
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1521445
일본의 데이터센터 스토리지 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2024-2029년)Japan Data Center Storage - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
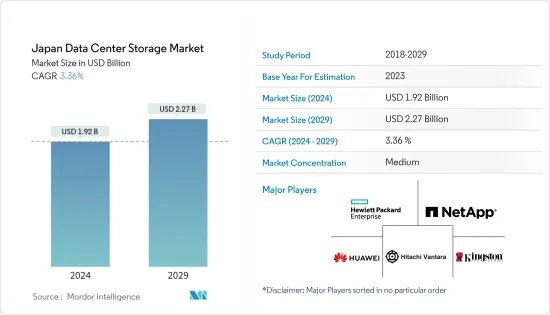
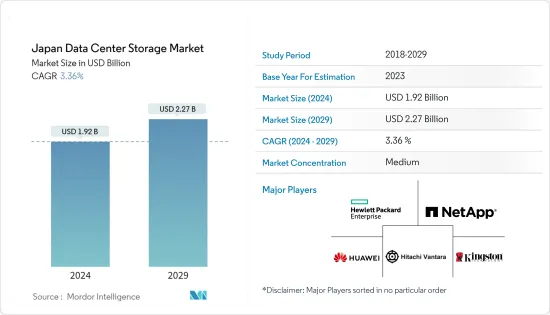
일본의 데이터센터 스토리지 시장 규모는 2024년 19억 2,000만 달러로 추정되며, 2029년에는 22억 7,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간(2024-2029년) 동안 3.36%의 CAGR로 성장할 것으로 예상됩니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 중소기업의 클라우드 컴퓨팅 수요 증가, 국내 데이터 보안에 대한 정부 규제, 국내 기업들의 투자 확대 등이 국내 데이터센터 수요를 촉진하는 주요 요인 중 하나로 꼽히며, 데이터센터 스토리지 장비에 대한 수요 증가로 이어지고 있습니다. 수요 증가로 이어지고 있습니다.
- 건설 중인 IT 부하 용량: 일본 데이터센터 시장의 IT 부하 용량은 2029년까지 2,000MW에 달할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 건설 중인 고층 공간: 일본의 바닥 면적은 2029년까지 1,000만 평방피트까지 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 계획 중인 랙: 2029년까지 국내 설치되는 랙의 총 수는 50만 개에 달할 것으로 예상되며, 2029년에는 도쿄에 가장 많은 수의 랙이 설치될 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 계획 중인 해저 케이블: 필리핀을 연결하는 해저 케이블은 30개에 육박하며, 대부분 건설 중. 2023년 개통 예정인 해저 케이블 중 하나는 동남아시아-일본 케이블 2(SJC2)로, 일본 치쿠라에서 시마까지 10,500km를 육지로 연결합니다.
일본의 데이터센터 스토리지 시장 동향
IT 및 통신 분야가 시장의 대부분을 차지
- 2020년 일본 어린이 인터넷 이용 실태 조사에서 고등학생의 하루 평균 인터넷 이용 시간이 4시간 8분으로 전년 대비 31분 증가해 인터넷 의존도가 높아지고 있는 것으로 나타났습니다. 조사에 따르면, 고등학생의 99.1%가 인터넷을 이용하고 있으며, 91.9%가 스마트폰으로 접속하는 것으로 나타났습니다. 이러한 추세는 예측 기간 동안 상당한 트래픽 점유에 기여할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 데이터센터는 국가 안보, 인터넷 인프라, 경제 성과에 있어 중요한 역할을 담당하고 있으며, 일본에서는 데이터센터 인프라가 빠르게 성장하고 있습니다. 이러한 성장은 클라우드 서비스에 대한 선호도 증가와 디지털 사용자 기반의 데이터 소비 및 생성 증가로 인해 데이터센터 및 스토리지 장치 사용량이 증가함에 따라 데이터센터 및 스토리지 장치 사용량이 증가하고 있기 때문입니다.
