
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1636204
북미의 폐기물 관리 시장 전망 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)North America Waste Management - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
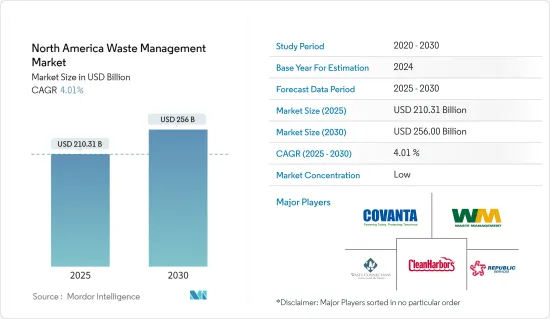
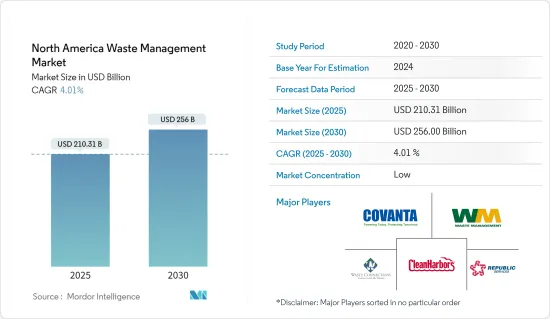
북미의 폐기물 관리 시장 규모는 2025년에 2,103억 1,000만 달러로 추정되며, 예측 기간 중(2025-2030년) 연평균 성장율(CAGR)은 4.01%로, 2030년에는 2,560억 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.
2024년 7월에 발표된 새로운 연방 플라스틱 오염 전략에 따라 2035년까지 미국 정부의 모든 업무에서 일회용 플라스틱이 단계적으로 퇴출될 예정입니다. 이 정책은 플라스틱으로 인해 쓰레기로 오염된 바다와 오염된 공기의 위기를 언급하고 있습니다.
단계적 폐기로 인해 대체 물질을 처리하고 잔류 플라스틱을 관리할 수 있는 첨단 재활용 기술과 시설의 필요성이 높아질 것으로 예상됩니다. 폐기물 관리 기업은 이러한 변화하는 요구 사항을 처리하기 위해 새로운 시스템과 인프라를 개발해야 할 것입니다.
연구 대상 시장은 또한 친환경 및 순환 경제 원칙으로의 전환을 반영하여 폐기물 에너지화 기술 개발과 폐기물 처리 방법의 개선이 성장하고 있습니다. 이러한 기술의 예로는 플라즈마 아크 가스화, 열분해, 로터리 킬른 등이 있습니다.
2024년 3월, 미국 에너지부의 바이오에너지 기술 사무소(BETO)와 국립재생에너지연구소(NREL)는 폐기물 에너지화 기술 지원의 다음 단계를 시작했습니다. 주 정부를 포함하도록 프로그램 자격이 확대되었으며, 이제 폐기물 자원을 추가로 포함하게 되었습니다.
이 프로그램은 주 정부의 자격을 확대하고 범위를 추가 폐기물 자원으로 확대하여 북미 폐기물 관리 시장을 촉진합니다. 이 노력는 폐기물 에너지화 기술의 보다 광범위한 채택을 장려하여 폐기물 관리 시장의 성장을 주도할 수 있습니다.
북미의 폐기물 관리 시장 동향
플라스틱 폐기물 문제가 증가함에 따른 폐기물 관리 시장 급증
- 미국 인구조사국에 따르면 2023년 미국은 약 9억 2,000만 파운드의 폐플라스틱을 수출하여 전년 대비 4.6% 감소했으며, 2015년 대비 80% 가까이 감소했습니다. 캐나다와 멕시코가 미국 플라스틱 스크랩 수출의 절반 이상을 차지하는 주요 수출 대상국이었습니다.
- 이러한 감소는 플라스틱 스크랩 처리를 위한 해외 시장에 대한 의존도가 줄어들고 있으며, 국내 재활용 및 폐기물 관리 솔루션의 강화 필요성이 커지고 있음을 시사합니다. 수출 기회가 축소됨에 따라 미국은 국경 내에서 더욱 강력한 재활용 인프라와 폐기물 관리 시스템을 개발해야 할 필요성이 커지고 있습니다.
- 캐나다에서는 2022년에 모든 출처에서 발생하는 폐기물 처리량이 50만 톤(+1.91%) 증가하여 2,662만 톤에 달했습니다. 이러한 증가는 관찰된 기간 중 가장 높은 폐기물 처리 수준입니다. 이러한 증가는 효과적인 관리가 필요한 폐기물의 양이 증가하고 있음을 보여주며, 폐기물 관리 전략 개선, 재활용 프로그램 강화, 종합적인 폐기물 감축 조치에 대한 수요를 강조합니다.
