
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1906918
친환경 건축자재 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Green Building Materials - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
친환경 건축자재 시장은 2025년 2억9,852만 달러로 평가되었고, 2026년 3억2,725만 달러로 성장할 것으로 전망되며, 2026-2031년 CAGR 9.62%로 성장을 지속하여, 2031년까지 5억 1,864만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.
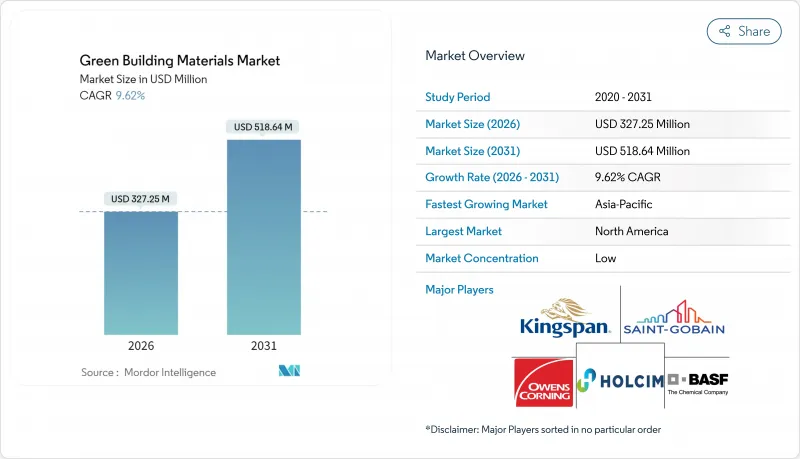
이 전망은 제로 방출 건설을 위한 지속적인 정책 압력, 기업의 넷 제로 목표에 대한 노력 증가, 저탄소 건축자재 기술의 급속한 보급 확대를 반영합니다. 유럽연합(EU), 미국 및 기타 주요 경제권에서의 규제의 정합화에 의해 기존의 분단이 해소되어 세계의 제조업체는 규모의 경제 효과를 누리고 제품 혁신을 가속할 수 있게 되었습니다. 수요는 또한 기존 제품과의 가격 차이를 줄이는 재정적 인센티브에 의해 지원되고 있으며 디지털 자재 추적 도구는 사용된 자재의 가치 스트림 수익 창출을 시작했습니다. 이러한 요인들이 결합되어 친환경 건축자재 시장이 지금까지 경험한 가운데 가장 빠른 도입 사이클을 일으키고 있습니다.
세계의 친환경 건축자재 시장 동향 및 인사이트
의무적인 에너지 절약 기준 강화
세계 각국의 건축 기준은 모든 가이드라인에서 구속력 있는 성능 기준으로 전환하고 있습니다. 유럽에서는 개정된 '건축물의 에너지 성능 지령'에 의해 2030년까지 모든 신축 건물에 있어서 현장에서의 화석 연료 배출량을 제로로 하는 것이 의무화되고, 기존 주택 스톡도 같은 해까지 최저 E등급으로의 개수가 요구됩니다. 미국도 이에 따라 2024년 국제 에너지 절약 기준(IECC)에서는 주 채용을 효율화하고 라이프사이클 탄소 배출량에 관한 규정을 추가하고 있습니다. 보다 엄격한 기준은 고성능 단열재, 저탄소 콘크리트 및 첨단 외관에 대한 수요를 촉진하고 디지털 컴플라이언스 플랫폼을 통해 제품의 지속가능성을 검증 할 수 있는 공급업체에게 유리하게 작동합니다. 집행 강화로 기존 건축자재의 컴플라이언스 비용이 더욱 상승하고 인증된 대체 재료에 지속적인 경쟁 우위가 탄생했습니다.
