
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1687201
창고 로봇 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Warehouse Robotics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
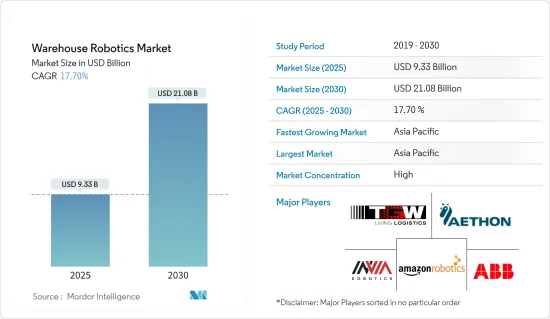
창고 로봇 시장 규모는 2025년에 93억 3,000만 달러로 추정되고, 예측 기간인 2025-2030년 CAGR 17.7%로 성장할 전망이며, 2030년에는 210억 8,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.

주요 하이라이트
- SKU 다양성의 확대가 창고 자동화 촉진 : 창고 로봇 시장은 SKU의 다양성 급증을 원동력으로 가속적으로 성장하고 있습니다. 50% 이상의 기업이 롱테일 소비자 수요에 부응하기 위해 SKU 수를 늘릴 것으로 예상되고 있습니다. 이 동향은 기존의 창고 모델을 재구축하고 있으며, 대량 팔레트 주문 시스템은 소량, 복수 SKU 주문으로 대체되고 있습니다. 이 과제에 대응하기 위해 자동소액입출고시스템(AS/RS)이 불가결하게 되었습니다. 이러한 시스템은 경량 크레인을 활용하여 토트, 케이스, 나무 상자를 관리하고 보관을 최적화하며 중요한 노동력과 배송 자원을 해방시킵니다.
- 창고 규모의 확대 : 창고는 2,000년의 6만 5,000평방 피트에서 2020년에는 20만 평방 피트 이상으로 확대되어 SKU 증가에 대응하고 있습니다.
- 소매업체 및 도매업체의 역학 변화 : 저스트인 타임 주문과 소비자 직송의 유통은 대형 팔레트 주문을 줄이고 자동화의 필요성을 가속화하고 있습니다.
- 피킹 로봇과 AGV : 최신 세대의 피킹 로봇과 무인 운송 차량(AGV)은 대규모 창고에서 방대한 SKU 범위에 걸쳐 소량의 주문을 처리하는 데 이상적입니다.
- 투자의 급증이 기술의 진보를 촉진 : 자본의 유입이 창고 자동화 기술을 전진시키고 있습니다. 벤처캐피털 기업들은 로봇공학에 적극적으로 투자하고 있으며, 창고 로봇 공학 신흥기업에 대한 자금조달액은 2020년 1분기에 전년 동기 대비 57% 증가한 3억 8,100만 달러에 달했습니다.
- Locus Robotics의 확대 : 2020년 6월, Locus Robotics는 연구 개발의 강화와 유럽 연합에의 진출을 위해 4,000만 달러를 조달했습니다.
- Amazon의 혁신 허브 : Amazon이 매사추세츠주에 최첨단 로봇 허브를 개발하기 위해 4,000만 달러를 투자한 것으로, 자동화의 진전이 기대됩니다.
- Shopify의 전략적 인수 : Shopify는 2019년에 6 River Systems를 4억 5,000만 달러로 인수하여 클라우드 기반 소프트웨어와 협동 모바일 로봇을 통합하여 풀필먼트 기능을 확대했습니다.
- 전자상거래 붐이 채용을 가속 : 전자상거래의 급성장은 창고 로봇의 채용을 촉진해 계속하고 있습니다. 온라인 소매의 급증에 따라, 효율적인 재고 관리 및 풀필먼트 업무가 불가결해지고 있습니다.
- 시장 규모 예측 : Cowen은 전자상거래에 있어서 창고 및 물류 로봇의 미국 시장은 2024년까지 80억 달러에 달할 것으로 예측했습니다.
- 새로운 플루필먼트 모델 : Albertsons와 Takeoff Technologies는 AI와 로봇을 활용한 도시형 플루필먼트 센터를 검사적으로 도입하여 도시의 소규모 창고 업무를 효율화합니다.
