
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1630373
패시브 광네트워크(PON) 장비 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Passive Optical Network (PON) Equipment - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
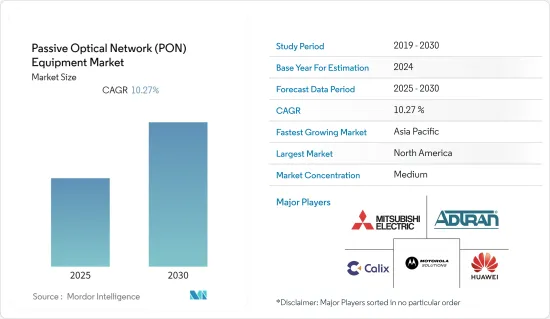
패시브 광네트워크(PON) 장비 시장은 예측 기간 동안 CAGR 10.27%를 기록할 것으로 예상됩니다.
주요 하이라이트
- 또한, 정부는 IoT 인프라의 원활한 흐름을 가능하게 하기 위해 광섬유가 풍부한 네트워크에서 스마트 시티 프로그램과 같은 이니셔티브를 취하고 있습니다. 광섬유 네트워크는 물, 전기, 폐수, 하수 관리, 보안, 통신과 같은 공공 서비스를 촉진하는 기술을 가능하게 합니다. 유엔에 따르면 2050년까지 전 세계 인구의 68% 이상이 도시에 거주할 것으로 추정되고 있어 전 세계적으로 스마트 시티 프로젝트가 활성화될 것으로 보입니다.
- 데이터 트래픽이 기하급수적으로 증가함에 따라 더 큰 용량의 네트워크에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. 패시브 광네트워크(PON)는 장거리에서 광대역을 제공할 수 있기 때문에 이 문제에 대한 효과적인 해결책이 될 수 있습니다. 대역폭에 대한 수요 증가는 패시브 광네트워크 시장의 성장을 촉진하는 주요 요인이 되고 있습니다. 소비자들은 비디오 스트리밍 및 기타 대역폭 집약적인 앱의 확산과 함께 더 빠르고 안정적인 네트워크를 원하고 있으며, PON은 액티브 부품이나 고가의 광섬유를 사용하지 않고도 상당한 거리에서 기가비트 속도를 제공할 수 있기 때문에 이러한 수요를 충족시키기에 적합합니다. 이러한 수요에 대응하기에 적합합니다.
- COVID-19로 인해 전 세계 각국은 예방 조치를 취했습니다. 학교는 휴교하고 지역사회는 재택근무를 요구했지만, 많은 조직은 직원들이 재택근무를 할 수 있는 방법을 모색하고 있었습니다. 통신사들은 초고속, 고신뢰성, 미래지향적인 광대역 네트워크를 제공하기 위해 광섬유 인프라를 구축하는 데 적극적으로 노력했습니다.
- 예를 들어, 세계 5G 대회에서 발표된 데이터에 따르면 중국의 월평균 모바일 사용자 온라인 트래픽은 5G에 힘입어 지난 3년 동안 7.8GB에서 14.9GB로 증가했습니다. 이는 원격 근무, 온라인 교육, 디지털 생활, 과학 연구, COVID-19 팬데믹 기간 동안 전염병 예방 및 통제를 용이하게 했습니다. 이러한 요인들은 예측 기간 동안 시장 성장률에 크게 기여했습니다.
패시브 광네트워크(PON) 시장 동향
GPON 장비가 크게 성장할 것으로 전망
- 확대 모바일 광대역(eMBB)은 5G NR과 4G LTE의 지연 개선으로 더 넓은 데이터 대역폭을 설명합니다. eMBB는 모바일 광대역 서비스를 고객에게 직접 제공함으로써 많은 사업자를 5G의 새로운 사용 사례로 이끌었습니다. 따라서 스펙트럼 효율과 전력이 개선되고 선진국과 개발도상국에서 스마트폰의 데이터 사용량이 증가함에 따라 디지털 서비스를 위한 충분한 용량을 보완하고 있습니다.
