태평양 지역은 중국, 인도, 일본, 한국의 위성 군집 확장 및 국가 우주 프로그램에 힘입어 예측 기간 동안 가장 빠르게 성장하는 시장이 될 것으로 예상됩니다. 안전한 위성 통신 및 지역 광학 단말기 개발에 대한 정부 지출 증가가 해당 지역 전반에 걸친 채택을 가속화하고 있습니다.
본 보고서에서는 세계의 광(레이저) 위성통신 시장을 조사했으며, 시장 개요, 시장 성장에 대한 각종 영향요인 분석, 기술 및 특허 동향, 법규제 환경, 사례 연구, 시장 규모 추이와 예측, 각종 구분 및 지역/주요 국가별 상세 분석, 경쟁 구도, 주요 기업 프로파일 등을 정리했습니다.
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
제2장 주요 요약
제3장 중요 인사이트
제4장 시장 개요
- 시장 역학
- 성장 촉진요인
- 억제요인
- 기회
- 과제
- 시장 시나리오 분석
- 미충족 요구와 화이트 스페이스
- 관련 시장 및 이업종과의 분야 횡단적 기회
- Tier 1/2/3 기업의 전략적 움직임
제5장 업계 동향
- 생태계 분석
- 밸류체인 분석
- 무역 분석
- 관세 데이터
- 사례 연구 분석
- 주요 회의 및 이벤트
- 투자 및 자금조달 시나리오
- 고객사업에 영향을 주는 동향/혼란
- 가격 분석
- 거시경제 전망
제6장 고객 환경 및 구매행동
- 의사결정 공정
- 이해관계자와 구매평가기준
- 채택 장벽과 내부 과제
- 다양한 최종 사용자 산업의 미충족 요구
- 시장 수익성
제7장 기술의 진보, AI에 의한 영향, 특허, 혁신, 장래의 응용
- 주요 기술
- 포인팅, 획득 및 추적(PAT) 시스템
- 자유 공간 광통신(FSO) 통신 단말기
- 고속 변조 및 인코딩(코히런트 모뎀)
- WDM/DWDM 광다중화
- 보완적 기술
- 하이브리드 RF-광 네트워크 아키텍처
- AI 구동형 네트워크 오케스트레이션과 날씨를 고려한 라우팅
- 우주광 스위칭 및 라우팅(광 메쉬 네트워크)
- 양자 통신 및 QKD 통합
- 기술 로드맵
- 특허 분석
- 미래의 응용
- AI/생성형 AI의 영향
- 성공 사례와 실세계에의 응용
제8장 지속가능성과 규제상황
- 지역 규제 및 규정 준수
- 지속가능성에 대한 노력
- 인증, 라벨, 환경 기준
제9장 광위성 통신 시장 : 플랫폼별
- 데이터 링크 유형별 광 위성 통신의 분류
- 우주-우주
- 우주-지상
- 우주-공중
- 위성 통신 단말
- 소형 위성
- 중형 위성
- 대형 위성
- 지상국 터미널
- 고정형
- 휴대용
- 공중 터미널
- 군용기
- 무인 항공기(UAV)
제10장 광위성 통신 시장 : 용도별
- 네트워크 백본 및 중계 통신
- 지구관측(EO) 및 원격 감지
- 과학연구 및 탐사
제11장 광위성 통신 시장 : 컴포넌트별
- 광학 프론트 엔드
- 송신 모듈
- 수신 모듈
- 포인팅, 획득 및 추적(PAT) 모듈
- 베이스밴드 모뎀 및 처리 일렉트로닉스
- 기타
제12장 광위성 통신 시장 : 레이저 유형별
- 동작 파장별 광 위성 통신의 분류
- C 밴드/1550 NM 밴드
- 근적외선 1064 NM 밴드
- 보조 비콘 파장(850-1000 nm)
- 깊은 우주 최적화 하이브리드 파장(1550/1064 NM)
- 반도체 다이오드 레이저
- 파이버 레이저
- 고체 레이저
- 기타
제13장 광위성 통신 시장 : 데이터 속도 등급별
- 저속/전술적(2.5GBPS 이하)
- 고속(2.5-10GBPS)
- 초고속/차세대(10GBPS 초과)
제14장 광위성 통신 시장 : 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 유럽
- 영국
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 스페인
- 이탈리아
- 아시아태평양
- 일본
- 인도
- 중국
- 호주
- 중동
- GCC 국가
- 기타
- 세계 기타 지역
- 라틴아메리카
- 아프리카
제15장 경쟁 구도
- 주요 진입기업의 전략, 강점
- 수익 분석
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 평가 매트릭스 : 주요 기업
- 기업평가 매트릭스 : 스타트업, 중소기업
- 기업평가와 재무재표
- 브랜드/제품 비교
- 경쟁 시나리오
제16장 기업 프로파일
- 주요 기업
- SPACEX
- MYNARIC AG
- BRIDGECOMM INC.
