
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1850986
핀테크 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Fintech - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
세계의 핀테크 시장은 2025년에 3,208억 1,000만 달러에 이르고, 2030년에는 6,528억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.

강력한 성장의 요인에는 크로스보더 전개를 용이하게 하는 규제의 조화, 거래의 흐름을 가속하는 실시간 결제 레일, 오픈 뱅킹 데이터에의 액세스 확대 등이 있습니다. 대형 플랫폼이 컨텍스트 파이낸스를 일상적인 디지털 저니에 통합하여 상거래와 금융 서비스 간의 격차를 줄이고 경쟁이 치열해지고 있습니다. 사기 방지, 여신 판단, 개인화된 혜택을 위한 인공지능 도구는 실험적인 파일럿에서 대규모 배포로 전환하고 있으며, 높은 데이터 용량을 가진 기업에 우위를 제공하고 있습니다. 동시에 수익성이 높은 핀테크 사업자에게는 자본 시장이 형성되어 제품 확대 및 전략적 인수를 위한 새로운 자금 조달이 가능해지고 있습니다.
세계의 핀테크 시장의 동향과 인사이트
핀테크 도입을 가속화하는 실시간 결제 의무화
미국 FedNow와 유럽 SEPA Instant Credit Transfer와 같은 중앙 은행 시스템은 결제에 대한 기대를 수시간에서 수초로 바꾸고 있습니다. 결제 가속화는 재무 관리, 소규모 대출 및 현금 흐름 분석에서 새로운 가치 제안의 뒷받침이 되었으며 핀테크 시장은 한때 저속 배치 처리에 의존했던 기업 고객의 개척에 기여하고 있습니다. 2025년에는 미국의 실시간 거래가 74억 건에 이를 것으로 예상되며 중국, 영국, 홍콩에서도 비슷한 기세를 볼 수 있습니다. 결제 요청, 자동 매칭, 저스트 인 타임 대출과 같은 오버레이 서비스를 통합하는 공급자는 동일한 레일에 뿌리를 둔 안정적인 수익원을 얻을 수 있습니다. 규제 당국이 명확한 마이그레이션 마감일을 설정하고 결제의 최종 규칙을 업데이트하여 가장 빠르게 도입이 진행됩니다. 결제 네트워크의 상호 운용성이 다음 장애물로 남아 있지만, 국내의 보다 신속한 결제 시스템을 연결하는 파일럿 테스트는 이미 실행 가능한 크로스보더 모델을 입증합니다.
데이터 액세스를 확장하는 오픈 뱅킹 및 API 표준화
유럽 PSD2와 브라질 오픈 파이낸스 제도는 통일된 API 사양을 통해 계좌 집계, 잔액 확인, 은행의 직접 결제를 대규모로 수행할 수 있음을 입증합니다. 표준화된 동의 흐름은 경쟁을 데이터 캡처에서 데이터 활용으로 이동시켜 예측적 인수와 초맞춤형 예산 구성 도구로 이어집니다. 규제 당국은 현재 개방 금융을 중요한 디지털 인프라로 취급하고 있으며 미국 대륙과 아시아태평양의 일부에서 도입이 진행되고 있습니다. 핀테크 은행이 제공하는 데이터를 가맹점, 통신 사업자, 소셜 시그널과 결합하는 플랫폼은 보다 풍부한 리스크 모델을 구축하고, 부채 불이행률을 낮추고, 신용 액세스를 확대합니다. 이 패턴은 소규모 공급업체가 타사 애널리틱스를 활용하고 고객 획득보다 서비스 품질로 기존 기업과 경쟁하는 상호 운용 가능한 핀테크 시장 생태계를 육성합니다.
