
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1850229
헬스케어 사이버 보안 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Healthcare Cyber Security - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
헬스케어 사이버 보안 시장은 2025년에 357억 8,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 899억 3,000만 달러로 확대될 전망이며, 2025년-2030년 18.59%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다.

지출의 급증은 기록적인 침입의 파도로부터 전자적으로 보호된 의료 정보를 보호하려는 업계 전반의 분주를 반영합니다. 의료 제공자는 2024년에 677건의 심각한 침해를 보고했으며, 1억 8,240만 건의 환자 기록이 유출되었습니다. 연방정부의 감독 강화, 특히 모든 새로운 연결 의료기기에 대한 식품의약국(FDA)의 제524B조의 요건은 제조자와 의료 제공업체에게 라이프사이클 보안 프로그램의 예산을 의무화합니다. 장비규칙과 병행하여 시민권국의 HIPAA 시행강화와 보건사회복지성의 자발적인 사이버 보안 및 성능 목표를 통해 이사회는 사이버 리스크를 기업의 톱 3의 과제로 밀어 올렸습니다. 정부로부터의 자금 제공은 이 기세를 증폭시키고 있습니다. 워싱턴의 2025년 통합 사이버 예산은 민간 기관에 130억 달러를 계상해, 그 일부는 레거시 시스템을 근대화하는 병원에 충당됩니다. 동시에 미국 병원 협회가 2024년 국가 행위자가 미국 시설을 표적으로 했다는 경고를 발행함으로써 제로 트러스트 프레임워크 및 실시간 모니터링 솔루션의 도입이 가속화되고 있습니다.
세계의 헬스케어 사이버 보안 시장 동향 및 인사이트
증가하는 사이버 공격의 빈도 및 고도화
보안 연구자들은 러시아, 중국, 북한, 이란과 관련된 적대 세력이 2024년 매일 병원 인프라를 조사하여 추정 2억 5,900만 건의 의료기록에 접촉하는 침해에 이르렀다는 것을 확인했습니다. 의료기록은 보험금 사기, 공갈, 간첩활동을 가능하게 하기 위해 부정 시장에서 고가로 거래되고 있습니다. 이 이중의 유용성은 집요한 정찰, 랜섬웨어, 공급망 공격의 원동력이 되고 있습니다. 인공지능 도구는 현재 스피어 피싱과 음성 딥페이크 사기를 자동화하고 사용자 기반 방어를 침식하고 있습니다. 공급자는 클라우드 워크로드 및 연결된 장치의 지속적인 모니터링, 다중 요소 인증 및 최소 권한 정책을 우선순위로 처리합니다.
규제 강화 및 규정 준수 부담
섹션 524B는 2023년 3월 이후 FDA에 제출된 모든 새로운 의료기기에 소프트웨어 부품표, 안전한 개발 증명 및 협력적인 취약성 공개 계획을 포함할 것을 의무화합니다. 시판 전 클리어런스를 넘어 제조자는 제품의 상업적 수명 동안 결함을 패치해야 합니다. 따라서 이러한 장비를 통합하는 병원은 펌웨어, 보안 권고 및 패치 상황을 실시간으로 추적할 수 있는 통합 리스크 관리 플랫폼의 예산을 확보해야 합니다. 동시에 HHS 사이버 보안 성능 목표는 불변 백업 및 특권 액세스 제어와 같은 기본 안전 가드를 개설하고 있으며, 많은 이사회는 이것을 사실 표준으로 취급합니다. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency가 권장하는 Identity, Credential 및 Access Management 프레임워크는 암호 중심 모델을 위험 기반 인증서 기반 인증으로 대체합니다.
소규모 의료기관의 예산 제약
소규모 병원에서는 영업 이익률이 2% 미만인 경우가 많으며 레이어드 보안 도구 및 24시간 365일 모니터링을 위한 충분한 자금이 없습니다. 최근의 폐쇄에 관한 조사에 따르면, 몸값 요구나 다운타임에 의해 유동성이 손상되면, 사이버 인시던트가 영구적인 폐쇄의 트리거가 될 수 있습니다. 의료 부문 조정 협의회는 사이버 보안을 Medicare의 허용 비용으로 분류할 것을 권장하지만, 환불 정책은 아직 검토 중입니다. 지속 가능한 자금이 출현하기 전까지는 구독 기반의 매니지드 감지 및 대응 서비스의 채용이 리스크 삭감의 주요 수단입니다.