- THALES ALENIA SPACE
- TESAT-SPACECOM GMBH & CO. KG
- BAE SYSTEMS
- HONEYWELL INTERNATIONAL INC.
- MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
- SONY SPACE COMMUNICATIONS
- AAC CLYDE SPACE
- NEC SPACE TECHNOLOGIES
- SKYLOOM GLOBAL
- GENERAL ATOMICS
- SPACE MICRO
- NORTHROP GRUMMAN
- SAFRAN
- 기타 기업
- WARPSPACE
- SITAEL
- ASTROGATE LABS
- ARCHANGEL LIGHTWORKS
- TRANSCELESTIAL
- CAILABS
- OLEDCOMM
- HENSOLDT
- ASTROLIGHT
- QINETIQ
제17장 조사 방법
제18장 부록
HBR 26.02.19The optical (laser) satellite communication market is projected to grow from USD 0.62 billion in 2025 to USD 1.56 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 20.4%, driven by the increasing adoption of laser intersatellite links and rising demand for high-capacity, secure data transmission across LEO and multi-orbit satellite networks.
| Scope of the Report | |
|---|---|
| Years Considered for the Study | 2021-2030 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2030 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Billion) |
| Segments | By Type, Data Range, Application and Region |
| Regions covered | North America, Europe, APAC, RoW |
"By platform, the airborne segment is projected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period."
By platform, the airborne segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period, driven by rising demand for high-throughput, low-probability-of-intercept communications on ISR aircraft, UAVs, and high-altitude platforms. Optical links enable secure air-to-satellite and air-to-air data transfer for real-time intelligence and sensor data sharing. Improvements in compact, vibration-tolerant laser terminals are also facilitating easier integration on airborne platforms.
"By application, the network backbone & relay communications segment is projected to be the most dominant during the forecast period."
By application, the Network Backbone and Relay Communications segment is projected to be the most dominant during the forecast period, driven by the shift toward space-based optical mesh networks. These networks support multi-Gbps inter-satellite data routing, reduce reliance on ground stations, and enable persistent global coverage. This is critical for broadband constellations and time-sensitive defense communications.
"The Asia Pacific is projected to be the fastest growing market during the forecast period."
The Asia Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing market during the forecast period, supported by expanding satellite constellations and national space programs in China, India, Japan, and South Korea. Increased government spending on secure satellite communications and local optical terminal development is accelerating adoption across the region.
The breakdown of profiles for primary participants in the Optical (laser) Satellite Communication Market is provided below:
- By Company Type: Tier 1 - 40%, Tier 2 - 30%, and Tier 3 - 30%
- By Designation: Directors - 20%, Managers - 10%, and Others - 70%
- By Region: North America - 40%, Europe - 20%, Asia Pacific - 20%, Middle East - 10% Rest of the World (RoW) - 10%
Research Coverage:
This market study covers the optical (laser) satellite communications market across various segments and subsegments. It aims to estimate the market size and growth potential across different regions. This study also includes an in-depth competitive analysis of the key players in the market, their company profiles, key observations on their products and business offerings, recent developments, and key market strategies they adopted.
Reasons to buy this report:
The report will provide market leaders and new entrants with the most accurate available estimates of revenue for the overall optical (laser) satellite communication market. It will also help stakeholders understand the competitive landscape and gain insights to position their businesses more effectively and plan suitable go-to-market strategies. The report will also help stakeholders understand the market pulse and provide information on key market drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities.
The report provides insights into the following pointers:
- Market Drivers (Expansion of LEO Broadband Constellations Requiring High-Capacity Optical Inter-Satellite Backbones, Growth in Earth Observation Data Volumes Requiring High-Speed Optical Downlinks), Restraints (Atmospheric Turbulence and Cloud Cover Affecting Space-to-Ground Optical Link Availability, Higher Optical Ground Station Density Increasing Capital and Operational Complexity), Opportunities (Emergence of Space-to-Air Optical Links Enabling Airborne Communication Nodes, RF Spectrum Congestion Supporting Adoption of Spectrum-Independent Optical Transport Links), Challenges Technology Readiness, Production Scale-Up, and Qualification Timelines Across Constellations, Pointing, Acquisition, and Tracking Precision Requirements for Mobile and Multi-Orbit Architectures.