BNPL 모델에 대한 규제 강화
영국, 미국 및 호주의 소비자 보호기관은 BNPL 상품을 크레딧으로 분류하고 가용성 검사, 표준화된 정보 공개 및 하드십 프로토콜을 의무화하는 규칙을 고안하고 있습니다. 공급자는 소프트풀 신용 정보 기관을 통합하고, 분쟁 해결 워크플로를 업그레이드하고, 지연 손해금 의존성으로부터 수익 모델을 조정해야 합니다. 컴플라이언스 비용은 상승하고 이미 대출 라이선스를 보유한 규제 대상 금융 기관과의 통합 및 제휴가 촉진됩니다. 소매업체는 단기적으로 BNPL 체크아웃의 도입이 지연될 수 있지만, 투명성이 높은 조건으로 인해 시간이 지남에 따라 대응 가능한 베이스가 확대될 수 있습니다. 핀테크 규제에 대응하는 데이터 필드와 상환 분석을 선점하고 통합한 기업은 통일된 프레임워크가 확립되면 안정적인 포지션을 구축할 수 있습니다.
부문 분석
네오뱅킹은 핀테크 시장 규모에서 차지하는 비율은 작지만, 2030년까지의 CAGR은 가장 빠른 18.7%를 기록할 것으로 예상되어 지점 중심에서 앱 중심 뱅킹으로의 결정적인 시프트를 나타냅니다. 기능 가속화, 투명한 가격 설정, 개인화된 인사이트를 통해 네오뱅크는 모바일 퍼스트의 젊은 소비자를 캡처할 수 있습니다. 기존 금융기관은 디지털 자회사와 코어뱅크의 근대화를 가속화함으로써 대응하며 경험 격차는 줄어들지만 기술 예산은 증가합니다. 디지털 결제 솔루션은 2024년 핀테크 시장 점유율의 46.2%를 차지하였으며 고객 획득에 필수적인 게이트웨이로 계속 유지됩니다. 공급자는 사기 분석, 로열티 통합 및 운전 자본 대출을 결제 레일에 통합하여 이익률이 낮은 처리를 고객 평생 수익을 높이는 번들 가치 제안으로 바꾸고 있습니다.
지갑과 카드의 경계를 넘어 인슈어테크, 웰스테크, 레그테크는 데이터 사이언스와 자동화가 레거시 프로세스를 근본적으로 대체하는 특수한 레인을 개척하고 있습니다. 이용 기반 보험과 AI를 활용한 클레임 트리아지는 보험사의 손해율을 낮추고 보험사와 클라우드 벤더의 합작투자를 유치하고 있습니다. 웰스 매니지먼트에서는 프랙셔널 오너십과 자동 리밸런싱이 투자의 민주화를 실현하고, 컴플라이언스 자동화 툴이 새로운 보고 의무를 수익화합니다. 단일 경험 내에서 여러 서비스 제안을 오케스트레이션 할 수 있는 능력은 미래의 승자를 정의하며 핀테크 플랫폼은 사용자가 지불, 크레딧, 저축 및 보호를 전환할 수 있는 모듈형 아키텍처로 향하고 있습니다.
지역 분석
아시아태평양은 2024년 핀테크 시장의 44.86%를 차지하였고, 2030년까지의 CAGR은 16.02%로 예상됩니다. 중국의 슈퍼 앱 생태계와 인도의 UPI 레일이 이 지역의 성장을 지원하고 있으며, 진입 장벽을 낮추는 동남아시아 디지털 뱅크 라이선스 프로그램도 이에 참여하고 있습니다. 각국 정부는 핀테크를 경제적 포섭을 위한 기술로 취급하고, e-KYC 규범을 합리화하고, 샌드박스를 육성하고 있습니다. 지역의 기존 기업은 신흥 기업에 자본을 주입하는 전략적 벤처 부문에서 대응하고 참신한 능력을 활용하면서 혼란 위험을 헤지하고 있습니다.
북미는 사용자에 대한 침투가 성숙하고 있음에도 불구하고 여전히 혁신적인 강국입니다. AI를 활용한 개인화, 암호화 자산 서비스, 클라우드 네이티브 코어 뱅킹은 규제 당국이 스테이블 코인과 디지털 자산의 수탁에 관한 명확한 지침을 보이는 가운데 서비스의 차별화를 도모하고 있습니다. 유명한 사이버 사고의 교훈을 반영하여 벤처 기업의 자금 조달은 안전한 데이터 교환 프로토콜을 가진 기업으로 집중되고 있습니다. 이 지역의 핀테크 시장은 입증된 수익 유지와 크로스셀링 지표를 보장하는 깊은 자본 시장의 혜택을 계속 받고 있습니다.
