
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1850221
스마트 센서 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Smart Sensors - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
스마트 센서 시장은 2025년에 770억 5,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 1,729억 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다.

이 성장 궤도는 엣지 인공지능, 자동차 및 헬스케어 규제 강화, 기업을 리액티브 모니터링에서 프레디 쿠티브 인텔리전스로 전환시키는 산업 자동화 프로그램의 융합에 의해 추진되고 있습니다. 자동차의 자동 긴급 브레이크 및 의료기기의 지속적인 환자 모니터링과 같은 안전 기능의 의무화는 신흥국 시장 전체에서 비재량적인 센서 수요로 이어지고 있습니다. 동시에 최신 센서 세대에 내장된 엣지 AI 코어는 대기 시간과 대역폭 병목 현상을 없애고 전력 제한 환경에서 실시간 분석을 가능하게 합니다. 갈륨과 게르마늄을 둘러싼 공급망 압력과 반도체 자급 자족 경쟁은 수량이 증가하더라도 평균 판매 가격을 견고하게 유지하며 제조업체에게 지속적인 연구개발 투자의 여지를 제공합니다. 예측 기간 동안 성능 차별화는 원시 감도 지표에서 온보드 인텔리전스, 사이버 보안 컴플라이언스 및 통합 유연성으로 전환하고 있습니다.
세계의 스마트 센서 시장 동향 및 인사이트
산업용 IoT에서 에너지 효율화 추진
법적 구속력이 있는 지속가능성 보고서는 측정가능한 kWh 절약과 CO2 감소를 실현하는 지능형 센서의 도입을 제조업체에게 촉구하고 있습니다. 유럽의 기업 지속가능성 보고 지침은 세분화된 에너지 메트릭을 요구하고 있으며 공장은 HVAC, 조명 및 기계 사용을 지속적으로 최적화하는 엣지 AI 센서의 설치를 추진하고 있습니다. SECO의 스마트 CNC 레트로 피트는 생산 폐기물을 30% 절감하고 예비 부품 비용을 10% 절감했습니다. 레히 슈타르베르케사의 5G 대응 공장에서도 비슷한 결과를 얻을 수 있어 에너지 효율화 프로젝트는 이사회 수준의 우선사항이 되었습니다. 조기에 도입한 기업이 2자리수의 비용 절감을 보고하면 후발 기업은 이에 따른 경쟁 압력에 직면하여 지능형 센서에 대한 수요의 자기 강화 사이클이 형성됩니다.
가전용 센서의 보급
스마트폰 및 웨어러블 단말기의 OEM 각사는 현재, 하나의 단말기에 대해 최대 12유형의 센서를 통합하여 대기질 측정, 고급 생체인증, 자기 학습형 액티비티 및 트래킹 등의 기능을 지원하고 있습니다. 보쉬는 2025년에 출시된 휴대폰의 절반 이상이 보쉬의 멀티 센서 모듈을 탑재하고 있음을 확인하고 있습니다. 대량의 소비자 수요는 산업용 및 자동차용 각 층에서 단위당 비용을 낮추는 스케일 이점을 제공하여 가격 성능의 새로운 임계값을 열어줍니다. 웨어러블용으로 완성된 소형화 및 밀리와트 레벨의 소비 전력은 현재 공장의 상태 모니터링 노드나 자율형 배송 로봇으로 이행하고 있어 엣지 대응 센서 스택의 업계 횡단적인 채용을 가속하고 있습니다.
