
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1636556
아시아태평양의 전자 폐기물 관리 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)APAC E-Waste Management - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
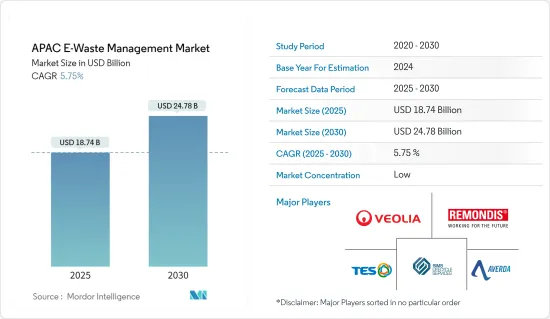
아시아태평양의 전자 폐기물 관리 시장 규모는 2025년 187억 4,000만 달러로 추정되고, 예측 기간(2025-2030년)의 CAGR은 5.75%로 전망되며, 2030년에는 247억 8,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.

아시아태평양은 급속한 기술 발전, 가전제품의 보급 확대, 강력한 경제 성장으로 인해 전자 폐기물이 크게 증가하고 있습니다. 중국, 인도, 일본이 주요 공헌국입니다.
2023년 8월 일본은 전자 폐기물의 과제를 해결하기 위해 ASEAN 국가와의 파트너십을 발표했습니다. 환경부 회의에서 설립된 이 협력관계는 전자 폐기물 처리에 관한 규제의 개발에 초점을 맞추었습니다. 일본은 2024년도 예산을 통해 폐기물 처리 사업자의 등록 및 인증 시스템의 구축을 지원합니다.
이 이니셔티브는 폐기물 수입 규제가 느려지기 때문에 환경 오염과 건강 위험에 시달리는 동남아시아의 전자 폐기물 처리를 개선하기 위한 것입니다. 일본은 또한 전기자동차 산업을 지원하고 국내 제한된 금속 자원을 줄이기 위해 전자 폐기물에서 귀중한 금속을 회수하려고 합니다.
한편, 2024년 5월 한국의 사모 주식 및 환경 관련 기업은 매립지 부문에 대한 투자를 증가 시켰습니다. 아피르마 캐피탈은 대형 매립지 운영회사인 젠텍을 5,000억 원(3억 6,800만 달러)으로 인수했습니다. 젠텍은 충청남도 당진시에서 대규모 매립지를 운영하고 있습니다. 이러한 관심 증가는 폐기물 관리에 대한 신뢰 증가를 반영하고, 전자 폐기물 처리 기술의 진보 가능성을 시사합니다.
아시아태평양의 전자 폐기물 관리 시장 동향
인도의 EPR 인증 플랫폼이 전자 폐기물의 재활용 효율성 향상
2022 회계연도 인도에서는 160만 톤이 넘는 전자 폐기물이 배출되어 52만 7,000톤이 회수 및 처리되었습니다. 2024년 3월 현재 정부는 이러한 심각화 과제를 해결하기 위해 확대 생산자 책임(EPR) 인증서를 거래하기 위한 온라인 플랫폼을 구축할 예정입니다. EPR의 의무화로 인해 생산자는 폐기 후 제품의 재활용에 대한 책임을 지고, 보다 재활용 가능하고 재사용 가능한 상품의 창출을 촉진합니다.
중앙오염관리위원회(CPCB)는 EPR 인증 시장의 투명성과 효율성을 높이기 위해 이 플랫폼을 감독합니다. 기업은 사내에서 폐기물을 관리하거나 재활용 기준을 초과하는 기업에서 EPR 증서를 조달함으로써 재활용 의무를 수행할 수 있습니다. CPCB는 미완료 EPR 목표에 대한 환경 보상 비율에 따라 이러한 증서의 지침과 가격을 설정합니다.
2022년 전자 폐기물(관리) 규정에서 EPR 지침을 시작한 이래 정부는 5,615건의 EPR 신청을 처리하고, 4,865건을 승인하고, 재활용업체로부터 285건의 신청을 받았으며, 196건을 허가했습니다. 주목할 점은 정부가 이미 폐전기 전자기기(WEEE)의 재활용 목표 10억 5,000만 톤을 돌파하고 있다는 점입니다. 정부는 현재 향후 플랫폼에서 이러한 노력을 강화하고 있습니다.
중국, 베이징 행사에서 전자 폐기물의 혁신과 지속가능성에 대한 노력을 강조
업계 전문가에 따르면 2022년 세계 최대 전자 폐기물 생산국인 중국은 1,200만 톤 이상의 전자 폐기물을 배출했습니다. 이른 것으로 2024년 4월 베이징의 계가원 외교거주구(DRC)는 중국의 폐기물 분별과 재활용의 약진에 스포트라이트를 맞춘 이벤트의 무대가 되었습니다. 이 전시회에서는 AI를 활용한 최첨단 폐기물 선별기가 전시되어 재활용 소재로 만든 제품이 소개되었습니다. 주목할만한 것은 이 행사에는 어린이를 위한 대화형 활동이 포함되어 있으며 재활용의 중요성이 강조되었다는 것입니다.
