
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1906932
북미의 프로세스 자동화 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)North America Process Automation - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
북미의 프로세스 자동화 시장은 2025년 406억 4,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 2026년에는 417억 7,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 추정되며, 2026-2031년 CAGR 2.79%로 성장을 지속하여, 2031년까지 479억 4,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 전망되고 있습니다.

완만한 성장은 대규모 도입 기반, 단계적 효율화 정책 및 엄격한 환경 규제로 인한 것입니다. 석유 및 가스 사업자가 주요 도입 주체인 것을 계속하고 있는 한편, 제약 제조업체는 연속 제조가 미국 식품의약품국(FDA)의 지원을 얻으면서 가장 급속한 확대를 나타내고 있습니다. 제어실 간 연결에서는 유선 프로토콜이 여전히 주류이지만 ISA100 및 WirelessHART의 성숙에 따라 무선 네트워크가 가장 높은 성장률을 보이고 있습니다. 제조업체가 예측 분석을 통해 운영 데이터를 수익화하면서 안전상 중요한 로직은 온프레미스로 유지하면서 클라우드 및 엣지 전개가 가속화되고 있습니다.
북미의 프로세스 자동화 시장 동향 및 인사이트
에너지 효율 및 운영 비용 절감에 대한 주목 고조
전기 요금 및 연료 가격의 상승으로 실시간 에너지 최적화가 경영진 수준의 우선 과제가 되고 있습니다. 하이델베르크 소재는 부하 변동에 따라 연소를 미세 조정하는 고급 프로세서 제어(APC) 소프트웨어를 도입한 후, 가마의 에너지 사용량을 15% 삭감하여 연간 280만 달러의 절약을 실현했습니다. 고대호 지역의 제철소에서도 비슷한 노력으로 겨울철 가격 상승 시 천연가스 사용량을 삭감하고 있습니다. 전력 수요 응답 프로그램에서는 전력 소비가 많은 프로세스를 오프 피크 시간대로 이행한 공장에 보상금이 지급되므로 센서의 개수 비용은 단기간에 회수 가능합니다. 지속적인 모니터링은 압축 공기 누출과 같은 숨겨진 손실을 나타냅니다. 이러한 손실은 공장 전기 요금의 20-30%를 차지하는 일이 적지 않습니다. 초기 파일럿 사업에서 절약 효과가 입증되면 기업 재무 부서는 더 큰 다년간 예산을 승인하고 프로세스 자동화 시장의 기세를 유지합니다.
안전 계장 시스템에 대한 수요 증가
산업 사고 증가로 규제 당국의 감시가 강화되고 안전 시스템의 갱신이 가속화되고 있습니다. ISA-84 표준에 따라 정유소는 5년마다 안전 무결성 수준(SIL)의 검증을 의무화했습니다. 에머슨의 DeltaV SIS는 로직 솔버와 프로세스 제어를 통합하여 설계 공수를 줄이고 테스트 정지 시간을 단축합니다. 셰브론은 새로운 주제를 받았으며 중복 로직 플랫폼에 4,500만 달러를 투자하여 여행 관련 생산 손실을 크게 줄였습니다. 공급업체는 트립이 발생하기 전에 밸브 스틱과 센서 드리프트를 감지하는 진단 기능을 번들로 제공합니다. 이러한 변화가 결합되어 프로세스 자동화 시장을 지원하는 인증된 하드웨어, 검증 툴, 라이프사이클 서비스 계약에 대한 수요를 끌어올리고 있습니다.
높은 초기 설비 투자액 및 통합의 복잡성
여러 공급업체가 혼합된 플랜트를 개조하는 경우 통합 비용이 총 프로젝트의 60%에 도달할 가능성이 있습니다. 엔지니어는 단기간의 운영 중단 중에 자체 태그 매핑, 미들웨어 개발, 전환 작업을 수행해야 하며 총 설치 비용이 증가합니다. 다운타임 초과가 발생하면 투자 회수 기간이 장기화됩니다. 화학제품 등 상품 가격의 영향을 받기 쉬운 업계에서는 마진의 변동에 따라 자금 조달 장애물이 높아집니다. 공급업체는 현재 에너지 절약 보증을 번들로 제공하고 있지만 CFO는 여전히 3년 미만의 투자 회수를 요구하고 있으며, 이는 프로세스 자동화 시장의 단기 보급을 제한하고 있습니다.