- Market Penetration: Comprehensive information on Optical (laser) Satellite Communication offered by the top players in the market
- Product Development/Innovation: Detailed insights on upcoming technologies, research & development activities, and product launches in the Optical (laser) Satellite Communication Market
- Market Development: Comprehensive information about lucrative markets across varied regions
- Market Diversification: Exhaustive information about new products, untapped geographies, recent developments, and investments in the Optical (laser) Satellite Communication Market
- Competitive Assessment: In-depth assessment of market share, growth strategies, products, and manufacturing capabilities of leading players in the Optical (laser) Satellite Communication Market
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES
- 1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
- 1.3 STUDY SCOPE
- 1.3.1 MARKETS COVERED AND REGIONAL SCOPE
- 1.3.2 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- 1.3.3 YEARS CONSIDERED
- 1.4 CURRENCY CONSIDERED
- 1.5 STAKEHOLDERS
- 1.6 SUMMARY OF CHANGES
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- 2.1 KEY INSIGHTS AND MARKET HIGHLIGHTS
- 2.2 KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS: MAPPING OF STRATEGIC DEVELOPMENTS
- 2.3 HIGH-GROWTH SEGMENTS
- 2.4 REGIONAL SNAPSHOT: MARKET SIZE, GROWTH RATE, AND FORECAST
- 2.5 BILL OF MATERIALS
- 2.6 TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP
- 2.7 BUSINESS MODELS
- 2.7.1 SPACE LASER TERMINAL OEM SALES FOR LEO AND DEFENSE CONSTELLATIONS
- 2.7.2 VERTICALLY INTEGRATED OPTICAL MESH NETWORKS BY CONSTELLATION OPERATORS
- 2.7.3 DATA RELAY AS A SERVICE USING OPTICAL LINKS
- 2.7.4 OPTICAL GROUND STATION NETWORK AND MANAGED SERVICES (OGSAAS)
3 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
- 3.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION MARKET
- 3.2 OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION MARKET, BY APPLICATION
- 3.3 OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION MARKET, BY LASER TYPE
- 3.4 OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION MARKET, BY COMPONENT
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 INTRODUCTION
- 4.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.2.1 DRIVERS
- 4.2.1.1 Expansion of LEO broadband constellations requiring high-capacity optical inter-satellite backbones
- 4.2.1.2 Growth in Earth observation (EO) data volumes requiring high-speed optical downlinks
- 4.2.1.3 Demand for resilient, low-intercept space networking in defense industry
- 4.2.1.4 Defense-led space programs accelerating adoption and industrialization of optical satellite communication
- 4.2.2 RESTRAINTS
- 4.2.2.1 Atmospheric turbulence and cloud cover affecting space-to-ground optical link availability
- 4.2.2.2 Higher optical ground station density increasing capital and operational complexity
- 4.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
- 4.2.3.1 Emergence of space-to-air optical links enabling airborne communication nodes
- 4.2.3.2 RF spectrum congestion supporting adoption of spectrum-independent optical transport links
- 4.2.4 CHALLENGES
- 4.2.4.1 Technology readiness, production scale-up, and qualification timelines across constellations
- 4.2.4.2 Pointing, acquisition, and tracking precision requirements for mobile and multi-orbit architectures
- 4.2.1 DRIVERS
- 4.3 MARKET SCENARIO ANALYSIS
- 4.3.1 MARKET PERSPECTIVE OF OPTICAL SATELLITE TERMINAL COUNT IN DIFFERENT SCENARIOS
