
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1851521
에너지 분야 사물인터넷(IoT) : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Internet Of Things In Energy - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
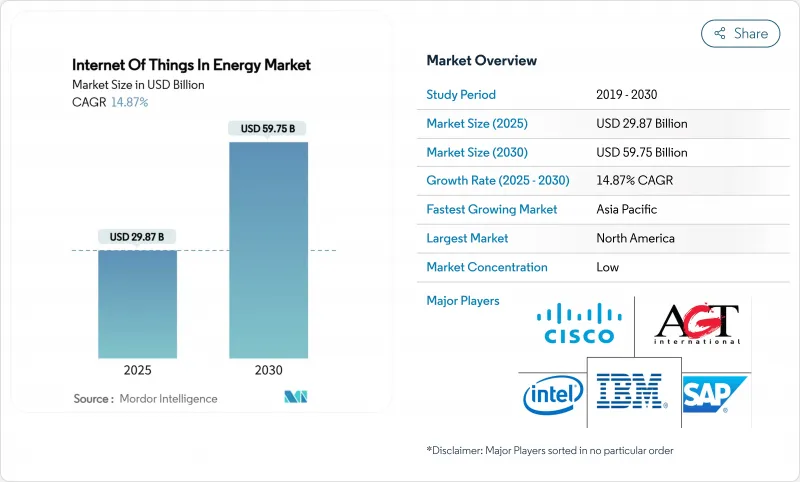
에너지 분야 사물인터넷(IoT)은 2025년에 298억 7,000만 달러가 되고, 2030년에는 CAGR 14.87%를 나타내 597억 5,000만 달러에 달하는 기세입니다.

실시간으로 그리드 최적화, 예측 자산 관리 및 자율 에너지 거래가 공존할 수 있도록 주요 경제권의 유틸리티자는 중앙 집권적인 명령 앤 컨트롤에서 분산 인텔리전스로 전환하고 있습니다. 스마트 미터, 지능형 변전소 리노베이션 및 에지 분석 스택에 대한 설비 투자가 증가하는 이유는 이러한 투자로 인해 정전 시간이 단축되고 유지 보수 예산이 줄어들기 때문입니다. 반도체의 가격이 안정되면서 저전력 광역 모듈이 3달러의 임계치를 밑돌게 되어 2차 피더, 지방의 태양광 발전소, 미터 뒤의 기기에 접속성을 가져왔습니다. 휴대폰 사업자, 위성 통신 플릿 및 민간 5G 제공업체는 단순한 센서 트래픽의 대역폭 비용을 좁히는 한편, 보호 릴레이 메시지의 확정적인 지연을 보장하는 하이브리드 네트워크의 제공에 집중하고 있습니다. 소프트웨어 공급업체는 AI 툴킷을 자산 성능 플랫폼에 통합하여 에너지 기업이 부품 고장을 조기에 예측하고 도매 시장에서 유연성 서비스를 수익화할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
세계의 에너지 분야 사물인터넷(IoT) 시장 동향과 인사이트
전력 회사의 스마트 미터 도입과 그리드 현대화의 의무화
규제 당국이 저전압 네트워크와 수요 반응 성과의 시각화를 요구하는 동안, 의무화된 고도 측정 인프라는 파일럿 단계를 넘어섰습니다. 하니웰과 버라이존은 현재 네이티브 5G 라디오를 미터에 통합하여 원격 펌웨어 업데이트, 자가 복구 메쉬 통신 및 자율 서비스 연결 해제를 가능하게 합니다. 노르웨이는 전국적인 배포를 완료했지만 라이브 소비 데이터를 확인한 가구는 불과 29.5%에 불과하며 소비자의 참여와 직관적인 앱이 어려운 절약을 실현할지 여부를 결정한다고 강조하고 있습니다. 따라서 유틸리티자는 기술적 개발과 고객 교육, 게임화된 대시보드, 요금 인센티브를 결합합니다. 첨단 미터는 섬세한 간격 데이터를 배전 관리 시스템에 공급하므로 옥상 태양광 발전의 백피드 및 전기자동차(EV) 클러스터링을 예측하고 과도한 용량을 구축하지 않고 균형을 맞출 수 있습니다.