- Kroger의 확대 : Kroger는 Ocado와 제휴하여 대규모 로봇 구동 시설을 갖춘 고객 풀필먼트 센터를 최대 20개소 개설할 계획입니다.
- 노동력 부족과 비용 절감이 혁신 촉진 : 노동력 부족에 대한 대응과 운영 비용 절감을 위해 창고 로봇의 활용이 진행되고 있습니다. 자동화는 불필요한 노동력의 이동을 줄이고 운영을 합리화함으로써 효율을 향상시킵니다.
- 낭비적인 운영 비용 : 미국 창고에서 낭비적인 움직임으로 인해 연간 43억 달러의 손실이 발생하고 로봇 솔루션의 중요성이 강조되었습니다.
- 산업용 로봇의 성장 : 산업용 로봇의 가동 대수는 2018년의 240만 8,000대에서 2021년에는 378만 8,000대로 증가할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.
- Alibaba의 인력 삭감 : 로봇 노동력을 도입함으로써 Alibaba는 창고의 노동력을 70% 삭감하고 동시에 숙련 노동자에게 더 많은 기회를 창출했습니다.
창고 로봇 시장 동향
이동 로봇(AGV 및 AMR)이 유형별 최대 부문
이동 로봇, 특히 무인 반송차(AGV)와 자율형 이동 로봇(AMR)이 창고 로봇 시장을 독점하고 있습니다. 이 부문은 2021년 세계 매출의 22.80%를 차지하며 자동화의 매우 중요한 원동력이 되고 있습니다.
- 강력한 성장 : 모바일 로봇은 가장 급성장하는 부문이며 CAGR은 16.64%로 예측되어 적응성이 높은 로봇 솔루션이 시장에서 선호되고 있음을 보여줍니다.
- 수익 예측 : 이 부문의 2021년 매출액은 22억 5,000만 달러, 2027년에는 56억 3,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측되고 있어, 창고에서의 채용이 증가하고 있는 것을 뒷받침하고 있습니다.
- 기술의 진보 : 센서 기술, AI, 컴퓨터 비전에 대한 투자로 모바일 로봇의 능력이 향상되고 있습니다. 선진적 자율형 로봇을 위한 아마존의 캔버스 기술 인수는 그 두드러진 예입니다.
- 산업에 대한 용도 : 모바일 로봇은 특히 소매업(2021년 시장 점유율 27.46%)이나 식음료 부문으로, 상품의 핸들링이나 온도 관리 환경의 효율성을 높이는 등, 산업을 불문하고 널리 이용되고 있습니다.
아시아태평양이 큰 시장 점유율을 차지할 전망
아시아태평양은 창고 로봇 시장에서 지배적이고 급성장하고 있는 지역으로, 2021년에는 세계 점유율의 46.72%를 차지했습니다.
- CAGR 예측 : 이 지역은 중국과 인도 등 국가에서 로봇 기술의 급속한 도입에 견인되어 CAGR 16.06%에서 선두를 유지할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 시장 규모 : 아시아태평양의 창고 로봇 시장은 2021년에 46억 2,000만 달러의 수익을 올렸으며, 2027년에는 112억 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.
- 전자상거래 확대 : 인도와 중국의 전자상거래 시장의 활황은 중요한 촉진요인이며, 인도 시장은 2020년 462억 달러에서 2030년에는 3,500억 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.
- 제조업의 리더십 : 아시아태평양의 세계 제조 거점으로서의 지위가 특히 중국, 일본, 한국에서의 창고 자동화 기술의 채용을 뒷받침하고 있습니다.
- 기술 혁신 : 아시아 기업은 AI를 활용한 로봇 솔루션에 투자하고 있습니다.
창고 로봇 산업 개요
창고 로봇 시장은 세계의 진출기업이 지배적이며 시장 구조는 통합되어 있습니다. 기존의 오토메이션 기업과 로봇 전업 기업이 산업의 최전선에 서서 연구, 제휴, 인수를 활용하여 시장에서의 지위를 유지하고 있습니다.
Honeywell의 로봇 허브 : Honeywell의 로봇 혁신 허브에 대한 5,000만 달러의 투자는 창고 자동화 부문을 선도하는 회사의 헌신을 보여줍니다.
