
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1683995
인도네시아의 제초제 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Indonesia Herbicide - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
■ 보고서에 따라 최신 정보로 업데이트하여 보내드립니다. 배송일정은 문의해 주시기 바랍니다.
인도네시아의 제초제 시장 규모는 2025년에 11억 4,000만 달러로 예측되고, 2030년에는 15억 4,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 예측 기간(2025-2030년)의 CAGR은 6.15%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다.
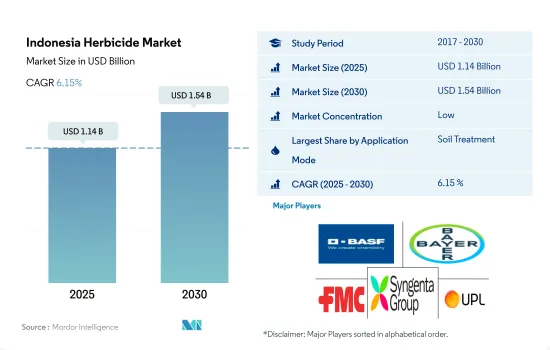
토양 처리 모드를 통한 전통적인 제초제 살포 방법과 초기 생육 단계의 잡초 방제 효과로 인해 채택이 증가할 수 있습니다.
- 인도네시아의 제초제 시장은 농업 활동 증가, 다양한 작물의 잡초 방제 필요성, 선진 농업 관행의 채택 등 여러 요인에 의해 주도되고 있습니다.
- 이 시장은 농부들이 잡초 관리에서 토양 처리의 이점을 인식함에 따라 예측 기간(2023-2029년) 동안 6.6%의 CAGR을 기록할 것으로 예상되는 토양 처리 부문에 의해 지배되고 있습니다. 토양 처리는 잡초를 효과적으로 방제하고 잡초 경쟁을 줄여 작물 생육을 개선하는 데 기여합니다.
- 잎 표면 살포는 인도네시아에서 일반적으로 사용되는 방법입니다. 제초제 시장은 예측 기간(2023-2029년) 동안 4억 6,120만 달러의 가치가 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다. 많은 수확량을 확보하고 작물의 품질을 유지해야 하는 필요성이 잎 표면 살포를 통한 제초제 사용의 주요 동인입니다. 잡초 교란은 품질과 수량 모두에서 낮은 작물 수확량에 영향을 미치며, 농부들은 수익성 있는 수확을 보장하기 위해 통합 해충 관리 전략에서 제초제를 사용하여 투자를 보호하기를 원합니다.
- 화학 처리 방법은 관개 시스템의 채택이 증가하고 정확하고 효과적인 잡초 방제를 위한 화학 처리의 장점으로 인해 향후 몇 년 동안 눈에 띄는 성장을 보일 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 인도네시아의 제초제 시장에서 훈증 소독의 시장 점유율은 예측 기간(2023-2029년) 동안 5.8%의 연평균 성장률을 기록할 것으로 예상됩니다. 농부들은 잡초를 퇴치하고 작물 수확량을 향상시킬 수 있는 보다 효율적이고 효과적인 방법을 찾고 있습니다. 효과적인 잡초 방제를 달성하는 데 유리하기 때문에 향후 몇 년 동안 잎 표면 살포가 선호되는 방법으로 계속 채택될 것으로 예상됩니다.
인도네시아의 제초제 시장 동향
쌀과 같은 주요 작물에서 잡초 발생이 증가하고 재배 면적이 확대되면서 시장을 견인할 수 있습니다.
- 인도네시아의 제초제 사용은 최근 몇 년 동안 눈에 띄게 증가했습니다. 제초제 소비가 크게 증가하여 농업 관행과 잡초 방제에서 이러한 제품에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있음을 나타냅니다. 2017년부터 2022년까지 인도네시아의 헥타르당 제초제 소비량은 30.7%로 크게 증가했습니다. 이러한 증가는 제초제의 이점에 대한 농부들의 높은 인식과 헥타르당 평균 농업 생산량을 늘리고자 하는 열망에 기인한 것으로 볼 수 있습니다. 다양한 종류의 제초제가 시중에 널리 보급된 것도 제초제 사용량 증가에 기여했습니다.