5G/LPWAN 모듈 비용 저하
칩 공급의 정상화로 인해 좁은 밴드 IoT 모듈의 가격은 2023년에서 2025년 사이에 28% 하락하여 센서의 대량 배치에서 중요한 비용 장벽이 제거되었습니다. 실험실 테스트에 따르면 LTE-M은 많은 대체 저전력 프로토콜보다 높은 처리량과 낮은 에너지 소비를 제공하며 이는 배터리 교체에 비용이 많이 드는 경우 중요합니다. 반도체 제조업체는 AI 가속을 통합한 마이크로컨트롤러를 재설계하고 있어 이상 검출을 엣지에서 실시할 수 있도록 하고 있습니다. 설문조사팀은 LoRa 게이트웨이를 경량 컴퓨팅 노드로 만들어 레거시 페이로드 형식을 손상시키지 않고 백홀 트래픽을 70% 줄일 수 있음을 입증했습니다. 에너지 기업은 현재 원격지의 풍력 발전소, 지역 변전소 및 밸브 어레이에 이러한 모듈을 장비하고 있으며 트럭이 거의 방문하지 않는 곳에 자산 인텔리전스를 배치하고 있습니다.
사이버 보안 및 OT/IT 융합 위험
운영 장비가 공공 네트워크에서 라우팅 가능할수록 공격 대상이 확대됩니다. EU의 사이버 탄력성 법은 2025년 8월에 시행되었으며 장비 제조업체는 소프트웨어 구성 요소를 문서화하고 적시에 패치를 발행해야 합니다. 많은 변전소는 아직 인증되지 않은 레거시 프로토콜을 사용하고 있으며, 침입에 관한 연구에 따르면 세분화이 취약하다면 멀웨어는 과금 서버에서 차단기 제어까지 몇 분 안에 피벗 할 수 있습니다. 무선 업데이트 파이프라인, 하드웨어 트러스트 트러스트, 제로 트러스트 세그먼테이션은 새로운 조달 프레임워크에서 필수적입니다. 효과적인 거버넌스는 정보 기술 팀과 운영 기술 팀의 긴밀한 협력에 달려 있습니다.
부문 분석
스마트 미터, 인텔리전트 센서, 게이트웨이, 에지 컨트롤러는 2024년 에너지 분야 사물인터넷(IoT) 시장 점유율의 41%를 차지했습니다. 하드웨어 파도는 유틸리티 기업의 디지털 트윈을 지원하고 세밀한 필드 데이터를 분석 클라우드로 밀어냅니다. 규제 당국이 공급업체에게 칩에서 클라우드까지 디바이스 무결성을 증명하도록 요청했기 때문에 보안 하드웨어 모듈과 신뢰할 수 있는 실행 환경이 주목을 받고 있습니다. IoT 보안 플랫폼은 2030년까지 시스템 평균의 2배가 되는 17.89%의 성장을 이룰 것으로 예측됩니다. 견고한 ARM 또는 x86 보드에 구축된 에지 서버는 밀리초 단위로 장애 감지를 수행하는 AI 가속기를 사용하여 제공됩니다. 도시바는 최근 펌웨어 블롭이 필드 디바이스를 만지기 전에 서명하고 컴플라이언스 심사 담당자의 감사 시간을 단축하는 키 관리 칩셋을 발표했습니다.
소프트웨어 및 서비스는 하드웨어의 선진을 끊는다. 공급업체가 디바이스, 연결성 및 구독 대시보드를 번들로 제공하는 전체 스택 제공 제품에 유틸리티 회사는 대가를 지불하고 있습니다. 매니지드 서비스 계약은 통합 위험을 공급업체에게 전가하기 때문에 데이터 사이언스의 인력이 부족한 지역에 매력적입니다. 그 결과 에너지 분야 사물인터넷(IoT) 확대에 서비스 수입이 더 큰 비율을 차지하게 되었습니다. 한편, 부품 공급업체는 반도체 흐름에 대한 지정학적 충격을 완충하기 위해 수요 센터 근처에 제조 기지를 옮기려고 합니다.