투자자의 확신 : GreyOrange와 Vecna Robotics와 같은 신흥 기업이 많은 돈을 모은 것은 창고 로봇의 성장 가능성에 대한 강한 자신감을 보여줍니다.
기술 리더가 시장 역학을 형성 : ABB Limited, Fanuc Corporation, Honeywell International Inc., KUKA AG, 야스카와 전기 등 주요 기업이 시장을 선도하고 있습니다. 이러한 기업은, AMR, AS/RS, AI 탑재 시스템등의 선진적인 솔루션을 개발하고 있습니다.
혁신적인 솔루션 : Swisslog의 KR 스칼라 로봇과 Locus Robotics의 RaaS(Robot-as-a-Service) 구독 모델은 전통적인 시장 접근 방식을 파괴하고 비용 효율적이고 사용하기 쉬운 자동화 솔루션을 제공합니다.
전략적 파트너십 : Berkshire Grey가 전 세계 소매업체와 2,300만 달러를 투자하여 식료품의 당일 정착 계약을 맺은 것처럼 전자상거래 플랫폼 및 물류 공급자와의 협업은 시장 확대를 위한 중요한 전략입니다.
시장의 향후 성공 요인 : 성공하기 위해서는 기업은 AI와 머신러닝의 진보에 초점을 맞추어 로봇의 능력을 강화할 필요가 있습니다. 다양한 창고 구성에 적응하는 유연한 솔루션, 소매업체와의 파트너십, 확대 가능한 자동화 플랫폼이 중요해집니다. 또, 높은 도입 비용 및 규제상의 과제에 대처하는 것도, 전산업에서 널리 채용되기 위해서는 불가결합니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트
- 시장 개요
- 산업의 매력-Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
- 산업 밸류체인 분석
- COVID-19의 산업에 대한 영향 평가
제5장 시장 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- SKU수 증가
- 기술 및 로봇에 대한 투자 증가
- 시장의 과제
- 엄격한 규제 요건
- 고비용
제6장 시장 세분화
- 유형별
- 산업용 로봇
- 분류 시스템
- 컨베이어
- 팔레타이저
- 자동 보관 및 검색 시스템(ASRS)
- 이동 로봇(AGV와 AMR)
- 기능별
- 보관
- 포장
- 픽업
- 기타
- 최종 사용자 산업별
- 음식
- 자동차
- 소매
- 전기 및 전자
- 제약
- 기타
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 유럽
- 영국
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 아시아
- 중국
- 한국
- 일본
- 호주 및 뉴질랜드
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 북미
제7장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 프로파일
- ABB Limited
- Kiva Systems(Amazon Robotics LLC)
- TGW Logistics Group GMBH
- Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd(Aethon Incorporation)
- InVia Robotics Inc.
- Fanuc Corporation
- Honeywell International Incorporation
- Toshiba Corporation
- Omron Adept Technologies
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation(Yaskawa Motoman)
- Kuka AG
- Fetch Robotics Inc.
- Geek Inc.
- Grey Orange Pte Ltd
- Hangzhou Hikrobot Technology Co. Ltd
- Syrius Robotics
- Locus Robotics
제8장 투자 분석
제9장 시장의 미래
AJY 25.05.02The Warehouse Robotics Market size is estimated at USD 9.33 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 21.08 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 17.7% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Key Highlights
- Expanding SKU Diversity Drives Warehouse Automation: The warehouse robotics market is witnessing accelerated growth driven by the surge in SKU diversity. Over 50% of businesses are expected to increase the number of SKUs to cater to long-tail consumer demands. This trend is reshaping traditional warehouse models, where large-pallet order systems are being replaced by small, multi-SKU orders. To meet this challenge, automated mini-load storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) are becoming vital. These systems leverage lightweight cranes to manage totes, cases, and crates, optimizing storage and freeing up crucial labor and delivery resources.
- Increase in Warehouse Size: Warehouses have expanded from 65,000 sq. ft in 2000 to over 200,000 sq. ft in 2020 to accommodate the rising volume of SKUs.
- Shift in Retailer-Wholesaler Dynamics: Just-in-time ordering and direct-to-consumer distribution are reducing large-pallet orders, accelerating the need for automation.