부문 분석
조직이 광대한 임상 생태계 내에서 특권 자격 증명을 관리하는 데 중점을 두고 있기 때문에 2024년 헬스케어 사이버 보안 시장 규모의 26.2%를 아이덴티티 액세스 관리 도구가 차지했습니다. 그러나 수요는 보안 정보 및 이벤트 관리 플랫폼으로 이행하고 있으며, 2030년까지 CAGR 19.1%로 성장이 예측되고 있습니다. 이 변화는 지속적인 로그의 상관과 행동 분석이 경계 관리에 비해 신속하게 침해를 포함할 수 있다는 합의를 반영합니다. 예측 기간 동안 사이버 보안 로드맵은 단일 안티바이러스에서 SIEM, SOAR 및 사용자 엔티티 분석을 통합한 통합 검색 스택으로 예산을 재분배하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
리스크 컴플라이언스 제품군은 HIPAA, GDPR(EU 개인정보보호규정) 및 디바이스의 시판 후 감시 감사를 위한 문서화를 간소화하기 때문에 견고합니다. 암호화 및 데이터 유출 방지 모듈은 특히 공급업체가 여러 클라우드 테넌트 간에 방사선 이미지와 검사 데이터를 공유해야 하는 경우 제로 트러스트 아키텍처 내에서 지원을 수집합니다. 머신러닝에 의해 구축된 새로운 행동 분석 솔루션은 '기타 솔루션' 버킷에 위치하며 정밀의료 워크로드를 실험하는 연구 기관에서 자주 시험적으로 도입됩니다.
네트워크 보안은 2024년 헬스케어 사이버 보안 시장 점유율의 34.3%를 유지했습니다. 이는 병원이 수술실, 제약 자동화 및 이미지 보존 시스템을 연결하는 VLAN을 계속 분할하기 때문입니다. 클라우드 워크로드에 대한 축족은 그럼에도 불구하고 우선 순위를 재구성합니다. 클라우드 보안 도구는 EHR 인스턴스를 하이퍼스케일 공급자로 마이그레이션하는 데 도움이 되며 CAGR 18.9% 증가가 예상됩니다.
엔드포인트 보호는 침대 측면의 주입 펌프에서 임상의의 스마트폰에 이르기까지 급증하는 장치의 이기종 혼합에 직면하고 있습니다. 애플리케이션 보안은 사내 개발 팀이 타사 API를 통합한 환자용 포털을 구축함에 따라 상승하며 런타임 보호 및 소프트웨어 구성 분석이 필요합니다. 14,000개가 넘는 헬스케어 IP 주소가 장치의 원격 측정을 공중 인터넷에 공개하고 있기 때문에 이전에 뒤로 접어들었던 의료 장치와 IoMT의 보안은 이제 이사회 수준의 문제가 되고 있습니다.
헬스케어 사이버 보안 시장은 솔루션 유형별(아이덴티티 액세스 관리, 리스크 컴플라이언스 관리 등), 보안 유형별(네트워크 보안, 엔드포인트 보안 등), 전개 모드별(온프레미스, 클라우드), 최종 사용자별(병원, 클리닉 등), 조직 규모별(대기업, 중소기업), 지역별로 분류됩니다. 시장 예측은 금액(달러)으로 제공됩니다.
