
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1523378
저분자 헤파린 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2024-2029년)Global Low Molecular Weight Heparin - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
저분자 헤파린 시장 규모는 2024년 44억 3,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2029년에는 61억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 예측 기간 동안 복합 연간 성장률(CAGR)은 6.60%로 성장할 전망입니다.

혈액 질환의 유병률 증가와 저분자 헤파린(LMWH) 항응고제의 도입은 시장 성장을 가속하는 중요한 요소 중 하나입니다. 예를 들어, 2023년 10월에 Journal of Cureus에 게재된 연구는 사우디아라비아의 Aseer Central Hospital에서 성인 외과 수술 환자의 심부정맥 혈전증의 유병률이 7%로 보고되었습니다. 심부정맥 혈전증은 병원에서 예방 가능한 사인 중 가장 많으며 발 정맥에서 폐로 혈전이 이동하여 발생하는 폐 색전증(PE)으로 인한 전체 사망의 10%를 차지합니다. 유사하게, 백혈병 림프종 협회(LLS)에 따르면, 미국에서는 약 3분에 한 명이 백혈병, 림프종, 골수종으로 진단되었습니다. 게다가 이 출처에 따르면 2023년에는 미국에서 184,720명이 백혈병과 림프종으로 진단되는 것으로 추정되고 있습니다. 게다가 미국에서는 2023년에 89,380명이 림프종으로 진단되었고, 호지킨 림프종이 8,830명, 비호지킨 림프종이 80,550명 새롭게 발병할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다. 저분자 헤파린은 혈액 응고의 예방에 사용되며 정맥 혈전 색전증, 기타 혈전 용해성 질환, 혈액암 등에 적응이 있습니다. 따라서, 이러한 질병의 증례 수 증가는 저분자 헤파린 제품 수요를 촉진하는 것으로 보입니다.
2022년 2월에 발표된 미국 위생연구소(NIH)의 데이터에 따르면, 달테파린이나 에녹사파린과 같은 LMWH는 급성 또는 선택적 입원 중 정맥 혈전 색전증(VTE) 예방, 심부정맥 혈전증(DVT)와 폐 색전증(PE)의 치료에 사용됩니다. 이 출처에 따르면 중증으로 입원하는 환자의 절반 이상은 혈전 색전증의 위험이 있으며, VTE는 병원 사망률의 5% - 10%를 차지하므로 정확한 VTE 위험 평가와 효과적인 치료가 필요합니다. 이러한 사례는 예측 기간 동안 시장 성장에 긍정적인 영향을 미칠 가능성이 높습니다.
그러므로 혈액 질환의 유병률 증가와 LMWH의 효능 증가와 같은 요인으로 인해 시장은 예측 기간 동안 성장할 것으로 예상됩니다. 그러나, 저분자 헤파린의 부작용은 시장 성장을 저해할 가능성이 높습니다.
세계의 저분자 헤파린 시장 동향
심부정맥 혈전증 부문은 예측 기간 동안 큰 성장이 예상된다.
심부정맥 혈전증(DVT)은 정맥 혈전증으로도 알려져 있으며, 정맥의 손상이나 혈류의 정체에 의해 체내의 심부에 있는 정맥에 혈전(피 덩어리)이 형성됨으로써 발병합니다. 혈전은 정맥의 혈류를 전체적으로 또는 부분적으로 멈춥니다. DVT는 일반적으로 하퇴, 대퇴, 골반에서 발생하지만 팔, 뇌, 장, 간, 신장에서 발생할 수 있습니다.
DVT의 유병률 증가는이 부문의 성장을 가속하는 주요 요인 중 하나입니다. 예를 들어, 2023년 9월에 Frontiers in Medicine에 게재된 연구에 따르면 간경변 환자의 DVT 유병률은 7.6%였습니다. 또한, 2023년 5월에 Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine 잡지에 발표된 또 다른 연구에 따르면 급성 및 만성 척수 손상 환자에서 DVT 발생률은 9.3%였습니다.
고위험 일반 수술 환자에서 DVT 및 폐 혈전 색전증 예방에서 LMWH는 예방제를 사용하지 않는 경우보다 더 효과적이므로 DVT 환자에서 LMWH 수요는 향후 몇 년동안 증가하여이 부문의 성장 를 촉진할 것으로 예상됩니다. 따라서, 상기 요인들 덕분에, 이들 제품의 채용이 대상 인구들 사이에서 증가하고 부문의 성장을 가속할 가능성이 높습니다.
