
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1550006
데이터센터 프로세서 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2024-2029년)Data Center Processor - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
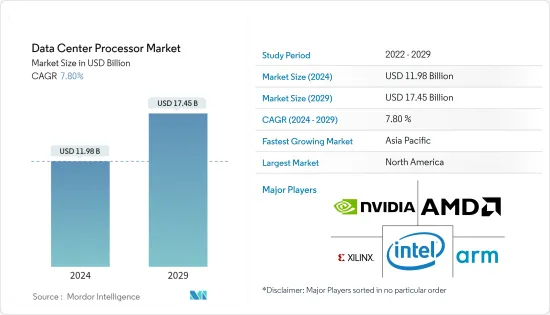
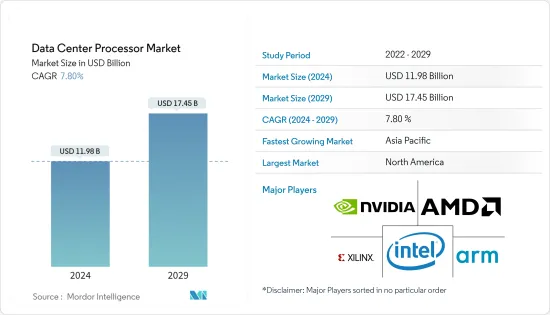
데이터센터 프로세서 시장 규모는 2024년 119억 8,000만 달러로 추정되며, 2029년에는 174억 5,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간(2024-2029년) 동안 7.80%의 CAGR로 성장할 것으로 예상됩니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 데이터센터 프로세서는 데이터센터 컴퓨팅 인프라의 핵심 구성요소입니다. 연산 처리, 논리 처리, 입출력 처리 등 다양한 작업을 수행하는 고성능 칩입니다. 데이터센터는 대용량 스토리지, 메모리, 처리 능력, 입출력 기능을 갖춘 고성능 컴퓨터인 서버에 의존하고 있습니다. 이러한 서버는 데이터센터 프로세서를 사용하여 계산 부하를 처리하고 애플리케이션을 실행합니다. 데이터센터 프로세서의 선택은 특정 작업과 요구사항에 따라 달라집니다. 범용 CPU는 많은 애플리케이션에 적합할 수 있지만, 인공지능(AI)이나 머신러닝(ML)과 같은 특수한 작업에는 이러한 작업 부하에 최적화된 프로세서가 선호될 수 있습니다.
- CPU 프로세서는 데이터센터에서 가장 흔하게 볼 수 있는 프로세서 유형입니다. 다양한 작업과 애플리케이션을 처리할 수 있어 다재다능하고 적응력이 뛰어납니다. 처음에는 그래픽을 많이 사용하는 애플리케이션을 위해 설계된 GPU 프로세서는 병렬 처리 능력으로 인해 데이터센터에 필수적인 요소로 자리 잡았으며, GPU는 고도의 병렬 계산을 수행하기 때문에 머신러닝, 인공지능, 빅데이터 분석에 적합합니다. 방대한 수의 코어를 탑재하고 있어 방대한 양의 데이터를 동시에 처리할 수 있어 처리 시간을 크게 단축하고 전반적인 성능을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
- FPGA 프로세서는 프로그래머블 하드웨어의 장점을 활용하여 특정 애플리케이션에 맞게 커스터마이징할 수 있는 장점을 가지고 있습니다. 회로를 유연하게 재구성할 수 있기 때문에 낮은 지연 시간과 높은 처리량이 필요한 작업에 적합하며, FPGA 프로세서는 암호화, 비디오 처리, 네트워크 패킷 처리와 같이 실시간 처리가 중요한 기능에 자주 사용됩니다.