지역별 분석
북미는 세계에서 가장 엄격한 PHI 규제, 성숙한 보험 제도, 1인당 높은 의료 IT 예산을 배경으로 2024년 34.5%의 헬스케어 사이버 보안 시장 점유율을 유지하고 있습니다. 2025년 민간 사이버 배분을 포함한 연방 정부의 자금 지원은 전자 차트의 현대화 및 클라우드 도입을 지원합니다. 미국은 또한 1억 명에 영향을 준 2024년 체인지 헬스케어 사건이라는 알려진 최대 규모의 정보 유출에 휩싸여 제로신뢰 로드맵과 제3자 리스크 감사가 확고해졌습니다. 캐나다의 범 캐나다 인공지능 전략과 멕시코의 사회보안 디지털화 이니셔티브는 SIEM 및 엔드포인트 감지 도구에 대한 지역 수요를 더욱 확대하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 CAGR 19.7%에서 가장 빠르게 성장하는 지역입니다. 일본, 한국, 인도에서는 국가 e-헬스 의무화로 클라우드에서 호스팅되는 환자 레지스트리와 안전한 ID 플랫폼이 통합되어 데이터 마스킹과 서비스로서의 암호화 현지 수요에 박차를 가하고 있습니다. 중국의 '건강한 중국 2030' 청사진에서는 사이버 보안이 스마트 병원을 실현하는 6개의 기둥 중 하나로 지정되어 국경을 넘어서는 데이터 흐름 규제에 대응하는 국내 방화벽 및 취약성 관리 벤더에 대한 주문이 증가하고 있습니다. 호주 연방 예산은 농촌의 원격 의료 보조금을 기둥으로 하고 있으며, 2022-2024년 디지털 헬스의 권유 요청이 92% 급증했습니다.
유럽의 프라이버시 중심 체제는 GDPR(EU 개인정보보호규정)의 벌금으로 이사회 수준의 책임이 명확해짐에 따라 꾸준한 성장을 보장합니다. 독일은 병원의 디지털화에 30억 유로를 할당하고 최소 15%를 IT 보안 강화에 충당하여 ID 오케스트레이션과 안전한 이메일 게이트웨이 조달을 촉진합니다. 프랑스는 지역 의료기관 간의 위협 인텔리전스 공유를 의무화하는 사이버 보안 부속 문서를 포함한 전자 건강 전략 'MaSante 2025'를 시행합니다. 영국의 NHS 'Data Saves Lives' 프로그램에서는 ISO 27001 인증 취득을 조건으로, 레거시인 페이징과 화상 처리 플랫폼의 근대화에 자금을 돌립니다.
중동 및 아프리카에서는 걸프 협력 회의 국가가 스마트 시티 병원을 건설하고 국가 사이버 보안 당국의 헬스케어 부문 통제 준수를 요구하고 도입이 가속화되고 있습니다. 남아프리카와 케냐는 클라우드 기반 예방 접종 레지스트리를 시험적으로 도입하고 환자 데이터를 파악하는 토큰화 계획도 도입하고 있습니다. 남미에서는 브라질의 오픈 헬스 이니셔티브와 아르헨티나의 전자 처방전이 꾸준히 확대되고 있으며, 모두 암호화 키 관리와 안전한 API 게이트웨이가 필요합니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 사이버 공격의 빈도 및 교묘화 증가
- 규제 의무 및 컴플라이언스의 부담
- 클라우드 기반 EHR 및 원격 의료의 급속한 도입
- 소규모 공급자의 낮은 보안 침투율
- 가치에 근거한 케어 모델에 연관된 의료기기의 보안
- IoMT 환경을 위한 제로 트러스트 프레임워크
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 소규모 공급자의 예산 제약
- 사이버 보안 전문 인력 부족
- 레거시 시스템의 상호 운용성 과제
- FDA 규제 대상 기기의 벤더 책임의 모호함
- 공급망 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
- 시장의 거시 경제 요인 평가
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 솔루션 유형별
- 아이덴티티 및 액세스 관리
- 리스크 및 컴플라이언스 관리
- 바이러스 대책 및 멀웨어 대책
- 보안 정보 및 이벤트 관리(SIEM)
- 침입 검지 및 방지(IDS/IPS)
- 암호화 및 데이터 유출 방지
- 기타 솔루션
- 보안 유형별
- 네트워크 보안
- 엔드포인트 보안
- 애플리케이션 보안
- 클라우드 보안
- 의료기기 및 IoMT 보안
- 전개 모드별
- 온프레미스
- 클라우드
- 최종 사용자별
- 병원 및 진료소
- 제약회사 및 바이오테크놀러지 기업
- 의료보험사
- 진단실험실
- 기타 최종 사용자
- 기업 규모별
- 대기업
- 중소기업
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 칠레
- 기타 남미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 영국
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 튀르키예
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 이집트
- 나이지리아
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- IBM Corporation
- AO Kaspersky Lab
- McAfee LLC
- Broadcom Inc.(Symantec)
- Trend Micro Inc.
