
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1851022
프라이빗 LTE 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Private LTE - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
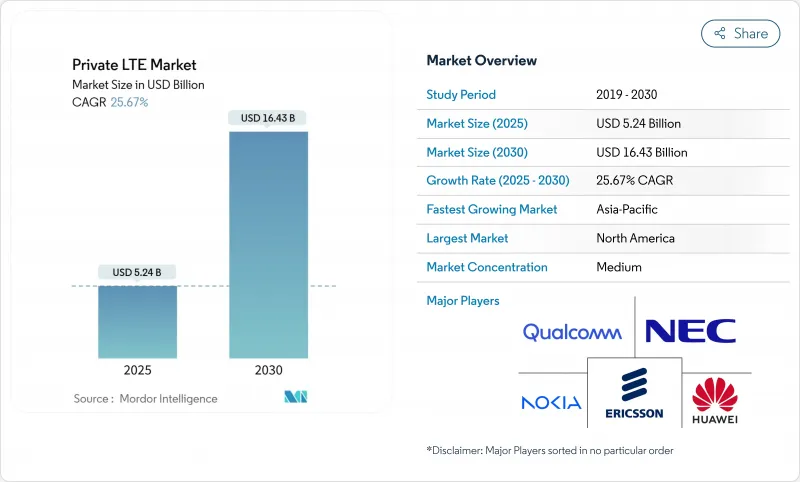
프라이빗 LTE 시장의 2025년 시장 규모는 52억 4,000만 달러로 예상되며, 2030년에는 164억 3,000만 달러에 이르고, CAGR 25.67%로 확대될 것으로 예측됩니다.

기업이 업무를 디지털화하고 미션 크리티컬 워크로드를 전용 셀룰러 인프라에 배치함에 따라 보안 중심의 결정론적 성능이 채택을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 공유 주파수 대역의 조기 상용화, 인더스트리 4.0 프로그램의 급속한 진전, 가혹한 환경에서의 초고신뢰성 저지연 통신(URLLC)의 필요성 증가는 모두 성장을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 산업 현장은 현재 예측 가능한 커버리지, 간소화된 서비스 품질 관리, 민감한 운영 데이터에 대한 완전한 관리 옵션을 제공하기 위해 공공 대체 서비스보다 프라이빗 LTE를 선호합니다. 엣지 컴퓨팅의 통합은 또 다른 촉진요인으로, 라운드트립 지연 없이 거대한 센서 스트림의 로컬 분석을 가능하게 합니다. 생태계 혁신 중에서 특히 개방형 RAN, 스몰셀 폼 팩터 및 CBRS 장치의 보급은 진입 장벽을 낮추고 프라이빗 LTE 시장의 대응 가능한 기반을 넓히고 있습니다.
세계의 프라이빗 LTE 시장의 동향과 인사이트
주파수 대역의 자유화로 기업 도입이 급증
주요 하이라이트
- 규제 당국은 미드밴드 주파수를 재할당하여 CBRS와 같은 프레임워크 하에서 기업이 고품질 주파수 대역에 접근할 수 있도록 합니다. 2023년 말까지 약 37만대의 CBRS 디바이스가 도입되었으며 공유 대역이 라이선스 취득의 장애물을 낮추고 네트워크 소유의 민주화를 실현함을 나타내고 있습니다. 합리적인 가격으로 간섭 관리된 액세스로 기존 독점 라이선스를 취득할 자원이 없었던 중견기업에도 프라이빗 LTE 시장이 개방되었습니다. 미국 이외에서는 독일, 일본, 호주가 공장, 항만, 공공시설에 맞춤형 커버리지 실적을 도입할 수 있는 로컬 라이선스를 발급하고 있습니다. 이 정책 전환은 공급업체의 생태계를 확대하고 스몰셀의 혁신을 자극하며 향후 3년간 프라이빗 LTE 네트워크의 도입이 기대되는 새로운 산업 사이트의 파이프라인을 형성하고 있습니다.
산업용 IoT가 제조업의 변화를 촉진
스마트 팩토리로의 도입은 30밀리초 이하의 대기 시간으로 수천 개의 센서를 유지할 수 있는 신뢰할 수 있는 무선 백본에 달려 있습니다. 프라이빗 LTE의 조기 도입 기업의 약 79%는 자동 유도 차량, AR 어시스트 유지보수, 디지털 트윈을 지원하기 위해 프라이빗 LTE를 도입한 후 6개월 이내에 플러스 ROI를 달성한 것으로 나타났습니다. 저밸런스 연결은 라인 밸런스 효율을 개선하고 예측 유지 보수, 품질 분석 및 공장 전체의 에너지 최적화를 촉진합니다. 제조업체 각사는 최초의 네트워크 가동 후 야드 관리나 작업자의 안전성을 확보하는 웨어러블 등의 이용 사례를 잇달아 발견하면서 프라이빗 LTE 시장에 자기 강화적인 채용 곡선을 만들어 내고 있습니다.