실시간 배전망 모니터링은 변압기, 피더 및 전압 조정기를 측정하는 프로그램 덕분에 2024년 수익의 38.5%를 차지했습니다. AI 오버레이는 옥상의 태양광 발전이 한낮에 급증했을 때 네트워크가 과전압을 회피하도록 설정 포인트를 그 자리에서 적응시킵니다. 커넥티드 EV 인프라가 CAGR로 가장 빠른 15.35%를 나타내는 이유는 충전기가 부하 자산과 축전 자산을 모두 겸하고 있기 때문입니다. 유틸리티자는 충전기를 무효 전력을 공급하고 낮 동안 잉여 전력을 흡수할 수 있는 유연한 노드로 간주합니다. 정부는 양방향 충전기에 보조금을 내고 오픈 프로토콜의 원격 측정을 요구하고 있습니다.
신재생에너지의 소유자가 더 높은 발전용량을 추구하는 가운데, 예지보전이 바로 뒤에 앞두고 있습니다. 해상풍력발전소에서는 현재 가혹한 해양환경에도 불구하고 나셀 센서로의 결정론적 링크를 유지하는 소프트웨어 정의 네트워킹 링이 통합되어 있습니다. 상업용 건물 내 수요 반응 프로그램은 중요한 시간대의 최대 전력을 최대 86%까지 절감합니다. 산업용 사용자는 에지 분석을 도입하여 단위 출력당 전력량을 줄이고, 이 지표는 ESG 스코어카드 및 투자자 스크리닝에 직접 반영됩니다.
지역 분석
에너지 분야 사물인터넷(IoT)은 북미가 2024년 매출의 38%를 차지했습니다. 송전망의 회복력에 대한 연방 정부의 투자, 주 수준의 청정 에너지 기준, 성숙한 휴대폰 발자국이 급속한 보급을 가능하게 합니다. 슈나이더 일렉트릭은 데이터센터의 부하가 변전소의 증설을 상회하는 속도로 상승하고 있으며, 유틸리티 기업은 IoT 센서를 도입하여 기존의 송전선에서 전체 전력을 좁힐 필요가 있다고 경고하고 있습니다. 캐나다의 원격지 마이크로그리드는 영구 동토에서는 섬유 드롭이 비싸기 때문에 위성 IoT를 재빨리 채용하고 있습니다. 멕시코의 에너지 개혁은 첫날부터 예측 분석을 요구하는 분산형 태양광 발전 투자자를 끌어들입니다.
아시아태평양은 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 17%로 가장 급성장하는 지역입니다. 일본의 슈퍼 솔라 프로젝트는 이론 효율 30% 이상의 페로브스카이트형 셀을 사용해 2030년까지 20GW를 목표로 하고 있습니다. 중국의 14차 5개년 계획에서 스마트 그리드 전개에는 송전 철탑에 내장된 다중 에너지 마이크로그리드와 5G 기지국이 포함됩니다. 인도의 자연에너지 추진은 IoT 센서와 정부 보조 클라우드 호스팅을 융합시켜 한국의 산업단지는 AI 엣지 박스를 공장에 장비하여 전력 피크를 절약하고 있습니다.
유럽에서는 엄격한 탄소 규제와 국경을 넘은 밸런싱 시장을 배경으로 꾸준한 확대를 보이고 있습니다. EU의 사이버 탄력성 법은 모든 IoT 예산에 보안 지출을 하드 코딩합니다. 독일 인더스트리 4.0 이니셔티브는 공장이 전력 품질 미터를 생산 스케줄링에 통합하고 단위당 와트 아워가 택트 타임만큼 중요한 KPI가 됨을 의미합니다. 영국 공공 부문의 에너지 효율화 프로그램에서는 건물 관리자가 분 단위로 인사이트를 얻은 후 이미 두 자리 절약을 기록했습니다. 프랑스에서는 원자력 발전소의 냉각 펌프를 진동 센서로 업그레이드하여 운전 면허를 연장하고, 북유럽의 송전망 오퍼레이터는 실시간 유연성을 위한 시장 플랫폼을 테스트하고 있습니다. 중동 및 아프리카는 이 곡선의 초기 단계에 있지만, 그린 수소 발전소와 연동된 메가 솔라와 축전 프로젝트가 미래 수요를 보장하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 전력 회사의 스마트 미터 도입과 그리드 근대화 의무화
- 5G/LPWAN 모듈 비용의 하락
- 분산형 재생 가능 오케스트레이션의 요구
- AI에 의한 예지보전의 ROI 사례
- 유연성의 수익화(V2G, P2P 에너지)
- 탄소 회계 데이터 규제
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 사이버 보안과 OT/IT 융합 위험
- 레거시와 SCADA 간의 상호 운용성의 갭
- 엣지 컴퓨트 인재의 희소성
- 반도체 공급의 변동
- 밸류체인 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 라이벌의 격렬함
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 구성 요소별
- 하드웨어
- 스마트 서모스탯
- 스마트 미터
- EV 충전소
- 기타 하드웨어
- 소프트웨어 및 분석
- IoT 플랫폼
- IoT 보안
- IoT 서비스
- 하드웨어
- 용도별
- 스마트 그리드 모니터링
- 에너지 관리 시스템
- 예측 유지보수
- 연결형 전기차 인프라
- 분산형 재생에너지 통합
- 수요 대응 및 유연성
- 연결 기술별
- 셀룰러(2G-5G)
- LPWAN(NB-IoT, LoRaWAN, Sigfox)
- 위성 IoT
- Wi-Fi/BLE
- PLC 및 기타
- 배포 모델별
- 클라우드
- 엣지
- On-Premise
- 최종 사용자별
- 전력 및 가스 사업
- 석유 및 가스 업스트림/미드스트림/다운스트림
- 상업 및 산업 시설
- 주택 및 프로슈머
- 재생에너지 발전소
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 러시아
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- ASEAN
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 사우디아라비아
- 튀르키예
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Cisco Systems
- IBM Corporation
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric
- Huawei Technologies
- Intel Corporation
- SAP SE
- Oracle Corporation
- AGT International
- Davra Networks
- Flutura Business Solutions
- Wind River Systems
- Silver Spring Networks
- Verizon Business
- Vodafone IoT