- 커넥티드 디바이스, 클라우드 컴퓨팅, 사물인터넷(IoT)의 확산과 함께 데이터 생성량이 전례 없이 빠르게 증가하고 있습니다. 이러한 데이터 급증은 데이터센터의 처리 및 분석 요구 사항을 충족시킬 수 있는 강력한 프로세서를 요구하고 있습니다. 또한, 데이터센터는 방대한 양의 실시간 데이터 처리 및 분석을 담당하고 있습니다. 데이터 기반 인사이트와 복잡한 계산에 대한 의존도가 높아짐에 따라, 프로세서는 높은 성능을 발휘하고 까다로운 워크로드를 효율적으로 처리할 수 있어야 합니다.
- 또한, 에너지 효율은 데이터센터 프로세서의 중요한 시장 촉진요인입니다. 데이터센터는 막대한 에너지를 소비하기 때문에 전력 소비를 최적화하는 것은 운영 비용과 환경에 미치는 영향을 줄이는 데 매우 중요합니다. 보다 효율적인 데이터센터 운영을 위해 와트당 성능이 높은 프로세서에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. 또한, 인공지능(AI) 및 머신러닝(ML) 기술의 채택이 증가함에 따라 AI 워크로드 처리 기능이 강화된 프로세서에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있으며, AI 및 ML 알고리즘은 복잡한 데이터 패턴을 처리 및 분석하고 정확한 예측을 위해 강력한 프로세서를 필요로 합니다. AI 워크로드에 최적화된 전용 프로세서에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다.
- 데이터센터 프로세서 시장에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 주요 거시경제 동향 중 하나는 GDP 성장입니다. 경제가 성장하면 기업은 데이터센터와 같은 IT 인프라에 대한 투자를 늘리는 경향이 있습니다. 기업은 늘어나는 데이터를 처리하기 위해 더 많은 컴퓨팅 파워를 필요로 하기 때문에 이러한 투자 증가는 데이터센터 프로세서에 대한 수요 증가로 이어집니다. 예를 들어, 미국은 대표적인 데이터센터 시장입니다. 미국 경제분석국(BEA)에 따르면 미국의 GDP는 2022년 25조 7,000억 달러에서 2023년 약 27조 3,600억 달러로 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 그러나 데이터센터 프로세서 시장은 성장과 잠재력을 저해하는 몇 가지 시장 억제요인에 직면해 있습니다. 데이터센터 프로세서의 높은 비용은 중소기업의 도입에 큰 장벽으로 작용하고 있으며, 이는 도입을 제한하고 있습니다. 또한, 업계의 급속한 기술 발전으로 인해 프로세서의 수명 주기가 짧아져 기업들이 최신 기술 혁신에 대응하기 어려워지고 있습니다.
데이터센터 프로세서 시장 동향
중앙처리장치(CPU) 부문이 시장 성장을 견인할 것으로 전망
- CPU 데이터센터 프로세서는 서버 프로세서라고도 하며, 데이터센터 기능에서 매우 중요한 구성요소입니다. 이 프로세서는 데이터센터 환경의 까다로운 작업 부하와 고성능 요구 사항을 처리하도록 특별히 설계되었으며, CPU 데이터센터 프로세서의 주요 특징 중 하나는 높은 코어 수입니다. 이러한 프로세서는 종종 8-64개 이상의 다중 코어를 갖추고 있습니다. 이를 통해 작업의 병렬 처리가 가능하여 데이터센터가 다양한 워크로드를 동시에 처리할 수 있습니다. 또한, 코어 수가 많기 때문에 리소스를 효율적으로 사용할 수 있어 데이터센터의 전반적인 성능을 극대화할 수 있습니다.
- 또 다른 중요한 특징은 CPU 데이터센터 프로세서의 클럭 속도가 빠르다는 것입니다. 클럭 속도는 프로세서가 명령을 실행하는 속도를 의미합니다. 클럭 속도가 빠르면 데이터 처리 속도도 빨라져 대량의 데이터를 실시간으로 처리해야 하는 데이터센터에서는 매우 중요합니다. 또한, CPU 데이터센터 프로세서에는 종종 터보부스트 기술이 탑재되어 있어 추가 성능이 필요할 때 일시적으로 클럭 속도를 높일 수 있습니다.
