
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1683977
아프리카 제초제 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Africa Herbicide - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
■ 보고서에 따라 최신 정보로 업데이트하여 보내드립니다. 배송일정은 문의해 주시기 바랍니다.
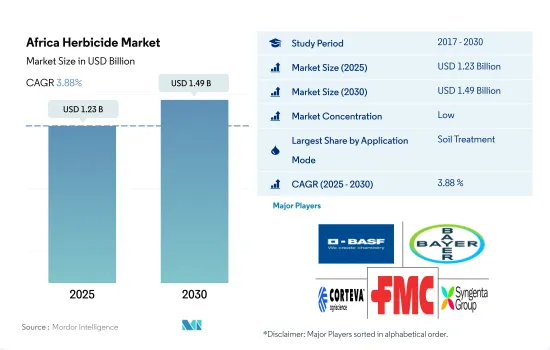
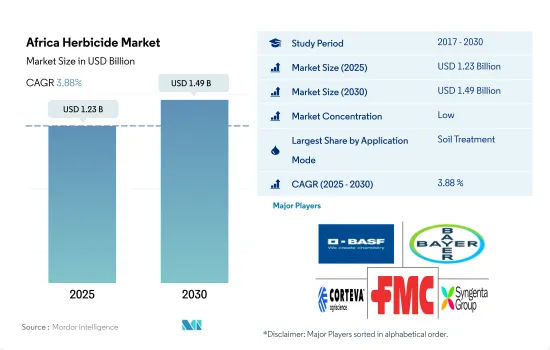
아프리카의 제초제 시장 규모는 2025년에 12억 3,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 14억 9,000만 달러에 이를 전망이며, 예측 기간 중 2025년부터 2030년까지 CAGR은 3.88%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다.
다양한 적용 모드의 채용은 작물의 성장 단계와 잡초의 유형에 크게 좌우됩니다.
- 아프리카의 농업 부문은 다양한 과제에 직면하고 있으며, 그 중에서도 잡초가 큰 위협이 되고 있습니다. 이 지역의 집약적인 농법, 불경기 및 주요 작물의 단일 재배는 다양한 잡초 종의 번식을 돕고 작물의 성장을 방해합니다. 다양한 사회경제적 요인들로 인해 농부들은 더 나은 잡초 관리와 작물 성장을 가속하기 위해 다양한 살포 방법으로 제초제 살포를 수행하고 있습니다.
- 제초제의 토양 처리 적용 모드는 주로 잡초의 성장 초기 단계에서 방제를 위한 예방 조치로 농부에서 채택되어 제초제의 추가 사용량과 생산 비용을 절감합니다. 이 적용 모드 시장 가치는 예측 기간 동안 1억 5,310만 달러 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 엽면 제초제 살포는 다음에 많이 채택되는 살포 모드이며, 다양한 작물의 넓은 잎 잡초를 방제하는 일반적인 전통 관행입니다. 엽면 살포법의 사용은 예측 기간 동안 성장하고 1억 40만 달러 시장 성장을 차지할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 물 부족 증가와 미세 관개 시스템의 발전은 화학 제초제를 균일하게 살포하는 화학 모드의 상승에 더 나은 잡초 관리를 제공합니다. 화학 관개 모드 시장은 2023년부터 2029년까지 5,440만 달러 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다.
- 제초제 훈증의 채용은 분무 드리프트 및 인체에 해를 끼칠 가능성과 같은 관련 위험 때문에 제한됩니다. 한편 토양 등에 침투하여 잡초를 효과적으로 방제할 수 있음을 알고 있습니다.
- 이 지역의 제초제 시장은 잡초 만연 증가를 배경으로 예측 기간 중에 3억 1,230만 달러의 성장이 전망되고 있습니다.
전통적인 제초 방법과 관련된 위험은 이 지역에서 제초제 요구를 증가시키고 있습니다.