- 최근 테스트, 계측, 보증 솔루션 및 첨단 정밀 광학 솔루션 제공업체인 VIAVI Solutions Inc.는 최대 10GbE까지의 네트워크 테스트, 턴업 및 성능 모니터링을 위한 소형 폼팩터 플러그형(SFP) VIAVI NITRO 라이프사이클 관리 플랫폼의 일부인 Fusion JMEP 10은 5G xHaul, 비즈니스 이더넷 서비스, 케이블용 DAA(Distributed Access Architecture), 파이버 옵티컬, 5G xHaul, 비즈니스 이더넷 서비스, 케이블용 DAA(Distributed Access Architecture) 및 Distributed Access Architecture), 파이버 액세스 네트워크용 GPON/XGSPON(Gigabit Passive Optical Networks) 등 10GbE의 이더넷 대역폭이 주류로 부상하고 있습니다.
- 5G와 광케이블의 호환성은 상호 호혜적인 파트너십을 가져옵니다. 가정에 광섬유를 연결하는 데 너무 비싸고 비용이 많이 들고 시간이 오래 걸리는 지역에서는 5G 고정 무선 액세스가 FTTH 배포의 격차를 메우고 커버리지를 확장 할 수 있습니다. 고객은 셀룰러 네트워크에서 Wi-Fi로 전환하여 5G 트래픽을 Wi-Fi 및 FTTH로 오프로드합니다. 이를 통해 RAN 용량과 가격을 효율적으로 관리하고 미션 크리티컬한 애플리케이션을 위해 5G 용량을 확보하여 가정 내 고객 경험을 개선할 수 있습니다. 모바일 장비 사용자들은 5G를 통해 더 빠른 속도와 세계 커버리지를 기대하며, 이를 위해서는 고성능의 모바일 전송 네트워크가 필요합니다. 또한, 이러한 전송을 제공하기 위해 이미 존재하는 패시브 광네트워크(PON) 기술 기반의 FTTH 네트워크가 사용될 것입니다.
- 전 세계적으로 GPON의 보급이 가속화됨에 따라 통신 사업자들도 다음 단계의 광케이블 보급을 위해 적극적으로 움직이고 있습니다. 10G PON 패시브 광네트워크 기술은 넓은 커버리지와 넓은 대역폭을 특징으로 하는 10G PON 패시브 광네트워크 기술은 향후 5년 내에 광 액세스 네트워크에 기가비트 시대가 빠르게 도래할 것입니다. 고속 광 액세스 네트워크를 구축할 때 하나의 시스템으로 30-40 가구에 기가비트 액세스를 제공할 수 있기 때문에 전 세계 사업자들은 이 기술을 선호하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양이 급성장
- 최근 초고속 인터넷과 5G 네트워크에 대한 관심이 높아지고 있습니다. 이 지역을 주도하는 것은 중국, 일본, 대만, 인도, 호주 등 신흥국입니다. 중국에는 5G를 위한 생태계가 구축되어 있으며, 예측 기간 동안 더욱 성장할 것으로 예상됩니다. 그러나 5G 기술은 현재 모바일 브로드밴드와 함께 핫스팟 기술로 작용할 것으로 예상되며, 성장은 완만할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 중국은 10G PON 기술로 대표되는 새로운 기가비트 초광대역 단계로 나아가고 있으며, 광네트워크의 기본 우위 측면에서 세계를 선도하고 있습니다. 주요 통신 사업자는 기가비트 광네트워크의 간결한 개발 계획을 효과적으로 수립하여 2021년까지 전국 300 개 이상의 도시에 기가비트 광대역 액세스 네트워크가 구축되어 8 천만 가구 이상에 서비스를 제공하고 전국 270만 명 이상에 서비스를 제공합니다. 기가비트 인터넷 접속 사용자가 대부분의 지방 통신 사업자로부터 기가비트 상용 패키지를 제공받았습니다. 신규 사용자 수는 불과 5개월 만에 전년도 총 사용자 수를 넘어섰습니다.