유럽의 규제 측면에서의 리더십은 핀테크의 궤도를 형성하고 있습니다. PSD2는 오픈 뱅킹 플랫폼을 홍보하고, MiCA는 암호화 자산 발행에 명확성을 제공하고, DORA는 엄격한 운영 탄력성 규칙을 설정합니다. 이러한 틀은 전문적인 Legtec 벤더와 컴플라이언스 Az A 서비스 제품을 만들어 새로운 수익 계층을 늘리고 있습니다. 유럽 대륙의 네오뱅크는 다통화 체제에 걸쳐 서비스를 현지화하는 한편 라이선스를 대규모로 확대합니다. 또한 Green Finance 요청은 거래 수준에서 스코프 3 배출량을 측정하는 기후 데이터 플랫폼을 자극합니다.
남미에서는 브라질의 PIX 인스턴트 지불 네트워크에 지원되어 보급 곡선이 상승하고 있습니다. 은행 계좌가 없는 인구가 많아 모바일을 주로 사용하기 때문에 지갑 제공업체, 디지털 금융업자, 마이크로 인슈어런스(소규모 보험) 방식에 비옥한 토양이 되고 있습니다. 샌드박스 테스트에 대한 규제의 개방성은 국제 자본을 유치하고, 국내의 선두기업은 저비용 송금 및 공공 요금 이력에 연관된 신용 점수를 제공함으로써 이 지역의 규모를 확대하고 있습니다. 인프라가 성숙함에 따라 이 지역은 다른 신흥 시장에 인재와 제품을 수출하고 있습니다.
중동 및 아프리카에는 다양한 비즈니스 기회가 있습니다. 걸프 협력 회의 국가는 디지털 뱅크 라이선스를 발행하고 정부가 지원하는 핀테크 가속기를 주최하며 AI 중심 금융 벤처에 국부를 투자합니다. 아프리카의 모바일 머니 레일은 거래량에서 여전히 세계를 선도하고 있으며, 송금 회랑은 해외 디아스포라 지갑과 통합되어 있습니다. 지역의 핀테크 테마에는 샤리아 준거 임베디드 금융, 저수수료 크로스보더 송금, 위성 농경학 데이터를 통해 촉진되는 농업 투자 대출 등이 포함됩니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 실시간 결제 의무화(FedNow, SEPA 즉시 신용이체)에 의한 핀테크 도입의 가속
- 오픈 뱅킹과 API 표준화(PSD2, 브라질 오픈 파이낸스) 데이터 액세스 확대
- 중국과 인도에서 CBDC의 실증 실험이 인프라 업그레이드를 추진
- 아시아의 전자상거래 플랫폼에서의 임베디드 금융의 상승
- 중동, 북아프리카 및 남미 중소기업의 신용 격차가 디지털 대출 플랫폼을 촉진
- ESG 관련 핀테크 솔루션이 유럽의 녹색 투자 펀드를 유인
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- BNPL 모델에 대한 규제 강화
- 교묘한 사기와 딥페이크에 의한 정체성 리스크
- 클라우드 집중에 의한 단일 장애점의 위험
- 자금 조달 둔화와 평가액의 수정에 의한 스케일 업의 억제
- 가치/공급망 분석
- 규제 전망
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력/소비자
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
- 투자 및 자금 조달 동향 분석
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 서비스 프로포지션별
- 디지털 결제
- 디지털 대출과 금융
- 디지털 투자
- 인슈어테크
- 네오뱅킹
- 최종 사용자별
- 소매
- 기업
- 사용자 인터페이스별
- 모바일 애플리케이션
- 웹/브라우저
- POS/IoT 디바이스
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 칠레
- 콜롬비아
- 기타 남미
- 유럽
- 영국
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 스페인
- 이탈리아
- 베네룩스(벨기에, 네덜란드, 룩셈부르크)
- 북유럽 국가(스웨덴, 노르웨이, 덴마크, 핀란드, 아이슬란드)
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 호주
- 동남아시아(싱가포르, 인도네시아, 말레이시아, 태국, 베트남, 필리핀)
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 사우디아라비아
- 남아프리카
- 나이지리아
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- PayPal Holdings Inc.