- 아프리카의 농업 부문은 남아프리카, 에티오피아, 나이지리아, 이집트, 케냐 등 국가에 집중하고 있습니다. 농업은 가장 중요한 부문 중 하나이며 인구의 대부분이 농업에 종사하고 있습니다. 이 부문은 사하라 이남의 아프리카 GDP에 약 14% 기여하고 있습니다. 다양한 생물 및 생물학적 과제 중 잡초는 농업 부문에 큰 위협이 되고 있습니다. 전통적인 잡초 관리 방법은 시간이 많이 걸리고 비용이 많이 들고 노동력이 필요하기 때문에 농부들은 잡초 방제의 주요 방법으로 제초제를 채택했습니다.
- 역사적인 기간에 제초제의 소비량은 크게 성장했습니다. 2017년에는 16만 2,000톤으로, 2022년에는 19만 8,100톤으로 증가했습니다. 소비의 성장은 잡초 확산 증가 및 제초제 채용 증가가 주요 원인입니다. 아프리카에서는 매년 평균적으로 잡초에 의해 최대 25%의 수율 손실이 발생합니다. 수율 손실 증가는 2023년부터 2029년까지 9,611톤의 제초제 소비 증가를 더욱 촉진할 전망입니다.
- 곡물 및 곡류 작물 생산자는 재배에 화학 제초제를 주로 이용하고 있으며, 2022년에는 45.1%를 차지했습니다. 이러한 작물이 우세한 것은 주로 재배면적이 많고, 단작농업이 다양한 잡초종의 생육에 유리하기 때문입니다. 잡초는 이 지역의 곡류 작물에 최대 34%의 잠재적 수율 손실을 초래합니다. 따라서 이러한 작물에서는 제초제의 사용률이 높아지고 있습니다.
- 이 지역의 제초제 시장은 예측 기간 동안 CAGR 4.1%를 나타낼 것으로 예측되며, 잡초 관리의 다른 방법과 관련된 문제를 해결할 것입니다.
아프리의 제초제 시장 동향
이 지역의 식량 수요 증가 및 작물의 높은 생산성 요구가 제초제 시장을 견인합니다.
- 최근, 아프리카에서는 제초제의 사용이 현저하게 급증하고 있습니다. 농업 관행 및 잡초 관리에서 제초제 수요가 증가함에 따라 제초제 소비량이 크게 증가하고 있습니다. 2017년부터 2022년까지 아프리카에서 1헥타르당 제초제 소비량은 89.3%라는 상당한 성장을 보였습니다. 이 급증은 제초제의 장점에 대한 농민의 의식 증가와 단위 토지 당 농업 생산성을 높이고자 하는 농민의 욕망으로 인한 것으로 간주됩니다. 시장에 다양한 제초제가 널리 퍼져 있는 것이 제초제 사용량 증가를 촉진하는데 중요한 역할을 하고 있습니다.
- 적절한 회전 및 다양화 없이 단일 제초제 또는 제한된 제초제 세트를 지속적이고 광범위하게 사용하면 저항성 잡초 개체군이 선택될 수 있습니다. 시간이 지남에 따라 이러한 저항성 잡초가 경관을 지배하게 되어 제초제의 방제 효과가 저하됩니다. 다른 작용기전의 제초제를 로테이션 사용함으로써, 저항성 잡초의 우점을 막을 수 있습니다. 일반적으로 파머 아마란서스로 알려진 아마란투스 팔메리(Amaranthus palmeri)에서 가장 널리 보이는 글리포세이트 내성 메커니즘은 2022년 남아프리카공화국에서 확인되었습니다. 글리포세이트는 다양한 작물의 잡초 관리에 자주 사용되는 농약입니다. 그러나 글리포세이트 내성 잡초 증가는 잡초 방제를 성공시키는 데 큰 장애가 되고 있습니다.