자본 집약이 채용 장벽으로 이어짐
프라이빗 LTE의 전개에는 무선 기기나 코어 기기, 탄력성이 있는 백홀, 사이트 공사, 그리고 지역에 따라서는 주파수 대역 사용료가 요구됩니다. 특히 중견기업에서는 초기 비용이 사내의 장애율을 상회하는 경우가 많습니다. 서비스형 네트워크 계약에 대한 관심이 증가하고 있는 이유는 운영 비용 구독이 자본 충격을 줄이고 지출을 생산성 향상과 일치시키기 때문입니다. 사이버 하드닝이나 다운타임 회피와 같은 무형의 장점을 정량화하는 것은 여전히 어려우며 예산 사이클을 장기화하고 있습니다. 개방형 RAN 하드웨어는 단가 절감을 보장하지만 셀룰러 전문 지식이 없는 조직의 경우 통합에 걸리는 오버헤드가 절약을 상쇄할 수 있습니다.
부문 분석
2024년 시장 세분화에서는 스몰셀, 패킷 코어 및 전송 장비에 대한 많은 지출을 반영하여 인프라 부문이 시장의 63%를 차지하였습니다. 그러나 서비스 수입은 CAGR 18.4%로 급속히 증가하고 있습니다. 이는 기업이 내부 기술 부족을 피하기 위해 시스템 통합자에 의존하기 때문입니다. Managed Services는 설계, 통합 및 24시간 365일 운영을 번들로 제공하며 공장 및 유틸리티자에게 예측 가능한 예산을 제공하는 동시에 Time-to-Value를 가속화하고 있습니다. 전문 서비스에 대한 수요는 그린필드 프로젝트에서 여전히 높지만 정기적인 관리 계약은 신규 계약에서 큰 점유율을 차지합니다.
무선 액세스 네트워크가 여전히 최대 자본을 차지하고 있지만 기업은 보안 정책을 시행하기 위해 현장 핵심 시스템을 강조하는 경향이 커지고 있습니다. 여러 플랜트 영역을 클라우드 대시보드에 연결하는 경우 전송 백홀 업그레이드를 양도할 수 없습니다. 벤더는 현재, '네트워크 인 어 박스' 키트(설정이 끝난 코어에 스몰 셀을 추가)를 추진하고 있어, 당일 액티베이션이 가능합니다. 펜트 네트웍스의 이러한 키트는 2025년 로스앤젤레스의 산불에서 긴급 대원의 통신을 유지하고 턴키 패키징이 기술에 익숙한 구매자를 넘어 프라이빗 LTE 시장을 넓히는 것을 강조하고 있습니다.
시분할 이중 통신은 2024년 매출의 55%를 차지하였고 CAGR은 17.1%로 가장 높을 것으로 예측됩니다. 비디오 감시 및 원격 측정의 비대칭 트래픽은 TDD의 동적 할당에 유리하며 희귀한 미드 밴드 채널의 처리량을 극대화합니다. 또한 TDD는 CBRS 대역 할당에 부합하기 때문에 새로운 프라이빗 LTE 시장 개발의 기본적인 입지를 강화할 것입니다.
주파수 분할 이중 통신은 업링크와 다운링크의 엄격한 분리가 중시되는 지연에 민감한 제어 시스템에서 수요를 유지합니다. 그러나 최신 스케줄러는 TDD 지터를 10ms 이하로 줄여 기존의 격차를 줄이고 있습니다. 향후 출시될 5G에서는 TDD 수치가 더욱 정교해져 기업이 5G NR 캐리어 어그리게이션으로 전환해도 현재 투자가 적절하게 유지될 수 있도록 보장합니다.
지역 분석
북미는 CBRS 프레임워크와 무선, 디바이스, 통합업체 파트너의 성숙한 에코시스템을 통해 2024년 매출의 38%를 차지하면서 선두에 섰습니다. 2024년 말 기준으로 세계 4,700개가 넘는 프라이빗 LTE와 5G 네트워크가 운영되기 시작했으며 미국이 상당한 점유율을 보유하였습니다. 제조업, 헬스케어, 유틸리티의 현지 5G 파일럿이 수요를 확대하여 하이퍼스케일러의 엣지 존이 주요 도시에서의 저지연 워크로드의 오프로드를 용이하게 합니다.