높은 초기 도입 비용
종합적인 스마트 센서 배포에는 엣지 게이트웨이, 사설 5G 네트워크 및 노동력 재교육에 대한 병행 투자가 필요한 경우가 많습니다. 많은 중소규모 공장에서는 총 투자액이 연간 매출액의 0.5%를 초과할 수 있어, 손익 분기점을 4분기 이상 미루게 됩니다. Milesight의 서울 중소기업용 턴키 IoT 키트는 LoRaWAN 게이트웨이와 컨트롤러를 결합해, 통합 마찰을 줄이고 있는데, 이 '올인원' 패키지조차도 자본 예산에 부담을 주고 있습니다. MEMS의 수량이 확대됨에 따라 비용면에서의 역풍은 완화되고 있지만, 예산면에 대한 경계감으로부터 향후 24개월간은 자금 제약이 있는 사업자의 채용이 억제될 전망입니다.
부문 분석
압력 센서는 2024년 218억 8,000만 달러의 매출을 계상했으며, 스마트 센서 시장에서 최대 28.40%의 점유율을 차지했습니다. 이 부문의 내구성은 ADAS의 브레이크, EV의 배터리 관리, 의료용 인공호흡기에서 탁월한 역할에 기인합니다. 실리콘 카바이드 다이어프램의 병행 기술 혁신으로 항공우주 및 수소 연료전지 스택의 작동 온도 범위는 600℃를 초과했습니다. 이미지 센서는 수익 기반에서는 작지만 자율 주행이 의무화되어 보행자 감지 카메라가 표준 장비가 됨에 따라 CAGR 19.20%의 성장이 예측됩니다. 세계 셔터와 이벤트 기반 픽셀을 통합하면 빠르게 변화하는 조명 하에서도 높은 콘트라스트 성능을 발휘할 수 있어 자동차 제조업체는 비싼 LiDAR을 중복하지 않고 AEB 규정을 준수할 수 있습니다.
수요의 다양화로 유닛의 경제성도 변화하고 있습니다. 온도, 습도, 유량 센서는 스마트 시티의 수도 네트워크 및 데이터센터의 열 관리 프로젝트에 통합되어 있으며, 6축 위치 센서는 협동 로봇에 필수가 되고 있습니다. 압력, 온도 및 상대 습도 감지를 융합한 하이브리드 모듈은 설치 비용을 절감하고 OEM의 스위칭 비용을 늘려 공급업체 인클로저를 강화합니다.
MEMS 디바이스는 성숙한 주조 에코시스템과 스마트폰용으로 조정된 비용 구조로 2024년 스마트 센서 시장 점유율의 46.00%를 차지했습니다. 보쉬만으로도 2024년에 60억 개 이상의 MEMS 유닛을 출하하고 있으며, 규모의 우위성이 두드러지고 있습니다. 그러나 포토닉 센서와 양자 센서는 CAGR 21.50%로 확대될 것으로 예측되며, 고정밀 네비게이션과 의료 진단에서 MEMS의 점유율을 빼앗을 가능성이 있습니다. 시티그룹은 양자센싱 시장 규모가 2030년까지 14억 달러에 이를 전망이며, 벤처캐피탈로부터의 자금 유입을 촉진할 것으로 예측했습니다. MEMS의 기존 기업은 BioMEMS 채널과 엣지 AI DSP 코어를 공동 통합함으로써 대응하며 기술 로드맵에 볼륨 바이어를 둘러싸고 있습니다.
3M을 포함한 미국-JOINT 프로그램과 같은 산업 컨소시엄은 첨단 기판의 국내 공급망을 확보하기 위해 재료의 연구 개발을 가속화하고 있습니다. MEMS 모듈에 내장된 뉴로모픽 컴퓨팅 타일에 대한 노력도 병행하여 진행되고 있으며, MEMS의 리더십을 지원하는 크기와 비용의 우위성을 희생하지 않고 인지 기능을 제공하는 것을 목표로 하고 있습니다.
지역 분석
아시아태평양은 2024년 세계 매출액의 44.30%를 차지했으며, 중국의 14차 5개년 계획에 따른 국산 센싱 IC에 대한 보조금과 일본 양자 센싱 연구개발 보조금에 의해 지원되고, 2030년까지 CAGR 19.70%로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다. 중국 국내 시장은 2024년 2,850억 위안(398억 달러)에 달했고, 자동차, 공장 자동화, 네트워크 통신이 각각 20% 이상의 점유율을 차지했습니다. 각 지역의 파운드리는 왕성한 수요와 낮은 투입 비용 인플레이션으로부터 혜택을 받으며, 수직 통합 OEM은 공급망 전체의 현지화를 진행하고 있습니다.