- Picking Robots and AGVs: The latest generation of picking robots and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) is ideal for handling small orders spread over vast SKU ranges in large warehouses.
- Surging Investments Fuel Technological Advancements: The influx of capital is propelling warehouse automation technologies forward. Venture capital firms have been actively investing in robotics, with funding for warehouse robotics startups reaching USD 381 million in Q1 2020, a 57% year-over-year increase.
- Locus Robotics' Expansion: In June 2020, Locus Robotics raised USD 40 million to enhance R&D and expand into the European Union.
- Amazon's Innovation Hub: Amazon's investment of USD 40 million to develop a cutting-edge robotics hub in Massachusetts is expected to boost automation advancements.
- Shopify's Strategic Acquisition: Shopify's USD 450 million acquisition of 6 River Systems in 2019 expanded its fulfillment capabilities, incorporating cloud-based software and collaborative mobile robots.
- E-commerce Boom Accelerates Adoption: The rapid growth of e-commerce continues to drive the adoption of warehouse robotics. Efficient inventory management and fulfillment operations are becoming critical as online retail surges.
- Projected Market Value: Cowen projects that the U.S. market for warehouse and logistics robots in e-commerce will reach nearly USD 8 billion by 2024.
- New Fulfillment Models: Albertsons and Takeoff Technologies have collaborated to pilot urban fulfillment centers powered by AI and robotics to streamline small urban warehouse operations.
- Kroger's Expansion: Kroger is planning to open up to 20 customer fulfillment centers in partnership with Ocado, featuring large-scale robot-driven facilities.
- Labor Shortages and Cost Reduction Drive Innovation: Warehouse robotics are being increasingly used to tackle labor shortages and reduce operational costs. Automation helps improve efficiency by reducing unnecessary labor movement and streamlining operations.
- Wasted Motion Costs: U.S. warehouses lose USD 4.3 billion annually due to wasted motion, emphasizing the importance of robotic solutions.
- Industrial Robots Growth: The operational stock of industrial robots is projected to grow from 2,408 thousand units in 2018 to 3,788 thousand units by 2021.
- Alibaba's Workforce Reduction: By deploying robotic labor, Alibaba reduced its warehouse workforce by 70%, while creating more opportunities for skilled labor.
Warehouse Robotics Market Trends
Mobile Robots (AGVs and AMRs) Largest Segment by Type
Mobile robots, particularly Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), dominate the warehouse robotics market. This segment captured 22.80% of global revenue in 2021, making it a pivotal driver of automation.
- Strong Growth: Mobile robots are the fastest-growing segment, with a CAGR of 16.64% forecasted, indicating a clear market preference for adaptable robotic solutions.
- Revenue Projections: The segment generated USD 2.25 billion in revenue in 2021 and is expected to grow to USD 5.63 billion by 2027, underlining the increased adoption in warehouses.
- Technological Advancements: Investments in sensor technology, AI, and computer vision are enhancing the capabilities of mobile robots. Amazon's acquisition of Canvas Technology for advanced autonomous robots is a notable example.
- Industry Applications: Mobile robots are widely used across industries, particularly in retail (27.46% market share in 2021) and food and beverage sectors, where they enhance efficiency in product handling and temperature-controlled environments.
Asia Pacific is Expected to Hold Significant Market Share
Asia-Pacific is the dominant and fastest-growing region in the warehouse robotics market, capturing 46.72% of the global share in 2021.
- CAGR Projections: The region is expected to maintain its leadership with a CAGR of 16.06%, driven by the rapid adoption of robotics technologies in countries like China and India.
- Market Size: The Asia-Pacific warehouse robotics market generated USD 4.62 billion in revenue in 2021, with forecasts estimating growth to USD 11.20 billion by 2027.
- E-commerce Expansion: The booming e-commerce market in India and China is a significant driver, with India's market expected to grow from USD 46.2 billion in 2020 to USD 350 billion by 2030.
- Manufacturing Leadership: Asia-Pacific's status as a global manufacturing hub is propelling the adoption of warehouse automation technologies, especially in China, Japan, and South Korea.
