
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1440361
미세잔존질환(MRD) : 세계 시장 점유율 분석, 업계 동향 통계, 성장 예측(2024-2029년)Global Minimal Residual Disease - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
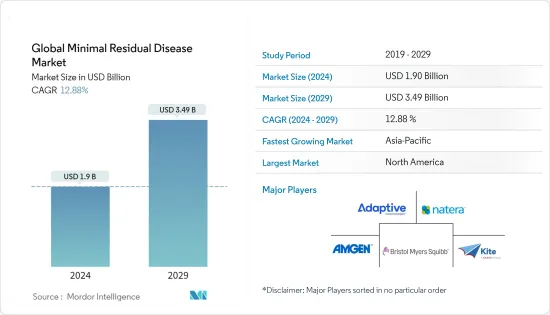
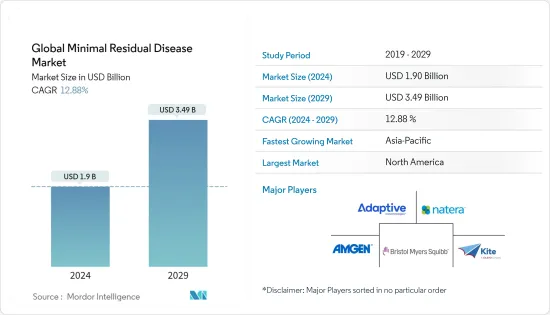
세계의 미세잔존 질환 시장 규모는 2024년 19억 달러로 추정되고, 2029년까지 34억 9,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 예측기간(2024-2029년) 동안 12.88%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 성장할 전망입니다.
COVID-19 감염의 팬데믹은 세계 건강 관리 시스템에 영향을 미치며 많은 건강 관리 시설에서 정상적인 진료가 중단되어 취약한 암 환자가 심각한 위험에 노출되었습니다. 신형 코로나 바이러스 감염(COVID-19)의 팬데믹이 시작된 이래로 신형 코로나 바이러스 감염 환자의 입원을 늘리고 입원하는 비신형 코로나 바이러스 감염 환자의 수를 줄이기 위한 조치가 취해지고 치료 연기로 이어집니다. 2020년 9월 “암 치료에 대한 COVID-19 감염병 팬데믹의 영향 : 세계적인 공동 연구”라는 제목의 연구에서는 2020년 4월 21일부터 5월 8일까지 6대륙 54개국의 합계 356개의 센터가 참여했다고 보고했습니다. 이 센터는 716,979명에게 서비스를 제공합니다. 매년 새롭게 암 환자가 발생합니다. 대부분(88.2%)이 팬데믹 중에 치료를 제공할 때 과제에 직면하고 있다고 보고했습니다. 55.34%가 선제 전략의 일환으로 서비스를 줄였으나, 그 밖의 일반적인 이유로는 시스템 과부하(19.94%), 개인보호구(PPE) 부족(19.10%), 직원 부족(17.98%), 의약품에 대한 액세스 제한(9.83%) 등을 들 수 있습니다. “암 환자에 대한 COVID-19의 임상적 영향은 무엇인가”라는 제목의 기사에 따르면, 2020년 6월, 암 환자의 COVID-19증, 특히 이 감염증의 심각한 영향에 대한 취약성이 높아졌습니다 따라서 일부 환자는 잠재적인 감염자와의 접촉을 줄이기 위해 항암제 치료를 늦추거나 일시정지하게 되었습니다. 팬데믹의 초기 단계에서는 시장에 악영향을 미쳤습니다. 이러한 연구는 암 치료가 심각한 영향을 받고 이후 시장 성장에 영향을 미친 것을 보여줍니다. 따라서 COVID-19 감염의 팬데믹은 시장 성장에 전반적으로 악영향을 미쳤습니다.
미세잔존질환 시장 성장을 가속하는 요인은 세계에서 다양한 유형의 암 유병률이 상승하고 있음과 발암물질의 존재를 확인하는 사람들의 의식이 높아지고 있습니다. 지속적인 암 치료를 받고 있는 환자는 미세잔존질환 시장을 전진시키는 가장 중요한 요소가 될 것으로 기대되고 있습니다. 또한, 치료를 위한 개인화된 의약품의 채용 증가 및 연구개발 활동 증가가 시장 성장에 기여하고 있습니다.