부문 분석
유선 네트워크는 안전상 중요한 루프를 보호하는 확정적인 성능으로 2025년 수익의 69.25%를 차지했습니다. 이 이점은 연결성 카테고리 내에서 가장 큰 프로세스 자동화 시장 규모에 대한 기여도를 보여줍니다. 그러나 메쉬 토폴로지가 부식성 또는 폭발성 영역에서 99.9%의 가용성을 실현함에 따라 무선 프로토콜의 신뢰성이 높아지고 있습니다. 엑손모빌사 베이타운의 성공 사례는 무선 도입으로 설치 예산을 40% 절감할 수 있음을 증명하고 있습니다. 신흥 사설 5G는 모바일 자산 추적 및 유선 연결이 필요없는 로봇에 대한 관심을 불러 일으키며 자산당 센서 수가 2자리 증가할 가능성을 시사합니다. 제조업체는 현재 이더넷 기반 컨트롤러와 WirelessHART 필드 장비를 결합한 하이브리드 아키텍처의 테스트 운영을 진행 중이며 가동 시간과 유연성의 균형을 이루고 있습니다.
선행 도입 기업은 기존의 배선 전제로 자본위원회를 통과하지 못한 일시적인 감시 프로젝트에서 즉각적인 성과를 수치화하고 있습니다. 서비스 계약자는 특히 일정이 압축된 턴어라운드에서 신속한 시운전을 높이 평가했습니다. 신뢰성 팀은 게이트웨이에 내장된 고급 진단 기능이 제어 루프를 위험에 빠뜨리기 전에 신호 저하를 확인할 수 있음을 확인했습니다. ISA/IEC 62443과 같은 산업용 사이버 보안 프레임워크의 병행 발전은 무선 공격 측면에 대한 우려를 완화하고 있습니다. 테스트 이용 사례가 영구적인 설치로 성숙함에 따라 무선 기술은 차이를 줄이고 프로세스 자동화 시장에서 점진적인 성장을 지속할 것입니다.
하드웨어 시스템은 2025년 시점에서 프로세스 자동화 시장 규모의 26.88%의 점유율을 유지하고 있으며, PLC, 분산 제어 시스템, 안전 로직 솔버에 대한 지속적인 수요를 반영하고 있습니다. 그러나 플랜트 관리자들은 경쟁 우위의 원천을 하우징이 아닌 알고리즘에 요구하는 경향이 강해지고 있습니다. 소프트웨어 플랫폼은 고급 제어, 제조 실행 및 분석 도구가 미사용 데이터를 파악함으로써 3.92%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 기록하고 있습니다. Schneider Electric의 EcoStruxure는 SCADA 및 클라우드 마이크로서비스를 융합시켜 엔지니어가 거의 실시간으로 지식에 따라 행동할 수 있도록 합니다.