- Beijing Mobile은 도시에 수백 개의 더블 기가비트 부티크 커뮤니티를 건설하고 F5G 건설을 서두르고 있습니다. 광저우전신과 화웨이가 발표한 첫 번째 FTTR 백서는 전광주택 네트워크 기술을 통해 기가비트 광대역 풀하우스 커버리지를 보장합니다. 디지털 경제의 견고한 기반을 강화하기 위해 항저우 이동은 '더블 5G' 디지털 도시 백서를 발표했습니다. 중국의 기가비트 광대역은 많은 장치와 단말기를 연결하고 가정, 기업, 비즈니스, 산업 제조 등 다중 시나리오 응용을 실현하고 소비자에게 안정적인 고속 대역폭 액세스 용량을 제공하기 위해 지속적으로 커버리지를 확대할 것으로 보입니다.
- 중국 통신사들은 5G에 594억 달러 이상을 투자하여 약 1조 2,500억 달러의 경제 효과를 창출했습니다. 이는 새로운 네트워크 인프라가 경제 성장에 크게 기여하고 있음을 보여줍니다. 과학기술부 부부장 샹리빈(湘立斌)은 5G의 상업적 활용이 긍정적인 피드백 루프에 진입했으며, 3년 이상의 개발 기간 동안 5G의 산업적 활용이 0에서 1로 증가했다고 지적했습니다. 이러한 요인들이 예측 기간 동안 시장 성장률에 기여한 것으로 분석했습니다.
패시브 광네트워크(PON) 산업 개요
패시브 광네트워크 장비 시장은 소수의 기업이 시장에 존재하기 때문에 적당히 통합되어 있습니다. 또한 이들 기업은 고객에게 다양한 기술을 제공하기 위해 대규모 투자를 하고 있습니다. 또한, 이들 기업은 시장 점유율을 확대하기 위해 전략적 파트너십, 인수, 제품 개발에 지속적으로 투자하고 있습니다. 각 회사의 현재 진행 상황은 다음과 같습니다.
- 2022년 5월 - 오스트리아 비엔나에서 열린 FTTH 컨퍼런스 2022에서 모바일 인터넷용 통신, 기업 및 소비자 기술 솔루션의 중요한 세계 공급업체인 ZTE Corporation(0763. HK/000063. SZ) )는 50기가비트 지원 패시브 광 네트워킹(50G PON)과 Wi-Fi 7 기술을 모두 제공하는 업계 최초의 광네트워크 장치(ONU) 프로토타입을 발표했다고 밝혔습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식의 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 소개
- 조사 가정과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 역학
- 시장 개요
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급 기업의 교섭력
- 구매자·소비자의 협상력
- 신규 참여업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간의 경쟁 강도
- COVID-19의 시장에 대한 영향 평가
제5장 시장 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 안전하고 신뢰성 높은 네트워크 운영에 대한 수요
- 기존 네트워크와 비교해 친환경 대체품
- 낮은 총소유비용과 높은 투자 수익률
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 운영자 인터페이스의 높은 컴포넌트 비용
제6장 시장 세분화
- 구조별
- 이더넷 패시브 광네트워크(EPON) 장비
- 기가비트 패시브 광네트워크(GPON) 장비
- 구성요소별
- 파장 분할 멀티플렉서/디멀티플렉서
- 광필터
- 광파워 스플리터
- 광케이블
- 광회선 단말기(OLT)
- 광네트워크 단말기(ONT)
- 지역별
- 북미
- 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
제7장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 개요
- ADTRAN, Inc.
- Calix, Inc.
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Motorola Solutions, Inc.
- Nokia Corporation
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Tellabs, Inc.
- Verizon Communications, Inc.