- 아프리카에서는 식량 수요가 증가하고 있기 때문에 농업 생산성 향상이 강하게 요구되고 있습니다. 제초제는 농작물 손실을 줄임으로써 농업 수율 증가에 크게 기여합니다. 인구의 식량 수요를 충족시킬 필요성으로 제초제에 대한 의존도가 높아지고 있습니다.
제초제 제품에 대한 의존도가 높고 제초제 수입 관세에 관한 규제의 변화가 이 지역의 유효성분 가격 변동으로 이어지고 있습니다.
- 아프리카 농업 부문에서는 잡초가 큰 위협이 되어 곡물과 주식 작물에서 최대 34%의 수율 손실을 초래합니다. 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 농부는 효과적인 잡초 방제를 위해 화학 제초제에 크게 의존합니다. 수작업에 의한 제초 및 기계 제초와 같은 대체 방법은 노동력 부족과 임금 상승으로 인해 비용이 많이 들기 때문입니다.
- 메트리부진은 옥수수, 당근, 토마토, 비트 루트, 아스파라거스, 순무, 콩, 유채과 식물, 박과 식물, 양파, 완두콩, 콩류, 밀, 상추, 담배, 딸기 등의 작물로 다양한 연간 활엽수와 잔디를 방제하는 제초제입니다. 메트리부진 가격은 2022년 1톤당 16,580.9달러로 기록되었으며 2017년보다 31.3% 상승했습니다. 이 가격 상승은 수요가 증가하고 아프리카 이외의 국가에서 수입되기 때문에 이용할 수 없는 것이 주요 원인입니다. 남아프리카는 주요 수입국으로 인도에서 메트리부진을 수입하고 있습니다.
- 아트라진은 남아프리카나 나이지리아와 같은 옥수수 생산국에서 주로 사용되는 제초제로, 옥수수 재배 면적의 약 88%가 잡초 방제를 위해 아트라진에 의존합니다. 아트라진의 용도는 육상 식용 작물, 비식용 작물, 숲, 주택 잔디, 골프장, 레크리에이션 지역, 방목지 등 다양하게 농장에서 널리 채용되고 있는 잡초 방제 수단이 되고 있습니다. 다양한 작물에서 사용되기 때문에 Atlas의 가격은 해마다 상승하고 있습니다. 2022년에는 2017년 기록된 가격에 비해 미터톤당 3,292.7달러의 성장을 경험했습니다.
- 글리포세이트는 주로 비용 효율성이 높기 때문에 이 지역에서 두 번째로 널리 사용되는 제초제로 널리 채택됩니다. 2022년 글리포세이트의 유효 성분 가격은 1톤당 1,143.2달러를 기록했습니다.
아프리카의 제초제 산업 개요
아프리카의 제초제 시장은 세분화되어 상위 5개사에서 27.04%를 차지하고 있습니다. 이 시장 주요 기업은 다음과 같습니다. BASF SE, Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, FMC Corporation 및 Syngenta Group(알파벳순 정렬).
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 주요 요약 및 주요 조사 결과
제2장 보고서 제안
제3장 서문
- 조사 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
- 조사 방법
제4장 주요 산업 동향
- 1헥타르당 농약 소비량
- 유효성분의 가격 분석
- 규제 프레임워크
- 남아프리카
- 밸류체인 및 유통채널 분석
제5장 시장 세분화
- 적용 모드별
- 화학 관개
- 엽면 살포
- 훈증
- 토양치료
- 작물 유형별
- 상업 작물
- 과일 및 야채
- 곡물
- 콩류 및 지방종자
- 잔디 및 관상용
- 국가별
- 남아프리카
- 기타 아프리카
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 주요 전략 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 상황
- 기업 프로파일(세계 수준 개요, 시장 수준 개요, 주요 사업 부문, 재무, 직원 수, 주요 정보, 시장 순위, 시장 점유율, 제품 및 서비스, 최근 동향 분석 포함)
- ADAMA Agricultural Solutions Ltd
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- FMC Corporation
- Nufarm Ltd
- Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd
- Syngenta Group
- UPL Limited
- Wynca Group(Wynca Chemicals)
제7장 CEO에 대한 주요 전략적 질문
제8장 부록
- 세계의 개요
- 개요
- Porter's Five Forces 분석 프레임워크
- 세계 밸류체인 분석
- 시장 역학(DROs)
- 정보원 및 참고문헌
- 도표 일람
- 주요 인사이트
- 데이터 팩
- 용어집
The Africa Herbicide Market size is estimated at 1.23 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 1.49 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 3.88% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Adoption of various application modes majorly depends upon the crop growth stage and weed type
- Africa's agricultural sector is facing various challenges, among which weeds are becoming a major threat to the sector. The region's intensive agricultural practices, no-tillage, and monoculture practices in major crops help various weed species to grow and hamper crop growth. Due to various socio-economic factors, farmers implement herbicide application through different application modes for better weed management and enhanced crop growth.
