
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1550039
마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기 - 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2024-2029년)Microprocessor Protective Relay - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
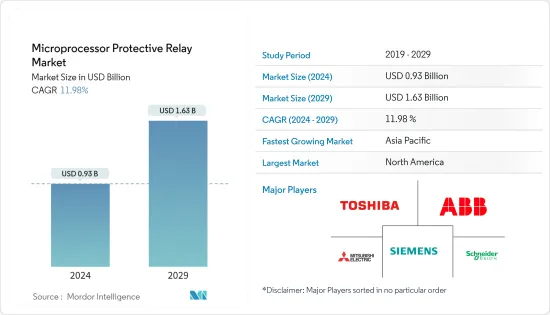
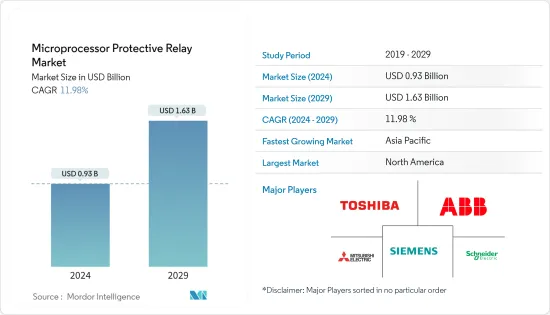
마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기 시장 규모는 2024년 9억 3,000만 달러로 추정되며 2029년에는 16억 3,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간(2024-2029) 동안 연평균 11.98% 성장할 것으로 예상됩니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기 시장은 전력 인프라 증가, 전력망 현대화 노력, 전기 안전 의식, 스마트 그리드 노력, 정부 지원으로 인해 크게 성장할 것으로 예상됩니다. 전력 시스템의 지속적인 확장과 기술 발전으로 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기에 대한 수요는 더욱 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 기후 변화로 인해 이상기후 발생 빈도가 높아지는 가운데, National Grid는 강력한 폭풍과 기온 상승에 대비한 인프라 강화의 시급성을 강조하고 있습니다. 그 결과, 2024년 3월에 뉴욕주 북부의 전력망을 강화하기 위한 40억 달러 규모의 계획을 발표했습니다. 이 대규모 투자는 새로운 변전소 건설과 버팔로, 로체스터, 시러큐스 인근 도시를 연결하는 1,000마일 이상의 송전선로를 대대적으로 개조하는 등 70개 프로젝트에 자금을 지원할 예정입니다.
- 세계의 신흥 및 선진국은 스마트 전력망 구축에 많은 투자를 하고 있으며, 이는 향후 몇 년 동안 계전기 시장을 촉진할 것으로 예상됩니다. 스마트 그리드는 자동 제어, 최신 통신 인프라, 고전력 변환기, 최신 에너지 관리 기술, 감지 및 계측 기술을 통해 신뢰성과 효율성을 높이기 위한 첨단 전력망 인프라입니다.
- 시장은 이러한 계전기와 관련된 높은 설치 비용의 형태로 주목할만한 장애물에 직면 해 있습니다. 대규모 산업 환경에서 보호 계전기는 종종 보조 회로가 필요하여 총 비용을 증가시킵니다. 또한 정기적인 유지보수는 운영 비용을 더욱 증가시킵니다. 또한, 시장은 조직화되지 않은 부문과의 치열한 경쟁으로 인해 어려움을 겪고 있습니다.
- 경제 전반의 건전성 및 지정학적 긴장과 같은 거시경제적 요인은 보호 계전기 시장의 성장 궤도를 형성하는 데 매우 중요합니다. 이러한 요인은 제조업, 산업, 유틸리티 등 주요 최종사용자 부문에 큰 영향을 미칩니다. 최근 분쟁, 특히 러시아-우크라이나 전쟁과 이스라엘-하마스 전쟁은 세계 공급망 문제를 악화시키고 모든 최종사용자 분야에 영향을 미치는 혼란을 초래했습니다.