- 4.4 UNMET NEEDS AND WHITE SPACES
- 4.4.1 LACK OF GLOBALLY STANDARDIZED OPTICAL COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS
- 4.4.2 LIMITED AVAILABILITY OF AFFORDABLE OPTICAL GROUND STATION NETWORKS
- 4.4.3 NEED FOR COMPACT AND LOW-POWER TERMINALS WITH PRECISION POINTING
- 4.4.4 WEATHER-RELATED AVAILABILITY LIMITATIONS
- 4.4.5 GAPS IN END-TO-END INFORMATION SECURITY FOR OPTICAL NETWORKS
- 4.4.6 ABSENCE OF MULTI-ORBIT OPTICAL RELAY INFRASTRUCTURE
- 4.4.7 LIMITED INTEGRATION BETWEEN OPTICAL COMMUNICATION AND ONBOARD PROCESSING
- 4.5 INTERCONNECTED MARKETS AND CROSS-SECTOR OPPORTUNITIES
- 4.5.1 SATELLITE MANUFACTURING & OISL-ENABLED CONSTELLATIONS
- 4.5.2 SATELLITE GROUND STATIONS
- 4.5.3 PHOTONICS, SEMICONDUCTORS, AND INTEGRATED OPTICAL COMPONENTS
- 4.5.4 DEFENSE ISR PLATFORMS - AIRBORNE AND NAVAL
- 4.6 STRATEGIC MOVES BY TIER 1/2/3 PLAYERS
5 INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 5.1 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
- 5.1.1 PROMINENT COMPANIES
- 5.1.2 PRIVATE AND SMALL ENTERPRISES
- 5.1.3 END USERS
- 5.2 VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 5.2.1 CONCEPT & RESEARCH
- 5.2.2 COMPONENT & MATERIAL DEVELOPMENT
- 5.2.3 OPTICAL TERMINAL MANUFACTURING
- 5.2.4 SYSTEM INTEGRATION & VALIDATION
- 5.2.5 POST-DEPLOYMENT SERVICE
- 5.3 TRADE ANALYSIS
- 5.3.1 IMPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 880260)
- 5.3.2 EXPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 880260)
- 5.4 TARIFF DATA
- 5.5 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
- 5.5.1 SPACE DEVELOPMENT AGENCY: TRANCHE 1 OPTICAL ISL NETWORK FOR DEFENSE COMMUNICATIONS
- 5.5.2 SPACEX STARLINK GEN2: OPTICAL CROSS-LINK NETWORK FOR GLOBAL BROADBAND
- 5.5.3 NASA TBIRD: TERABIT-CLASS LASER DOWNLINK DEMONSTRATION
- 5.5.4 ESA HYDRON: HIGH-THROUGHPUT OPTICAL NETWORK FOR EUROPEAN SATCOM
- 5.6 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS (2026-2027)
- 5.7 INVESTMENT AND FUNDING SCENARIO
- 5.8 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
- 5.9 PRICING ANALYSIS
- 5.9.1 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE, BY REGION, 2021-2024
- 5.9.2 INDICATIVE PRICING ANALYSIS, BY PLATFORM, 2024
- 5.10 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 5.10.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.10.2 GDP TRENDS AND FORECAST
- 5.10.3 TRENDS IN SPACE INDUSTRY
6 CUSTOMER LANDSCAPE AND BUYER BEHAVIOR
- 6.1 INTRODUCTION
- 6.2 DECISION-MAKING PROCESS
- 6.3 BUYER STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING EVALUATION CRITERIA
- 6.3.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS
- 6.3.2 BUYING EVALUATION CRITERIA
- 6.4 ADOPTION BARRIERS AND INTERNAL CHALLENGES
- 6.5 UNMET NEEDS FROM VARIOUS END-USE INDUSTRIES
- 6.6 MARKET PROFITABILITY
- 6.6.1 REVENUE POTENTIAL
- 6.6.2 COST DYNAMICS
- 6.6.3 MARGIN OPPORTUNITIES, BY APPLICATION
7 TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCEMENTS, AI-DRIVEN IMPACT, PATENTS, INNOVATIONS, AND FUTURE APPLICATIONS
- 7.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 7.1.1 POINTING, ACQUISITION, AND TRACKING (PAT) SYSTEMS
- 7.1.2 FREE-SPACE OPTICAL (FSO) COMMUNICATION TERMINALS
- 7.1.3 HIGH-SPEED MODULATION & CODING (COHERENT MODEMS)
- 7.1.4 WDM/ DWDM OPTICAL MULTIPLEXING
- 7.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES
- 7.2.1 HYBRID RF-OPTICAL NETWORK ARCHITECTURES
- 7.2.2 AI-DRIVEN NETWORK ORCHESTRATION & WEATHER-AWARE ROUTING
- 7.2.3 SPACE OPTICAL SWITCHING & ROUTING (OPTICAL MESH NETWORKING)
- 7.2.4 QUANTUM COMMUNICATION & QKD INTEGRATION