규제 당국이 디지털 배치 기록 및 에너지 강도 감사를 요구하는 분야에서는 소프트웨어 기세가 가속화되고 있습니다. 제약 회사는 FDA의 품질 설계(QbD) 요구 사항을 충족하기 위해 인라인 분광 분석 및 모델 예측 제어를 도입하여 소프트웨어 침투율을 높입니다. 반면에 오픈소스 히스토리컬 데이터 관리 시스템 및 컨테이너 오케스트레이션은 공급업체 잠금의 우려를 줄여줍니다. 하드웨어는 결정론적 제어에서 여전히 중요하지만, 차별화는 소프트웨어가 가치를 어떻게 능숙하게 추출할 수 있는지에 달려 있습니다. 이 전환은 서비스 및 구독 수익을 확대하고 프로세스 자동화 시장의 장기 성장을 강화합니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 애널리스트 서포트(3개월간)
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 에너지 효율화 및 운영 비용 절감에 대한 주목 증가
- 안전 계장 시스템에 대한 수요 증가
- 산업용 IoT 플랫폼의 보급
- 예측 보전 및 처방적 보전 분석으로의 전환
- 탄소 집약도 페널티가 디지털 프로세스 제어 가속
- 숙련 노동자의 고령화가 원격 조작 및 자율 운전 추진
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 높은 초기 설비 투자액 및 통합의 복잡성
- 기존 설비의 상호 운용성에 관한 과제
- 운영 사이버 보안 인력 부족
- 장기 서비스 계약에 의한 록인 효과에 의한 벤더 변경 제한
- 업계 가치 및 밸류체인 분석
- 규제 상황 및 기준
- 기술 전망(엣지 및 AI 분석)
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
- 산업 자동화의 중점 분야 분석(미국 및 캐나다)
- 거시 경제 동향의 영향(인플레이션 연동형 설비 투자, 리쇼어링)
- 유행 회복 테마(V자 회복, 중간 회복 및 침체)
- 미국 : 베이스라인 변동형 최종 사용자 실적
- 캐나다 : 베이스라인 변동형 최종 사용자 실적
- 공급 관련 과제 및 정책 자극책
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 통신 프로토콜별
- 유선
- 무선
- 시스템 유형별
- 하드웨어
- SCADA
- 분산 제어 시스템(DCS)
- 프로그래머블 로직 컨트롤러(PLC)
- 휴먼 머신 인터페이스(HMI)
- 프로세스 안전 시스템
- 밸브 및 액추에이터
- 전동 모터
- 센서 및 트랜스미터
- 소프트웨어
- 고급 프로세스 제어(ARC, MVC, 추론)
- 데이터 분석 및 보고 작성
- 제조 실행 시스템(MES)
- 기타 소프트웨어
- 하드웨어
- 컴포넌트별
- 하드웨어
- 소프트웨어
- 서비스
- 전개 모드별
- 온프레미스
- 클라우드 및 엣지
- 최종 사용자 업계별
- 석유 및 가스
- 화학제품 및 석유화학제품
- 전력 및 유틸리티
- 상하수도
- 식품 및 음료
- 펄프 및 제지
- 제약
- 기타 최종 사용자 산업
- 국가별
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- General Electric Company
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Omron Corporation
- Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- Delta Electronics, Inc.
- Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- Phoenix Contact GmbH & Co. KG
- Bosch Rexroth AG
- Beckhoff Automation GmbH & Co. KG
- Festo SE & Co. KG
- Endress Hauser Group Services AG
- Aspen Technology, Inc.
- AVEVA Group plc
- Azbil Corporation
제7장 시장 기회 및 장래 전망
AJY 26.01.26The North America process automation market is expected to grow from USD 40.64 billion in 2025 to USD 41.77 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 47.94 billion by 2031 at 2.79% CAGR over 2026-2031.
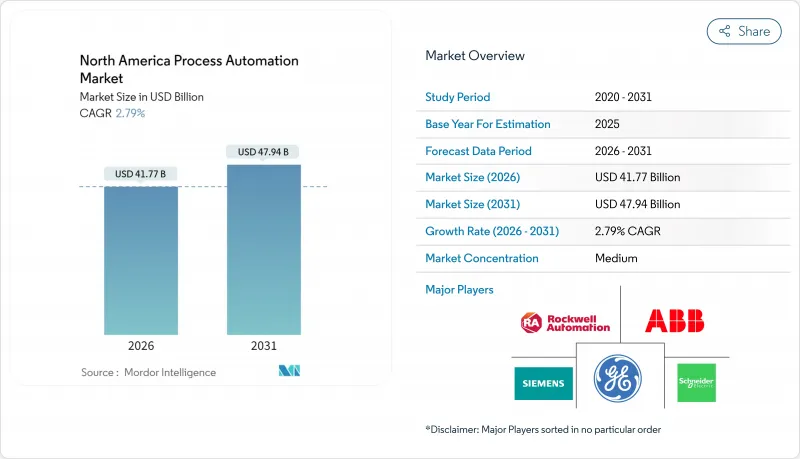
Moderate growth stems from a large installed base, incremental efficiency initiatives, and stricter environmental mandates. Oil and gas operators remain the principal adopters, while pharmaceutical manufacturers post the fastest expansion as continuous manufacturing gains U.S. Food and Drug Administration support. Wired protocols still dominate control-room links, yet wireless networks post the highest growth as ISA100 and WirelessHART mature. Cloud and edge deployments accelerate as manufacturers monetize operational data through predictive analytics while keeping safety-critical logic on-premises.