베이징시 대외환경위생서비스센터가 주최한 이 이벤트는 AI, IoT, 빅데이터, 클라우드컴퓨팅의 진보를 활용해 전자 폐기물과 싸우는 중국의 결의를 강조했습니다. 중국 퍼블릭 디플로마시 협회(CPDA) 산하의 중국 국제 프레스 커뮤니케이션 센터(CIPCC)는 COVID-19의 대유행으로 일시 중단하고 있던 미디어 교류의 일환으로 이번 방문을 실현시켰습니다. 이 프로그램은 90여 개국에서 100여 명의 저널리스트를 초청하여 미디어 교류에 중점을 두고 현재 진행 중인 중국 개발에 대한 견해를 제공했습니다.
이러한 쇼케이스와 이니셔티브를 통해 중국은 지속 가능한 전자 폐기물 관리 기술의 프론트 러너라는 이야기를 만들고 있습니다. 이 전략적 움직임은 중국 세계의 지위를 강화하고 국제 환경 대화에서 중국의 소프트 파워와 영향력을 증폭시키는 것을 목표로 합니다.
아시아태평양의 전자 폐기물 관리 산업 개요
아시아태평양의 전자 폐기물 관리 시장에서는 Sims Recycling Solutions 및 TES-AMM과 함께 Veolia Group, Remondis, Averda와 같은 대기업이 치열한 경쟁을 벌이고 있습니다. 특히 베올리아 그룹과 리몬디스는 고급 재활용 기술에 중점을 두고 다양한 전자 폐기물의 흐름에 대응하는 서비스 포트폴리오를 넓히고 있다는 점에서 두드러지고 있습니다.
시장을 선도하는 이들 기업은 지속가능성을 최우선으로 하고 지방정부와의 파트너십을 맺어 전자 폐기물 수집과 재활용 인프라를 강화하고 있습니다. 인도의 전자 폐기물 산업에서 유력한 기업인 Attero는 광범위한 회수 네트워크와 최첨단 재활용 기술을 보유하고 있습니다. 이러한 기업들은 기술, 규제상황, 지속가능한 노력에 전략적으로 주력함으로써 아시아태평양의 전자폐기물 시장을 전진시켜 보다 효율적이고 환경을 배려한 전자 폐기물 관리에 대한 길을 열고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 성과
- 조사의 전제
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
- 분석 방법
- 조사 단계
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트
- 현재의 시장 시나리오
- 기술 동향
- 공급망 및 벨류체인 분석에 대한 인사이트
- 업계 규제에 관한 인사이트
- 업계의 기술적 진보에 관한 인사이트
제5장 시장 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 급속한 기술진보에 의한 전자 폐기물량 증가
- 도시화 및 산업화
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 높은 재활용 비용
- 전자 폐기물의 복잡성
- 시장 기회
- 리사이클 기술의 진보
- 관민 파트너십
- 업계의 매력-Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자 및 소비자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
제6장 시장 세분화
- 재료 유형별
- 금속
- 플라스틱
- 유리
- 기타 재료
- 배출원 유형별
- 소비자용 전자 기기
- 산업용 전자 기기
- 가전제품
- 기타
- 용도별
- 매립지
- 재활용
- 기타 용도
- 국가별
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
제7장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도 개요
- 기업 프로파일
- Veolia Group
- Remondis
- Averda
- Sims Recycling Solutions
- TES-AMM
- Enviro-Hub Holdings Ltd
- Blue Planet Environmental Solutions Pte Ltd
- ECO Recycling Ltd(Ecoreco)
- Attero
- JOMAR Life Research Laboratory
- 기타 기업
제8장 시장 기회 및 향후 동향
제9장 부록
AJY 25.02.12The APAC E-Waste Management Market size is estimated at USD 18.74 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 24.78 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.75% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Asia-Pacific region is experiencing a significant rise in electronic waste due to rapid technological advancements, increased adoption of consumer electronics, and strong economic growth. China, India, and Japan are major contributors.
In August 2023, Japan announced a partnership with ASEAN countries to address e-waste challenges. This collaboration, established during an environment ministers' meeting, focuses on developing regulations for e-waste disposal. Japan will assist in creating registration and certification systems for waste management businesses, funded through its fiscal year 2024 budget.
This initiative aims to improve e-waste handling in Southeast Asia, which has struggled with environmental contamination and health risks due to lax waste import regulations. Japan also seeks to recover valuable metals from e-waste, supporting its electric vehicle industry and mitigating its limited domestic metal resources.
Meanwhile, in May 2024, South Korea's private equity and environmental firms increasingly invested in the landfill sector. Affirma Capital acquired Jentec, a major landfill operator, for KRW 500 billion (USD 368 million). Jentec operates a large landfill in Dangjin, South Chungcheong Province. This growing interest reflects increased confidence in waste management and suggests potential advancements in e-waste treatment technologies.