- 7.3 TECHNOLOGY ROADMAP
- 7.4 PATENT ANALYSIS
- 7.5 FUTURE APPLICATIONS
- 7.6 IMPACT OF AI/GENAI
- 7.6.1 TOP USE CASES AND MARKET POTENTIAL
- 7.6.2 CASE STUDIES OF AI IMPLEMENTATION
- 7.6.3 INTERCONNECTED ECOSYSTEM AND IMPACT ON MARKET PLAYERS
- 7.6.4 CLIENTS' READINESS TO ADOPT AI/GENAI
- 7.7 SUCCESS STORIES AND REAL-WORLD APPLICATIONS
- 7.7.1 TESAT-SPACECOM: MULTI-ORBIT LASER DATA RELAY INTEGRATION
- 7.7.2 MYNARIC AG: INDUSTRIAL-SCALE OPTICAL CROSSLINKS FOR PROLIFERATED LEO CONSTELLATIONS
- 7.7.3 SPACEX: OPTICAL INTER-SATELLITE LINKS ENABLING SPACE-BASED NETWORK BACKBONES
8 SUSTAINABILITY AND REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 8.1 REGIONAL REGULATIONS AND COMPLIANCE
- 8.1.1 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- 8.1.2 INDUSTRY STANDARDS
- 8.2 SUSTAINABILITY INITIATIVES
- 8.2.1 CARBON IMPACT REDUCTION
- 8.2.2 ECO-APPLICATIONS
- 8.3 CERTIFICATIONS, LABELING, AND ECO-STANDARDS
9 OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION MARKET, BY PLATFORM (MARKET SIZE & FORECAST TO 2030 - IN VALUE, USD MILLION)
- 9.1 INTRODUCTION
- 9.2 CLASSIFICATION OF OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION BY DATA LINK TYPE
- 9.2.1 SPACE-TO-SPACE
- 9.2.2 SPACE-TO-GROUND
- 9.2.3 SPACE-TO-AIR
- 9.3 SATELLITE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL
- 9.3.1 RAPID CONSTELLATION EXPANSION TO DRIVE NEED FOR MODULAR OPTICAL TERMINALS
- 9.3.2 USE CASE: SDA'S TRANCHE 1 DEPLOYMENT OF MYNARIC (GERMANY) CONDOR TERMINALS FOR HIGH-CAPACITY LEO TRANSPORT
- 9.3.3 SMALL SATELLITE
- 9.3.4 MEDIUM SATELLITE
- 9.3.5 LARGE SATELLITE
- 9.4 GROUND STATION TERMINAL
- 9.4.1 RISE OF HIGH-RATE OPTICAL DOWNLINK MISSIONS TO DRIVE SEGMENTAL GROWTH
- 9.4.2 USE CASE: SA'S HYDRON OPTICAL GROUND STATIONS ENABLING MULTI-GBPS DOWNLINKS FOR DEMONSTRATION MISSIONS
- 9.4.3 FIXED
- 9.4.4 PORTABLE 111 9.5 AIRBORNE TERMINAL
- 9.5.1 NEED FOR SECURE, HIGH-THROUGHPUT AIRBORNE CONNECTIVITY TO DRIVE ADOPTION OF OPTICAL TERMINALS
- 9.5.2 USE CASE: DARPA BLACK DIAMOND DEMONSTRATION OF AIRBORNE OPTICAL LINKS FOR ISR PLATFORMS
- 9.5.3 MILITARY AIRCRAFT
- 9.5.4 UNMANNED AERIAL VEHICLE (UAV)
10 OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION MARKET, BY APPLICATION (MARKET SIZE & FORECAST TO 2030 - IN VALUE, USD MILLION)
- 10.1 INTRODUCTION
- 10.2 NETWORK BACKBONE & RELAY COMMUNICATIONS
- 10.2.1 RISING INTER-SATELLITE DATA TRAFFIC TO DRIVE SHIFT TOWARD OPTICAL BACKHAUL FOR BACKBONE AND RELAY COMMUNICATIONS
- 10.2.2 USE CASE: AMAZON KUIPER (US) LASER LINK ARCHITECTURE ENABLING HIGH-CAPACITY SPACE-BASED BACKHAUL
- 10.3 EARTH OBSERVATION (EO) & REMOTE SENSING
- 10.3.1 HIGH-RESOLUTION EO MISSIONS TO ACCELERATE ADOPTION OF OPTICAL LINKS FOR RAPID DATA OFFLOAD AND REAL-TIME DISSEMINATION
- 10.3.2 USE CASE: ESA'S EDRS OPTICAL RELAY SYSTEM ENABLING NEAR-REAL-TIME EO DATA TRANSFER FOR SENTINEL MISSIONS
- 10.4 SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH & EXPLORATION
- 10.4.1 DEEP SPACE AND SCIENTIFIC MISSIONS ADOPT OPTICAL LINKS TO OVERCOME RF LIMITATIONS IN LONG-DISTANCE, DATA-HEAVY COMMUNICATION
- 10.4.2 USE CASE: JAXA (JAPAN) OPTICAL TERMINAL DEMONSTRATIONS FOR LUNAR SURFACE-TO-ORBIT COMMUNICATION UNDER LUPEX
11 OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION MARKET, BY COMPONENT (MARKET SIZE & FORECAST TO 2030 - IN VALUE, USD MILLION)
- 11.1 INTRODUCTION
- 11.2 OPTICAL FRONT-END
- 11.2.1 PRECISION OPTICAL FRONT-ENDS TO GAIN TRACTION AS CONSTELLATIONS DEMAND HIGHER LINK QUALITY AND TIGHTER POINTING TOLERANCES
- 11.3 TRANSMIT MODULE