- ZTE Corporation
제8장 투자 분석
제9장 시장 기회와 향후 동향
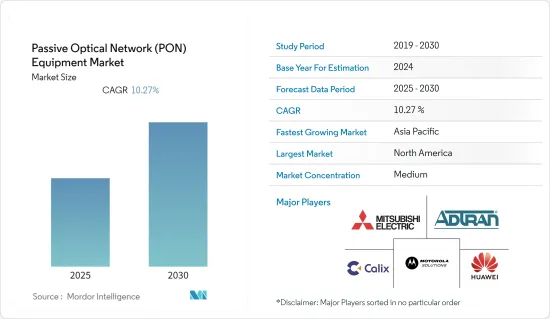
ksm 25.01.23The Passive Optical Network Equipment Market is expected to register a CAGR of 10.27% during the forecast period.
Key Highlights
- Additionally, governments are taking initiatives like smart city programs with fiber optic-rich networks to enable the smooth flow of IoT infrastructure. Fiber optic network allows the technology to drive utilities like water, electricity, wastewater, sewerage management, security, and communication. According to the UN, over 68% of the global population is estimated to live in urban areas by 2050, which will fuel more smart city projects globally.
- The demand for networks with greater capacity is increasing as data traffic keeps growing exponentially. Because they can deliver high bandwidths across great distances, passive optical networks (PONs) present a viable solution to this issue. The rising need for bandwidth is the primary factor driving the passive optical network market growth. Consumers demand faster and more dependable networks as video streaming and other bandwidth-intensive apps proliferate. Due to their ability to deliver gigabit speeds over considerable distances without the use of active components or pricey optical fiber, PONs are uniquely suited to meet this demand.
- Due to the COVID-19 outbreak, countries worldwide implemented preventive measures. While schools were closed and communities were asked to stay at home, many organizations were finding ways to enable employees to work from their homes. Telecom companies actively made efforts to build full-fiber infrastructure to deliver an ultrafast, ultra-reliable, and futureproof broadband network.
- For instance, the average monthly mobile user in China's online traffic increased from 7.8 GB to 14.9 GB over the past three years, driven by 5G, according to data released at the global 5g convention. It facilitated remote work, online education, digital life, scientific research, and epidemic prevention and control during the COVID-19 pandemic. These factors significantly contribute to the market growth rate during the forecast period.
Passive Optical Network (PON) Market Trends
GPON Equipments is Expected to Grow Significantly
- Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) provides greater data bandwidth due to latency improvements on 5G NR and 4G LTE. It led most operators towards new use cases for 5G by delivering mobile broadband services directly to customers. It, thus, complements ample capacity for digital services, owing to better spectral efficiency, power, and increasing smartphone data usage in developed & developing countries.
- Recently, VIAVI Solutions Inc., a test, measurement, assurance solutions, and advanced precision optical solutions provider, announced Fusion JMEP 10, a small form-factor pluggable (SFP+) Gigabit Ethernet transceiver for network test, turn-up, and performance monitoring up to 10 GbE. The Fusion JMEP 10, which is part of the VIAVI NITRO lifecycle management platform, addresses10 GbE emergence as the dominant Ethernet bandwidth for applications such as 5G xHaul, Business Ethernet Services, Distributed Access Architecture (DAA) for Cable and Gigabit Passive Optical Networks (GPON/XGSPON) for Fiber Access Networks.
- The compatibility of 5G and fiber results in a reciprocal partnership. In areas where connecting fiber to the home is challenging, expensive, or takes too long, 5G fixed wireless access can fill in the gaps in FTTH deployments and expand coverage. Customers leave the cellular network for Wi-Fi, offloading 5G traffic to Wi-Fi and FTTH. It facilitates managing RAN capacity and prices effectively, freeing up 5G capacity for mission-critical applications and improving the customer experience at home. Users of mobile devices anticipate substantially faster speeds and global coverage from 5G, which requires a high-performance mobile transport network. Further, to offer that transport, a passive optical network (PON) technology-based FTTH networks already in existence are used.
- With the accelerating rollout of GPON worldwide, telecom operators are also actively moving toward the next step in fiber rollouts. The Gigabyte era will rapidly enter optical access networks during the next five years. The 10G PON passive optical network technology is distinguished by its broad coverage and high bandwidth. When installing high-speed optical access networks, operators around the world favor this technology since it can give Gigabyte access to 30-40 households on a single system.