- 다른 많은 국가와 마찬가지로 인도네시아에서도 제초제에 대한 내성 잡초의 개발은 농업 관행에서 우려되는 문제입니다. 시간이 지남에 따라 특정 제초제를 반복적이고 독점적으로 사용하면 제초제 내성 잡초가 출현할 수 있습니다. 이러한 내성 잡초는 제초제를 뿌려도 생존하고 번식할 수 있어 농부들의 잡초 방제를 더욱 어렵게 만듭니다.
- 예를 들어, 논에서 가장 성가신 잡초는 차이니즈 스플란 그룹(Leptochloa chinensis(L.) Nees)입니다. 인도네시아의 대부분의 저지대 벼 농부들은 습관적으로 많은 양의 제초제를 윤작 없이 반복적으로 살포하기 때문에 중국 물달개비의 저항성이 증가합니다.
- 제초제 내성 작물 재배를 통해 농부들은 다양한 작용 방식의 제초제를 사용할 수 있어 효과적인 잡초 관리가 가능하고 잡초 경쟁으로 인한 수확량 손실을 줄일 수 있습니다. 이는 결과적으로 더 나은 잡초 방제를 달성하고 작물 생산성을 극대화하기 위해 제초제 살포율을 높이고 여러 제초제를 사용하게 되었습니다.
제초제에 대한 수요 증가와 수입 관세로 인해 국내 활성 성분 가격이 크게 변화하고 있습니다.
- 인도네시아의 제초제 시장에서의 아틀라진 가격은 2020년부터 2022년에 걸쳐 37.9% 상승하여 1톤당 1만 3,800달러에 달했습니다. 아트라진은 다양한 작물의 광엽 및 풀 잡초를 방제하는 데 사용되는 제초제로, 옥수수, 옥수수, 수수, 사탕수수 등 밭작물에서 가장 많이 사용됩니다. 이 제초제는 잡초를 효과적으로 관리함으로써 작물 생산량을 최대 6%까지 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
- 파라코트는 농부들이 고된 노동력을 절약하고, 침입성 잡초로부터 보호하며, 콩, 옥수수, 면화 등 농업적으로 중요한 작물을 생산하기 위해 널리 사용하는 제초제입니다. 파라코트 디클로라이드는 현재 인도네시아의 농부들이 팜유, 고무, 코코아 등의 농장에서 잡초를 방제하기 위해 사용하는 비선택적 접촉 제초제입니다.
- 글리포세이트는 2022년 1톤당 미화 1,100달러로 평가되었습니다. 인도네시아에서 일반적으로 사용되는 제초제로, 농부들은 농작물에서 잡초와 기타 원치 않는 식물을 관리하고 근절하기 위해 이 약품에 크게 의존하고 있습니다. 그러나 제초제 종류를 적절히 교체하지 않으면 내성 잡초가 출현할 위험이 높아집니다. 이는 농작물 생산에 심각한 위협이 되고 글리포세이트의 시장 수요에 부정적인 영향을 미쳐 향후 가격에도 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
- 인도네시아의 제초제 시장은 여러 국가로부터의 수입에 크게 의존하고 있습니다. 특히 중국, 말레이시아, 미국, 독일, 인도는 인도네시아에 제초제를 가장 많이 수입하는 국가입니다. 이들 수입국은 인도네시아 농업 부문의 제초제 수요를 충족하는 데 중요한 역할을 하고 있습니다.
인도네시아의 제초제 산업 개요
인도네시아의 제초제 시장은 세분화되어 있으며 상위 5개사에서 1.77%를 차지하고 있습니다. 이 시장 주요 기업은 다음과 같습니다. BASF SE, Bayer AG, FMC Corporation, Syngenta Group and UPL Limited(sorted alphabetically).