North America Process Automation Market Trends and Insights
Rising Focus on Energy-Efficiency and OPEX Reduction
Escalating electricity and fuel prices make real-time energy optimization a board-level priority. Heidelberg Materials cut kiln energy use by 15% and saved USD 2.8 million annually after installing advanced process control software that fine-tunes combustion in response to load swings. Similar initiatives in Great Lakes steel mills reduce natural-gas intensity during winter price spikes. Demand response programs reward plants that shift power-intensive steps to off-peak hours, creating quick payback on sensor retrofits. Continuous monitoring uncovers hidden losses such as compressed-air leaks, which often consume 20-30% of a plant's electricity bill. Once initial pilots validate savings, corporate finance teams release larger multiyear budgets, sustaining the process automation market momentum.
Heightened Demand for Safety-Instrumented Systems
Industrial incidents have tightened regulatory scrutiny, accelerating safety-system upgrades. ISA-84 now obliges refineries to verify safety integrity levels at five-year intervals. Emerson's DeltaV SIS integrates logic solvers with process control, trimming engineering hours and reducing test downtime. Chevron invested USD 45 million in redundant logic platforms after new state mandates, slashing trip-related lost-production events. Vendors bundle diagnostics that flag valve stiction and sensor drift before trips occur. Together, these changes lift demand for certified hardware, validation tools, and lifecycle service contracts that underpin the process automation market.
High Upfront CAPEX and Integration Complexity
Retrofitting a multi-vendor plant can push integration costs to 60% of project value. Technicians must map proprietary tags, develop middleware, and stage cutovers during short turnarounds, inflating total installed cost. Payback lengthens when downtime overruns occur. Financing hurdles magnify in commodity-price-sensitive sectors like chemicals, where margins fluctuate. Vendors now bundle energy-savings guarantees, yet CFOs still insist on under-three-year returns, limiting near-term process automation market uptake.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Proliferation of Industrial IoT Platforms
- Shift Toward Predictive and Prescriptive Maintenance Analytics
- Operational Cybersecurity Talent Deficit
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Wired networks secured 69.25% of 2025 revenue thanks to deterministic performance that safeguards safety-critical loops. That dominance translates to the largest process automation market size contribution within connectivity categories. Yet wireless protocols are gaining credibility as mesh topologies deliver 99.9% availability in corrosive or explosive zones. ExxonMobil's success at Baytown proves wireless deployment can slash installation budgets by 40%. Emerging private 5G spurs interest in mobile asset tracking and untethered robotics, foreshadowing double-digit sensor counts per asset. Manufacturers now pilot hybrid architectures that pair Ethernet-based controllers with WirelessHART field instruments, striking a balance between uptime and flexibility.
First adopters quantify quick wins in temporary monitoring projects that would never clear the capital committee under traditional cabling assumptions. Service contractors appreciate faster commissioning, especially on turnarounds with compressed schedules. Reliability teams confirm that advanced diagnostics embedded in gateways pinpoint signal degradation before it imperils control loops. Parallel growth in industrial cybersecurity frameworks such as ISA/IEC 62443 calms worries over radio attack surfaces. As test use cases mature into permanent installations, wireless will narrow its gap, sustaining incremental gains in the process automation market.
Hardware systems retained a 26.88% share of the process automation market size in 2025, reflecting the enduring need for PLCs, distributed control systems, and safety logic solvers. However, plant managers increasingly view algorithms, not enclosures, as the source of competitive edge. Software platforms post a 3.92% CAGR as advanced control, manufacturing execution, and analytics tools mine untapped data. Schneider Electric's EcoStruxure blends SCADA with cloud micro-services, letting engineers act on insights in near real time.
Software gains momentum wherever regulators demand digital batch records or energy-intensity audits. Pharmaceutical firms embed inline spectroscopy and model-predictive control to satisfy FDA quality-by-design mandates, lifting software penetration. Meanwhile, open-source historians and container orchestration reduce vendor lock-in fears. Hardware still matters for determinism, but differentiation now hinges on how adeptly software extracts value. This pivot enlarges service and subscription revenue, reinforcing the long-term expansion of the process automation market.