APAC E-Waste Management Market Trends
India's Upcoming EPR Certificate Platform to Boost E-Waste Recycling Efficiency
In the financial year 2022, India produced over 1.6 million metric tons of e-waste, with 527 thousand metric tons being collected and processed. As of March 2024, the government plans to roll out an online platform for trading Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) certificates to combat this escalating challenge. EPR mandates hold producers accountable for recycling their products post-disposal, thereby promoting the creation of more recyclable and reusable goods.
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) oversees this platform to boost transparency and efficiency in the EPR certificate market. Companies can fulfill recycling obligations by managing waste internally or procuring EPR certificates from entities surpassing their recycling benchmarks. The CPCB will set the guidelines and pricing for these certificates, pegged to a percentage of the environmental compensation for unmet EPR targets.
Since the inception of EPR directives in the E-Waste (Management) Rules of 2022, the government has processed 5,615 EPR applications, approving 4,865, and has received 285 applications from recyclers, granting 196. Notably, the government has already surpassed its recycling goal of 1.05 billion metric tons for Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE). It is now looking to bolster these efforts with the upcoming platform.
China Highlights E-Waste Innovations and Sustainability Initiatives at Beijing Event
Industry experts note that in 2022, China, the world's largest producer of electronic waste, churned out over 12 million metric tons. Fast-forward to April 2024, when the Qijiayuan Diplomatic Residence Compound (DRC) in Beijing set the stage for an event spotlighting China's waste sorting and recycling strides. The exhibition featured cutting-edge AI-driven waste-sorting machinery and showcased products crafted from recycled materials. Notably, the event included interactive activities for children, emphasizing the importance of recycling.
Hosted by the Beijing Municipal Center for Foreign-related Environment Sanitation Services, the event underscored China's resolve to combat e-waste, leveraging advancements in AI, IoT, big data, and cloud computing. The China International Press Communication Center (CIPCC), under the China Public Diplomacy Association (CPDA), facilitated this visit as part of a media exchange initiative reignited after a pause during the COVID-19 pandemic. The program hosted 100+ journalists from 90+ nations, focusing on media exchange and offering insights into China's ongoing developments.
Through such showcases and initiatives, China is crafting a narrative of being a frontrunner in sustainable e-waste management technology. This strategic move aims to bolster China's global standing, amplifying its soft power and influence in international environmental dialogues.
APAC E-Waste Management Industry Overview
The e-waste management market in Asia-Pacific sees intense competition, with major firms like Veolia Group, Remondis, and Averda, alongside Sims Recycling Solutions and TES-AMM, leading the charge. Veolia Group and Remondis, in particular, stand out for their emphasis on advanced recycling technologies and broadening service portfolios to handle diverse electronic waste streams.
These market leaders prioritize sustainability, forging partnerships with local governments to bolster e-waste collection and recycling infrastructure. Attero, a prominent player in India's e-waste landscape, has a widespread collection network and cutting-edge recycling methods. Collectively, these firms are propelling the APAC e-waste market forward through a strategic focus on technology, regulatory adherence, and sustainable initiatives, paving the way for a more efficient and eco-conscious e-waste management landscape.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Technological Trends
- 4.3 Insights into Supply Chain/Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Insights into Governement Regualtions in the Industry
- 4.5 Insights into Technological Advancements in the Industry
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Rapid Technological Advancements Drive Increasing E-Waste Volumes
- 5.1.2 Urbanization and Industrialization
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 High Cost of Recycling
- 5.2.2 Complexity of E-Waste
- 5.3 Market Opportunities
- 5.3.1 Advancements in Recycling Technologies
- 5.3.2 Public-Private Partnerships
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 5.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Material Type
- 6.1.1 Metal
- 6.1.2 Plastic
- 6.1.3 Glass
- 6.1.4 Other Materials
- 6.2 By Source Type
- 6.2.1 Consumer Electronics
- 6.2.2 Industrial Electronics
- 6.2.3 Household Appliances
- 6.2.4 Other Sources
- 6.3 By Application
- 6.3.1 Landfill
- 6.3.2 Recycled
- 6.3.3 Other Applications
- 6.4 By Country
- 6.4.1 China
- 6.4.2 Japan
- 6.4.3 India
- 6.4.4 South Korea
- 6.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 Veolia Group
- 7.2.2 Remondis
- 7.2.3 Averda
- 7.2.4 Sims Recycling Solutions
- 7.2.5 TES-AMM
- 7.2.6 Enviro-Hub Holdings Ltd
- 7.2.7 Blue Planet Environmental Solutions Pte Ltd
- 7.2.8 ECO Recycling Ltd (Ecoreco)
- 7.2.9 Attero
- 7.2.10 JOMAR Life Research Laboratory*
- 7.3 Other Companies



