- 11.3.1 HIGH-EFFICIENCY LASER TRANSMITTERS TO SCALE RAPIDLY AS SATELLITES MIGRATE TO MULTI-GIGABIT OPTICAL UPLINKS
- 11.4 RECEIVE MODULE
- 11.4.1 ADVANCED PHOTONIC RECEIVERS TO GAIN MOMENTUM AS NETWORKS PUSH FOR HIGHER SENSITIVITY AND LOWER SIGNAL LOSS
- 11.5 POINTING, ACQUISITION, AND TRACKING (PAT) MODULE
- 11.5.1 SOPHISTICATED PAT SYSTEMS TO SURGE IN DEMAND AS MULTI-ORBIT CONSTELLATIONS REQUIRE ULTRA-STABLE BEAM ALIGNMENT
- 11.6 BASEBAND MODEM & PROCESSING ELECTRONICS
- 11.6.1 ADVANCED MODEM ELECTRONICS TO GROW IN DEMAND AS HIGHER-ORDER MODULATION AND ADAPTIVE CODING ENTER MAINSTREAM OPTICAL SATCOM
- 11.7 OTHERS
12 OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION MARKET, BY LASER TYPE (MARKET SIZE & FORECAST TO 2030 - IN VALUE, USD MILLION)
- 12.1 INTRODUCTION
- 12.2 CLASSIFICATION OF OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION BY OPERATING WAVELENGTH
- 12.2.1 C-BAND/1550 NM BAND
- 12.2.2 NEAR-IR 1064 NM BAND
- 12.2.3 AUXILIARY BEACON WAVELENGTHS (850-1000 NM)
- 12.2.4 DEEP SPACE-OPTIMIZED HYBRID WAVELENGTHS (1550/1064 NM)
- 12.3 SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE LASER
- 12.3.1 DEMAND FOR COMPACT, LOW-SWAP TERMINALS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 12.3.2 USE CASE: HIGH-VOLUME LEO CONSTELLATION DEPLOYMENTS ENABLED BY LOW-SWAP SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE LASERS
- 12.3.2.1 Indium phosphide (InP) Laser
- 12.3.2.2 Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) Laser
- 12.3.2.3 Antimonide Laser
- 12.4 FIBER LASER
- 12.4.1 GROWING NEED FOR HIGHER POWER AND SUPERIOR BEAM QUALITY TO DRIVE SEGMENTAL GROWTH
- 12.4.2 USE CASE: LONG-DISTANCE OPTICAL BACKHAUL IMPROVED USING HIGH-BEAM-QUALITY FIBER LASERS
- 12.4.2.1 YAG Laser
- 12.4.2.2 YVO4 and DPSSL Variants
- 12.5 SOLID-STATE LASER
- 12.5.1 DEEP SPACE AND HIGH-ENERGY MISSIONS TO DRIVE DEMAND FOR SOLID-STATE LASERS OFFERING LONG-TERM STABILITY AND HIGH RELIABILITY
- 12.5.2 USE CASE: DEEP SPACE TELEMETRY CHALLENGES ADDRESSED WITH HIGH-STABILITY SOLID-STATE LASERS
- 12.5.2.1 Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser
- 12.5.2.2 Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Laser
- 12.6 OTHER LASERS
13 OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION MARKET, BY DATA RATE CLASS
- 13.1 INTRODUCTION
- 13.2 LOW/TACTICAL (<= 2.5 GBPS)
- 13.2.1 USE CASE: TACTICAL RECONNAISSANCE DATA EXFILTRATION ENHANCED USING LOW-RATE OPTICAL TERMINALS DURING ESA OPS-SAT EXPERIMENTS
- 13.3 HIGH (2.5-10 GBPS)
- 13.3.1 USE CASE: AIRBUS (EUROPE) SPACE DATA HIGHWAY RELAYING MULTI-GIGABIT EO PAYLOAD DATA USING 1.8 GBPS LASER LINKS
- 13.4 ULTRA-HIGH/NEXT-GEN (> 10 GBPS)
- 13.4.1 USE CASE: MIT LINCOLN LABORATORY (US) TERA-BIT-CLASS FREE-SPACE OPTICAL LINK DEMONSTRATED BETWEEN AIRBORNE AND GROUND TERMINALS
14 OPTICAL SATELLITE COMMUNICATION MARKET, BY REGION
- 14.1 INTRODUCTION
- 14.2 NORTH AMERICA
- 14.2.1 US
- 14.2.1.1 Rapid commercial constellation expansion to drive growth
- 14.2.2 CANADA
- 14.2.2.1 National space modernization and emerging LEO programs to drive market
- 14.2.1 US
- 14.3 EUROPE
- 14.3.1 UK
- 14.3.1.1 Rising demand for secure, high-capacity data transmission across defense, government, and commercial space programs to drive market
- 14.3.2 GERMANY
- 14.3.2.1 Increasing demand for data from Earth observation and climate monitoring missions to drive market
- 14.3.3 FRANCE
- 14.3.3.1 Growing demand for Earth observation, climate monitoring, and scientific satellites to drive market
- 14.3.4 SPAIN
- 14.3.4.1 Strong institutional space programs and ground infrastructure advantages to drive market