The North America Process Automation Market Report is Segmented by Communication Protocol (Wired, Wireless), System Type (Hardware, Software), Component (Hardware, Software, Services), Deployment Mode (On-Premises, Cloud and Edge), End-User Industry (Chemical and Petrochemical, Power and Utilities, Water and Wastewater, Food and Beverage, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- General Electric Company
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Omron Corporation
- Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- Delta Electronics, Inc.
- Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- Phoenix Contact GmbH & Co. KG
- Bosch Rexroth AG
- Beckhoff Automation GmbH & Co. KG
- Festo SE & Co. KG
- Endress+Hauser Group Services AG
- Aspen Technology, Inc.
- AVEVA Group plc
- Azbil Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising focus on energy-efficiency and OPEX reduction
- 4.2.2 Heightened demand for safety-instrumented systems
- 4.2.3 Proliferation of Industrial IoT platforms
- 4.2.4 Shift toward predictive and prescriptive maintenance analytics
- 4.2.5 Carbon-intensity penalties accelerating digital process control
- 4.2.6 Aging skilled workforce driving remote and autonomous operations
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront CAPEX and integration complexity
- 4.3.2 Brown-field interoperability challenges
- 4.3.3 Operational cybersecurity talent deficit
- 4.3.4 Long-term service-contract lock-ins limiting vendor switch
- 4.4 Industry Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape and Standards
- 4.6 Technological Outlook (Edge and AI analytics)
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Industrial-Automation Hot-Spots Analysis (US and Canada)
- 4.9 Macroeconomic Trend Impact (inflation-linked capex, reshoring)
- 4.10 Pandemic Recovery Themes (V-shape / Mid-range / Slump)
- 4.11 US - Base-Variable End-user Performance
- 4.12 Canada - Base-Variable End-user Performance
- 4.13 Supply-related Challenges and Policy Stimulus
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Communication Protocol
- 5.1.1 Wired
- 5.1.2 Wireless
- 5.2 By System Type
- 5.2.1 Hardware
- 5.2.1.1 SCADA
- 5.2.1.2 Distributed Control System (DCS)
- 5.2.1.3 Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
- 5.2.1.4 Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
- 5.2.1.5 Process Safety Systems
- 5.2.1.6 Valves and Actuators
- 5.2.1.7 Electric Motors
- 5.2.1.8 Sensors and Transmitters
- 5.2.2 Software
- 5.2.2.1 Advanced Process Control (ARC, MVC, Inferential)
- 5.2.2.2 Data Analytics and Reporting
- 5.2.2.3 Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
- 5.2.2.4 Other Software
- 5.2.1 Hardware
- 5.3 By Component
- 5.3.1 Hardware
- 5.3.2 Software
- 5.3.3 Services
- 5.4 By Deployment Mode
- 5.4.1 On-Premises
- 5.4.2 Cloud and Edge
- 5.5 By End-user Industry
- 5.5.1 Oil and Gas
- 5.5.2 Chemical and Petrochemical
- 5.5.3 Power and Utilities
- 5.5.4 Water and Wastewater
- 5.5.5 Food and Beverage
- 5.5.6 Pulp and Paper
- 5.5.7 Pharmaceutical
- 5.5.8 Other End-user Industry
- 5.6 By Country
- 5.6.1 United States
- 5.6.2 Canada
- 5.6.3 Mexico
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes global overview, market overview, core segments, financials, strategy, market share, products and services, recent developments)
- 6.4.1 ABB Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Siemens AG
- 6.4.3 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.4 General Electric Company
- 6.4.5 Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- 6.4.6 Emerson Electric Co.
- 6.4.7 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 6.4.8 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.9 Omron Corporation
- 6.4.10 Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Delta Electronics, Inc.
- 6.4.12 Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- 6.4.13 Phoenix Contact GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.14 Bosch Rexroth AG
- 6.4.15 Beckhoff Automation GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.16 Festo SE & Co. KG
- 6.4.17 Endress+Hauser Group Services AG
- 6.4.18 Aspen Technology, Inc.
- 6.4.19 AVEVA Group plc
- 6.4.20 Azbil Corporation
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment
- 7.2 Investment Analysis


