북미는 특히 자동차용 ADAS와 항공우주용 센싱 분야에서 계속 기술적인 견인 역할을 하고 있습니다. 인공지능 대응 어비오닉스 공동 개발을 위한 하니웰과 NXP의 전략적 파트너십은 이 지역이 기능 안전 및 엣지 컴퓨팅에 주력하고 있음을 보여줍니다. 미국에서는 CHIPS 법보조금과 같은 산업정책 상의 우대조치가 지속되고 있으며, ams의 오스람과 GlobalFoundries에 의한 MEMS 라인의 온쇼어링이 촉진되어 지역의 회복력이 향상되고 있습니다.
유럽은 수량에서는 APAC에 뒤지지만, 규제의 훈풍을 받고 있습니다. EU의 일반 안전 규칙 II는 모든 신차에 센서 스위트를 탑재할 것을 의무화하는 기준을 정하고 있어, 경기 후퇴기에서도 안정된 대수 증가를 보증하고 있습니다. 또한 기업의 이산화탄소 감소 목표는 독일, 프랑스, 북유럽의 빌딩 자동화 및 산업 효율 센서에 대한 수요를 자극하고 있습니다.
중동, 아프리카, 남미의 신흥 시장에서는 스마트 시티와 자원 부문의 디지털화라는 과제를 통해 센서 도입이 가속화되고 있습니다. 사우디아라비아의 기가 프로젝트는 고밀도 환경, 교통 관리 센서, 그리드가 필요하며, 칠레의 구리산에는 채굴 효율을 높이기 위해 견고한 진동 센서가 설치되어 있습니다. 저지연 위성 백홀 솔루션은 연결 장벽을 완화하고 이러한 지역이 레거시 통신 인프라 없이 고급 감지를 채택할 수 있도록 합니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 산업용 IoT에서의 에너지 효율 향상
- 가전제품 센서의 보급
- 자동차 및 e헬스의 안전의무
- 소형화 및 무선 기술의 진보
- 온센서 엣지 AI가 대기 시간 감소
- ESG 주도의 라이브 모니터링 도입
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 높은 초기 도입 비용
- 복잡한 설계 및 통합 스킬의 갭
- IoT 사이버 보안 노출
- 희토류 원소 포장 공급 위험
- 밸류체인 및 공급망 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 유형별
- 플로우 센서
- 습도 센서
- 위치 센서
- 압력 센서
- 온도 센서
- 이미지 및 광학 센서
- 기타 유형
- 기술별
- MEMS
- CMOS
- 광학 분광법
- 양자 및 광자
- 기타 기술
- 컴포넌트별
- 아날로그-디지털 컨버터
- 디지털-아날로그 컨버터
- 증폭기
- 트랜시버/RF 프론트엔드
- 임베디드 AI 코어
- 기타 컴포넌트
- 용도별
- 항공우주 및 방위
- 자동차 및 운송
- 헬스케어 및 의료기기
- 산업 자동화
- 빌딩 및 홈 오토메이션
- 가전
- 농업 및 환경
- 기타 용도
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 유럽
- 영국
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 튀르키예
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 나이지리아
- 케냐
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- ABB
- Honeywell International
- Eaton Corporation
- Analog Devices
- Infineon Technologies
- NXP Semiconductors
- STMicroelectronics
- Siemens AG
- TE Connectivity
- Legrand
- General Electric
- Vishay Intertechnology
- Bosch Sensortec
- Texas Instruments
- Omron Corporation
- Sensirion AG
- Murata Manufacturing
- Sony Semiconductor
- Samsung Electronics
- Robert Bosch GmbH
제7장 시장 기회 및 향후 전망
AJY 25.11.07The smart sensors market reached USD 77.05 billion in 2025 and is forecast to rise to USD 172.90 billion by 2030, translating into a robust 17.54% CAGR.