- 또한 CPU 데이터센터 프로세서는 가상화를 지원하도록 설계되었습니다. 가상화를 통해 하나의 물리적 서버에서 여러 가상 머신을 실행할 수 있어 리소스 활용도를 극대화하고 하드웨어 비용을 절감할 수 있으며, CPU 데이터센터 프로세서에는 하드웨어 지원 가상화와 같은 기능이 포함되어 있어 가상화 환경의 성능과 보안을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 성능을 향상시킵니다.
- 시장 촉진요인 중 하나는 모바일 기기, 소셜 미디어, 사물인터넷 등 다양한 소스에서 생성되는 데이터의 급격한 증가입니다. 이 방대한 양의 데이터를 실시간으로 처리하고 분석해야 하기 때문에 강력하고 고성능의 프로세서가 필요합니다. 데이터 처리 시장이 계속 성장함에 따라 데이터센터 사업자들은 늘어나는 컴퓨팅 요구사항을 충족하기 위해 첨단 CPU 프로세서에 투자할 수밖에 없는 상황입니다.
- 클라우드 컴퓨팅 서비스의 급속한 확장도 시장 성장을 크게 촉진할 것으로 예상됩니다. 클라우드 플랫폼은 확장성, 유연성, 비용 효율성을 제공함으로써 많은 기업들에게 필수적인 요소로 자리 잡았습니다. 클라우드 서비스에 대한 수요 증가에 대응하기 위해 데이터센터는 무거운 워크로드를 처리하고 최적의 성능을 제공할 수 있는 프로세서를 도입해야 합니다. 따라서 클라우드 컴퓨팅의 진화하는 요구사항을 충족하기 위해 보다 강력하고 에너지 효율적인 CPU 프로세서가 지속적으로 요구되고 있습니다.
- Cloudscene에 따르면 2024년 3월 현재 미국에는 5,381개의 데이터센터가 있으며, 이는 전 세계 어느 나라보다 많은 것으로 보고됐습니다. 독일에 521개, 영국에 514개가 더 있습니다. 여러 지역에서 데이터센터에 대한 투자가 증가하면서 시장 성장을 견인하고 있는 것으로 보입니다. 예를 들어, 2023년 10월 Vantage Data Centers는 유럽의 여러 데이터센터 자산에 대한 투자 거래를 완료했습니다. 이 회사는 DigitalBridge, Infranity 및 MEAG가 이끄는 투자자 컨소시엄과 투자 제휴를 완료했다고 발표했습니다. 이번 투자 파트너십은 안정화된 유럽 데이터센터 6곳으로 구성되어 있으며, 밸류에이션은 약 27억 달러(한화 약 3,700억 원)에 달합니다.
북미가 가장 큰 시장 점유율을 차지
- 미국 데이터센터 프로세서 시장은 기술 발전, 데이터 집약적 애플리케이션의 확산, 고성능 컴퓨팅에 대한 요구로 인해 크게 성장하고 있습니다. 기업들이 클라우드 기반 솔루션으로 전환함에 따라 북미에서는 강력한 데이터센터에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. 이에 따라 증가하는 데이터를 처리하고 원활한 성능을 제공할 수 있는 강력한 프로세서에 대한 요구가 증가하고 있습니다.
- 미국에서는 인터넷, AI, 5G, IoT, 고성능 컴퓨팅 등 첨단 기술 도입이 진행됨에 따라 높은 데이터 전송 속도가 요구되고 있으며, 이는 시장 성장을 견인하고 있습니다. 서비스형 소프트웨어 솔루션 기업이자 온라인 미디어 모니터링 업체인 멜트워터(Meltwater)에 따르면, 2023년 10월 기준 미국의 인터넷 보급률은 91.8%에 달합니다.
- 데이터센터는 많은 양의 에너지를 소비하기 때문에 운영 비용과 환경에 대한 우려가 커지고 있습니다. 이에 따라 성능 저하 없이 전력 소비를 최적화할 수 있는 에너지 효율적인 프로세서에 대한 관심이 높아지고 있습니다.