마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기 시장 동향
공공사업 부문이 큰 시장 점유율을 차지
- 보호 계전기는 특히 발전 및 배전 유틸리티 기업에서 지속적인 수요가 있을 것으로 예상됩니다. 국제에너지기구(IEA)는 2024년 전 세계 전력 수요가 3.3% 증가할 것으로 전망하고 있습니다. 전기 안전에 대한 인식이 높아지고 전력 시스템 고장으로 인한 영향을 최소화해야 할 필요성이 증가함에 따라, 전력 유틸리티의 첨단 보호 시스템 도입에 대한 중요성이 점점 더 커지고 있습니다. 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기는 고장 감지 및 대응에 있어 정확성, 선택성 및 지능을 향상시켜 전기 장비, 인력 및 전체 전력 시스템의 안전을 보장합니다.
- 세계 각국은 전력 인프라를 현대화하고, 재생에너지에 적응하고, 진화하는 산업계의 요구를 충족시키기 위해 투자를 강화하고 있습니다. 더 많은 재생에너지 프로젝트가 개발되고 전력망에 연결됨에 따라 전체 전력 시스템은 더욱 복잡하고 다양해지고 있습니다. 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기는 이러한 새로운 재생에너지원을 기존 전력망 인프라에 안전하고 안정적으로 통합하는 데 있어 매우 중요한 역할을 하고 있습니다.
- 예를 들어, 호주는 2030년까지 태양광, 풍력 등 재생에너지로 전력의 82%를 생산한다는 목표를 세웠으며, 태양광발전은 이 목표 달성에 크게 기여할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기는 전력망에서 발생할 수 있는 고장을 감지하고 분리하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 신속한 고장 감지를 통해 영향을 받는 구간을 신속하게 분리하여 연쇄 고장을 방지하고 다운타임을 최소화할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 재생에너지 시스템과 전체 전력망의 신뢰성과 성능을 유지할 수 있습니다.
- 많은 지역에서 재생에너지 프로젝트가 전력망에 원활하게 통합되기 위해 준수해야 하는 특정 전력망 코드와 표준이 있습니다. 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기는 그리드 연결 및 동기화에 필요한 보호 및 통신 기능을 제공함으로써 이러한 표준을 준수할 수 있습니다.
아시아태평양이 큰 시장 점유율을 차지
- 아시아태평양의 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기 시장의 성장은 전력 인프라의 증가, 전력망 현대화 노력, 전기 안전 의식, 스마트 그리드에 대한 노력, 정부 지원 등의 요인에 의해 주도되고 있습니다. 전력 시스템의 지속적인 확장과 기술 발전으로 이 지역의 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기에 대한 수요는 더욱 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 아시아태평양은 급속한 산업화, 도시화 및 인구 증가로 인해 전력 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. 이 지역의 국가들은 전력 인프라의 확장 및 업그레이드에 지속적으로 투자하고 있으며, 이에 따라 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기를 포함한 신뢰할 수 있는 보호 시스템에 대한 필요성이 증가하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 유엔에 따르면 인도는 향후 몇 년 안에 인구가 가장 많은 국가가 될 것으로 예상되며, 2030년에는 15억 명, 2050년에는 16억 6,000만 명에 이를 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 아시아태평양의 많은 국가들은 전력 공급의 효율성, 신뢰성 및 품질을 향상시키기 위해 전력망 현대화에 주력하고 있습니다. 여기에는 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기와 같은 첨단 보호 및 제어 기술의 도입이 포함됩니다. 또한, 노후화된 전력 인프라의 업그레이드와 재생에너지원의 통합도 첨단 보호 솔루션에 대한 수요를 촉진하고 있습니다.
- 2023년 10월, 인도 태양에너지공사(SECI)는 인도 시장에서 약 1GW 규모의 주 간 송전망 연계 태양광 프로젝트 개발 입찰을 시작했습니다. 개발되는 태양광 프로젝트는 개발업체와 SECI 간에 25년간 전력 구매 계약을 체결하게 됩니다. 이러한 기가 와트 규모의 태양광발전 입찰이 시작되고 프로젝트가 개발됨에 따라 향후 몇 년 동안 태양광발전 시장에 활력을 불어넣을 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 예를 들어, 인도의 재생에너지 발전설비 용량(수력 포함)은 2024년 4월 기준 191.67GW이며, 2030년까지 500GW의 재생에너지를 건설할 계획입니다. 따라서, 중국의 재생에너지 수요 증가는 예측 기간 동안 시장 성장에 기여할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 아시아태평양에서는 전력 시스템의 고도의 모니터링, 제어 및 자동화를 가능하게 하는 스마트 그리드 기술의 도입이 진행되고 있습니다. 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기는 실시간 모니터링, 원격 제어 및 통신 기능을 제공하여 그리드의 신뢰성과 효율적인 운영을 지원함으로써 스마트 그리드 애플리케이션에서 중요한 역할을 하고 있습니다.