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 주요 요약과 주요 조사 결과
제2장 보고서 제안
제3장 소개
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
- 조사 방법
제4장 주요 산업 동향
- 헥타르당 농약 소비량
- 유효성분의 가격 분석
- 규제 프레임워크
- 인도네시아
- 밸류체인과 유통채널 분석
제5장 시장 세분화
- 적용 모드
- 화학 처리
- 잎 표면 살포
- 훈증
- 토양 처리
- 작물 유형
- 상업 작물
- 과일 및 채소
- 곡물
- 콩류 및 유지종자
- 잔디 및 관상용
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 주요 전략 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 상황
- 기업 프로파일(세계 수준 개요, 시장 수준 개요, 주요 사업 부문, 재무, 직원 수, 주요 정보, 시장 순위, 시장 점유율, 제품 및 서비스, 최근 동향 분석 포함)
- ADAMA Agricultural Solutions Ltd
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- FMC Corporation
- Nufarm Ltd
- PT Biotis Agrindo
- Syngenta Group
- UPL Limited
- 윈카 그룹(Wynca Chemicals)
제7장 CEO에 대한 주요 전략적 질문
제8장 부록
- 세계의 개요
- 개요
- Five Forces 분석 프레임워크
- 세계의 밸류 체인 분석
- 시장 역학(DROs)
- 출처 및 참고문헌
- 도표 일람
- 주요 인사이트
- 데이터 팩
- 용어집
The Indonesia Herbicide Market size is estimated at 1.14 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 1.54 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 6.15% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
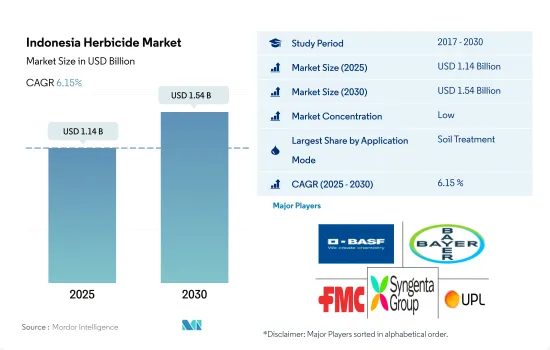
Traditional method of applying herbicides through soil treatment mode and its effectiveness in controlling weeds in early growth stage may increase the adoption
- The herbicide market in Indonesia is driven by several factors, such as increasing agricultural activities, the need for weed control in various crops, and the adoption of advanced agricultural practices.
- The market is dominated by the soil treatment segment, which is expected to record a CAGR of 6.6%, by value, during the forecast period (2023-2029) as farmers recognize the benefits of soil treatment in weed management. Soil treatment offers effective weed control and lower weed competition, contributing to better crop establishment.
- Foliar application is a commonly used method in Indonesia. The herbicide market is expected to increase by a value of USD 461.2 million during the forecast period (2023-2029). The need to obtain large yields and retain crop quality is the major driver for using herbicides by foliar application. Weed disturbance affects low crop yields, both quality and quantity, and farmers want to protect their investment through the use of herbicides in integrated pest management strategies to ensure a profitable harvest.
- The chemigation method is anticipated to witness notable growth in the coming years due to the increasing adoption of irrigation systems and the advantages of chemigation for precise and effective weed control.
- The market share of fumigation in Indonesia's herbicide market is expected to record a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period (2023-2029). Farmers are looking for more efficient and effective ways to combat weeds and enhance crop yields. They are expected to continue the adoption of foliar as a preferred method in the coming years due to its benefits in achieving effective weed control.
Indonesia Herbicide Market Trends
Growing weed infestation in major crops like rice and extending cultivation areas under this crop may drive the market
- Herbicide use in Indonesia has seen a notable increase in recent years. There has been a significant rise in herbicide consumption, indicating a growing demand for these products in agricultural practices and weed control. Between 2017 and 2022, herbicide consumption per hectare in Indonesia witnessed a significant growth of 30.7%. This increase can be attributed to farmers' heightened awareness of the benefits of herbicides and their desire to enhance the average agricultural output per hectare. The wide availability of a diverse range of herbicides in the market has contributed to the rise in herbicide usage.