- Palo Alto Networks Inc.
- Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- Fortinet Inc.
- CrowdStrike Holdings Inc.
- FireEye Inc.(Trellix)
- Imperva Inc.
- Claroty Ltd.(Medigate)
- Cynerio Ltd.
- Sophos Group plc
- Proofpoint Inc.
- Rapid7 Inc.
- CynergisTek Inc.
- Clearwater Compliance LLC
- Sensato Cybersecurity Solutions
- SecureLink Inc.
제7장 시장 기회 및 향후 전망
AJY 25.11.07The healthcare cybersecurity market stands at USD 35.78 billion in 2025 and is forecast to expand to USD 89.93 billion by 2030, progressing at an 18.59% CAGR during 2025-2030.
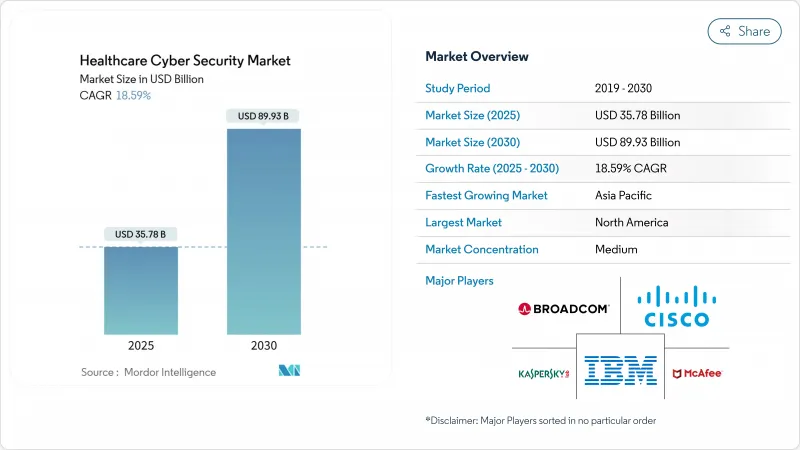
The spending surge reflects an industry-wide scramble to defend electronic protected health information against a record wave of intrusions. Healthcare providers reported 677 major breaches in 2024 that exposed 182.4 million patient records, underscoring the sector's high-value data and persistent threat landscape. Heightened federal oversight, notably the Food and Drug Administration's Section 524B requirements for all new connected medical devices, obliges manufacturers and providers to budget for life-cycle security programs. Parallel to device rules, the Office for Civil Rights' stiffer HIPAA enforcement and the Department of Health and Human Services' voluntary cybersecurity performance goals have pushed boards to elevate cyber risk to a top-three enterprise issue. Government funding amplifies the momentum: Washington's 2025 consolidated cyber budget earmarks USD 13 billion for civilian agencies, a portion of which flows to hospitals modernizing legacy systems. Simultaneously, the American Hospital Association's alert that nation-state actors targeted United States facilities in 2024 catalyzes the uptake of zero-trust frameworks and real-time monitoring solutions.
Global Healthcare Cyber Security Market Trends and Insights
Escalating Frequency and Sophistication of Cyber-Attacks
Security researchers confirmed that adversaries linked to Russia, China, North Korea, and Iran probed hospital infrastructure daily in 2024, culminating in breaches that touched an estimated 259 million medical records. Health records command a premium on illicit markets because they enable insurance fraud, blackmail, and espionage. This dual utility fuels relentless reconnaissance, ransomware, and supply-chain attacks. Artificial-intelligence tooling now automates spear-phishing and voice deep-fake scams, eroding user-based defenses. Providers respond by prioritizing continuous monitoring, multi-factor authentication, and least-privilege policies across cloud workloads and connected devices.
Regulatory Mandates and Compliance Burden
Section 524B requires every new medical device submitted to the FDA after March 2023 to include a Software Bill of Materials, secure development attestations, and a plan for coordinated vulnerability disclosure. Beyond pre-market clearance, manufacturers must patch flaws for the product's commercial life. Hospitals integrating these devices, therefore, budget for integrated risk management platforms able to track firmware, security advisories, and patch status in real time. Simultaneously, the HHS Cybersecurity Performance Goals outline baseline safeguards-such as immutable backups and privileged access controls-that many boards treat as de facto standards. Identity, Credential, and Access Management frameworks endorsed by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency replace password-centric models with risk-based, certificate-driven authentication.