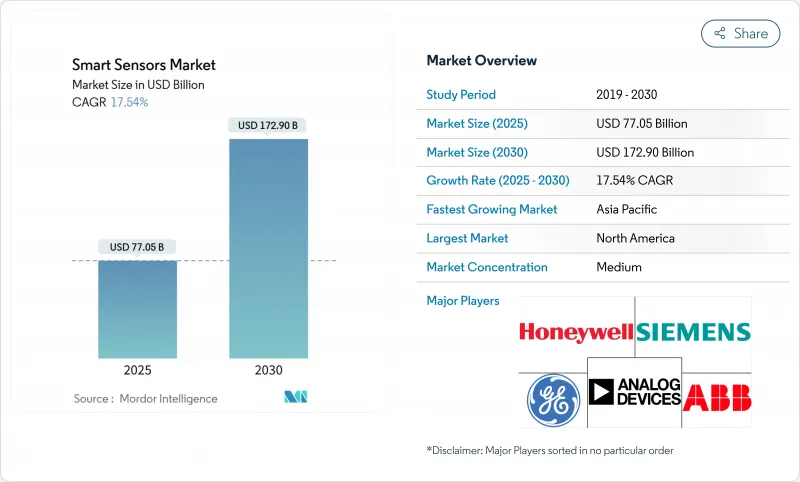
This growth trajectory is propelled by the convergence of edge artificial intelligence, tightening automotive and healthcare regulations, and industrial automation programs that are moving enterprises from reactive monitoring to predictive intelligence. Mandatory safety features such as automatic emergency braking in vehicles and continuous patient monitoring in medical devices are translating into non-discretionary sensor demand across developed markets. At the same time, edge-AI cores embedded in the latest sensor generations eliminate latency and bandwidth bottlenecks, allowing real-time analytics within power-constrained environments. Supply-chain pressures around gallium and germanium and the race for semiconductor self-sufficiency are keeping average selling prices firm even as unit volumes rise, giving manufacturers headroom for sustained R&D investment. Over the forecast period, performance differentiation is shifting from raw sensitivity metrics to on-board intelligence, cyber-security compliance, and integration flexibility-factors now decisive in procurement shortlists.
Global Smart Sensors Market Trends and Insights
Energy-efficiency Push Across Industrial IoT
Legally binding sustainability reporting is prompting manufacturers to deploy intelligent sensors that deliver measurable kWh savings and CO2 reductions. The European Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive requires granular energy metrics, pushing factories to install edge-AI sensors that continuously optimise HVAC, lighting, and machine utilisation. SECO's smart CNC retrofit cut production waste by 30% and spare-parts spend by 10%, showcasing hard-dollar returns that justify fleet-wide rollouts. Similar results at Lech-Stahlwerke's 5G-enabled mill have turned energy-efficiency projects into board-level priorities. As early adopters report double-digit cost reductions, laggards face competitive pressure to follow suit, creating a self-reinforcing demand cycle for intelligent sensors.
Consumer-electronics Sensor Proliferation
Smartphone and wearable OEMs now integrate up to a dozen sensor types per device, supporting features such as air-quality measurement, advanced biometrics, and self-learning activity tracking. Bosch confirms that more than half of 2025 handset launches ship with its multi-sensor modules. High-volume consumer demand delivers scale economies that drive per-unit cost down across industrial and automotive tiers, opening new price-performance thresholds. Miniaturisation and milliwatt-level power consumption perfected for wearables are now migrating into factory condition-monitoring nodes and autonomous delivery robots, accelerating cross-industry adoption of edge-ready sensor stacks.