북미가 저분자 헤파린 시장을 독점할 전망
북미는 질병 부담 증가, 노인 인구 증가, 제품 승인 수 증가로 시장을 독점할 것으로 예상됩니다. 예를 들어, United Health Foundation이 발표한 통계에 따르면, 미국의 65세 이상의 노인 인구는 2022년에는 5,800만명을 넘어, 국민의 17.3%를 차지하고, 이 숫자는 2040년에는 7,310만명, 22%에 이를 것으로 추정됩니다. 정맥 혈전 색전증의 위험은 연령과 강하게 관련되어 있기 때문에 LMWH에 대한 수요도 증가할 것으로 보입니다.
2024년 1월 미국 생물공학정보센터가 업데이트한 데이터에 따르면 미국에서는 최대 20만 명이 심부정맥혈전증을 앓고 있습니다. 그 중 5만명이 폐색전증을 발병하고 있습니다. 폐색전증(PE)으로 이어지는 심부정맥혈전증(DVT)은 심근경색, 뇌졸중에 이어 세 번째로 많은 심혈관계 질환입니다. 이러한 대상 인구 증가는 궁극적으로 LMWH 제품의 채택을 뒷받침하고 시장 성장에 긍정적인 영향을 미칩니다.
따라서 노인 인구 부담 증가와 혈액 질환 유병률 증가 등의 요인이 시장 성장에 기여할 것으로 예상됩니다.
세계의 저분자 헤파린 산업 개요
저분자 헤파린 시장은 세계적으로 그리고 지역적으로 사업을 전개하는 다수의 기업이 존재하기 때문에 경쟁은 적당합니다. 경쟁 구도에는 주요 시장 점유율을 보유한 여러 회사의 국제 및 지역 기업 분석이 포함됩니다. 주요 기업으로는 Changzhou Qianhong Bio-Pharma, Aspen Holdings, Leopharma A/S, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, Sanofi, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited, B. Braun Medical Inc., Pfizer Inc., Abbott, Novartis AG 등이 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 역학
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 세계의 혈액 질환의 유병률 증가
- LMWH 항응고제의 도입
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 저분자 헤파린의 부작용
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자/소비자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
제5장 시장 세분화(시장 규모-달러)
- 제품 유형별
- 에녹사파린
- 달테파린
- 틴자 팔린
- 폰다 파리누쿠스
- 기타
- 용도별
- 심부정맥 혈전증
- 급성관 증후군(ACS)
- 폐색전증
- 기타(동맥혈전증, 바이패스 수술, 신장 투석, 수혈)
- 최종 사용자별
- 병원
- 진료소
- 외래수술센터(ASC)
- 기타(제약,바이오테크놀러지 기업, 연구소, 연구 기관)
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 호주
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- GCC
- 남아프리카
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 프로파일
- Aspen Holdings
- Changzhou Qianhong Bio-Pharma
- Leopharma A/S
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
- B. Braun Medical Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Sanofi
- Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited
- Abbott Laboratories
- Novartis AG
제7장 시장 기회와 앞으로의 동향
BJH 24.08.09The Global Low Molecular Weight Heparin Market size is estimated at USD 4.43 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 6.10 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 6.60% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
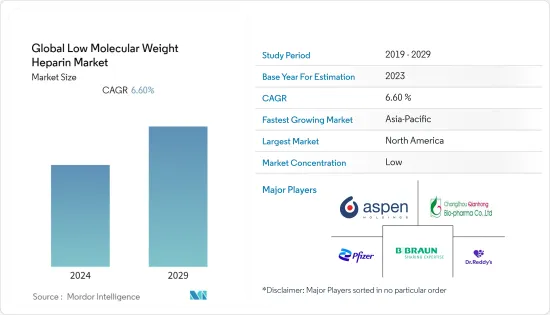
The increasing prevalence of blood disorders and the introduction of low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) anticoagulants are among the significant factors driving the growth of the market. For instance, the study published in the Journal of Cureus in October 2023 reported the prevalence of deep vein thrombosis was 7% among adult surgical patients in Aseer Central Hospital in Saudi Arabia. Deep vein thrombosis is the most common preventable cause of death in hospitals, accounting for 10% of all deaths from pulmonary embolism (PE), which occurs when a blood clot from a vein in the leg travels to the lungs. Similarly, according to the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (LLS), around every 3 minutes, one individual in the United States is diagnosed with leukemia, lymphoma, or myeloma. Moreover, as per the same source, 184,720 people in the United States were estimated to be diagnosed with leukemia and lymphoma in 2023. In addition, 89,380 people were expected to be diagnosed with lymphoma in the United States in 2023, with 8,830 new cases of Hodgkin's lymphoma and 80,550 new cases of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Low-molecular-weight heparin is used for the prevention of blood clotting and is indicated for venous thromboembolism, other thrombolytic disorders, and blood cancers. Thus, the rising cases of such disorders are likely to fuel the demand for low-molecular-weight heparin products.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) data published in February 2022, LMWH such as dalteparin and enoxaparin is used to prevent venous thromboembolic disease (VTE) during an acute or elective hospital stay, as well as to treat deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). As per the same source, over half of the patients admitted to hospitals who are severely ill are at risk of thromboembolic illness, and VTE is responsible for 5% to 10% of hospital mortality, necessitating accurate VTE risk assessment and effective treatment. Such instances will likely positively impact the market's growth over the forecast period.