Asia-Pacific Region to Witness the Fastest Growth
- Recently, there is an increased emphasis on high-speed internet and 5G network. The major driving countries in the region for the same are emerging countries, including China, Japan, Taiwan, India, and Australia. China includes an established ecosystem for 5G and is expected to grow further in the forecast period. However, the 5G technology is expected to serve as a hotspot technology with the current mobile broadband; the growth is expected to be gradual.
- China is advancing towards a new Gigabit ultra-wide stage, represented by 10G PON technology, and leading the global in terms of optical networks' fundamental advantages. Primary telecom providers effectively put up concise development plans for a gigabit optical network. Over 300 cities nationwide had a gigabit broadband access network in 2021, serving more than 80 million households. More than 2.7 million National Gigabit internet access consumers have received gigabit commercial packages from most provincial telecommunications providers. The number of new users surpassed the total number from the previous year in just five months.
- In addition to building hundreds of double Gigabyte boutique communities throughout the city, Beijing Mobile will hasten the construction of F5G. The first FTTR White Paper, published by Guangzhou Telecom and Huawei, ensures Gigabit broadband full house coverage through an all-optical residential network technology. To strengthen the firm foundation of the digital economy, Hangzhou Mobile published the "Double 5G" Digital City White Paper. China's Gigabit Broadband will continue to broaden its coverage to connect many devices and terminals, achieve multi-scenario applications such as home, enterprise, business, and industrial manufacturing, and give consumers reliable, high-speed bandwidth access capacity.
- Chinese telecom companies have invested more than USD 59.4 billion in 5G, generating more than USD 59.4 billion in 5G, generating an estimated USD 1.25 trillion in economic output. It shows the significant contribution new network infrastructure makes to economic growth. The commercial use of 5G entered a positive feedback loop, according to Xiang Libin, vice-minister of science and technology, and noted that after more than three years of development, industry-oriented 5G applications have increased from zero to one. These factors are analyzed to contribute to the market growth rate during the forecast period.
Passive Optical Network (PON) Industry Overview
The market for passive optical network equipment is moderately consolidated due to the presence of a few companies in the market. Also, these companies are investing extensively in offering customers a wide range of technologies. Moreover, these companies continuously invest in strategic partnerships, acquisitions, and product development to gain market share. Some of the current advancements by the companies are listed below.
- May 2022 - At the FTTH Conference 2022 in Vienna, Austria, ZTE Corporation (0763. HK / 000063.SZ), a significant global supplier of telecoms, enterprise, and consumer technology solutions for the mobile internet, declared that it had unveiled the prototype of the first Optical Network Unit (ONU) in the industry to offer both 50-Gigabit-Capable Passive Optical Networking (50G PON) and Wi-Fi 7 technologies.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.2.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.2.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.2.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.3 Assessment on the Impact of COVID-19 on the market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Demand for secure and reliable network operation
- 5.1.2 Eco-friendly substitute as compared to traditional networks
- 5.1.3 Low total cost of ownership and high return on investment
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 High component cost at operator interface
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Structure
- 6.1.1 Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON) Equipment
- 6.1.2 Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) Equipment
- 6.2 By component
- 6.2.1 Wavelength Division Multiplexer/De-Multiplexer
- 6.2.2 Optical filters
- 6.2.3 Optical power splitters
- 6.2.4 Optical cables
- 6.2.5 Optical Line Terminal (OLT)
- 6.2.6 Optical Network Terminal (ONT)
- 6.3 By Geography
- 6.3.1 North America
- 6.3.2 Europe
- 6.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 6.3.4 Latin America
- 6.3.5 Middle East & Africa
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 ADTRAN, Inc.
- 7.1.2 Calix, Inc.
- 7.1.3 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- 7.1.4 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 7.1.5 Motorola Solutions, Inc.
- 7.1.6 Nokia Corporation
- 7.1.7 Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- 7.1.8 Tellabs, Inc.
- 7.1.9 Verizon Communications, Inc.
- 7.1.10 ZTE Corporation



