High Upfront Deployment Cost
Comprehensive smart sensor rollouts frequently require parallel investment in edge gateways, private 5G networks, and workforce reskilling. For many small and midsized plants, total outlay can exceed 0.5% of annual revenue, deferring breakeven beyond four fiscal quarters. Milesight's turnkey IoT kit for Seoul SMEs bundles LoRaWAN gateways and controllers to lower integration friction, yet even this "all-in-one" package strains capital budgets. Cost headwinds are easing as MEMS volumes scale, but budgetary caution is expected to temper adoption among cash-constrained operators over the next 24 months.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Automotive & E-health Safety Mandates
- On-sensor Edge-AI Lowers Latency
- Complex Design & Integration Skill Gap
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Pressure sensors contributed USD 21.88 billion in 2024, translating to the largest 28.40% share of the smart sensors market. The segment's durability stems from its irreplaceable role in ADAS braking, EV battery management, and medical ventilators. Parallel innovation in silicon-carbide diaphragms now extends operating envelopes above 600 °C for aerospace and hydrogen fuel-cell stacks. Image sensors, while smaller in revenue terms, are forecast to grow at 19.20% CAGR as autonomous driving mandates make pedestrian-detection cameras standard equipment. Integration of global-shutter and event-based pixels is allowing high-contrast performance under rapidly changing lighting, enabling vehicle OEMs to comply with AEB regulations without expensive LiDAR redundancy.
Demand diversification is also reshaping unit economics. Temperature, humidity, and flow sensors are piggy-backing on smart-city water-grid and data-center thermal-management projects, while six-axis position sensors are becoming mandatory in collaborative robots. Hybrid modules that blend pressure, temperature, and relative humidity sensing deliver installation savings and strengthen vendor lock-in by raising switching costs for OEMs.
MEMS devices captured 46.00% of smart sensors market share in 2024 due to mature foundry ecosystems and cost structures tuned for smartphone volumes. Bosch alone shipped over 6 billion MEMS units in 2024, underscoring the scale advantage. However, photonic and quantum-enhanced sensors are projected to expand at 21.50% CAGR and could clip MEMS share in high-precision navigation and medical diagnostics. Citigroup estimates the quantum sensing addressable market could reach USD 1.4 billion by 2030, catalyzing venture capital inflows. MEMS incumbents are responding by co-integrating BioMEMS channels and edge-AI DSP cores to keep volume buyers within their technology roadmap.
Industry consortia such as the US-JOINT program, which includes 3M, are accelerating material R&D to secure domestic supply chains for advanced substrates. A parallel push into neuromorphic compute tiles embedded in MEMS modules aims to deliver cognitive functionality without sacrificing the size-cost advantage that underpin MEMS leadership.
The Smart Sensors Market is Segmented by Type (Flow Sensor, Humidity Sensor, Position Sensor, Pressure Sensor, and More), by Technology (MEMS, CMOS, Optical Spectroscopy, and More), by Component (Analog-To-Digital Converter, Digital-To-Analog Converter, Amplifier, and More), by Application (Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, and More), and by Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific delivered 44.30% of 2024 global revenue and is expected to record a 19.70% CAGR through 2030, underpinned by China's 14th Five-Year Plan subsidies for domestic sensing ICs and Japan's coordinated quantum-sensing R&D grants. China's domestic market hit CNY 285 billion (USD 39.8 billion) in 2024, with automotive, factory automation, and network communications each capturing above-20% share. Regional foundries benefit from captive demand and lower input-cost inflation, prompting vertically integrated OEMs to localise entire supply chains.
North America remains technological bellwether, particularly in automotive ADAS and aerospace sensing. Honeywell's strategic partnership with NXP to co-develop AI-ready avionics exemplifies the region's focus on functional safety and edge compute. Ongoing US industrial-policy incentives, including CHIPS Act grants, are encouraging on-shoring of MEMS lines by ams OSRAM and GlobalFoundries, improving regional resilience.
