
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1444714
세계 미생물 농약 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 업계 동향과 통계, 성장 예측(2024-2029년)Microbial Pesticides - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
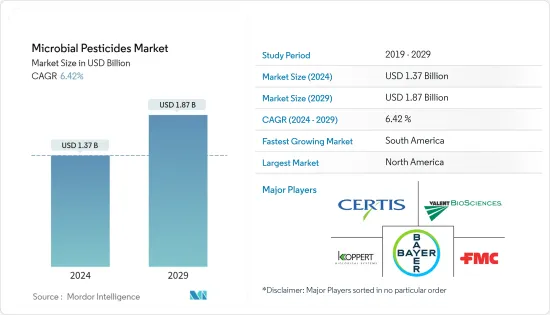
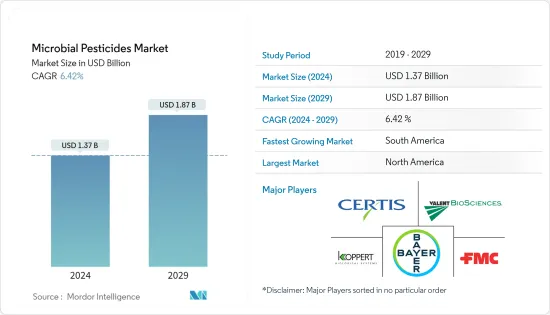
미생물 농약 시장 규모는 2024년 13억 7,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2029년까지 18억 7,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 예측 기간(2024년-2029년) 동안 복합 연간 성장률(CAGR) 6.42%로 성장할 전망입니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 작물 보호에서 화학농약이나 합성농약의 만연이 계속되고 있는 한편, 인간과 동물의 건강 및 환경에 대한 우려가 미생물농약 증가를 촉진하는 중요한 역할을 하고 있습니다. 일부 국가는 잔류 농약의 수에 대한 규제에 중점을 두고 수입에 대한 엄격한 접근법을 채택하고 있습니다. 식품의 안전성과 품질에 대한 수요가 증가함에 따라 합성 살충제보다 미생물 살충제의 인기가 높아지고 있습니다.
- 통합 해충 관리 프로그램(IPM)에 미생물 살충제를 통합하면 작물 수율에 영향을주지 않고 합성 살충제의 필요성을 크게 줄일 수 있습니다. 식량농업기관(FAO)에 따르면 2021년 총 수확면적은 14억 6,500만 헥타르로 미생물이나 곤충 침입이 적은 작물 생산 수요 증가로 전년 14억 4,270만 헥타르를 웃돌았습니다.
- 경작 가능한 토지가 감소하는 가운데 기술 변화가 농업 생산성을 높이는 주요 촉진요인이 되고 있습니다. 수익 증가, 지식 향상 및 커뮤니케이션 채널 향상으로 많은 국가의 소비자들은 유기적인 방식으로 생산되는 고품질의 저비용 식품을 찾고 있습니다. 동시에 천연 자원을 보호하고 환경 압력을 제한하며 농촌 생존 가능성과 동물 복지에 더 많은 관심을 기울이는 기술을 사용하여 식품 생산에 대한 수요도 높아지고 있습니다. 따라서 정부는 지속가능한 농업시스템을 위한 새로운 농업기술의 도입을 주장합니다.
미생물 농약 시장 동향
유기 토지 증가와 새로운 농업 기술 적응
- 새로운 농업 기술의 적응이 진행됨에 따라 미생물 살충제와 같은 제품이 더 안전하게 현장에서 사용됩니다. 지속 가능한 농업 지원과 주류 농업 수용을 통해 농부는 화학농약의 사용을 최소화하여 비용, 생산성, 환경을 절약할 수 있습니다. 지속가능한 농업에서 미생물 농약의 사용은 여러 환경 및 사회적 우려를 해결하고 생산자, 노동자, 소비자에게 혁신적이고 경제적으로 실행 가능한 기회를 제공합니다. 이것은 미생물 살충제 시장의 성장의 주요 추진력 중 하나입니다.
- 유기 무역협회(OTA)에 따르면 2020년 미국의 유기 매출은 619억 2,000만 달러로 전년 대비 12.4%의 성장률을 기록했습니다. 경제적인 관점에서 이 유기 매출의 성장률을 그 절반 이하의 성장률인 4.9%에 달한 식품 및 비식품의 미국 시장 전체와 비교하면, 소비자 행동이 유기로 이행하고 있는 것은 분명합니다.
- 유기농 식품은 유독한 살충제, 합성 비료, GMO를 포함하지 않는 식품을 제공하는 농업 시스템에서 생산되기 때문에 인기를 끌고 있습니다. 따라서 유기농 제품은 고품질로 간주되며 건강과 환경 모두에 더 안전한 것으로 간주됩니다.