- 데이터센터는 AI 및 머신러닝과 같은 신흥 기술의 지역적 요구 사항을 충족하기 위해 이기종 혼합 컴퓨팅 아키텍처를 채택하고 있습니다. 이러한 추세는 CPU, GPU, 전용 가속기를 통합하여 뛰어난 성능과 유연성을 제공하고 있습니다.
- 데이터 트래픽의 급증은 기업 및 소비자가 생성하는 데이터를 지원하는 여러 데이터센터의 개발 수요를 증가시키고 있습니다. 미국에서는 클라우드 컴퓨팅 서비스 및 애플리케이션의 이용이 지속적으로 증가하면서 대규모 하이퍼스케일 클라우드 기반 데이터센터가 개발될 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 이 지역에서는 여러 기업이 데이터센터 용량 확장에 투자하여 광 트랜시버 시장 확대를 촉진하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 아마존은 2023년 9월 미국 오하이오주 뉴 올버니에 5곳의 새로운 데이터센터에 35억 달러를 투자할 것이라고 발표했습니다. 이 데이터센터는 2030년까지 완공될 것으로 알려졌으며, 5곳의 데이터센터와 이를 지원하는 건물 건설은 2025년에 시작될 예정입니다. 이번 투자는 아마존이 이 주에 데이터센터를 확장하기 위해 약속한 78억 달러의 첫 번째 부분이라고 밝혔습니다. 이번 합의는 구글이 최근 발표한 뉴 올버니에 위치한 3개의 데이터센터에 대한 17억 달러 규모의 확장 계획에 이은 것입니다.
데이터센터 프로세서 산업 개요
데이터센터 프로세서 시장은 인텔(Intel Corporation), 엔비디어(NVIDIA Corporation), 어드밴스드 마이크로 디바이스(Advanced Micro Devices Inc.), 자일링스(Xilinx Inc.), ARM Holdings PLC와 같은 주요 기업들에 의해 반고체화되어 있습니다. 조사 대상 시장의 기업들은 진화하는 소비자의 요구에 부응하기 위해 끊임없이 첨단 제품 혁신을 위해 노력하고 있습니다.
2024년 2월: 엔비디아는 AI 데이터센터 혁명을 촉진하기 위해 GPU 생산량을 늘렸다고 발표했습니다. 구글이 새로 출시한 Gemma 제품군의 경량 모델에 대한 최적화를 시작했습니다. 양사는 엔비디아의 데이터센터, 클라우드 및 GPU 강화 PC에서 실행되는 모델의 성능을 가속화하는 아키텍처를 개발했으며, 엔비디아의 H200 프로세서의 초기 재고는 2024년 후반에 출하될 예정입니다.
2023년 12월: 인텔이 뉴욕에서 열린 AI Everywhere 행사에서 5세대 제온 스케일러블 프로세서를 발표했습니다. 인텔은 2023년 1월 4세대 인텔 제온 프로세서를 발표했지만, 경쟁사에 뒤처지지 않기 위해 코드명 '에메랄드 래피즈(Emerald Rapids)로도 알려진 5세대 칩을 발표했습니다. 이 새로운 프로세서는 이전 세대 제온 프로세서인 사파이어 래피즈(Sapphire Rapids)에 비해 평균 21%의 컴퓨팅 성능 향상과 16%의 메모리 속도 향상을 통해 다양한 고객 워크로드에서 와트당 평균 36%의 성능 향상을 달성할 수 있다고 인텔은 밝혔습니다. 주장하고 있습니다. 이를 통해 인텔은 가장 지속가능한 데이터센터 프로세서로서 더 적은 전력 소비로 프로세서 부하가 높은 작업을 수행할 수 있다고 밝혔습니다.