- 일본은 2028년까지 거의 모든 가구를 고속 광섬유망에 연결하는 것을 목표로 하는 정부 정책을 시행하고 있으며, 해저 케이블과 데이터센터 분산화에 약 5,000억 엔을 할당하여 보안과 경제 발전을 강화하고 있습니다. 데이터센터를 통한 IT 인프라의 고도화로 기업들은 더 많은 양의 데이터를 관리하고 처리할 수 있게 되었고, 플래시 스토리지 추가를 포함한 스토리지 인프라의 확장이 필요하게 되었습니다. 이에 따라 기존 데이터센터 및 신규 데이터센터 건설이 추진되고 있습니다. 데이터센터 수의 증가는 IT 인프라의 스토리지 장치 수요와 직결됩니다.
- 데이터센터 서비스 수요는 애플리케이션 성능 향상, 스토리지 요구사항 확대, 애플리케이션 보급과 인터넷 사용 증가로 인한 모바일 데이터 사용 증가로 인한 데이터센터 워크로드 증가로 인해 데이터센터 서비스 수요는 더욱 증가할 것으로 예상된다, 데이터센터 워크로드 증가로 인해 더욱 촉진될 것입니다. 전 세계 기업들이 클라우드 데이터 스토리지로 전환함에 따라 데이터센터 서비스에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다.
- 2021년 이후 일본 이동통신 사업자들이 기지국 배치 및 인구 커버리지에 대한 야심찬 목표를 세우고 5G 구축을 가속화하고 있는 것은 통신 분야의 우위가 높아지는 것을 반영합니다. 스마트폰의 보급과 5G 네트워크 이용 확대는 데이터 트래픽의 급증에 기여하여 일본 데이터센터의 성장에 긍정적인 영향을 미칠 것입니다. 그 결과, 데이터 스토리지 및 데이터센터 스토리지 장비에 대한 수요가 증가하여 전체 시장의 가치를 높이고 있습니다.
하이브리드 스토리지가 큰 비중을 차지할 전망
- 일본 정부 디지털청은 중앙정부와 지방정부를 대상으로 클라우드 서비스 도입을 적극적으로 추진하고 있습니다. 이러한 이니셔티브의 일례로 2022년 10월에 발표한 '정부 클라우드' 서비스 연내 도입에 대한 발표가 있습니다. 데이터센터 하이브리드 스토리지(Data Center Hybrid Storage)라고 불리는 이 접근방식은 온프레미스 및 클라우드 스토리지 솔루션을 결합하여 두 환경의 장점을 결합하여 데이터 저장 및 관리의 유연성을 제공합니다.
- 하이브리드 스토리지에서 온프레미스 및 클라우드 스토리지 솔루션의 통합은 기업이 특정 법적 요건을 충족하기 위해 스토리지 전략을 조정하여 데이터 무결성과 법규 준수를 보장할 수 있도록 돕습니다. 이러한 하이브리드 스토리지 솔루션의 도입은 국내 데이터 스토리지에 대한 수요 증가에 기여하고 있습니다.
- 일본 경제산업성(METI)은 2017년부터 보조금을 통해 클라우드 서비스를 포함한 IT 도입 촉진에 일익을 담당해 왔습니다. 또한, 2021년에 후생노동성은 COVID-19 팬데믹의 영향을 받은 조직에 '일하는 방식 개혁 추진 보조금'을 제공하여 클라우드 서비스 및 기타 IT 장비의 계약 비용과 설비 비용을 부담함으로써 원격 근무로의 전환을 지원했습니다. 비즈니스가 확장되고 진화함에 따라 데이터센터는 다양한 산업의 연결 요구를 충족시키기 위해 성장하고 있으며, 유연성, 확장성 및 원격 근무를 위해 하이브리드 인프라와 클라우드 기능에 대한 의존도가 높아지고 있습니다. 데이터 트래픽의 증가는 기업에서 스토리지의 중요성을 강화하고 하이브리드 스토리지 솔루션의 시장 가치를 높이는 요인으로 작용하고 있습니다.