Budget Constraints in Small Providers
Smaller hospitals often run on operating margins below 2%, leaving inadequate reserves for layered security tooling and 24X7 monitoring. Investigations into recent closures show cyber incidents can trigger permanent shutdowns when ransom demands and downtime erode liquidity. The Healthcare Sector Coordinating Council recommends classifying cybersecurity as an allowable Medicare expense, yet reimbursement policy remains under review. Until sustainable funding emerges, adoption of subscription-based managed detection and response services is the primary avenue for risk reduction.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid Cloud-Based EHR and Tele-Health Adoption
- Low Security Penetration Among Smaller Providers
- Shortage of Specialized Cyber-Security Talent
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Identity and Access Management tools accounted for 26.2% of the healthcare cybersecurity market size in 2024 as organizations focused on controlling privileged credentials inside sprawling clinical ecosystems. However, demand is shifting toward Security Information and Event Management platforms, which are forecast to grow at 19.1% CAGR to 2030. The change reflects a consensus that continuous log correlation and behavioral analytics offer faster breach containment than perimeter controls alone. Over the forecast period, cybersecurity roadmaps show budget reallocation from stand-alone antivirus toward converged detection stacks that integrate SIEM, SOAR, and user-entity analytics.
Risk and compliance suites remain steady because they streamline documentation for HIPAA, GDPR, and device post-market surveillance audits. Encryption and data-loss-prevention modules gain traction within zero-trust architectures, especially where providers must share radiology images and lab data across multiple cloud tenants. Emerging behavioral analytics solutions built with machine learning sit in the "other solutions" bucket and are frequently piloted in research institutes experimenting with precision medicine workloads.
Network security retained 34.3% of the healthcare cybersecurity market share in 2024 because hospitals continue to segment VLANs connecting operating rooms, pharmaceutical automation, and picture-archiving systems. The pivot to cloud workloads is nonetheless reshaping priorities: cloud security tools are poised for an 18.9% CAGR, propelled by migrations of EHR instances to hyperscale providers.
Endpoint protection confronts proliferating device heterogeneity, from bedside infusion pumps to clinician smartphones. Application security rises as in-house development teams build patient-facing portals that integrate third-party APIs, necessitating runtime protection and software composition analysis. Medical-device and IoMT security, once an afterthought, is now a board-level issue because more than 14,000 healthcare IP addresses expose device telemetry to the public internet-a statistic that rallies funding for agentless network detection and regulated device patch orchestration.
Healthcare Cybersecurity Market is Segmented by Solution Type (Identity and Access Management, Risk and Compliance Management, and More), Security Type (Network Security, Endpoint Security, and More), Deployment Mode (On-Premises and Cloud), End User (Hospitals and Clinics, and More), Organization Size (Large Enterprises and Small and Medium Enterprises), and by Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America maintained 34.5% healthcare cyber security market share in 2024, backed by the world's strictest PHI regulations, a mature insurance system, and high per-capita health IT budgets. Federal funding, including the 2025 civilian cyber allocation, underwrites modernization of electronic health records and cloud adoption. The United States also endured the largest known breach the 2024 Change Healthcare incident affecting 100 million individuals which solidified zero-trust roadmaps and third-party risk audits. Canada's Pan-Canadian Artificial Intelligence Strategy and Mexico's social-security digitization initiatives further enlarge regional demand for SIEM and endpoint detection tools.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing territory at 19.7% CAGR. National e-health mandates in Japan, South Korea, and India integrate cloud-hosted patient registries with secure identity platforms, spurring local demand for data-masking and encryption-as-a-service offerings. China's Healthy China 2030 blueprint designates cybersecurity one of six enabling pillars for smart hospitals, boosting orders for domestic firewall and vulnerability-management vendors that meet cross-border data flow restrictions. Australia's federal budget anchors subsidies for rural tele-health, leading to a 92% jump in digital-health solicitation requests from 2022-2024.