- 14.3.5 ITALY
- 14.3.5.1 Rising demand for secure, high-capacity communication technologies to drive market
- 14.3.1 UK
- 14.4 ASIA PACIFIC
- 14.4.1 JAPAN
- 14.4.1.1 Advanced space technology programs and defense modernization to drive market
- 14.4.2 INDIA
- 14.4.2.1 Next-generation Earth observation and growing broadband connectivity needs to drive market
- 14.4.3 CHINA
- 14.4.3.1 Large-scale space modernization and sovereign communication programs to drive market
- 14.4.4 AUSTRALIA
- 14.4.4.1 Increasing collaboration with global constellation operators and allied space agencies to drive market
- 14.4.1 JAPAN
- 14.5 MIDDLE EAST
- 14.5.1 GCC COUNTRIES
- 14.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 14.5.1.1.1 Government's space investments and defense demand for secure, high-speed connectivity to drive market
- 14.5.1.2 UAE
- 14.5.1.2.1 Increasing demand for rapid data transfer between satellites and ground stations to drive market
- 14.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 14.5.2 REST OF MIDDLE EAST
- 14.5.1 GCC COUNTRIES
- 14.6 REST OF THE WORLD
- 14.6.1 LATIN AMERICA
- 14.6.1.1 Connectivity gaps and expanding space programs to support laser SATCOM adoption
- 14.6.2 AFRICA
- 14.6.2.1 Digital connectivity demand and government push for modern satellite infrastructure to drive market
- 14.6.1 LATIN AMERICA
15 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 15.1 INTRODUCTION
- 15.2 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN, 2021-2025
- 15.3 REVENUE ANALYSIS, 2020-2024
- 15.4 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2024
- 15.5 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 15.5.1 STARS
- 15.5.2 EMERGING LEADERS
- 15.5.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
- 15.5.4 PARTICIPANTS
- 15.5.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 15.5.5.1 Company footprint
- 15.5.5.2 Region footprint
- 15.5.5.3 Platform footprint
- 15.5.5.4 Application footprint
- 15.5.5.5 Component footprint
- 15.6 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 15.6.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
- 15.6.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
- 15.6.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
- 15.6.4 STARTING BLOCKS
- 15.6.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING: STARTUPS/SMES
- 15.6.5.1 List of startups/SMEs
- 15.6.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of startups/SMEs
- 15.7 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS
- 15.7.1 FINANCIAL METRICS
- 15.8 BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- 15.9 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
- 15.9.1 PRODUCT LAUNCHES/DEVELOPMENTS
- 15.9.2 DEALS
- 15.9.3 OTHERS
16 COMPANY PROFILES
- 16.1 KEY PLAYERS
- 16.1.1 SPACEX
- 16.1.1.1 Business overview
- 16.1.1.2 Products offered
- 16.1.1.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.1.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.1.3.2 Other developments
- 16.1.1.4 MnM view
- 16.1.1.4.1 Right to win
- 16.1.1.4.2 Strategic choices
- 16.1.1.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 16.1.2 MYNARIC AG
- 16.1.2.1 Business overview
- 16.1.2.2 Products offered
- 16.1.2.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.2.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.2.3.2 Others
- 16.1.2.4 MnM view
- 16.1.2.4.1 Right to win
- 16.1.2.4.2 Strategic choices
- 16.1.2.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 16.1.3 BRIDGECOMM INC.