- 하이브리드 클라우드에서 데이터 가용성과 접근성을 보장하기 위해 다양한 서비스 제공업체들이 첨단 스토리지 솔루션을 도입하고 있습니다. 특히 HPE GreenLake와 같은 기업들은 2022년 플랫폼 업그레이드와 새로운 클라우드 서비스 등 최적화된 하이브리드 스토리지 시스템을 출시하고 있습니다. 대규모 데이터 저장 용량을 보유한 대기업들이 이러한 제품 포트폴리오를 채택하면서 일본 내 하이브리드 스토리지에 대한 수요를 더욱 촉진하고 있습니다.
- 일본의 인터넷 사용자 수가 크게 증가하여 2021년부터 2022년까지 84만 4,000명(0.7%)이 증가했습니다. 인터넷 트래픽의 급증은 2019년 COVID-19 이전 수준의 1.6배에 달하며, COVID-19로 인한 재택근무, 원격수업, 화상회의, 비디오 스트리밍의 증가에 기인한 것으로 추정됩니다. 클라우드 스토리지와 음성 회의 서비스의 인기가 높아짐에 따라 원격 근무를 채택하는 기업이 늘어나면서 하이브리드 스토리지를 사용하는 데이터센터가 등장하고 있습니다. 하드 드라이브와 SSD의 기능을 결합한 하이브리드 스토리지 솔루션의 도입은 SSD의 빠른 액세스 기능과 하드 드라이브의 대용량 스토리지를 활용하고, 캐싱을 통해 자주 액세스하는 데이터의 액세스 속도를 최적화하는 혁신적인 접근 방식을 보여주고 있습니다. 접근 방식을 보여줍니다.
일본의 데이터센터 스토리지 산업 개요
일본의 데이터센터 스토리지 시장은 중간 정도의 파편화를 보이고 있으며, 주요 기업들이 시장 점유율의 대부분을 차지하고 있습니다. 이 시장에서 주목할 만한 기업으로는 Hewlett Packard Enterprise, NetApp Inc., Huawei Technologies, Hitachi Vantara LLC, Kingston Technology Company Inc. 등이 있습니다. 이 기업들은 시장 점유율을 높이고 수익성을 강화하기 위해 전략적으로 협력하고 있습니다.
2023년 8월, Kioxia Corporation은 엔터프라이즈 및 데이터센터 인프라를 위해 설계된 새로운 PCIe 5.0 SSD를 출시하여 스토리지 솔루션의 발전에 기여했습니다.
2023년 8월, Kioxia Corporation은 데이터센터급 솔리드 스테이트 드라이브(SSD) 라인업에 KIOXIA CD8P 시리즈를 추가한다고 발표했습니다. 성능을 활용할 수 있는 범용 서버 및 클라우드 환경에 적합합니다. 이러한 데이터센터 애플리케이션은 24시간 365일 운영되는 데이터센터에서 대규모 가상화 시스템에 분산된 복잡한 혼합 워크로드를 생성할 수 있습니다.
기타 혜택:
- 엑셀 형식의 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 소개
- 조사 상정과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 역학
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- IT 인프라 확대에 의한 시장 성장 확대
- 하이퍼스케일 데이터센터에 대한 투자 증가에 의한 시장 성장 확대
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 높은 초기 투자 비용이 시장 성장 방해
- 밸류체인/공급망 분석
- 업계의 매력 - Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참여업체의 위협
- 구매자/소비자의 협상력
- 공급 기업의 교섭력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간의 경쟁 강도
- COVID-19의 영향 평가
제5장 시장 세분화
- 스토리지 기술
- 네트워크 연결 스토리지(NAS)
- 스토리지 에어리어 네트워크(SAN)
- 직접 연결 스토리지(DAS)
- 기타 기술
- 스토리지 유형
- 기존 스토리지
- 올 플래시 스토리지
- 하이브리드 스토리지
- 최종사용자
- IT·통신
- BFSI
- 정부기관
- 미디어 및 엔터테인먼트
- 기타 최종사용자
제6장 경쟁 상황
- 기업 개요
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- NetApp Inc.