- GE Digital
- Emerson Electric
- Siemens Gamesa(renewable IoT)
- Landis Gyr
- Kamstrup
제7장 시장 기회와 향후 전망
KTH 25.11.13The Internet of Things in the energy market stood at USD 29.87 billion in 2025 and is on course to reach USD 59.75 billion by 2030, reflecting a 14.87% CAGR.
Utilities across major economies are moving from centralized command-and-control to distributed intelligence so that real-time grid optimization, predictive asset care, and autonomous energy trading can co-exist. Capital spending on smart meters, intelligent substation retrofits, and edge analytics stacks has risen because these investments cut outage minutes and lower maintenance budgets. Semiconductor pricing has stabilized, allowing low-power wide-area modules to fall below the USD 3 threshold, which brings connectivity to secondary feeders, rural solar farms, and behind-the-meter devices. Cellular operators, satellite fleets, and private 5G providers are converging on hybrid network offers that guarantee deterministic latency for protection relay messages while squeezing bandwidth costs for simple sensor traffic. Software vendors have responded by embedding AI toolkits inside asset performance platforms so that energy firms can predict component failures early and monetize flexibility services in wholesale markets.
Global Internet Of Things In Energy Market Trends and Insights
Utility Smart-Meter Roll-Outs and Grid-Modernization Mandates
Mandated advanced metering infrastructure has moved beyond the pilot stage as regulators demand visibility of low-voltage networks and demand response outcomes. Honeywell and Verizon now embed native 5G radios into meters, enabling remote firmware updates, self-healing mesh communication, and autonomous service disconnects. Norway completed nationwide roll-outs yet only 29.5% of households checked live consumption data, underscoring that consumer engagement and intuitive apps decide whether hard savings materialize. Utilities therefore pair technical deployment with customer education, gamified dashboards, and tariff incentives. Advanced meters feed granular interval data to distribution management systems so that rooftop solar back-feed and electric vehicle (EV) clustering can be forecast and balanced without over-building capacity.
Falling 5G/LPWAN Module Cost
Chip supply normalization pushed narrow-band IoT module prices down by 28% between 2023 and 2025, removing a key cost barrier for high-volume sensor roll-outs. Laboratory tests show LTE-M offers higher throughput and lower energy consumption than many alternative low-power protocols, which is important where battery swaps are costly. Semiconductor makers are redesigning micro-controllers with integrated AI acceleration so that anomaly detection can occur at the edge. Research teams have proved that turning LoRa gateways into lightweight compute nodes trims backhaul traffic by 70% without breaking legacy payload formats. Energy firms now equip remote wind farms, rural substations, and valve arrays with these modules, placing asset intelligence where trucks rarely visit.