- Ant Group Co. Ltd.
- Stripe Inc.
- Block Inc.(Square, Cash App)
- Adyen NV
- Coinbase Global Inc.
- Robinhood Markets Inc.
- Revolut Ltd.
- Klarna Bank AB
- N26GmbH
- SoFi Technologies Inc.
- Nubank(Nu Holdings)
- Wise plc
- Afterpay Ltd.
- FIS Global
- Fiserv Inc.
- Intuit Inc.
- M-PESA(Vodafone/Safaricom)
- Paytm Digital Payments Ltd.
- Razorpay Software Pvt Ltd.
제7장 시장 기회와 미래 전망
CSM 25.11.20The global fintech market reached USD 320.81 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to climb to USD 652.80 billion by 2030, reflecting a sturdy 15.27% CAGR over the period.
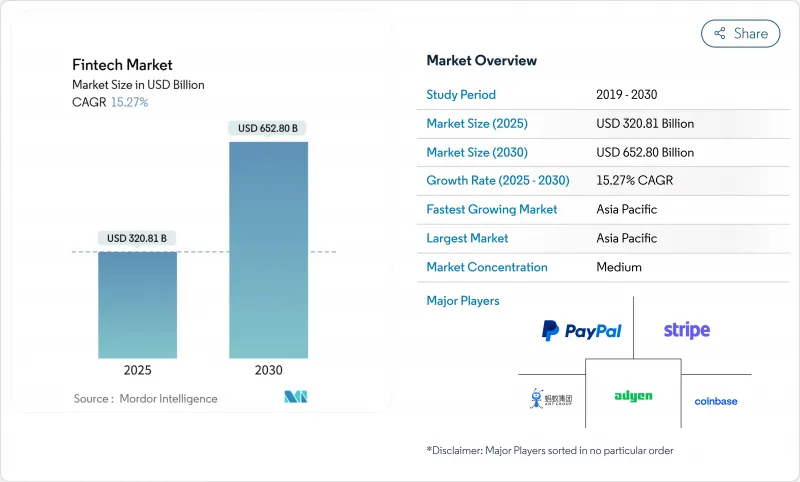
Strong tailwinds include harmonizing regulations that ease cross-border expansion, real-time payment rails that accelerate transaction flows, and widening access to open-banking data. Competitive intensity is heightening as platform giants embed contextual finance into everyday digital journeys, shrinking the gap between commerce and financial services. Artificial-intelligence tools for fraud prevention, credit decisioning, and personalized offers are moving from experimental pilots to scale deployments, tilting the advantage toward firms with deep data capabilities. Simultaneously, capital markets are reopening for profitable fintech operators, enabling fresh funding for product expansion and strategic acquisitions.
Global Fintech Market Trends and Insights
Real-time payments mandates accelerating fintech adoption
Central-bank systems such as FedNow in the United States and SEPA Instant Credit Transfer in Europe are transforming settlement expectations from hours to seconds. Faster clearing underpins new value propositions in treasury management, micro-lending, and cash-flow analytics, helping the fintech market reach enterprise customers that once relied on slower batch processes. In 2025, U.S. real-time transactions are expected to hit 7.4 billion, and similar momentum is visible in China, the United Kingdom, and Hong Kong. Providers that integrate overlay services-request to pay, automated reconciliation, and just-in-time financing-gain sticky revenue streams grounded in the same rails. Adoption is most rapid where regulators set explicit migration deadlines and update settlement finality rules. Payment-network interoperability remains the next hurdle, but pilots linking domestic faster-payment systems already demonstrate viable cross-border models.
Open-banking & API standardization broadening data access
PSD2 in Europe and Brazil's Open Finance regime prove that uniform API specifications can unlock account aggregation, balance verification, and direct-from-bank payments at scale. Standardized consent flows shift competition away from data hoarding toward data utilization, encouraging predictive underwriting and hyper-personalized budgeting tools. Regulators now treat open finance as critical digital infrastructure, prompting adoption across the Americas and parts of Asia-Pacific. Fintech platforms that pair bank-sourced data with merchant, telecom, or social signals create richer risk models, lowering default rates and broadening credit access. The pattern is fostering interoperable fintech market ecosystems where smaller providers tap third-party analytics to compete against incumbents on service quality rather than raw customer reach.