- 16.1.3.1 Business overview
- 16.1.3.2 Products offered
- 16.1.3.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.3.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.3.3.2 Other developments
- 16.1.3.4 MnM view
- 16.1.3.4.1 Right to win
- 16.1.3.4.2 Strategic choices
- 16.1.3.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 16.1.4 THALES ALENIA SPACE
- 16.1.4.1 Business overview
- 16.1.4.2 Products offered
- 16.1.4.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.4.3.1 Product Launches
- 16.1.4.3.2 Deals
- 16.1.4.3.3 Other developments
- 16.1.4.4 MnM view
- 16.1.4.4.1 Right to win
- 16.1.4.4.2 Strategic choices
- 16.1.4.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 16.1.5 TESAT-SPACECOM GMBH & CO. KG
- 16.1.5.1 Business overview
- 16.1.5.2 Product offered
- 16.1.5.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.5.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.5.3.2 Other developments
- 16.1.5.4 MnM view
- 16.1.5.4.1 Right to win
- 16.1.5.4.2 Strategic choices
- 16.1.5.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 16.1.6 BAE SYSTEMS
- 16.1.6.1 Business overview
- 16.1.6.2 Products offered
- 16.1.6.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.6.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.7 HONEYWELL INTERNATIONAL INC.
- 16.1.7.1 Business overview
- 16.1.7.2 Products offered
- 16.1.7.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.7.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.8 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
- 16.1.8.1 Business overview
- 16.1.8.2 Products offered
- 16.1.8.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.8.3.1 Product launches/developments
- 16.1.8.3.2 Other developments
- 16.1.9 SONY SPACE COMMUNICATIONS
- 16.1.9.1 Business overview
- 16.1.9.2 Products offered
- 16.1.9.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.9.3.1 Product developments
- 16.1.9.3.2 Deals
- 16.1.10 AAC CLYDE SPACE
- 16.1.10.1 Business overview
- 16.1.10.2 Products offered
- 16.1.10.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.10.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.10.3.2 Other developments
- 16.1.11 NEC SPACE TECHNOLOGIES
- 16.1.11.1 Business overview
- 16.1.11.2 Products offered
- 16.1.11.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.11.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.11.3.2 Other developments
- 16.1.12 SKYLOOM GLOBAL
- 16.1.12.1 Business overview
- 16.1.12.2 Products offered
- 16.1.12.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.12.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.13 GENERAL ATOMICS
- 16.1.13.1 Business overview
- 16.1.13.2 Products offered
- 16.1.13.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.13.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.13.3.2 Other developments
- 16.1.14 SPACE MICRO
- 16.1.14.1 Business overview
- 16.1.14.2 Products offered
- 16.1.14.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.14.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.14.3.2 Other developments
- 16.1.15 NORTHROP GRUMMAN
- 16.1.15.1 Business overview
- 16.1.15.2 Products offered
- 16.1.15.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.15.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.15.3.2 Other developments
- 16.1.16 SAFRAN
- 16.1.16.1 Business overview
- 16.1.16.2 Products offered
- 16.1.16.3 Recent developments
- 16.1.16.3.1 Deals
- 16.1.16.3.2 Other developments
- 16.1.1 SPACEX
- 16.2 OTHER PLAYERS
- 16.2.1 WARPSPACE
- 16.2.2 SITAEL
- 16.2.3 ASTROGATE LABS
- 16.2.4 ARCHANGEL LIGHTWORKS
- 16.2.5 TRANSCELESTIAL
- 16.2.6 CAILABS
- 16.2.7 OLEDCOMM
- 16.2.8 HENSOLDT
- 16.2.9 ASTROLIGHT
- 16.2.10 QINETIQ
17 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 17.1 RESEARCH DATA
- 17.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 17.1.1.1 Key data from secondary sources
- 17.1.2 PRIMARY DATA
- 17.1.2.1 Primary sources
- 17.1.2.2 Key data from primary sources
- 17.1.3 BREAKDOWN OF PRIMARY INTERVIEWS
- 17.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 17.2 FACTOR ANALYSIS
- 17.2.1 INTRODUCTION
- 17.2.2 DEMAND-SIDE INDICATORS
- 17.2.3 SUPPLY-SIDE INDICATORS
- 17.3 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
- 17.3.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 17.3.1.1 Market size estimation methodology (demand side)
- 17.3.1.2 Market size illustration - US ground station optical satellite communication market size
- 17.3.2 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- 17.3.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 17.4 DATA TRIANGULATION
- 17.5 RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS
- 17.6 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS
- 17.7 RISK ASSESSMENT
18 APPENDIX
- 18.1 LONG LIST OF COMPANIES
- 18.2 DISCUSSION GUIDE
- 18.3 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS' SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL
- 18.4 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS
- 18.5 RELATED REPORTS
- 18.6 AUTHOR DETAILS