Cyber-Security and OT/IT Convergence Risk
As operational equipment becomes routable on public networks, attack surfaces multiply. The EU Cyber Resilience Act will come into force in August 2025, obliging device makers to document software components and issue timely patches. Many substations still run legacy protocols that lack authentication, and intrusion studies show malware can pivot from billing servers to breaker controls in minutes if segmentation is weak. Over-the-air update pipelines, hardware root-of-trust, and zero-trust segmentation are becoming mandatory across new procurement frameworks. Effective governance hinges on closer collaboration between information-technology and operational-technology teams.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Distributed-Renewable Orchestration Needs
- AI-Driven Predictive-Maintenance ROI Cases
- Legacy-SCADA Interoperability Gap
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Smart meters, intelligent sensors, gateways, and edge controllers collectively secured 41% of the Internet of Things in the energy market share in 2024. The hardware wave anchors utility digital twins and pushes granular field data into analytics clouds. Security hardware modules and trusted execution environments gain notice because regulators now ask vendors to prove device integrity from chip to cloud. IoT security platforms are forecast to compound at 17.89% through 2030, twice the system average, as the cost of a single operational breach can erase multi-year efficiency savings. Edge servers built on ruggedised ARM or x86 boards are shipping with AI accelerators that handle fault detection in milliseconds. Toshiba recently unveiled a key-management chipset that signs firmware blobs before they touch the field device, trimming audit times for compliance reviewers.
Software and services follow hardware's beachhead. Utilities are paying for full-stack offerings where the vendor bundles devices, connectivity, and a subscription dashboard. Managed service contracts appeal in regions short of data-science talent because they shift integration risk to the supplier. As a result, services revenue is taking a larger slice of the expanding Internet of Things in the energy market. Meanwhile, component suppliers are moving manufacturing closer to demand centres to buffer any geopolitical shock to semiconductor flows.
Real-time distribution grid monitoring accounted for 38.5% of 2024 revenue thanks to programs that instrument transformers, feeders, and voltage regulators. AI overlays adapt set-points on the fly so that networks avoid over-voltage when rooftop solar spikes midday. Connected EV infrastructure shows the fastest 15.35% CAGR because chargers double as both load and storage assets. Utilities view them as flexible nodes that can supply reactive power and soak up midday excess. Governments are subsidising bidirectional chargers and demanding open-protocol telemetry, which funnels more devices into the Internet of Things in the energy market.
Predictive maintenance sits close behind as renewable owners chase higher capacity factors. Offshore wind farms now integrate software-defined networking rings that maintain deterministic links to nacelle sensors despite harsh marine environments. Demand-response programs inside commercial buildings have trimmed peak kW draw by up to 86% during critical intervals. Industrial users deploy edge analytics to lower electricity per unit of output, a metric that directly feeds ESG scorecards and investor screens.
The Internet of Things in the Energy Market Report is Segmented by Component (Hardware, Software and Analytics, Iot Platforms, and More), Application (Smart Grid Monitoring, Energy Management Systems, Predictive Maintenance, and More), Connectivity Technology (Cellular (2G-5G), Satellite IoT, and More), Deployment Model (Cloud, Edge, and More), End-User (Electric and Gas Utilities, Residential and Prosumer, and More), and Geography
Geography Analysis
North America commanded 38% of 2024 revenue for the Internet of Things in the energy market. Federal investment in grid resilience, state-level clean-energy standards, and a mature cellular footprint enable rapid adoption. Schneider Electric warns that data-centre load is climbing faster than substation build-outs, forcing utilities to deploy IoT sensors to squeeze every amp from existing lines. Canada's remote microgrids are early satellite IoT adopters because fibre drops are expensive in permafrost. Mexico's energy reform is attracting distributed solar investors who demand predictive analytics from day one.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region at a 17% CAGR through 2030. Japan's super-solar project targets 20 GW by 2030 using perovskite cells with a theoretical efficiency beyond 30%. China's smart-grid rollout under the 14th Five-Year Plan includes multi-energy microgrids and 5G base stations embedded in transmission pylons. India's renewables push blends IoT sensors with government-subsidised cloud hosting, while South Korean industrial parks equip factories with AI edge boxes to shave power peaks.