북미의 폐기물 관리를 형성하는 국가 전략
- 2024년 6월, 미국 농무부(USDA), 미국 환경보호청(EPA), 미국 식품의약국(FDA), 백악관은 식품 손실 및 폐기물 감소와 유기물 재활용을 위한 국가 전략을 발표했습니다.
- 이 전략은 2030년까지 음식물 손실과 폐기물을 50% 줄이는 동시에 유기물 재활용을 강화하는 것을 목표로 합니다. 이 전략은 기후 변화 대응, 식량 안보 개선, 환경 정의 증진이라는 보다 광범위한 목표를 지원합니다.
- 미국 농무부, 환경보호국 및 식품의약국(FDA)은 이러한 목표를 달성하기 위해 새로운 연구에 자금을 지원하고, 인식 개선 캠페인을 시작하며, 지역사회 규모의 재활용 인프라 구축에 주력할 것입니다. 또한 폐기물 감축에 전념하는 업계 리더들과 파트너십을 구축할 것입니다.
- 이러한 전략은 고급 솔루션에 대한 수요를 증가시켜 폐기물 관리 시장에 큰 영향을 미칠 것으로 예상됩니다. 유기성 폐기물의 양이 증가함에 따라 기업은 서비스를 확장하고 재활용 프로세스를 개선해야 합니다. 이러한 수요 증가는 이 분야의 성장을 견인할 것으로 예상됩니다. 또한, 이 전략은 더 많은 협업과 더 효율적인 자원 배분을 장려하여 북미의 전반적인 폐기물 관리 관행을 개선합니다.
북미의 폐기물 관리 산업 개요
북미의 폐기물 관리 시장은 다양한 솔루션을 제공하는 여러 주요 업체들이 경쟁하는 환경이 특징입니다. 와 리퍼블릭 서비스(Republic Services Inc.)가 이 지역의 광범위한 수거, 재활용, 폐기 네트워크를 장악하고 있는 주요 선두주자입니다. 웨이스트 커넥션즈사(Waste Connections Inc.)도 중요한 지위를 차지하고 있으며, 특히 중소규모 시장에서 종합적인 폐기물 및 재활용 서비스를 제공합니다.
지속 가능성, 기술 혁신, 규제 준수는 이 시장의 주요 동인입니다. 예를 들어, 폐기물 관리 회사는 매립지 가스 에너지화 프로젝트에 막대한 투자를 하여 매립지에서 메탄을 포집하여 재생 에너지를 생산함으로써 온실가스 배출을 줄이고 에너지 지속 가능성을 지원하고 있습니다. 이는 매립지에서 폐기물을 전환하고 순환 경제를 촉진하기 위해 고급 재활용 프로그램과 폐기물 제로 정책을 시행하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 성과
- 조사의 전제
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
- 분석 방법
- 조사 단계
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트
- 현재의 시장 시나리오
- 기술 동향
- 공급체인, 가치체인 분석에 대한 통찰
- 업계 규제에 관한 통찰
- 업계의 기술적 진보에 관한 통찰
제5장 시장 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 환경 의식 증가
- 폐기물 관리 기술의 혁신
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 높은 자본 비용과 운영 비용
- 시장 기회
- 재활용 및 퇴비화 프로그램 증가
- 새로운 폐기물 에너지화 솔루션
- 업계의 매력 - Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 진입업자의 위협
- 구매자, 소비자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
제6장 시장 세분화
- 폐기물 유형별
- 산업폐기물
- 지자체 고형 폐기물
- 전자폐기물
- 플라스틱 폐기물
- 바이오메디컬 및 기타(건설폐기물 포함)
- 처리 방법별
- 매립처분
- 소각
- 재활용
- 국가별
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
제7장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도 개요
- 기업 프로파일
- Waste Management, Inc.
- Republic Services, Inc.
- Waste Connections, Inc.
- Clean Harbors, Inc.
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- Veolia North America
- Rumpke Waste & Recycling
- Heritage Environmental Services
- Waste Pro USA
- EnviroServe*
- 기타 기업
제8장 시장 기회와 앞으로의 동향
제9장 부록
HBR 25.02.10The North America Waste Management Market size is estimated at USD 210.31 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 256.00 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.01% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Single-use plastic will be phased out of all US government operations by 2035 under a new federal plastic pollution strategy unveiled in July 2024. The policy cites a crisis of littered oceans and poisoned air due to plastics.
The phase-out is expected to boost the need for advanced recycling technologies and facilities capable of processing alternative materials and managing residual plastics. Waste management companies will need to develop new systems and infrastructure to handle these evolving requirements.