- The herbicide soil treatment application mode is majorly adopted by farmers as a precaution to control weeds in their early growth stages, which reduces further herbicide use and production costs. The market value for this application mode is expected to increase by USD 153.1 million during the forecast period.
- Foliar herbicide application is the next most adopted application mode and common traditional practice for controlling broadleaf weeds in various crops, which is effective in rapid action by targeting the weed species. The use of the foliar method is expected to grow during the forecast period, accounting for a market value growth of USD 100.4 million.
- Increasing water shortages and advancements in micro-irrigation systems help in the rise of the chemigation mode, which provides the uniform distribution of chemical herbicide applications for better weed management. The market for the chemigation mode will grow by USD 54.4 million during 2023-2029.
- The adoption of herbicide fumigation is limited due to its associated risks, such as spray drift and potential harm to human health. On the other hand, it has been found to effectively control weeds by penetrating the soil and other areas.
- The herbicide market in the region is expected to grow by USD 312.3 million during the forecast period, driven by the increasing weed infestations.
The risk associated with the traditional weeding methods is increasing the need for herbicides in the region
- The African agricultural sector is majorly concentrated in countries like South Africa, Ethiopia, Nigeria, Egypt, and Kenya. Agriculture is one of the most important sectors, and the majority of the population works in it. The sector contributes around 14% to Sub-Saharan Africa's GDP. Among various biotic and abiotic challenges, weeds are becoming a major threat to the agricultural sector. Traditional weed management practices are associated with being time-consuming, becoming more expensive, and needing more labor, and these factors divert farmers to adopt herbicides as a primary method for weed control.
- There was a significant growth in herbicide consumption during the historical period. In 2017, it was 162.0 thousand metric ton, which increased to 198.1 thousand metric ton in 2022. The consumption growth is majorly attributed to the increasing weed infestations and rise in herbicide adoption. On average, every year, weeds are causing yield loss of up to 25% in Africa. The increasing yield losses further drive the herbicide consumption growth by 9,611 metric ton during 2023-2029.
- Grain and cereal crop growers are majorly utilizing chemical herbicides in their cultivation, which accounted for 45.1% in 2022. The dominance of these crops is mainly due to their higher cultivation area and monoculture agriculture practices favoring various weed species to grow. Weeds cause a potential yield loss of up to 34% to cereals crops in the region. This resulted in higher utilization of herbicides in these crops.
- The herbicide market in the region is projected to register a CAGR of 4.1% during the forecast period, which will solve the problems associated with other methods of weed management.
Africa Herbicide Market Trends
Rising food demand in the region coupled with need for high productivity of the crops will drive the herbicide market
- In recent years, the use of herbicides in Africa has experienced a notable surge. There has been a substantial increase in the consumption of herbicides, reflecting a growing demand for these products in agricultural practices and weed management. From 2017 to 2022, herbicide consumption per hectare in Africa witnessed a significant growth of 89.3%. This upsurge can be attributed to the increased awareness among farmers regarding the advantages of herbicides and their desire to enhance agricultural productivity per unit of land. The wide availability of diverse herbicides in the market has played a significant role in driving the upswing in herbicide usage.