Regulatory clamp-down on BNPL models
Consumer-protection agencies in the United Kingdom, the United States, and Australia are drafting rules that classify BNPL products as credit, mandating affordability checks, standardized disclosures, and hardship protocols. Providers must integrate soft-pull credit bureaus, upgrade dispute-resolution workflows, and adjust revenue models away from late-fee dependency. Compliance costs rise, encouraging consolidation and alliances with regulated lenders that already hold lending licenses. Retailers may experience slower BNPL checkout adoption in the near term, but transparent terms could expand the addressable base over time. Fintech firms that pre-emptively embed regulation-ready data fields and repayment analytics create defensible positions once uniform frameworks crystallize.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- CBDC pilots in China & India driving infrastructure upgrades
- Rise of embedded finance among Asian e-commerce platforms
- Sophisticated fraud & deepfake-based identity risks
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Neobanking accounts for a modest slice of the fintech market size yet posts the fastest 18.7% CAGR to 2030, signaling a decisive shift from branch-centric to app-centric banking. Feature velocity, transparent pricing, and personalized insights allow neobanks to capture young, mobile-first consumers. Established lenders react with digital subsidiaries and accelerated core-bank modernization, narrowing the experiential gap but raising technology budgets. Digital-payments solutions hold 46.2% of the fintech market share in 2024 and remain vital gateways for customer acquisition. Providers layer fraud-analytics, loyalty integrations, and working-capital loans onto payment rails, turning low-margin processing into bundled value propositions that lift customer lifetime revenue.
Expanding beyond wallets and cards, insurtech, wealth-tech, and reg-tech carve specialized lanes where data science and automation can upend legacy processes. Usage-based insurance and AI-driven claims triage cut carrier loss ratios, attracting joint ventures between insurers and cloud vendors. In wealth management, fractional ownership and automated rebalancing democratize investing, while compliance-automation tools monetize new reporting mandates. The ability to orchestrate multiple service propositions within a single experience defines future winners, pushing fintech platforms toward modular architectures that let users toggle between payments, credit, savings, and protection.
The Fintech Market is Segmented by Service Proposition (Digital Payments, Digital Lending and Financing, Digital Investments, Insurtech, and Neobanking), by End-User (Retail and Businesses), by User Interface (Mobile Applications, Web / Browser, and POS / IoT Devices), and by Region (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, & Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific commanded 44.86% of the fintech market in 2024 and is on track for a 16.02% CAGR through 2030. China's super-app ecosystem and India's UPI rails anchor regional growth, joined by Southeast Asian digital-bank license programs that lower entry barriers. Governments treat fintech as a lever for economic inclusion, streamlining e-KYC norms and nurturing sandboxes. Regional incumbents respond with strategic venture arms that inject capital into start-ups, hedging disruption risk while tapping novel capabilities.
North America remains an innovative powerhouse despite maturing user penetration. AI-driven personalization, crypto-asset services, and cloud-native core banking differentiate offerings as regulators provide clearer guidance on stablecoins and digital-asset custody. Venture funding gravitates toward firms with secure data-exchange protocols, reflecting lessons from high-profile cyber incidents. The fintech market in the region continues to benefit from deep capital markets that reward proven revenue retention and cross-selling metrics.
Europe's regulatory leadership shapes its fintech trajectory. PSD2 catalyzed open-banking platforms, MiCA brings clarity to crypto-asset issuance, and DORA sets stringent operational-resilience rules. These frameworks spawn specialized reg-tech vendors and compliance-as-a-service products, adding new revenue layers. Continental neobanks localize services across multi-currency regimes while passporting licenses to scale. Additionally, green-finance imperatives stimulate climate-data fintech platforms that measure scope-3 emissions at the transaction level.
South America showcases rising adoption curves anchored by Brazil's PIX instant-payment network. Large unbanked populations and mobile-first behavior create fertile ground for wallet providers, digital lenders, and micro-insurance schemes. Regulatory openness to sandbox testing attracts international capital, and domestic champions scale regionally by offering low-cost remittances and credit scoring tied to utility-bill histories. As the infrastructure matures, the region exports talent and product frameworks to other emerging markets.