- 아시아태평양의 각국 정부는 증가하는 에너지 수요에 대응하고 송전망의 신뢰성을 향상시키기 위해 전력 부문에 대한 투자를 늘리고 있습니다. 이러한 노력에는 고급 보호 및 제어 시스템 도입이 포함되는 경우가 많으며, 이는 마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기에 대한 수요를 견인하고 있습니다.
마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기 산업 개요
마이크로프로세서 보호 계전기 시장은 경쟁이 치열하고 세분화되어 있으며 ABB, Siemens AG, Toshiba Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Schneider Electric과 같은 대기업이 진출해 있습니다. 시장 참여자들은 제품 라인업을 강화하고 지속가능한 경쟁 우위를 확보하기 위해 제휴 및 인수와 같은 전략을 채택하고 있습니다.
- 2024년 1월, Fanox Electronics는 광범위한 애플리케이션을 위한 최첨단 고보호 계전기 솔루션을 발표하며 이정표를 달성했습니다. 이 회사의 주력 제품인 SIR-C 오버헤드 제어 및 피더 보호 시스템은 오버헤드 제어/RTU와 피더 보호 계전기의 두 가지 역할을 수행합니다. 이 혁신적인 시스템은 1차 및 2차 배전 전류, 전압, 주파수 모니터링을 포함한 종합적인 기능을 자랑합니다. 또한 SIR-C는 24-230 Vdc/ac의 보조 전원을 통해 탄력적이고 신뢰할 수 있는 성능을 보장합니다.
- 2023년 8월, 지멘스는 전력망의 안정성을 모니터링하고 시스템 효율성을 보장하며 모터 및 압축기와 같은 중요한 구성요소의 수명을 연장하도록 설계된 SIRIUS 3UG5 라인 모니터링 계전기를 출시했습니다. 이 계전기는 병원이나 공정 산업과 같이 안정적인 전력 공급이 가장 중요한 까다로운 환경에 특히 적합합니다.
기타 혜택:
- 엑셀 형식의 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 소개
- 조사 상정과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트
- 시장 개요
- 업계의 매력 - Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급 기업의 교섭력
- 소비자의 협상력
- 신규 참여업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간의 경쟁 관계
- 업계 밸류체인 분석
- COVID-19의 부작용과 기타 거시경제 요인이 시장에 미치는 영향
제5장 시장 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 전력 소비 성장
- 재생에너지원 이용 증가
- 시장 과제
- 비용 상승과 미조직 부문과의 경쟁 격화
제6장 시장 세분화
- 전압 범위별
- 저전압
- 중전압
- 고전압
- 최종 이용 산업별
- 유틸리티
- 산업용
- 기타 최종 이용 산업(철도, 병원 등)
- 용도별
- 송전선
- 부스바
- 피더
- 변압기
- 발전기
- 모터
- 기타 용도
- 지역별
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 호주·뉴질랜드
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
제7장 경쟁 상황
- 기업 개요
- ABB Ltd
- Schneider Electric SE
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Siemens AG
- Bender GmbH & Co. KG
- Eaton Corporation PLC
- General Electric Company
- Rockwell Automation
- Littelfuse Inc
- Toshiba Corporation
- Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories
- L&T Electrical & Automation(Schneider Electric SE)
- Fanox Electronics
- NR Electric Co. Ltd
제8장 시장 전망
ksm 24.09.26The Microprocessor Protective Relay Market size is estimated at USD 0.93 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 1.63 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 11.98% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
Key Highlights
- The microprocessor protective relay market is projected to grow significantly due to the increasing power infrastructure, grid modernization efforts, electrical safety awareness, smart grid initiatives, and government support. With the continued expansion of power systems and technological advancements, the demand for microprocessor protective relays is expected to increase further.