- Continuous and extensive use of a single herbicide or a limited set of herbicides without proper rotation or diversification can lead to the selection of resistant weed populations. Over time, these resistant weeds dominate the landscape, making herbicides less effective in controlling them. Rotation of herbicides with different modes of action to prevent the dominance of resistant weed populations. The most prevalent glyphosate resistance mechanism in Amaranthus palmeri, commonly known as palmer amaranth, was seen in the Republic of South Africa in 2022. Glyphosate is a frequently used pesticide for weed management in a variety of crops. However, the rise of glyphosate-resistant weed populations offers a considerable obstacle to successful weed control.
- Africa's rising food demand has led to a determined push to boost agricultural productivity. Herbicides contribute significantly to increased agricultural yields by lowering crop losses. The necessity to fulfill the population's food requirements drives the reliance on herbicides.
Heavy reliance on herbicide products and changing regulations on import tariffs on herbicides are leading to fluctuating active ingredient prices in the region
- In the African agriculture sector, weeds have emerged as a substantial threat, leading to yield losses of up to 34% in cereals and staple food crops. To address this issue, farmers heavily rely on chemical herbicides for effective weed control, as alternative methods like hand weeding and mechanical weeding have become cost-prohibitive due to labor shortages and rising wages.
- Metribuzin is a herbicide for control of various annual broadleafs and grasses in crops like maize, carrots, tomatoes, beetroot, asparagus, turnip, soybeans, brassicas, cucurbits, onions, peas, beans, wheat, lettuce, tobacco, and strawberries. The price of metribuzin was recorded as USD 16,580.9 per metric ton in 2022, which was 31.3% more than in 2017. This price increase is majorly attributed to the rising demand and unavailability as it is imported from other non-African countries. South Africa is the major importing country, and it imports metribuzin from India.
- Atrazine is the predominant herbicide utilized in maize-producing nations such as South Africa and Nigeria, with approximately 88% of the maize area relying on atrazine for weed control. Its application extends to numerous terrestrial food crops, non-food crops, forests, residential turf, golf courses, recreational areas, and rangelands, making it a widely adopted weed control measure on farms. Due to its expanding usage across different crops, the price of atrazine has been consistently rising each year. In 2022, it experienced a growth of USD 3,292.7 per metric ton compared to the price recorded in 2017.
- Glyphosate is extensively adopted as the region's second most prevalent herbicide, mainly owing to its cost-effectiveness. As of 2022, the price of glyphosate's active ingredient was recorded at USD 1,143.2 per metric ton.
Africa Herbicide Industry Overview
The Africa Herbicide Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 27.04%. The major players in this market are BASF SE, Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, FMC Corporation and Syngenta Group (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Consumption Of Pesticide Per Hectare
- 4.2 Pricing Analysis For Active Ingredients
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1 South Africa
- 4.4 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD and Volume, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Application Mode
- 5.1.1 Chemigation
- 5.1.2 Foliar
- 5.1.3 Fumigation
- 5.1.4 Soil Treatment
- 5.2 Crop Type
- 5.2.1 Commercial Crops
- 5.2.2 Fruits & Vegetables
- 5.2.3 Grains & Cereals
- 5.2.4 Pulses & Oilseeds
- 5.2.5 Turf & Ornamental
- 5.3 Country
- 5.3.1 South Africa
- 5.3.2 Rest of Africa
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ADAMA Agricultural Solutions Ltd
- 6.4.2 BASF SE
- 6.4.3 Bayer AG
- 6.4.4 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.5 FMC Corporation
- 6.4.6 Nufarm Ltd
- 6.4.7 Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd
- 6.4.8 Syngenta Group
- 6.4.9 UPL Limited
- 6.4.10 Wynca Group (Wynca Chemicals)
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR CROP PROTECTION CHEMICALS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
샘플 요청 목록



