The market studied is also witnessing growth in the development of waste-to-energy technologies and improved waste processing methods, reflecting a shift toward more eco-friendly and circular economy principles. Examples of these technologies are plasma arc gasification, pyrolysis, and rotary kilns.
In March 2024, the US Department of Energy's Bioenergy Technologies Office (BETO) and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) launched the next phase of Waste-to-Energy Technical Assistance. The program eligibility has been expanded to include state governments, and the scope now includes additional waste resources.
The program promotes the North American waste management market by broadening state governments' eligibility and expanding the scope to include additional waste resources. This initiative encourages more widespread adoption of waste-to-energy technologies, which can drive growth in the waste management market.
North America Waste Management Market Trends
Waste Management Market Surges in Response to Escalating Plastic Waste Concerns
- In 2023, the United States exported approximately 920 million pounds of scrap plastic, marking a 4.6% decrease from the previous year and a nearly 80% drop from 2015, according to the US Census Bureau. Canada and Mexico were the leading destinations for these exports, accounting for over half of the US plastic scrap exports.
- This decline suggests a reduced reliance on international markets for plastic scrap disposal, signaling a growing need for enhanced domestic recycling and waste management solutions. As export opportunities contract, there is an increasing imperative for the United States to develop a more robust recycling infrastructure and waste management systems within its borders.
- In Canada, waste disposal from all sources increased by 0.5 million tonnes (+1.91%) in 2022, reaching 26.62 million tonnes. This rise represents the highest waste disposal level in the observed period. The increase underscores a growing volume of waste that needs effective management, highlighting the demand for improved waste management strategies, enhanced recycling programs, and comprehensive waste reduction measures.
National Strategy Shaping North American Waste Management
- In June 2024, the US Department of Agriculture (USDA), US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the White House launched the National Strategy for Reducing Food Loss and Waste and Recycling Organics.
- This initiative aims to reduce food loss and waste by 50% by 2030 while enhancing the recycling of organic materials. The strategy supports broader objectives of combating climate change, improving food security, and promoting environmental justice.
- The USDA, EPA, and FDA will fund new research, launch awareness campaigns, and focus on building community-scale recycling infrastructure to achieve these goals. They will also foster partnerships with industry leaders dedicated to waste reduction.
- This strategy is expected to significantly impact the waste management market by increasing the demand for advanced solutions. As the volume of organic waste rises, companies must expand their services and enhance recycling processes. This increased demand is anticipated to drive growth in the sector. Moreover, the strategy encourages greater collaboration and more efficient resource allocation, improving overall waste management practices in North America.
North America Waste Management Industry Overview
The North American waste management market is characterized by a competitive landscape with several key players offering various solutions. Waste Management Inc. and Republic Services Inc. are significant leaders, dominating the region's extensive collection, recycling, and disposal networks. Waste Connections Inc. also holds a significant position, providing comprehensive waste and recycling services, especially in smaller and mid-sized markets.
Sustainability, technological innovation, and regulatory compliance are major drivers in this market. For instance, Waste Management Inc. has invested heavily in landfill gas-to-energy projects, capturing methane from landfills to produce renewable energy, which helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and supports energy sustainability. Similarly, Republic Services Inc. has implemented advanced recycling programs and zero-waste initiatives to divert waste from landfills and promote a circular economy.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Technological Trends
- 4.3 Insights on Supply Chain/Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Insights into Governement Regualtions in the Industry
- 4.5 Insights into Technological Advancements in the Industry
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Growing Environmental Awareness
- 5.1.2 Innovations In Waste Management Technologies
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 High Capital and Operational Costs
- 5.3 Market Opportunities
- 5.3.1 Growth in Recycling and Composting Programs
- 5.3.2 Emerging Waste-to-Energy Solutions
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 5.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Waste type
- 6.1.1 Industrial waste
- 6.1.2 Municipal solid waste
- 6.1.3 E-waste
- 6.1.4 Plastic waste
- 6.1.5 Biomedical + Others (Including Construction Waste)
- 6.2 By Disposal methods
- 6.2.1 Landfill
- 6.2.2 Incineration
- 6.2.3 Recycling
- 6.3 By Country
- 6.3.1 United States
- 6.3.2 Canada
- 6.3.3 Mexico
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 Waste Management, Inc.
- 7.2.2 Republic Services, Inc.
- 7.2.3 Waste Connections, Inc.
- 7.2.4 Clean Harbors, Inc.
- 7.2.5 Covanta Holding Corporation
- 7.2.6 Veolia North America
- 7.2.7 Rumpke Waste & Recycling
- 7.2.8 Heritage Environmental Services
- 7.2.9 Waste Pro USA
- 7.2.10 EnviroServe*
- 7.3 Other Companies



