- With climate change heightening the frequency of extreme weather events, National Grid emphasizes the urgency of bolstering its infrastructure against potent storms and rising temperatures. Consequently, in March 2024, the company unveiled a USD 4 billion initiative aimed at fortifying the power grid in upstate New York. This substantial investment will fund 70 projects, encompassing the construction of new substations and the extensive reconstruction of over 1,000 miles of transmission lines that link towns in proximity to Buffalo, Rochester, and Syracuse.
- Developing and developed countries worldwide are significantly investing in the construction of smart power grids, which is anticipated to propel the market for relays in the coming years. Smart grids are advanced electric power grid infrastructures for enhanced reliability and efficiency and work with automated control, modern communications infrastructure, high-power converters, modern energy management techniques, and sensing and metering technologies.
- The market faces a notable hurdle in the form of the higher installation costs associated with these relays. In large industrial settings, the protection relays often necessitate supplementary circuitry, elevating the total cost. Moreover, their regular maintenance further adds to operational expenses. Compounding this, the market contends with mounting competition from the unorganized sector.
- Macroeconomic factors, like the overall economic health and geopolitical tensions, are pivotal in shaping the growth trajectory of the protective relay market. These factors have a pronounced effect on key end-user sectors, spanning manufacturing, industrial, and utilities. Recent conflicts, notably the Russia-Ukraine and Israel-Hamas wars, have exacerbated global supply chain challenges, leading to disruptions that reverberated across all end-user segments.
Microprocessor Protective Relay Market Trends
Utilities Segment to Hold Significant Market Share
- Protective relays are poised to see continued demand from utilities, particularly in power generation and distribution. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projected that global electricity demand will increase by 3.3% in 2024. With growing awareness of electrical safety and the need to minimize the impact of power system faults, there is an increasing emphasis on deploying sophisticated protection systems in utilities. Microprocessor protective relays offer enhanced accuracy, selectivity, and intelligence in detecting and responding to faults, ensuring the safety of electrical equipment, personnel, and the overall power system.
- Global nations are ramping up investments to modernize their power infrastructures, adapting them for renewable energy and aligning with evolving industry needs. As more renewable energy projects are developed and connected to the grid, the overall power system becomes more complex and diverse. Microprocessor protective relays play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and reliable integration of these new renewable energy sources into the existing grid infrastructure.
- For instance, Australia has set a goal of generating 82% of its electricity through renewable sources like solar PV and wind by 2030, and solar PV is expected to be a significant contributor to achieving this target.
- Microprocessor protective relays are instrumental in detecting and isolating faults that may occur within the power grid. They provide rapid fault detection, allowing for quick isolation of the affected section, preventing cascading failures, and minimizing downtime. This aids in maintaining the reliability and performance of the renewable energy systems and the overall grid.
- Many regions have specific grid codes and standards that renewable energy projects need to adhere to for seamless integration into the power grid. Microprocessor protective relays enable compliance with these codes by providing the necessary protection functions and communication capabilities required for grid connection and synchronization.
Asia-Pacific to Register a Significant Market Share
- The growth of the microprocessor protective relay market in Asia-Pacific is driven by factors like increasing power infrastructure, grid modernization efforts, electrical safety awareness, smart grid initiatives, and government support. With the continued expansion of power systems and advancements in technologies, the demand for microprocessor protective relays is expected to further increase in the region.
- Asia-Pacific is experiencing rapid industrialization, urbanization, and population growth, leading to an increased demand for electricity. As countries in the region continue to invest in expanding and upgrading their power infrastructure, the need for reliable protection systems, including microprocessor protective relays, is growing. For instance, according to the United Nations, India will become the most populated country in the coming years, with a population of 1.5 billion by 2030 and 1.66 billion by 2050.
- Many countries in Asia-Pacific are focusing on modernizing their power grids to improve efficiency, reliability, and quality of electricity supply. This includes the incorporation of advanced protection and control technologies like microprocessor protective relays. The upgrading of aging power infrastructure and the integration of renewable energy sources also drive the demand for advanced protection solutions.