기타 혜택:
- 엑셀 형식의 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 소개
- 조사 가정과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트
- 시장 개요
- 기술 현황
- 딥러닝, 퍼블릭 클라우드 인터페이스, 기업 인터페이스가 데이터센터 엑셀러레이터에 미치는 영향
- 각 벤더의 기술 업데이트/개발 상황
- 업계의 밸류체인 분석
- 업계의 매력 - Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참여업체의 위협
- 소비자의 협상력
- 공급 기업의 교섭력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간의 경쟁 관계
- COVID-19의 영향과 기타 거시경제 요인이 시장에 미치는 영향
- 셋업에 기반한 시장 시나리오 - 온프레미스 vs 클라우드
제5장 시장 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- HPC 데이터센터의 AI도입 증가
- 데이터센터 설비와 클라우드 기반 서비스 전개 증가
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 한정된 AI 하드웨어 전문가와 인프라에 대한 우려
제6장 시장 세분화
- 프로세서별
- CPU(중앙처리장치)
- GPU(그래픽처리장치)
- FPGA(필드 프로그래머블 게이트 어레이)
- ASIC(특정 용도용 집적회로) - AI 전용 엑셀러레이터 전용
- 네트워킹 엑셀러레이터(SmartNIC, DPU)
- 용도별
- 인공지능(딥러닝, 머신러닝)
- 데이터 분석/그래픽스
- 하이 퍼포먼스 컴퓨팅(HPC)/사이언티픽 컴퓨팅
- 지역별
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아
- 호주 및 뉴질랜드
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
제7장 경쟁 상황
- 기업 개요
- Intel Corporation
- NVIDIA Corporation
- Advanced Micro Devices Inc.
- Xilinx Inc.
- Arm Holdings PLC
- Super Micro Computer Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Imagination Technologies Limited
- Advantech Co. Ltd
제8장 투자 분석
제9장 시장 전망
ksm 24.09.13The Data Center Processor Market size is estimated at USD 11.98 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 17.45 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 7.80% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
Key Highlights
- A data center processor is a critical component of a data center's computing infrastructure. It is a high-performance chip that performs various tasks, including arithmetic, logic, and input/output operations. Data centers rely on servers, which are high-performance computers with large storage space, memory, processing power, and input/output capabilities. These servers use data center processors to handle the computational workload and run applications. The choice of processors in a data center depends on the specific tasks and requirements. General-purpose CPUs may be suitable for many applications, but processors optimized for these workloads may be preferred for specialized tasks like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
- CPU processors are the most common type of processors found in data centers. They provide the capability to handle various tasks and applications, making them versatile and adaptable. Initially designed for graphics-intensive applications, GPU processors have become indispensable in data centers due to their parallel processing capabilities. GPUs perform highly parallel computations, making them suitable for machine learning, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics. Their massive number of cores enables them to process vast amounts of data simultaneously, significantly reducing processing time and improving overall performance.
- FPGA processors offer the advantage of programmable hardware, allowing customization to specific applications. They provide the flexibility to reconfigure their circuitry, making them suitable for tasks that require low latency and high throughput. FPGA processors are often used for functions such as encryption, video processing, and network packet processing, where real-time processing is crucial.
- With the proliferation of connected devices, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things, the amount of data being generated is increasing at an unprecedented rate. This surge in data necessitates powerful processors that can handle data centers' processing and analysis requirements. Further, data centers are responsible for processing and analyzing vast real-time data. As industries increasingly rely on data-driven insights and complex computations, processors must deliver high performance and efficiently handle demanding workloads.
- Moreover, energy efficiency is a significant market driver for data center processors. Data centers consume enormous amounts of energy, and optimizing power consumption is crucial for reducing operational costs and environmental impact. Processors that offer higher performance per watt are in high demand as they allow for more efficient data center operations. Moreover, the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies is driving the demand for processors with enhanced capabilities in handling AI workloads. AI and ML algorithms require powerful processors to process and analyze complex data patterns and make accurate predictions, driving the need for specialized processors optimized for AI workloads.