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- Hitachi Vantara LLC
- Kingston Technology Company Inc.
- Pure Storage Inc.
- Lenovo Group Limited
- Fujitsu Limited
- Seagate Technology LLC
- Western Digital Corporation
제7장 투자 분석
제8장 시장 기회와 향후 동향
ksm 24.07.31The Japan Data Center Storage Market size is estimated at USD 1.92 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 2.27 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 3.36% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
Key Highlights
- The increasing demand for cloud computing among SMEs, government regulations for local data security, and growing investment by domestic players are some of the major factors driving the demand for data centers in the country, leading to a growing need for data center storage equipment.
- Under Construction IT Load Capacity: The upcoming IT load capacity of the Japan data center market is expected to reach 2,000 MW by 2029.
- Under Construction Raised Floor Space: The country's construction of raised floor area is expected to increase to 10 million sq. ft by 2029.
- Planned Racks: The country's total number of racks to be installed is expected to reach 500K units by 2029. Tokyo is expected to house the maximum number of racks by 2029.
- Planned Submarine Cables: There are close to 30 submarine cable systems connecting the Philippines, and many are under construction. One such submarine cable that is estimated to start service in 2023 is Southeast Asia-Japan Cable 2 (SJC2), which stretches over 10,500 Kilometers with landing points from Chikura, Japan, to Shima, Japan.
Japan Data Center Storage Market Trends
IT & Telecommunication Segment to Hold Major Share in the Market
- In 2020, a survey on internet usage among Japanese children revealed that high school students spent an average of 4 hours and 8 minutes online daily, marking a 31-minute increase from the previous year and underlining the escalating reliance on the internet. The survey found that 99.1% of high schoolers use the internet, with 91.9% accessing it through smartphones. This trend is anticipated to contribute to significant traffic occupancy in the forecast period.
- Data centers play a crucial role in national security, internet infrastructure, and economic performance, and Japan is witnessing rapid growth in its data center infrastructure. This growth is propelled by an increasing preference for cloud services and the rising consumption and generation of data by an expanding digital user base, leading to higher data center and storage device usage.
- Japan has implemented a government policy aiming to connect nearly all households to a high-speed fiber optic network by 2028, with an allocation of approximately JPY 50 billion for subsea cable and data center decentralization to enhance security and economic development. The advancement of IT infrastructure through data centers has enabled businesses to manage and process larger volumes of data, requiring the scaling of storage infrastructure, including the addition of flash storage. It drives to existing data centers or the construction of new ones. The growth in the number of data centers is directly linked to the demand for storage devices in IT infrastructure.
- The demand for data center services is further fueled by increasing data center workloads, driven by the need for improved application performance, expanding storage requirements, and rising mobile data usage due to the proliferation of applications and increased internet usage. As businesses worldwide shift to cloud data storage, the demand for data center services is on the rise.
- The acceleration of the 5G rollout by Japan's mobile operators since 2021, with ambitious targets for base station deployment and population coverage, reflects the growing dominance of the telecommunications sector. The widespread adoption of smartphones and the increasing use of 5G networks contribute to a surge in data traffic, positively impacting the growth of data centers in Japan. This, in turn, augments the demand for data storage and data center storage equipment, thereby increasing the overall market value.
Hybrid Storage Expected To Hold Significant Share
- The Government of Japan's Digital Agency actively promotes the adoption of cloud services for both central and local government offices. An example of this initiative is the announcement made in October 2022, wherein the agencies of the Government of Japan committed to adopting "Government Cloud" services for the fiscal year. This approach combines on-premises and cloud storage solutions, referred to as data center hybrid storage, leveraging the strengths of both environments and offering flexibility in storing and managing data.
- The integration of on-premises and cloud storage solutions in hybrid storage supports enterprises in tailoring their storage strategies to meet specific legal requirements, ensuring data integrity and legal compliance. This adoption of hybrid storage solutions contributes to the increasing need for data storage in the country.