Europe, while trailing APAC in volume, benefits from regulatory pull. The EU General Safety Regulation II sets a baseline of mandatory sensor suites in every new vehicle, guaranteeing steady volume ramps even in economic downturns. Additionally, corporate carbon-reduction targets are stimulating demand for building-automation and industrial-efficiency sensors across Germany, France, and the Nordics.
Emerging markets in the Middle East, Africa, and South America show accelerating sensor uptake through smart-city and resource-sector digitisation agendas. Saudi Arabia's giga-projects require dense environmental and traffic-management sensor grids, whereas Chilean copper mines are installing ruggedised vibration sensors to raise extraction efficiency. Low-latency satellite backhaul solutions are easing connectivity barriers, allowing these regions to adopt advanced sensing without legacy telecom infrastructure.
- ABB
- Honeywell International
- Eaton Corporation
- Analog Devices
- Infineon Technologies
- NXP Semiconductors
- STMicroelectronics
- Siemens AG
- TE Connectivity
- Legrand
- General Electric
- Vishay Intertechnology
- Bosch Sensortec
- Texas Instruments
- Omron Corporation
- Sensirion AG
- Murata Manufacturing
- Sony Semiconductor
- Samsung Electronics
- Robert Bosch GmbH
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Energy-efficiency push across industrial IoT
- 4.2.2 Consumer-electronics sensor proliferation
- 4.2.3 Automotive and e-health safety mandates
- 4.2.4 Miniaturisation and wireless advances
- 4.2.5 On-sensor edge-AI lowers latency
- 4.2.6 ESG-driven live-monitoring adoption
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront deployment cost
- 4.3.2 Complex design and integration skill gap
- 4.3.3 IoT cybersecurity exposure
- 4.3.4 Rare-earth packaging supply risk
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Flow Sensors
- 5.1.2 Humidity Sensors
- 5.1.3 Position Sensors
- 5.1.4 Pressure Sensors
- 5.1.5 Temperature Sensors
- 5.1.6 Image/Optical Sensors
- 5.1.7 Other Types
- 5.2 By Technology
- 5.2.1 MEMS
- 5.2.2 CMOS
- 5.2.3 Optical Spectroscopy
- 5.2.4 Quantum and Photonic
- 5.2.5 Other Technologies
- 5.3 By Component
- 5.3.1 Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 5.3.2 Digital-to-Analog Converter
- 5.3.3 Amplifier
- 5.3.4 Transceiver / RF Front-End
- 5.3.5 Embedded AI Core
- 5.3.6 Other Components
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Aerospace and Defence
- 5.4.2 Automotive and Transportation
- 5.4.3 Healthcare and Medical Devices
- 5.4.4 Industrial Automation
- 5.4.5 Building and Home Automation
- 5.4.6 Consumer Electronics
- 5.4.7 Agriculture and Environmental
- 5.4.8 Other Applications
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.2 Germany
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 Russia
- 5.5.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 APAC
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 Rest of APAC
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 UAE
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.2.3 Kenya
- 5.5.5.2.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ABB
- 6.4.2 Honeywell International
- 6.4.3 Eaton Corporation
- 6.4.4 Analog Devices
- 6.4.5 Infineon Technologies
- 6.4.6 NXP Semiconductors
- 6.4.7 STMicroelectronics
- 6.4.8 Siemens AG
- 6.4.9 TE Connectivity
- 6.4.10 Legrand
- 6.4.11 General Electric
- 6.4.12 Vishay Intertechnology
- 6.4.13 Bosch Sensortec
- 6.4.14 Texas Instruments
- 6.4.15 Omron Corporation
- 6.4.16 Sensirion AG
- 6.4.17 Murata Manufacturing
- 6.4.18 Sony Semiconductor
- 6.4.19 Samsung Electronics
- 6.4.20 Robert Bosch GmbH
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment



