다양한 암으로 고통받는 사람의 수가 증가하는 것은 미세잔존질환 시장 성장의 중요한 촉진요인입니다. 예를 들어 미국 임상종양학회의 2021년 2월 보고서에 따르면 미국에서는 추정된 235,760명의 성인(남성 119,100명, 여성 116,6600명)이 폐암으로 진단될 것으로 예상되고 있습니다. 예를 들어, Globocan 잡지(2020년)에서는 인도에서는 18.3%의 신규 암 증례가 있으며, 자궁경부암이 전암의 9.4%를 차지하고 있는 것을 알았습니다. 예를 들어, 미국 암 협회(ACS)가 발표한 2022년 1월의 최신 통계에 따르면, 2021년에는 미국에서 약 26,560명의 새로운 위암 증례가 검출될 것으로 예측되고 있으며, 그 내역은 남성 16,160명, 여성 10,400명입니다. 국립 유방암 재단이 발표한 통계에 따르면 2021년 7월 시점에서 유방암 환자의 약 63%가 국소기 유방암, 27%가 국소기 유방암, 6%가 원격(전이) 유방암으로 진단되고 있습니다.
게다가 세계에서 혈액암의 유병률이 상승하고 있기 때문에 보다 우수한 치료 옵션과 잔존 암세포의 제거 정밀도에 대한 수요가 높아지고 있어 잔존질환을 최소화하는 시장에 대한 수요가 증가할 수 있습니다. 미국암협회가 발표한 통계에 따르면 2022년 1월에 미국에서 새롭게 34,920명의 다발성 골수종으로 진단된 것으로 추정되고 있습니다.
그러나 연구개발 활동 비용이 높기 때문에 예측 기간 동안 시장 성장이 방해될 수 있습니다.
미소잔존질환 시장 동향
차세대 시퀀싱(NGS) 부문은 예측 기간 동안 최고의 CAGR을 나타낼 것으로 예상됩니다.
차세대 시퀀싱는 질병과 관련된 유전적 변이를 연구하기 위해 DNA 또는 RNA의 서열을 결정하는 데 사용되는 기술입니다. 특정 시점에서 많은 DNA의 서열을 결정할 수 있기 때문에 초병렬 시퀀싱이라고도 합니다.
차세대 시퀀싱 기술의 성장을 추진하는 요인으로는 세계적으로 암 발생률이 증가하고 있는 것, 창약, 임상 처치, 정밀의료에 있어서의 차세대 시퀀싱의 서비스 및 용도에 대한 수요 증가, 차세대 시퀀싱용으로 확립된 최신 기술의 채용 등을 들 수 있습니다.
최근, 환자의 미세잔존질환을 보다 정확하게 모니터링하기 위해 차세대 시퀀싱를 포함하는 새로운 분석법이 개발되었습니다. 차세대 시퀀싱은 기존에 사용된 형태학적 검사 및 세포유전학적 검사보다 더 높은 감도를 제공합니다. 2020년 1월 Journal of Molecular Diagnostics에 게재된 '급성 골수성 백혈병 환자에서 DNA 수준에서의 돌연변이와 염색체 재배열의 동시 분석을 위한 새로운 차세대 시퀀싱 전략'이라는 제목의 논문에 따르면, 다음이 밝혀졌습니다. 차세대 시퀀싱은 한 번의 실행으로 모든 게놈 병변을 검출할 수 있다고 약속합니다. 게다가, 환자는 여러 분자 이상이 빈번하게 존재하기 때문에 차세대 시퀀싱은 새로 진단된 모든 급성 골수성 백혈병에 적용됩니다.