- One of the key macroeconomic trends that can affect the data center processors market is GDP growth. As the economy expands, companies are inclined to increase their investments in IT infrastructure, such as data centers. This increased investment leads to a higher demand for data center processors, as businesses require more computing power to handle the growing volume of data. For instance, the United States is a prominent data center market. According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), the US GDP increased from USD 25.7 trillion in 2022 to about USD 27.36 trillion in 2023.
- However, the data center processor market faces several market restraints that can hinder its growth and potential. The high cost of data center processors is a significant barrier for small and medium-sized businesses, limiting their adoption. Additionally, the rapid technological advancements in the industry lead to a shorter lifecycle of processors, making it challenging for businesses to keep up with the latest innovations.
Data Center Processor Market Trends
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) Segment is Expected to Drive the Growth of the Market
- CPU data center processors, also known as server processors, are a crucial component in the functioning of data centers. These processors are specifically devised to handle the demanding workload and high-performance requirements of data center environments. One of the primary features of CPU data center processors is their high core count. These processors often have multiple cores, ranging from 8 to 64 or more. This allows for parallel processing of tasks, enabling data centers to handle various workloads simultaneously. The high core count also ensures efficient resource utilization, maximizing the data center's overall performance.
- Another essential feature is the high clock speed of CPU data center processors. Clock speed refers to how fast a processor can execute instructions. Higher clock speeds result in faster data processing, which is crucial for data centers that need to handle large amounts of data in real time. Additionally, CPU data center processors often have turbo boost technology, temporarily increasing the clock speed when additional performance is required.
- Also, CPU data center processors are designed to support virtualization. Virtualization facilitates multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, maximizing resource utilization and reducing hardware costs. CPU data center processors include features like hardware-assisted virtualization, improving virtualized environments' performance and security.
- One of the primary market drivers is the exponential growth of data generated by various sources like mobile devices, social media, and the Internet of Things. This vast amount of data must be processed and analyzed in real time, requiring powerful, high-performance processors. As the market for data processing continues to grow, data center operators are compelled to invest in advanced CPU processors to meet the increasing computational requirements.
- The rapid expansion of cloud computing services is also anticipated to drive market growth significantly. Cloud platforms have become essential to many businesses, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. To support the growing demand for cloud services, data centers must deploy processors that can handle the heavy workloads and provide optimal performance. As a result, there is a constant need for more robust and energy-efficient CPU processors to cater to the evolving requirements of cloud computing.
- According to Cloudscene, as of March 2024, there were a reported 5,381 data centers in the United States, the most of any country worldwide. A further 521 were in Germany, while 514 were in the United Kingdom. The increasing investments in data centers in several regions are likely to aid the growth of the market. For instance, in October 2023, Vantage Data Centers closed an investment deal for several European data center assets. The company announced it had completed an investment partnership with DigitalBridge and a consortium of investors led by Infranity and MEAG. The investment partnership initially comprises six stabilized European data centers and is valued at approximately USD 2.7 billion, including Vantage's stake.
North America Holds the Largest Market Share
- The American data center processor market has experienced substantial growth due to technological advancements, the proliferation of data-intensive applications, and the need for high-performance computing. The migration of businesses to cloud-based solutions has fueled the demand for robust data centers in North America. This has driven the need for powerful processors that can handle the increasing volume of data and provide seamless performance.
- The high adoption of the Internet and advanced technologies like AI, 5G, IoT, and high-performance computing in the United States is driving the need for a high data transmission rate, which drives the market's growth. According to Meltwater, a software-as-a-service solution company and an online media monitoring company, as of October 2023, the internet penetration rate in the United States was 91.8%.
- Data centers consume large amounts of energy, resulting in heightened operational costs and environmental concerns. As a result, there is a rising emphasis on energy-efficient processors that can optimize power consumption without compromising performance.
- Data centers are embracing heterogeneous computing architectures to meet the region's requirements of emerging technologies like AI and machine learning. This trend has led to the integration of CPUs, GPUs, and specialized accelerators, offering superior performance and flexibility.