Middle East and Africa present heterogeneous opportunity sets. Gulf Cooperation Council states issue digital-bank licenses, host government-backed fintech accelerators, and invest sovereign wealth in AI-centric finance ventures. Africa's mobile-money rails remain the world leading in transaction volume, and remittance corridors integrate with diaspora wallets abroad. Regional fintech themes include Sharia-compliant embedded finance, low-fee cross-border transfers, and agricultural-input lending facilitated via satellite agronomy data.
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- PayPal Holdings Inc.
- Ant Group Co. Ltd.
- Stripe Inc.
- Block Inc. (Square, Cash App)
- Adyen N.V.
- Coinbase Global Inc.
- Robinhood Markets Inc.
- Revolut Ltd.
- Klarna Bank AB
- N26 GmbH
- SoFi Technologies Inc.
- Nubank (Nu Holdings)
- Wise plc
- Afterpay Ltd.
- FIS Global
- Fiserv Inc.
- Intuit Inc.
- M-PESA (Vodafone / Safaricom)
- Paytm Digital Payments Ltd.
- Razorpay Software Pvt Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Real-time Payments Mandates (FedNow, SEPA Instant Credit Transfer) Accelerating Fintech Adoption
- 4.2.2 Open-Banking & API Standardization (PSD2, Brazil Open Finance) Broadening Data Access
- 4.2.3 CBDC Pilots in China & India Driving Fintech Infrastructure Upgrades
- 4.2.4 Rise of Embedded-Finance Among Asian E-commerce Platforms
- 4.2.5 SME Credit Gap in MENA & South America Fueling Digital Lending Platforms
- 4.2.6 ESG-Linked Fintech Solutions Attracting Green-Investment Funds in Europe
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Regulatory Clamp-down on BNPL Models
- 4.3.2 Sophisticated Fraud & Deepfake?based Identity Risks
- 4.3.3 Cloud-Concentration Risk Creating Single Points-of-Failure
- 4.3.4 Funding Winter & Valuation Corrections Curbing Scale-ups
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Investment & Funding Trend Analysis
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Service Proposition
- 5.1.1 Digital Payments
- 5.1.2 Digital Lending and Financing
- 5.1.3 Digital Investments
- 5.1.4 Insurtech
- 5.1.5 Neobanking
- 5.2 By End-User
- 5.2.1 Retail
- 5.2.2 Businesses
- 5.3 By User Interface
- 5.3.1 Mobile Applications
- 5.3.2 Web / Browser
- 5.3.3 POS / IoT Devices
- 5.4 By Region
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Chile
- 5.4.2.4 Colombia
- 5.4.2.5 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.2 Germany
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Spain
- 5.4.3.5 Italy
- 5.4.3.6 Benelux (Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg)
- 5.4.3.7 Nordics (Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Finland, and Iceland)
- 5.4.3.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 India
- 5.4.4.3 Japan
- 5.4.4.4 South Korea
- 5.4.4.5 Australia
- 5.4.4.6 South-East Asia (Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, and Philippines)
- 5.4.4.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.3 South Africa
- 5.4.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.4.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 PayPal Holdings Inc.
- 6.4.2 Ant Group Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.3 Stripe Inc.
- 6.4.4 Block Inc. (Square, Cash App)
- 6.4.5 Adyen N.V.
- 6.4.6 Coinbase Global Inc.
- 6.4.7 Robinhood Markets Inc.
- 6.4.8 Revolut Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Klarna Bank AB
- 6.4.10 N26 GmbH
- 6.4.11 SoFi Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.12 Nubank (Nu Holdings)
- 6.4.13 Wise plc
- 6.4.14 Afterpay Ltd.
- 6.4.15 FIS Global
- 6.4.16 Fiserv Inc.
- 6.4.17 Intuit Inc.
- 6.4.18 M-PESA (Vodafone / Safaricom)
- 6.4.19 Paytm Digital Payments Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Razorpay Software Pvt Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment



