북미가 시장을 독점
- 화학제초제나 살충제의 영향에 대한 의식이 높아짐에 따라, 특히 통합적인 잡초관리의 경우, 대체제로서 생물제초제를 채용할 수 있습니다. 생물 제초제는 식물 독, 병원체 및 기타 미생물로 구성된 제초제입니다. 생물학적 잡초 방제로 사용됩니다.
- 생물 제초제는 곰팡이, 박테리아, 원생 동물과 같은 미생물로부터의 화합물 및 이차 대사산물, 또는 식물 독성 식물의 잔류물, 추출물 또는 다른 식물 종으로부터 유래된 단일 화합물로서 수득됩니다. 이 지역 수요는 그린 농업에 대한 관심 증가와 재등록 및 성능 문제로 인해 기존 제품의 대부분이 손실되는 등 많은 요인에 의해 움직이고 있습니다.
- 제품 개발로 미생물 살충제 수요도 높아지고 있습니다. 현재 시장에서는 기존의 화학 살충제와 경쟁하고 이를 보충할 수 있는 보다 우수한 생물학적 활성 성분 및 제품을 사용할 수 있습니다. 미생물생물농약부문은 지속가능한 식량생산에 대한 의식 증가, 화학물질의 과잉사용에 대한 농가의 우려, 화학작물 보호 비용 증가에 의해 추진되고 있습니다. 이 지식 증가는 미국의 생물 부문의 급성장에 반영되어 미생물 살충제를 사용할 수있는 좋은 기회를 제공합니다.
- 또한, 2021년 6월 EPA는 새로운 미생물 활성 성분인 Bacillus velezensis RTI301 균주 및/또는 Bacillus subtilis RTI477 균주를 포함한 5개의 생물농약 제품을 등록했습니다. 이 생물 농약 제품은 2개의 제조 제품과 3개의 최종 용도 제품으로 구성되어 있으며, 천연 박테리아를 이용하여 묘목과 농작물을 곰팡이 성장으로부터 보호합니다. EPA는 또한 용도가 등록된 제품이 대상외의 생물종에 영향을 미치지 않는다고 결론지었습니다. 따라서 국내에서 새로운 미생물 성분을 승인하기 위해 EPA가 취한 이러한 적극적인 노력은 미생물 농약 시장의 성장의 원동력이 되고 있습니다.
미생물 농약 산업 개요
미생물 살충제 시장은 매우 세분화되어 있으며, 많은 기업들이 시장 점유율의 대부분을 지배하고 있으며, 몇몇 중소기업과 사설 브랜드도 존재합니다. Bayer CropScience AG, FMC Corporation, Koppert Biological Systems, Valent Biosciences Corporation 및 Certis USA LLC는 조사 대상 시장에서 유명한 기업의 일부입니다. 신제품 출시, 제휴, 인수는 국내 시장의 대기업이 채용하는 주요 전략입니다. 혁신과 확장 외에도 R&D 투자 및 새로운 제품 포트폴리오 개발은 향후 몇 년동안 중요한 전략이 될 수 있습니다. 미생물 살충제를 개발하는 기업 간의 대규모 인수는 바이오 제품에 대한 관심이 빠르게 증가하고 있음을 보여줍니다. 시장관계자들은 확대되는 마켓플레이스에서 생물학 조사 부문을 다양화하기 위해 이 시장에 많은 투자를 하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 역학
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체 제품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 격렬
제5장 시장 세분화
- 성분의 유형
- 박테리아 기반 살충제
- 균류 기반의 살충제
- 바이러스 기반 살충제
- 기타 성분의 유형
- 제품 유형
- 미생물 살균제
- 미생물 살충제
- 기타 제품 유형
- 용도
- 곡물 및 곡류
- 콩류 및 지방종자
- 과일 및 채소
- 기타 용도
- 지역
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 기타 북미
- 유럽
- 스페인
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 러시아
- 이탈리아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 가장 채용된 전략
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Valent BioSciences
- Certis USA LLC
- Bio Works Inc.
- Agri Life
- Marrone Bio Innovations
- Novozymes Biologicals
- Bayer CropScience
- Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd
- IsAgro Spa
- De Sangosse
- FMC Corporation
제7장 시장 기회와 미래 동향
BJH 24.03.15The Microbial Pesticides Market size is estimated at USD 1.37 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 1.87 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 6.42% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
Key Highlights
- While the prevalence of chemical or synthetic pesticides in crop protection is continuing, concerns about human and animal health and the environment are playing key roles in driving the growth of microbial pesticides. Several countries are adopting a stringent approach concerning the number of imports, focusing on regulating the number of pesticide residues. Due to the growing demand for food safety and quality, microbial pesticides are gaining popularity over their synthetic counterparts.
- When incorporated into an integrated pest management program (IPM), the use of microbial pesticides will reduce the need for synthetic pesticides to a very large extent without affecting crop yield rates. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the total area harvested in 2021 accounted for 1,465.0 million hectares, higher than the previous year with 1,442.7 million hectares due to increased demand for crop production with little microbiological and insect infestation.