- The upsurge in data traffic has created elevated demand for developing several data centers that support data generated by businesses and consumers. The use of cloud-computing services and applications will continue to grow in the US, leading to the development of large hyperscale cloud-based data centers.
- Several companies are investing in data center capacity expansions in the region, thereby driving the expansion of the optical transceiver market. For instance, in September 2023, Amazon announced it would invest USD 3.5 billion in five new data centers in New Albany, Ohio, United States. It is reported that they will be finished by 2030. The construction is set to commence in 2025 on the five data centers and supporting buildings. The investment is claimed to be an initial part of Amazon's USD 7.8 billion commitment to expand data centers in the state. The agreement follows Google's recent announcement of a planned USD 1.7 billion expansion of its three data centers in New Albany.
Data Center Processor Industry Overview
The data center processor market is semi-consolidated with significant players like Intel Corporation, NVIDIA Corporation, Advanced Micro Devices Inc., Xilinx Inc., and Arm Holdings PLC. The players in the studied market are striving to constantly innovate advanced products to cater to the evolving needs of consumers.
February 2024: Nvidia announced that it ramped up GPU production to fuel the AI data center revolution. The company launched optimizations for Google's newly released Gemma family of lightweight models. The two companies developed architecture to accelerate the model's performance running in Nvidia data centers, in the cloud, and on GPU-enhanced PCs. The initial stock of Nvidia's H200 processors is set to ship in the second half of 2024.
December 2023: Intel launched its 5th-generation Xeon Scalable processors at the AI Everywhere event in New York. Intel released the fourth generation of its Intel Xeon processors in January 2023, but to keep pace with its competitors, it has unveiled the fifth generation of the chips, also known by its code name Emerald Rapids. These new processors offer a 21% average compute performance gain and 16% better memory speeds than the previous generation of Xeon processors, Sapphire Rapids, enabling 36% higher average performance per watt across a diverse range of customer workloads - Intel claims. This would facilitate users' undertaking processor-intensive tasks while utilizing less overall power, with Intel describing them as their most sustainable data center processors.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Technology Snapshot
- 4.2.1 Impact of Deep Learning, Public Cloud Interface, and Enterprise Interface on Data Center Accelerators
- 4.2.2 Technological Updates/Developments by Various Vendors
- 4.3 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.5 Impact of COVID-19 Aftereffects and Other Macroeconomic Factors on the Market
- 4.6 Market Scenario Based on the Setup - On-premise vs Cloud
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Increasing Deployment of AI in HPC Data Centers
- 5.1.2 Increasing Deployment of Data Center Facilities and Cloud-based Services
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 Limited AI Hardware Experts and Infrastructural Concerns
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Processor
- 6.1.1 CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- 6.1.2 GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
- 6.1.3 FPGA (Field-programmable Gate Array)
- 6.1.4 ASIC (Application-specific Integrated Circuit) - Only AI-dedicated Accelerators
- 6.1.5 Networking Accelerators (SmartNIC and DPUs)
- 6.2 By Application
- 6.2.1 Artificial Intelligence (Deep Learning and Machine Learning)
- 6.2.2 Data Analytics/Graphics
- 6.2.3 High-performance Computing (HPC)/Scientific Computing
- 6.3 By Geography
- 6.3.1 North America
- 6.3.2 Europe
- 6.3.3 Asia
- 6.3.4 Australia and New Zealand
- 6.3.5 Latin America
- 6.3.6 Middle East and Africa
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Intel Corporation
- 7.1.2 NVIDIA Corporation
- 7.1.3 Advanced Micro Devices Inc.
- 7.1.4 Xilinx Inc.
- 7.1.5 Arm Holdings PLC
- 7.1.6 Super Micro Computer Inc.
- 7.1.7 Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd
- 7.1.8 Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- 7.1.9 Imagination Technologies Limited
- 7.1.10 Advantech Co. Ltd



