- In October 2023, the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) launched a tender in the Indian market to develop about 1 GW of interstate transmission grid-connected solar projects. The solar projects to be developed will witness the signing off of a 25-year power purchase agreement between developers and SECI. The onset of such gigawatt-scale solar tenders and the development of projects are expected to create a spur in the solar energy market in the coming years.
- For instance, India's installed renewable power capacity (including hydro) was 191.67 GW as of April 2024. By 2030, the country intends to build 500 GW of renewable energy. Thus, increasing demand for renewable energy in the country is expected to contribute to market growth during the forecast period.
- Asia-Pacific is witnessing the adoption of smart grid technologies, which enable advanced monitoring, control, and automation of power systems. Microprocessor protective relays play a crucial role in smart grid applications by providing real-time monitoring, remote control, and communication capabilities, supporting the reliable and efficient operation of the grid.
- Governments in Asia-Pacific are implementing initiatives and making investments in the power sector to meet the growing energy demand and improve grid reliability. These initiatives often include the deployment of advanced protection and control systems, driving the demand for microprocessor protective relays.
Microprocessor Protective Relay Industry Overview
The microprocessor protective relay market is highly competitive and fragmented, with major players like ABB Ltd, Siemens AG, Toshiba Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, and Schneider Electric. Players in the market are adopting strategies such as partnerships and acquisitions to enhance their product offerings and gain sustainable competitive advantage.
- January 2024: Fanox Electronics achieved a milestone by introducing cutting-edge high-protection relay solutions tailored for a wide array of applications. Its flagship offering, the SIR-C Overhead Control and Feeder Protection System, serves a dual role as an overhead control/RTU and a feeder protection relay. This innovative system boasts comprehensive functionalities, including monitoring primary and secondary distribution currents, voltages, and frequencies. Moreover, the SIR-C guarantees a resilient and dependable performance with an auxiliary power supply ranging from 24 to 230 Vdc/ac.
- August 2023: Siemens introduced the SIRIUS 3UG5 line monitoring relays, designed to oversee grid stability, guarantee system efficiency, and prolong the lifespan of crucial components like motors and compressors. These relays are particularly suited for demanding environments, such as hospitals and the process industry, where a reliable power supply is paramount.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumption and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.2.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.2.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.2.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.3 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Impact of COVID-19 Aftereffects and Other Macroeconomic Factors on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Growth in Electricity Consumption
- 5.1.2 Increasing Use of Renewable Energy Sources
- 5.2 Market Challenges
- 5.2.1 Higher Cost and Increasing Competition from Unorganized Sector
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Voltage Range
- 6.1.1 Low-voltage
- 6.1.2 Medium-voltage
- 6.1.3 High-voltage
- 6.2 By End-user Industry
- 6.2.1 Utilities
- 6.2.2 Industrial
- 6.2.3 Other End-user Industries (Railway, Hospitals, etc.)
- 6.3 By Application
- 6.3.1 Transmission Line
- 6.3.2 Bus Bar
- 6.3.3 Feeder
- 6.3.4 Transformer
- 6.3.5 Generator
- 6.3.6 Motor
- 6.3.7 Other Applications
- 6.4 By Geography
- 6.4.1 North America
- 6.4.2 Europe
- 6.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 6.4.4 Australia and New Zealand
- 6.4.5 Latin America
- 6.4.6 Middle East and Africa
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 ABB Ltd
- 7.1.2 Schneider Electric SE
- 7.1.3 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 7.1.4 Siemens AG
- 7.1.5 Bender GmbH & Co. KG
- 7.1.6 Eaton Corporation PLC
- 7.1.7 General Electric Company
- 7.1.8 Rockwell Automation
- 7.1.9 Littelfuse Inc
- 7.1.10 Toshiba Corporation
- 7.1.11 Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories
- 7.1.12 L&T Electrical & Automation (Schneider Electric SE)
- 7.1.13 Fanox Electronics
- 7.1.14 NR Electric Co. Ltd



