- The Ministry of Economics, Trade, and Industry (METI) has played a role in promoting IT adoption, including cloud services, through subsidies provided since FY2017. Additionally, in 2021, the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (MHLW) offered a "Workstyle Reform Promotion" subsidy to organizations affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, supporting their transition to remote work by covering contracting fees and equipment costs for cloud services and other IT devices. As businesses expand and evolve, data centers are growing to meet the connectivity needs of various industries, with an increasing reliance on hybrid infrastructure and cloud capabilities for flexibility, scalability, and remote work. The rising data traffic reinforces the importance of storage for businesses, contributing to an increased market value for hybrid storage solutions.
- Various service providers are deploying advanced storage solutions to ensure data availability and access in hybrid clouds. Notably, companies like HPE GreenLake have introduced optimized hybrid storage systems, including platform upgrades and new cloud services in 2022. Large enterprises with substantial data storage capacities are adopting such product portfolios, further driving the demand for hybrid storage in the country.
- The number of internet users in Japan saw a significant increase, rising by 844 thousand (0.7%) between 2021 and 2022. The surge in internet traffic, 1.6 times higher than pre-COVID-19 levels in 2019, can be attributed to the pandemic-driven rise in at-home videoconferencing, distance learning, and video streaming. The growing popularity of cloud storage and audio conferencing services has led more companies to embrace remote work, contributing to the emergence of data centers utilizing hybrid storage. The introduction of hybrid storage solutions, combining the functionality of hard drives and SSDs, demonstrates an innovative approach where cache utilization optimizes access speed for frequently accessed data, capitalizing on the fast access capabilities of SSDs and the greater storage capacity of hard drives.
Japan Data Center Storage Industry Overview
The Japan Data Center Storage market exhibits a moderate level of fragmentation, with a majority of the market share held by key players. Noteworthy companies in this market include Hewlett Packard Enterprise, NetApp Inc., Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd., Hitachi Vantara LLC, and Kingston Technology Company Inc. These entities strategically engage in collaborative initiatives to enhance their market share and bolster profitability.
In August 2023, Kioxia Corporation introduced new PCIe 5.0 SSDs designed for Enterprise and Data Center Infrastructures, contributing to advancements in storage solutions.
In August 2023, Kioxia Corporation announced the addition of the KIOXIA CD8P Series to its lineup of data center-class solid state drives (SSDs). The KIOXIA CD8P Series is well-suited to general purpose server and cloud environments that can take advantage of PCIe 5.0 (32GT/s x4) performance. These data center applications can generate complex mixed workloads spread across large scale virtualized systems in 24x7 operational data centers.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumption & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Dynamics
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Expansion of IT Infrastructure to Increase Market Growth
- 4.2.2 Increased Investments in Hyperscale Data Centers To Increase Market Growth
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Initial Investment Cost To Hinder Market Growth
- 4.4 Value Chain / Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.6 Assessment of COVID-19 Impact
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Storage Technology
- 5.1.1 Network Attached Storage (NAS)
- 5.1.2 Storage Area Network (SAN)
- 5.1.3 Direct Attached Storage (DAS)
- 5.1.4 Other Technologies
- 5.2 Storage Type
- 5.2.1 Traditional Storage
- 5.2.2 All-Flash Storage
- 5.2.3 Hybrid Storage
- 5.3 End-User
- 5.3.1 IT & Telecommunication
- 5.3.2 BFSI
- 5.3.3 Government
- 5.3.4 Media & Entertainment
- 5.3.5 Other End-Users
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Company Profiles
- 6.1.1 Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- 6.1.2 NetApp Inc.
- 6.1.3 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- 6.1.4 Hitachi Vantara LLC
- 6.1.5 Kingston Technology Company Inc.
- 6.1.6 Pure Storage Inc.
- 6.1.7 Lenovo Group Limited
- 6.1.8 Fujitsu Limited
- 6.1.9 Seagate Technology LLC
- 6.1.10 Western Digital Corporation