Europe shows steady expansion on the back of stringent carbon laws and cross-border balancing markets. The EU Cyber Resilience Act hard-codes security spending into every IoT budget. Germany's Industry 4.0 initiatives mean factories integrate power-quality meters with production scheduling so that watt-hours per unit become a KPI as important as takt time. The United Kingdom's public-sector energy efficiency program has already logged double-digit savings after building managers gained minute-level insights. France upgrades nuclear station cooling pumps with vibration sensors to extend operating licenses, and Nordic grid operators test market platforms for real-time flexibility. The Middle East and Africa are earlier in the curve but mega solar-and-storage projects linked to green-hydrogen plants guarantee future demand.
- Cisco Systems
- IBM Corporation
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric
- Huawei Technologies
- Intel Corporation
- SAP SE
- Oracle Corporation
- AGT International
- Davra Networks
- Flutura Business Solutions
- Wind River Systems
- Silver Spring Networks
- Verizon Business
- Vodafone IoT
- GE Digital
- Emerson Electric
- Siemens Gamesa (renewable IoT)
- Landis+Gyr
- Kamstrup
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Utility smart-meter roll-outs and grid-modernization mandates
- 4.2.2 Falling 5G/LPWAN module costs
- 4.2.3 Distributed-renewable orchestration needs
- 4.2.4 AI-driven predictive-maintenance ROI cases
- 4.2.5 Flexibility monetisation (V2G, P2P energy)
- 4.2.6 Carbon-accounting data regulations
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Cyber-security and OT/IT convergence risk
- 4.3.2 Legacy-SCADA interoperability gaps
- 4.3.3 Edge-compute talent scarcity
- 4.3.4 Semiconductor-supply volatility
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.1.1 Smart Thermostats
- 5.1.1.2 Smart Meters
- 5.1.1.3 EV Charging Stations
- 5.1.1.4 Other Hardware
- 5.1.2 Software and Analytics
- 5.1.3 IoT Platforms
- 5.1.4 IoT Security
- 5.1.5 IoT Services
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Smart Grid Monitoring
- 5.2.2 Energy Management Systems
- 5.2.3 Predictive Maintenance
- 5.2.4 Connected EV Infrastructure
- 5.2.5 Distributed-Renewable Integration
- 5.2.6 Demand Response and Flexibility
- 5.3 By Connectivity Technology
- 5.3.1 Cellular (2G-5G)
- 5.3.2 LPWAN (NB-IoT, LoRaWAN, Sigfox)
- 5.3.3 Satellite IoT
- 5.3.4 Wi-Fi/BLE
- 5.3.5 PLC and Other
- 5.4 By Deployment Model
- 5.4.1 Cloud
- 5.4.2 Edge
- 5.4.3 On-premise
- 5.5 By End-user
- 5.5.1 Electric and Gas Utilities
- 5.5.2 Oil and Gas Up/Mid/Down-stream
- 5.5.3 Commercial and Industrial Facilities
- 5.5.4 Residential and Prosumer
- 5.5.5 Renewable Power Plants
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Russia
- 5.6.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 India
- 5.6.4.3 Japan
- 5.6.4.4 South Korea
- 5.6.4.5 ASEAN
- 5.6.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 Turkey
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Cisco Systems
- 6.4.2 IBM Corporation
- 6.4.3 Siemens AG
- 6.4.4 Schneider Electric
- 6.4.5 Huawei Technologies
- 6.4.6 Intel Corporation
- 6.4.7 SAP SE
- 6.4.8 Oracle Corporation
- 6.4.9 AGT International
- 6.4.10 Davra Networks
- 6.4.11 Flutura Business Solutions
- 6.4.12 Wind River Systems
- 6.4.13 Silver Spring Networks
- 6.4.14 Verizon Business
- 6.4.15 Vodafone IoT
- 6.4.16 GE Digital
- 6.4.17 Emerson Electric
- 6.4.18 Siemens Gamesa (renewable IoT)
- 6.4.19 Landis+Gyr
- 6.4.20 Kamstrup
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment

