아시아태평양은 2025년부터 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)이 가장 높은 12.8%로 예상됩니다. 중국은 국가가 지원하는 공장과 광산의 네트워크를 전개하고, 일본은 mm파와 미드밴드로 로컬 5G 라이선스를 발행하고, 한국은 고밀도의 섬유 백본을 활용해 캠퍼스 코어를 호스팅합니다. 인도의 최근 주파수 정책 변경으로 자동차 공장과 제약 공장에서의 테스트가 진행되고 있습니다. 호주에서는 주로 원격지의 철광석과 리튬 채굴을 간소화하기 위해 이미 50개 이상의 프라이빗 LTE 시스템이 운영되고 있으며, ACMA에 따르면 시장은 2027년까지 6억 9,500만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.
GSMA에 따르면 유럽은 전개수로 2위를 달리고 있으며 2023년 중반까지 세계 개인 설치수의 약 40%를 차지하였습니다. 독일의 3.7-3.8GHz 대역 로컬 라이선스로 제조업 도입에 박차를 가하고 있으며, 영국의 공유 액세스 프레임워크는 항만과 농장용 라이선스를 간소화하고 있습니다. European 5G Observatory에 따르면 2024년 3월까지 개척 밴드의 73%가 할당되어 산업용 네트워크의 견고한 스펙트럼 기반이 형성되었습니다. 보다폰이 2,500개소에서 오픈 RAN을 전개할 것으로 발표하면서, 유럽 대륙 전체에서 설비 비용이 절감되어, 턴키 프로젝트를 요구하는 기업 바이어에게 간접적인 혜택을 가져올 것으로 기대되고 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 주파수 자유화와 CBRS 상용화
- 산업용 IoT와 인더스트리 4.0의 보급
- 가혹한 현장에서의 미션 크리티컬한 URLLC 수요
- 5G SA로의 원활한 이행 경로
- On-Premise 엣지 AI 대역폭 요건
- 오픈 RAN 스몰 셀 에코시스템에 의한 TCO 절감
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 높은 자본 지출과 불확실한 ROI
- 통합인력 부족
- 세분화된 디바이스 밴드 지원
- 민간 5G 파일럿 사업에 의한 예산의 카니발리제이션
- 밸류체인 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력/소비자
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
- 투자분석
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 컴포넌트별
- 인프라
- 무선 액세스(RAN)
- 코어(EPC/5GC)
- 백홀과 수송
- 서비스
- 전문 서비스
- 매니지드 서비스
- 인프라
- 기술별
- 주파수 분할 이중화(FDD)
- 시분할 이중화(TDD)
- 전개 모델별
- 집중형(C-RAN)
- 분산형
- 스펙트럼별
- 라이선싱
- 언라이선스(MulteFire, 5GHz)
- 공유(CBRS, LAA)
- 최종 사용자 업계별
- 제조업
- 에너지 및 유틸리티
- 광업, 석유 및 가스
- 운송 및 물류
- 공공 안전과 방위
- 헬스케어
- 기업/캠퍼스
- 기타
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 사우디아라비아
- 카타르
- 이스라엘
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 나이지리아
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Nokia
- Ericsson
- Huawei Technologies
- NEC Corp.
- Qualcomm
- Druid Software
- Sierra Wireless
- JMA Wireless
- Ruckus Networks(CommScope)
- Celona
- Airspan Networks
- Cisco Systems
- ZTE Corp.
- Samsung Electronics
- Airspan Networks
- Athonet(HPE)
- Motorola Solutions
- Mavenir Systems
- Amazon AWS Private 5G
- Verizon Business
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
제7장 시장 기회와 미래 전망
CSM 25.11.20The private LTE market is valued at USD 5.24 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 16.43 billion by 2030, expanding at a 25.67% CAGR.
Security-focused, deterministic performance is propelling adoption as enterprises digitize operations and place mission-critical workloads on dedicated cellular infrastructure. Early commercialization of shared spectrum, rapid progress on Industry 4.0 programs, and the rising need for ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC) in harsh settings all reinforce growth. Industrial sites now favour private LTE over public alternatives because it delivers predictable coverage, streamlined quality-of-service management, and the option to retain full control of sensitive operational data. Edge computing integration is another accelerant, enabling local analytics on massive sensor streams without round-trip delays. Ecosystem innovation-in particular, open RAN, small-cell form factors, and CBRS device proliferation-is lowering entry barriers and widening the private LTE market addressable base.