- Technological Innovation: Companies in Asia are investing in AI-powered robotics solutions. Geek+, a Chinese robotics company, has made significant advancements with its AI-powered logistics robots, competing with established global players.
Warehouse Robotics Industry Overview
The warehouse robotics market is dominated by global players, with a consolidated market structure. Established automation companies and specialized robotics firms are at the forefront of the industry, leveraging research, partnerships, and acquisitions to maintain their market positions.
Honeywell's Robotics Hub: Honeywell's USD 50 million investment in a Robotics Innovation Hub showcases the company's commitment to leading the warehouse automation sector.
Investor Confidence: Emerging players such as GreyOrange and Vecna Robotics have raised substantial funds, indicating strong confidence in the growth potential of warehouse robotics.
Technology Leaders Shape Market Dynamics: Key players like ABB Limited, Fanuc Corporation, Honeywell International Inc., KUKA AG, and Yaskawa Electric Corporation lead the market. These companies are developing advanced solutions, including AMRs, AS/RS, and AI-powered systems.
Innovative Solutions: Swisslog's KR SCARA robots and Locus Robotics' RaaS (robots-as-a-service) subscription model are disrupting traditional market approaches, providing cost-effective and accessible automation solutions.
Strategic Partnerships: Collaboration with e-commerce platforms and logistics providers, such as Berkshire Grey's USD 23 million contract with a global retailer for same-day grocery fulfillment, is a key strategy for market expansion.
Factors Driving Future Success in the Market: To succeed, companies need to focus on AI and machine learning advancements to enhance robotic capabilities. Flexible solutions that adapt to various warehouse configurations, partnerships with retailers, and scalable automation platforms will be critical. Addressing high implementation costs and regulatory challenges will also be essential to ensure wider adoption across industries.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.2.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.2.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.2.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.3 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Assessment of the Impact of COVID-19 on the Industry
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Increasing Number of SKUs
- 5.1.2 Increasing Investments in Technology and Robotics
- 5.2 Market Challenges
- 5.2.1 Stringent Regulatory Requirements
- 5.2.2 High Cost
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Type
- 6.1.1 Industrial Robots
- 6.1.2 Sortation Systems
- 6.1.3 Conveyors
- 6.1.4 Palletizers
- 6.1.5 Automated Storage and Retrieval System (ASRS)
- 6.1.6 Mobile Robots (AGVs and AMRs)
- 6.2 By Function
- 6.2.1 Storage
- 6.2.2 Packaging
- 6.2.3 Trans-shipment
- 6.2.4 Other Functions
- 6.3 By End-user Industry
- 6.3.1 Food and Beverage
- 6.3.2 Automotive
- 6.3.3 Retail
- 6.3.4 Electrical and Electronics
- 6.3.5 Pharmaceutical
- 6.3.6 Other End-user Industries
- 6.4 By Geography
- 6.4.1 North America
- 6.4.1.1 United States
- 6.4.1.2 Canada
- 6.4.2 Europe
- 6.4.2.1 United Kingdom
- 6.4.2.2 Germany
- 6.4.2.3 France
- 6.4.3 Asia
- 6.4.3.1 China
- 6.4.3.2 South Korea
- 6.4.3.3 Japan
- 6.4.4 Australia and New Zealand
- 6.4.5 Latin America
- 6.4.6 Middle East and Africa
- 6.4.1 North America
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 ABB Limited
- 7.1.2 Kiva Systems (Amazon Robotics LLC)
- 7.1.3 TGW Logistics Group GMBH
- 7.1.4 Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd (Aethon Incorporation)
- 7.1.5 InVia Robotics Inc.
- 7.1.6 Fanuc Corporation
- 7.1.7 Honeywell International Incorporation
- 7.1.8 Toshiba Corporation
- 7.1.9 Omron Adept Technologies
- 7.1.10 Yaskawa Electric Corporation (Yaskawa Motoman)
- 7.1.11 Kuka AG
- 7.1.12 Fetch Robotics Inc.
- 7.1.13 Geek+ Inc.
- 7.1.14 Grey Orange Pte Ltd
- 7.1.15 Hangzhou Hikrobot Technology Co. Ltd
- 7.1.16 Syrius Robotics
- 7.1.17 Locus Robotics



