Europe's privacy-centric regime ensures steady growth as GDPR fines crystallize board-level accountability. Germany allocates EUR 3 billion to hospital digitization with at least 15% reserved for IT security enhancements, stimulating procurement of identity orchestration and secure email gateways. France implements its "MaSante 2025" e-health strategy with a cybersecurity annex that mandates threat-intelligence sharing among regional health agencies. The United Kingdom's NHS "Data Saves Lives" program directs funds to modernize legacy paging and imaging platforms, contingent upon ISO 27001 certification.
The Middle East and Africa exhibit accelerating adoption as Gulf Cooperation Council states build smart-city hospitals and seek compliance with the National Cybersecurity Authority's Healthcare Sector Controls. South Africa and Kenya pilot cloud-based immunization registries accompanied by tokenization schemes that de-identify patient data. South America registers steady expansion led by Brazil's open-health initiatives and Argentina's electronic prescription rollout, both of which require encryption key management and secure API gateways.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- IBM Corporation
- AO Kaspersky Lab
- McAfee LLC
- Broadcom Inc. (Symantec)
- Trend Micro Inc.
- Palo Alto Networks Inc.
- Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- Fortinet Inc.
- CrowdStrike Holdings Inc.
- FireEye Inc. (Trellix)
- Imperva Inc.
- Claroty Ltd. (Medigate)
- Cynerio Ltd.
- Sophos Group plc
- Proofpoint Inc.
- Rapid7 Inc.
- CynergisTek Inc.
- Clearwater Compliance LLC
- Sensato Cybersecurity Solutions
- SecureLink Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating frequency and sophistication of cyber-attacks
- 4.2.2 Regulatory mandates and compliance burden
- 4.2.3 Rapid cloud-based EHR and tele-health adoption
- 4.2.4 Low security penetration among smaller providers
- 4.2.5 Medical-device security tied to value-based care models
- 4.2.6 Zero-trust frameworks for IoMT environments
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Budget constraints in small providers
- 4.3.2 Shortage of specialised cyber-security talent
- 4.3.3 Legacy system interoperability challenges
- 4.3.4 Vendor-liability ambiguity for FDA-regulated devices
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Assesment of Macroeconomic Factors on the Market
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Solution Type
- 5.1.1 Identity and Access Management
- 5.1.2 Risk and Compliance Management
- 5.1.3 Antivirus and Antimalware
- 5.1.4 Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- 5.1.5 Intrusion Detection / Prevention (IDS/IPS)
- 5.1.6 Encryption and Data-Loss Prevention
- 5.1.7 Other Solutions
- 5.2 By Security Type
- 5.2.1 Network Security
- 5.2.2 Endpoint Security
- 5.2.3 Application Security
- 5.2.4 Cloud Security
- 5.2.5 Medical-Device / IoMT Security
- 5.3 By Deployment Mode
- 5.3.1 On-premise
- 5.3.2 Cloud
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Hospitals and Clinics
- 5.4.2 Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology Firms
- 5.4.3 Health-insurance Providers
- 5.4.4 Diagnostic Laboratories
- 5.4.5 Other End Users
- 5.5 By Organisation Size
- 5.5.1 Large Enterprises
- 5.5.2 Small and Medium Enterprises
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Chile
- 5.6.2.4 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 France
- 5.6.3.3 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Spain
- 5.6.3.6 Russia
- 5.6.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 Japan
- 5.6.4.3 India
- 5.6.4.4 South Korea
- 5.6.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Egypt
- 5.6.5.2.3 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.2.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 6.4.2 IBM Corporation
- 6.4.3 AO Kaspersky Lab
- 6.4.4 McAfee LLC
- 6.4.5 Broadcom Inc. (Symantec)
- 6.4.6 Trend Micro Inc.
- 6.4.7 Palo Alto Networks Inc.
- 6.4.8 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Fortinet Inc.
- 6.4.10 CrowdStrike Holdings Inc.
- 6.4.11 FireEye Inc. (Trellix)
- 6.4.12 Imperva Inc.
- 6.4.13 Claroty Ltd. (Medigate)
- 6.4.14 Cynerio Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Sophos Group plc
- 6.4.16 Proofpoint Inc.
- 6.4.17 Rapid7 Inc.
- 6.4.18 CynergisTek Inc.
- 6.4.19 Clearwater Compliance LLC
- 6.4.20 Sensato Cybersecurity Solutions
- 6.4.21 SecureLink Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment

