Global Private LTE Market Trends and Insights
Spectrum Liberalization Unlocks Enterprise Deployment Surge
Key Highlights
- Regulators are reallocating mid-band frequencies, giving enterprises unprecedented access to high-quality spectrum under frameworks such as CBRS. Around 370,000 CBRS devices had been deployed by end-2023, underscoring how shared bands reduce licensing hurdles and democratize network ownership.Affordable, interference-managed access has opened the private LTE market to mid-sized firms that previously lacked resources for exclusive licences. Beyond the United States, Germany, Japan, and Australia have issued local licences that let factories, ports, and utilities implement bespoke coverage footprints. The policy shift is expanding vendor ecosystems, stimulating small-cell innovation, and creating a pipeline of new industrial sites expected to deploy private LTE networks over the next three years.
Industrial IoT Drives Manufacturing Transformation
Smart-factory rollouts now hinge on reliable wireless backbones capable of sustaining thousands of sensors with latencies below 30 ms. Nearly 79% of early adopters said they achieved positive ROI within six months after installing private LTE to support automated guided vehicles, AR-assisted maintenance, and digital twins. Low-variance connectivity improves line-balance efficiency, which in turn drives predictive maintenance, quality analytics, and plant-wide energy optimisation. Manufacturers consistently discover incremental use cases, such as yard management and worker-safety wearables, once the initial network is live, creating a self-reinforcing adoption curve inside the private LTE market.
Capital Intensity Creates Adoption Barriers
Private LTE deployments involve radio and core equipment, resilient backhaul, site works and, in some regions, spectrum fees. Upfront costs often exceed internal hurdle rates, especially for mid-tier firms. Interest in network-as-a-service contracts is rising because OPEX subscriptions reduce capital shock and match spending to productivity gains. Quantifying intangible benefits such as cyber-hardening and downtime avoidance remains challenging, prolonging budget cycles. Open RAN hardware promises lower unit prices, yet integration overheads can erase savings for organisations lacking cellular expertise.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Mission-Critical Communications Enable Remote Operations
- Seamless Migration Path Toward 5G SA
- Integration Complexity Slows Implementation Velocity
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The infrastructure segment held 63% of the private LTE market in 2024, reflecting heavy spending on small cells, packet cores, and transport gear. Yet, services revenue is rising faster at an 18.4% CAGR because organisations lean on system integrators to sidestep internal skills shortages. Managed offerings bundle design, integration, and 24/7 operations, giving factories and utilities predictable budgets while accelerating time-to-value. Professional services demand remains high during greenfield projects, but recurring managed contracts are capturing a larger share of new bookings.
Radio access networks still account for the biggest slice of capital, though enterprises increasingly emphasise onsite core systems to enforce security policies. Transport backhaul upgrades are non-negotiable when connecting multiple plant zones to cloud dashboards. Vendors now promote "network-in-a-box" kits-pre-configured core plus small cells-capable of same-day activation. One such kit from Pente Networks maintained communications for emergency crews during the 2025 Los Angeles wildfires, highlighting how turnkey packaging broadens the private LTE market beyond technically-savvy buyers.
Time-division duplexing captured 55% of revenue in 2024 and is projected to sustain the highest 17.1% CAGR. Asymmetric traffic in video surveillance and telemetry favours TDD's dynamic allocation, maximising throughput within scarce mid-band channels. TDD also aligns with CBRS band allocations, reinforcing its position as the default in new private LTE market deployments.
Frequency-division duplexing retains a foothold in latency-sensitive control systems where strict separation of uplink and downlink is prized. However, modern schedulers reduce TDD jitter to sub-10 ms, narrowing the historical gap. Upcoming 5G releases will further refine TDD numerologies, assuring enterprises that today's investment will remain relevant once they transition to 5G NR carrier aggregation.
The Private LTE Market Report is Segmented by Component (Infrastructure and Services), Technology (Frequency-Division Duplexing (FDD) and Time Division Duplex (TDD)), Deployment Model (Centralized (C-RAN), Distributed), End-User Industry (Industrial (Manufacturing, Energy and Utilities, Mining and Oil and Gas, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America led with 38% of 2024 revenue thanks to the CBRS framework and a mature ecosystem of radio, device, and integrator partners. More than 4,700 private LTE and 5G networks were operational worldwide by end-2024, and a substantial share was in the United States. Local 5G pilots in manufacturing, healthcare, and utilities amplify demand, while hyperscaler edge zones make low-latency workload offload straightforward across major metros.