다양한 에러 수정 차세대 방법론의 소개, 미세잔존질환의 검출이 용이해졌습니다. 최근 분자 바코딩은 차세대 시퀀싱 라이브러리를 만드는 데 사용되는 개별 DNA 분자의 바코딩을 기반으로 몇 가지 오류 수정 차세대 시퀀싱 접근법을 개발하는 데 사용되었습니다. 국립 바이오테크놀러지 정보센터가 2021년 6월 발표한 '차세대 시퀀싱에 의한 미세잔존질환 모니터링'이라는 제목의 논문에 따르면 차세대 시퀀싱은 미진단 미세잔존질환의 유병률을 줄일 가능성이 있다는 것이 밝혀졌습니다. 이는 급성 림프성 백혈병(ALL) 환자의 생존에 중요한 조기 관리를 가능하게 합니다.
또한 기업의 연구개발 활동에 대한 투자, 첨단 기술 도입, 최소 잔존 병변을 평가하는 어세이 개발에 대한 주력 강화는 예측 기간 동안 차세대 시퀀싱의 성장을 증가시킬 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 2020년 1월, Adaptive Biotechnologies는 GlaxoSmithKline과 협력하여 clonoSEQ 분석을 사용하여 GSK의 혈액학 제품 포트폴리오의 미세잔존질환(MRD)을 평가했습니다.
북미는 예측 기간 동안 상당한 시장 점유율을 가질 것으로 예상됩니다.
암 발생률 증가, 최소한의 잔존질환을 검출하기 위한 차세대 및 중합효소 연쇄반응 기술에 대한 수요 증가, 최신 기술의 채용, 단백질체학, 유전체학, 종양학의 확립된 조사 인프라가, 북미의 암 시장 성장을 가속하는 요인입니다.
미국에서의 혈액암의 발생률과 유병률 증가에 의해 암세포가 잔존하는 리스크가 증가하고 있어 잔존질환을 최소한으로 억제하는 시장에 대한 수요가 높아질 가능성이 있습니다. 미국암협회가 발표한 2022년 통계에 따르면 2022년 미국에서 다발성 골수종의 신규 사례수는 34,470명입니다. 또한 같은 출처에 따르면 2022년 급성 림프성 백혈병(ALL)의 신규 사례 수는 약 6,660명입니다. 백혈병 및 림프종 협회가 발표한 통계에 따르면, 2021년에는 미국 환자에서 새롭게 90,390명의 림프종 증례가 진단된 것으로 추정되고 있으며, 이 중 8,830명이 호지킨 림프종, 81,560명이 비호지킨 림프종입니다.
또한, 미세잔존질환을 검출하기 위한 치료법 및 검사 개발에 기업이 점점 더 주력하고 있는 것도 시장 성장에 기여하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, Invitae는 2022년 2월에 다양한 종양 유형에 걸쳐 개인화된 미세잔존질환 검사에 대한 실제 데이터를 생성하기 위한 연구를 시작했습니다. 마찬가지로, 2020년 4월에 이니바타는 이전에 암으로 진단받은 환자의 혈장 샘플에서 잔존질환과 재발을 검출하고 모니터링하기 위한 분석인 RaDaR을 시작했습니다. RaDaR 분석은 Inivata의 입증된 InVision 리퀴드 바이오시 플랫폼 기술을 기반으로 구축되었으며, 고감도의 특이적 돌연변이 검출을 위한 내장 제어 및 오류 수정을 통합한 차세대 시퀀싱 플랫폼입니다.
미세잔존질환 산업 개요
미세잔존질환 시장은 경쟁이 심하고 여러 주요 기업으로 구성되어 있습니다. 양사는 환자에게 더 나은 치료법 및 검출법을 제공하기 위한 연구개발 활동에 투자하고 있으며 시장에서의 지위를 유지하기 위해 제휴 및 인수와 같은 다양한 비즈니스 전략을 채택하고 있습니다. 주요 기업로는 Adaptive Biotechnologies, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Natera, Kite Pharma, Amgen Inc 등이 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제 조건 및 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 역학
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 암의 이환율 증가
- 연구개발 투자 증가
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 고액의 연구개발비
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체 제품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 격렬
제5장 시장 세분화
- 검사 수법별
- 중합효소 연쇄반응
- 형광 In situ 하이브리드화(FISH)
- 차세대 시퀀싱(NGS)
- 검출 대상별
- 백혈병
- 림프종
- 고형 종양
- 기타
- 최종 사용자별
- 병원
- 검사 센터
- 전문 클리닉
- 지역별
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 남미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 프로파일
- Adaptive Biotechnologies
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- Amgen Inc.