- Technological change is the major driving factor for boosting agricultural productivity as arable land decreases. With higher incomes, greater knowledge, and improved communication channels, consumers in many countries demand low-cost food with high quality produced through organic methods. At the same time, the demand for food to be produced using techniques that conserve natural resources, limit environmental pressures, and pay greater attention to rural viability and animal welfare is also increasing. Therefore, governments insist on adopting new farm technologies for sustainable farming systems.
Microbial Pesticides Market Trends
Increasing Organic Land and Adaptation of New Farming Technologies
- The increasing adaptation of new farm technologies led to safer field applications of products like microbial pesticides. Sustainable farming support and acceptance within mainstream agriculture drive farmers toward minimizing the use of chemical pesticides, thereby saving costs, productivity, and the environment. The use of microbial pesticides in sustainable agriculture addresses several environmental and social concerns and offers innovative and economically viable opportunities for growers, laborers, and consumers. This is one of the major drivers for the market's growth of microbial pesticides.
- According to Organic Trade Association (OTA), in 2020, Organic sale in the United States was USD 61.92 billion, with a growth rate of 12.4% from the previous year. If we compare this growth rate of organic sales from an economic perspective with the total United States market for food and non-food products, which grew at less than half the rate, at 4.9%, the consumer behavior shift towards organic is clear.
- Organic food has gained popularity because it is produced in an agricultural system that provides food free from toxic pesticides, synthetic fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). So organic products are seen as being of high quality and are considered safer for both health and the environment.
North America Dominates the Market
- With increasing awareness of the effects of chemical herbicides and pesticides, bioherbicides can be adopted as an alternative, especially for integrated weed management. Bioherbicides are herbicides consisting of phytotoxins, pathogens, and other microbes. It is used as biological weed control.
- Bioherbicides are obtained as compounds and secondary metabolites from microbes such as fungi, bacteria, and protozoa, or phytotoxic plant residues, extracts, or single compounds derived from other plant species. Demand in the region is driven by a number of factors, including the increased interest in green agricultural practices and the loss of many conventional products to reregistration and/or performance issues.
- Product development has also driven up the demand for microbial pesticides. Better biological active ingredients and products are available in the present market that can compete with and complement conventional chemical pesticides. The microbial biopesticide sector is driven by a growing awareness of sustainable food production, farmers' concerns about excessive chemical use, and the rising expense of chemical crop protection. This increased knowledge is reflected in the booming biological sector in the United States, which provides an excellent opportunity to use microbial pesticides.
- Furthermore, in June 2021, EPA registered five biopesticide products containing Bacillus velezensis strain RTI301 and/or Bacillus subtilis strain RTI477, new microbial active ingredients. These biopesticide products consisted of two manufacturing and three end-use products, utilizing natural bacteria to protect seedlings and/or agricultural crops from fungal growth. EPA also concluded the products with registered uses would not affect any nontarget species. Thus, such active initiatives taken by the EPA to approve new microbial ingredients in the country are a driving factor for the growth of the microbial pesticide market.
Microbial Pesticides Industry Overview
The market for microbial pesticides is extremely fragmented, with a large number of firms controlling the majority of the market share, along with several small companies and private labels. Bayer CropScience AG, FMC Corporation, Koppert Biological Systems, Valent Biosciences Corporation, and Certis USA LLC are some of the prominent companies in the market studied. New product launches, partnerships, and acquisitions are the major strategies adopted by the leading companies in the market in the country. Along with innovations and expansions, investments in R&D and developing novel product portfolios will likely be crucial strategies in the coming years. The major acquisitions between companies to develop microbial pesticides indicate that the focus on bio-based products is increasing rapidly. The players in the market are investing heavily in this market to diversify their biological research divisions in the expanding marketplace.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Ingredient Type
- 5.1.1 Bacteria-based Pesticides
- 5.1.2 Fungi-based Pesticides
- 5.1.3 Virus-based Pesticides
- 5.1.4 Other Ingredient Types
- 5.2 Product Type
- 5.2.1 Microbial Fungicide
- 5.2.2 Microbial Insecticide
- 5.2.3 Other Product Types
- 5.3 Application
- 5.3.1 Grains & Cereals
- 5.3.2 Pulses & Oilseeds
- 5.3.3 Fruits & Vegetables
- 5.3.4 Other Applications
- 5.4 Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Spain
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Germany
- 5.4.2.5 Russia
- 5.4.2.6 Italy
- 5.4.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Africa
- 5.4.5.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Most Adopted Strategies
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Valent BioSciences
- 6.3.2 Certis USA LLC
- 6.3.3 Bio Works Inc.
- 6.3.4 Agri Life
- 6.3.5 Marrone Bio Innovations
- 6.3.6 Novozymes Biologicals
- 6.3.7 Bayer CropScience
- 6.3.8 Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd
- 6.3.9 IsAgro Spa
- 6.3.10 De Sangosse
- 6.3.11 FMC Corporation



