- In Indonesia, like in many other countries, the development of resistant weeds to herbicides is a concern in agricultural practices. Over time, repeated and exclusive use of certain herbicides can lead to the emergence of herbicide-resistant weed populations. These resistant weeds are able to survive and reproduce even when herbicides are applied, making weed control more challenging for farmers.
- For instance, the most troublesome weed in rice fields is the Chinese sprangletop (Leptochloa chinensis (L.) Nees). Most lowland rice farmers in Indonesia habitually apply large dosages of herbicides repeatedly without rotation, resulting in increased resistance in Chinese sprangletop.
- The cultivation of herbicide-tolerant crops allows farmers to employ herbicides with different modes of action, enabling effective weed management and reducing yield losses caused by weed competition. This, in turn, has led to higher application rates and the use of multiple herbicides in order to achieve better weed control and maximize crop productivity.
The increasing demand for herbicides and import tariffs are majorly altering the active ingredient prices in the country
- The price of atrazine in the Indonesian herbicide market has observed a noteworthy surge of 37.9% to USD 13.8 thousand per metric ton between 2020 and 2022. Atrazine is a herbicide that is utilized for controlling broadleaf and grassy weeds in various crops, with its highest usage in field corn, sweet corn, sorghum, and sugarcane. By effectively managing weeds, this herbicide can enhance crop production by up to 6%.
- Paraquat is a herbicide that farmers widely use to save arduous labor, protect against invasive weeds, and produce agronomically important crops like soy, corn, and cotton, among others. Paraquat dichloride is a non-selective contact herbicide currently used by farmers in Indonesia to control weeds on plantations, such as palm oil, rubber, and cocoa.
- Glyphosate was valued at USD 1.1 thousand per metric ton in 2022. It is a commonly used herbicide in Indonesia, and farmers heavily rely on it to manage and eradicate weeds and other unwanted plants in their crops. However, a lack of proper rotation of herbicide types has resulted in a heightened risk of resistant weed emergence. This poses a significant threat to crop production and may have negative consequences for the market demand for glyphosate, potentially impacting its pricing in the years to come.
- The herbicide market in Indonesia heavily depends on imports from various countries. In particular, China, Malaysia, the United States, Germany, and India are the top importers of herbicides to Indonesia. These importing countries play a crucial role in meeting the herbicide demands of the country's agricultural sector.
Indonesia Herbicide Industry Overview
The Indonesia Herbicide Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 1.77%. The major players in this market are BASF SE, Bayer AG, FMC Corporation, Syngenta Group and UPL Limited (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Consumption Of Pesticide Per Hectare
- 4.2 Pricing Analysis For Active Ingredients
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1 Indonesia
- 4.4 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD and Volume, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Application Mode
- 5.1.1 Chemigation
- 5.1.2 Foliar
- 5.1.3 Fumigation
- 5.1.4 Soil Treatment
- 5.2 Crop Type
- 5.2.1 Commercial Crops
- 5.2.2 Fruits & Vegetables
- 5.2.3 Grains & Cereals
- 5.2.4 Pulses & Oilseeds
- 5.2.5 Turf & Ornamental
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ADAMA Agricultural Solutions Ltd
- 6.4.2 BASF SE
- 6.4.3 Bayer AG
- 6.4.4 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.5 FMC Corporation
- 6.4.6 Nufarm Ltd
- 6.4.7 PT Biotis Agrindo
- 6.4.8 Syngenta Group
- 6.4.9 UPL Limited
- 6.4.10 Wynca Group (Wynca Chemicals)
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR CROP PROTECTION CHEMICALS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
샘플 요청 목록



