- Kite Pharma
- Natera
- SYNIMMUNE GmbH
- Navidea Biopharmaceuticals
- Novartis
- AstraZeneca
- iRepertoire
제7장 시장 기회 및 미래 동향
AJY 24.03.15The Global Minimal Residual Disease Market size is estimated at USD 1.9 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 3.49 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 12.88% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
The COVID-19 pandemic affected healthcare systems globally and resulted in the interruption of usual care in many healthcare facilities, exposing vulnerable patients with cancer to significant risks. Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, measures have been taken to increase the admissions of covid patients and reduce the number of non-covid patients in the hospitals, leading to postponing the treatment. A study titled 'Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Cancer Care: A Global Collaborative Study' in September 2020 reported that a total of 356 centers from 54 countries across six continents participated between April 21 and May 8, 2020. These centers serve 716,979 new patients with cancer a year. Most of them (88.2%) reported facing challenges in delivering care during the pandemic. Although 55.34% reduced services as part of a preemptive strategy, other common reasons included an overwhelmed system (19.94%), lack of personal protective equipment (19.10%), and staff shortage (17.98%), and restricted access to medications (9.83%). According to an article titled 'What is the Clinical Impact of COVID-19 on Cancer Patients?' in June 2020, the increased vulnerability of cancer patients to COVID-19, particularly to the severe effects of this infectious disease, has led some patients to delay or pause their anti-cancer treatments to reduce their exposure to potentially infected people, and this condition during initial pandemic phase affected the market adversely. Such studies indicate that cancer care was severely impacted, subsequently impacting the market growth. Hence, there is an overall negative impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the market's growth.
The factors propelling the growth of the minimal residual disease market are the rising prevalence of various types of cancer worldwide and the increasing awareness among people to confirm the presence of carcinogens. The patients undergoing continued cancer treatment are expected to be the most important element driving the minimal residual disease market forward. In addition, the rising adoption of personalized medicines for the treatment and rising research and development activities contribute to the market's growth.
The increasing number of people suffering from various cancers is the key driving factor for the minimal residual disease market growth. For instance, as per the American Society of Clinical Oncology February 2021 report, an estimated 235,760 adults (119,100 men and 116,6600 women) in the United States were expected to be diagnosed with lung cancer. For instance, Globocan, 2020, it found that there are 18.3% new cases of cancers in India, and cervical cancer accounted for 9.4% of all cancers. For instance, according to statistics published by the American Cancer Society (ACS) updates from January 2022, approximately 26,560 new cases of stomach cancer are projected to be detected in the United States in 2021, with 16,160 males and 10,400 women. According to the statistics published by the National Breast Cancer Foundation, in July 2021, approximately 63% of breast cancer patients have been diagnosed with local-stage breast cancer, 27% with regional stage, and 6% with a distant (metastatic) disease.
In addition, the rising prevalence of blood cancer worldwide increases the demand for better treatment options and accuracy in removing the residual cancerous cells, which is likely to increase the demand for a minimal residual disease market. According to the statistics published by the American Cancer Society, in January 2022, 34,920 new cases of multiple myeloma were estimated to be diagnosed in the United States.
However, the high cost of research and development activities will likely hinder the market's growth over the forecast period.
Minimal Residual Disease Market Trends
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Segment Expects to Register a Highest CAGR in the Forecast Period
Next-generation sequencing is a technology used to determine the sequence of DNA or RNA to study the genetic variations associated with the disease. It is also called as massively-parallel sequencing as it enables the sequencing to determine the sequencing of many DNA at a particular time.
The factors propelling the growth of next-generation sequencing technology are increasing incidences of cancer globally, rising demand for next-generation sequencing services and applications in drug development, clinical procedures, precision medicines, and adoption of the latest technology established for next-generation sequencing.