Therefore, owing to factors such as the increasing prevalence of blood disorders and the significant effectiveness of LMWH, the market is anticipated to witness growth over the forecast period. However, the adverse effects of low molecular weight heparin are likely to impede market growth.
Global Low Molecular Weight Heparin Market Trends
The Deep Vein Thrombosis Segment is Expected to Witness Significant Growth During the Forecast Period
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), also known as venous thrombosis, occurs when a thrombus (blood clot) forms in veins deep within the body due to injury to the veins or sluggish blood flow. Blood clots can fully or partially stop blood flow through a vein. DVTs are commonly found in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis but can also occur in the arm, brain, intestines, liver, or kidney.
The increasing prevalence of DVT is one of the major factors driving the segment's growth. For instance, in September 2023, according to the study published in Frontiers in Medicine, the prevalence of DVT was 7.6% in patients with liver cirrhosis. Additionally, in May 2023, another study published in Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine reported that the incidence of DVT was 9.3% among patients with acute and chronic spinal cord injury.
As LMWHs are more effective than no prophylaxis in preventing DVT and pulmonary thromboembolism in high-risk general surgical patients, the demand for LMWH in patients suffering from DVT is anticipated to increase over the coming years, driving the segment's growth. Hence, owing to the above factors, the adoption of these products will likely increase among the target population, driving the segment's growth.
North America is Expected to Dominate the Low Molecular Weight Heparin Market
North America is expected to dominate the market due to the growing burden of diseases, the rising geriatric population, and the rising number of product approvals. For instance, the statistics published by the United Health Foundation highlighted that there were more than 58 million individuals aged 65 and above in the United States, representing 17.3% of the nation's population, in 2022; the figure is estimated to reach 73.1 million, or 22%, by 2040. As the risk of venous thromboembolism is strongly associated with age, the demand for LMWH will also likely increase.
In January 2024, the data update by the National Center for Biotechnology Information showed that up to 200,000 people in the United States were affected with deep venous thrombosis. Among those, 50,000 cases resulted in pulmonary embolism. Deep venous thrombosis (DVT), which leads to pulmonary embolism (PE), is the third most common cardiovascular disease after myocardial infarction and stroke. Such an increase in the target population will ultimately boost the adoption of LMWH products, positively impacting market growth.
Therefore, factors such as the growing burden of the geriatric population and the high prevalence of blood disorders are expected to contribute to market growth.
Global Low Molecular Weight Heparin Industry Overview
The low molecular heparin market is moderately competitive due to the presence of several companies operating globally as well as regionally. The competitive landscape includes an analysis of a few international and local companies holding major market shares. Some of the key players include Changzhou Qianhong Bio-Pharma, Aspen Holdings, Leopharma A/S, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, Sanofi, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited, B. Braun Medical Inc., Pfizer Inc., Abbott, and Novartis AG.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increased Prevalence of Blood Disorders Worldwide
- 4.2.2 Introduction of LMWH Anticoagulants
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Adverse Effects of Low Molecular Weight Heparin
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (Market Size by Value - USD)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Enoxaparin
- 5.1.2 Dalteparin
- 5.1.3 Tinzaparin
- 5.1.4 Fondaparinux
- 5.1.5 Others
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Deep Vein Thrombosis
- 5.2.2 Acute coronary syndrome (ACS)
- 5.2.3 Pulmonary Embolism
- 5.2.4 Others (Aerial Thrombosis, Bypass Surgery, Kidney Dialysis, and Blood Transfusions )
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Hospitals
- 5.3.2 Clinics
- 5.3.3 Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- 5.3.4 Others (Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies and Research Laboratories and Institutes)
- 5.4 Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 South Korea
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.4.1 GCC
- 5.4.4.2 South Africa
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5 South America
- 5.4.5.1 Brazil
- 5.4.5.2 Argentina
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Company Profiles
- 6.1.1 Aspen Holdings
- 6.1.2 Changzhou Qianhong Bio-Pharma
- 6.1.3 Leopharma A/S
- 6.1.4 Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
- 6.1.5 B. Braun Medical Inc.
- 6.1.6 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.1.7 Sanofi
- 6.1.8 Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited
- 6.1.9 Abbott Laboratories
- 6.1.10 Novartis AG

