Asia-Pacific records the fastest 12.8% CAGR from 2025 to 2030. China deploys state-backed factory and mine networks, Japan issues local 5G licences in millimetre and mid-bands, and South Korea capitalises on its dense fibre backbone to host campus cores. India's recent spectrum policy changes have unlocked trials in automotive and pharmaceutical plants. Australia already operates more than 50 private LTE systems, primarily to streamline remote-area iron ore and lithium extraction, and its market is forecast to hit AUD 695 million by 2027, according to ACMA.
Europe ranks second in deployment count, holding roughly 40% of global private installations by mid-2023, according to GSMA. Germany's 3.7-3.8 GHz local licences spur manufacturing adoption; the United Kingdom's Shared Access framework simplifies licences for ports and farms. The European 5G Observatory reports that 73% of pioneer bands were assigned by March 2024, forming a solid spectral foundation for industrial networks. Vodafone's pledge to roll out open RAN on 2,500 sites is expected to reduce equipment costs across Continental Europe, indirectly benefiting enterprise buyers seeking turnkey private LTE projects.
- Nokia
- Ericsson
- Huawei Technologies
- NEC Corp.
- Qualcomm
- Druid Software
- Sierra Wireless
- JMA Wireless
- Ruckus Networks (CommScope)
- Celona
- Airspan Networks
- Cisco Systems
- ZTE Corp.
- Samsung Electronics
- Airspan Networks
- Athonet (HPE)
- Motorola Solutions
- Mavenir Systems
- Amazon AWS Private 5G
- Verizon Business
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Spectrum liberalization and CBRS commercialization
- 4.2.2 Industrial IoT and Industry 4.0 uptake
- 4.2.3 Mission-critical URLLC demand in harsh sites
- 4.2.4 Seamless migration path toward 5G SA
- 4.2.5 On-prem edge-AI bandwidth requirements
- 4.2.6 Lower TCO via Open RAN small-cell ecosystems
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High CAPEX and uncertain ROI
- 4.3.2 Scarcity of integration talent
- 4.3.3 Fragmented device-band support
- 4.3.4 Budget cannibalisation by private 5G pilots
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Investment Analysis
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Infrastructure
- 5.1.1.1 Radio Access (RAN)
- 5.1.1.2 Core (EPC/5GC)
- 5.1.1.3 Backhaul and Transport
- 5.1.2 Services
- 5.1.2.1 Professional Services
- 5.1.2.2 Managed Services
- 5.1.1 Infrastructure
- 5.2 By Technology
- 5.2.1 Frequency-Division Duplexing (FDD)
- 5.2.2 Time-Division Duplexing (TDD)
- 5.3 By Deployment Model
- 5.3.1 Centralised (C-RAN)
- 5.3.2 Distributed
- 5.4 By Spectrum
- 5.4.1 Licensed
- 5.4.2 Unlicensed (MulteFire, 5 GHz)
- 5.4.3 Shared (CBRS, LAA)
- 5.5 By End-user Industry
- 5.5.1 Manufacturing
- 5.5.2 Energy and Utilities
- 5.5.3 Mining and Oil and Gas
- 5.5.4 Transportation and Logistics
- 5.5.5 Public Safety and Defense
- 5.5.6 Healthcare
- 5.5.7 Enterprise / Campuses
- 5.5.8 Others
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Spain
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 Japan
- 5.6.4.3 India
- 5.6.4.4 South Korea
- 5.6.4.5 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.3 Qatar
- 5.6.5.1.4 Israel
- 5.6.5.1.5 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Nokia
- 6.4.2 Ericsson
- 6.4.3 Huawei Technologies
- 6.4.4 NEC Corp.
- 6.4.5 Qualcomm
- 6.4.6 Druid Software
- 6.4.7 Sierra Wireless
- 6.4.8 JMA Wireless
- 6.4.9 Ruckus Networks (CommScope)
- 6.4.10 Celona
- 6.4.11 Airspan Networks
- 6.4.12 Cisco Systems
- 6.4.13 ZTE Corp.
- 6.4.14 Samsung Electronics
- 6.4.15 Airspan Networks
- 6.4.16 Athonet (HPE)
- 6.4.17 Motorola Solutions
- 6.4.18 Mavenir Systems
- 6.4.19 Amazon AWS Private 5G
- 6.4.20 Verizon Business
- 6.4.21 General Dynamics Mission Systems
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment



