Recently, new assays, including next-generation sequencing, were developed to monitor minimal residual disease more precisely in the patients. Next-Generation Sequencing offers greater sensitivity than conventionally employed morphologic and cytogenetic tests. According to an article published by the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics in January 2020, titled 'A New Next-Generation Sequencing Strategy for the Simultaneous Analysis of Mutations and Chromosomal Rearrangements at DNA Level in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients' it has been found that the next-generation sequencing offers the promise of detecting all genomic lesions in a single run. In addition, next-generation sequencing applies to every newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia because of the frequent prevalence of multiple molecular aberrations among patients.
The introduction of various error-corrected next-generation methodologies has made the detection of minimal residual diseases easy. Molecular barcoding has recently been used to develop several error-corrected next-generation sequencing approaches based on barcoding the individual DNA molecules used for next-generation sequencing library creation. According to an article published by the National Center for Biotechnology Information in June 2021, titled "Minimal Residual Disease Monitoring with Next-Generation Sequencing," it has been found that next-generation sequencing has the potential to reduce the prevalence of undiagnosed minimal residual diseases, allowing for early management, which is critical for Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) patient survival.
Moreover, the companies' investment in research and development activities, adoption of advanced technology, and increasing their focus on developing assays to assess minimal residual disease are likely to increase the growth of next-generation sequencing over the forecast period. For instance, in January 2020, Adaptive Biotechnologies collaborated with GlaxoSmithKline to use its clonoSEQ Assay to assess minimal residual disease (MRD) in GSK's portfolio of hematology products.
North America is Expected to Have the Significant Market Share during the Forecast Period
The increasing incidences of cancer, rising demand for next-generation and polymerase chain reaction techniques for detecting minimal residual diseases, adoption of the latest technology, and established research infrastructure for proteomics, genomics, and oncology are the factors propelling the growth of the market in the North American region.
The increasing incidences and prevalence of hematological cancers in the United States have increased the risk of people having residual cancerous cells, which is likely to increase the demand for minimal residual disease market. According to the statistics published by the American Cancer Society 2022, 34,470 new cases of multiple myeloma in the United States in 2022. In addition, as per the same source, about 6,660 new cases of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) in 2022. As per the statistics published by the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, in 2021, 90,390 new lymphoma cases were expected to be diagnosed in patients in the United States, of which 8,830 cases would be of Hodgkin lymphoma and 81,560 cases of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Moreover, the increasing focus of the companies on developing treatments and tests for detecting minimal residual disease is also contributing to the market's growth. For instance, in February 2022, Invitae launched a study to generate real-world data on personalized minimal residual disease tests across various tumor types. Similarly, in April 2020, Inivata launched an assay, RaDaR, to detect and monitor residual disease and recurrence in the plasma samples of patients previously diagnosed with cancer. The RaDaR assay is built on Inivata's proven InVision liquid biopsy platform technology, a next-generation sequencing platform that incorporates built-in controls and error correction for highly sensitive and specific variant detection.
Minimal Residual Disease Industry Overview
The minimal residual disease market is highly competitive and consists of several major players. The companies are investing in research and development activities to provide patients with better treatment and detection methods and adopt various business strategies such as collaboration and acquisitions to withhold their positions in the market. Some key players are Adaptive Biotechnologies, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Natera, Kite Pharma, and Amgen Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Prevalence of Cancer
- 4.2.2 Increasing Investment in Research and Development
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Cost of Research and Development Activities
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (Market Size by Value - USD million)
- 5.1 By Test Technique
- 5.1.1 Polymerase Chain Reaction
- 5.1.2 Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
- 5.1.3 Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
- 5.2 By Detection Target
- 5.2.1 Leukemia
- 5.2.2 Lymphoma
- 5.2.3 Solid Tumors
- 5.2.4 Others
- 5.3 By End-user
- 5.3.1 Hospitals
- 5.3.2 Laboratory centers
- 5.3.3 Specialty Clinics
- 5.4 Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.4.5 South America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Company Profiles
- 6.1.1 Adaptive Biotechnologies
- 6.1.2 Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- 6.1.3 Amgen Inc.
- 6.1.4 Kite Pharma
- 6.1.5 Natera
- 6.1.6 SYNIMMUNE GmbH
- 6.1.7 Navidea Biopharmaceuticals
- 6.1.8 Novartis
- 6.1.9 AstraZeneca
- 6.1.10 iRepertoire

