정부 인센티브 및 인증 제도
세액 공제, 그린 본드, 우대 대출이 프로젝트의 경제성을 변화시키고 있습니다. 미국 인플레이션 억제법 섹션 45L은 대상 주택 1개당 최대 5,000달러를 제공했으며, 179D 공제는 보다 대규모 상업 시설 개수에도 적용 범위를 확대했습니다. 캐나다는 청정 에너지 인프라에 100억 캐나다 달러를 할당하고 인증 재료로의 자본 유입을 촉진하고 있습니다. LEED, WELL, ENERGY STAR 등의 프로그램이 할인 대출과 연동하여 개발자는 선진 제품에 따른 15-25%의 가격 프리미엄을 상쇄 가능하게 되었습니다. 이러한 우대 조치는 비용 중심 부문에서 채택을 가속화하고 최신 인증 포트폴리오를 유지하는 제조업체에게 안정적인 수익원을 창출합니다.
인증 재료의 높은 초기 비용
인증 제품은 일반적으로 시험 비용, 특수 가공, 소량 생산으로 15-25%의 가격 프리미엄이 발생합니다. 이 프리미엄은 주택 건설 분야에서 특히 두드러지며 구매자가 초기 비용에 중점을 두기 때문에 수명주기 비용 절감 효과가 간과되기 쉽습니다. 카본 네거티브 콘크리트 및 바이오 베이스 단열재 등 신제품에는 연구개발비의 상각비용도 늘릴 수 있습니다. 생산량 증가 및 탄소 가격 설정에 의한 비용차가 감소함에 따라 이 비용은 감소하는 경향이 있지만, 특히 강력한 인센티브 제도가 없는 개발도상지역에서는 높은 초기 비용이 단기적인 도입 장벽으로 남아 있습니다.
부문 분석
저탄소 콘크리트 시멘트는 2025년 친환경 건축자재 시장의 24.17%를 차지했으며, 기존 시멘트와 관련된 세계 온실가스 배출량 8%의 감소가 업계의 긴급 과제임을 보여줍니다. 강도를 유지하면서 45%의 CO2를 고정화하는 광물 탄산화 공정 등의 획기적인 기술은 시험 단계에서 한정적인 상업 규모로 이행하고 있습니다. 하이델베르크 머티리얼스의 렌푸르트 프로젝트는 연간 7만 톤의 CO2를 회수할 예정이며, 주류 기술로서의 실현 가능성을 나타내고 있습니다. 구조용 강재에는 통상 93%의 스크랩이 함유되어, 수명 종료시에는 98%의 회수율을 달성하기 위해, 재생 금속 수요는 안정되어 있습니다. 엔지니어드 우드 제품, 특히 크로스 라미네이트 소재(CLT)는 개발자들이 신속한 조립, 경량 기초, 현장에서의 탄소 저장 등의 이점을 활용하면서 확대를 계속하고 있습니다. 미네랄 울 단열재는 새로운 불연성 제품 라인을 통해 주력 제품으로서의 지위를 유지하고 있습니다. 한편, 셀룰로오스 및 바이오폼 단열재는 재생가능한 원료와 높은 단열 성능에 지지되어 CAGR 10.17%로 진전하고 있습니다. 재활용 플라스틱 복합재는 수명 주기 평가를 통한 마이크로플라스틱 유출에 대한 우려로 인해 더욱 선택적으로 성장하고 있지만, 목재 폴리머 보드는 외장 갑판 및 외관의 틈새 시장에 침투를 계속하고 있습니다.
재료마다 성장 전망은 다릅니다. 저탄소 바인더는 비행 중 탄소 포집 보조금의 혜택을 받고 있으며 탄소 가격 제도가 확대되면 가속화될 것입니다. 매스 팀버 시장은 인증 임업의 확대와 건축 기준법의 높이 제한 검토에 의존합니다. 셀룰로오스의 성장 궤도는 충분한 사용된 종이 원료의 확보 및 효소 처리 플랜트의 규모 확대에 달려 있습니다. 전반적으로 소재 혁신은 경쟁 차별화를 강화하고 기존 기업에 대해 순환 경제의 특징, 검증된 탄소 풋 프린트 및 디지털 여권을 모든 제품 라인에 통합하는 것을 강요합니다.
지역별 분석
북미는 2025년 친환경 건축자재 시장 규모의 40.35%를 차지했으며, 수년에 걸친 ENERGY STAR과 LEED 프로그램, 주 수준의 제로 에너지 대응 건축 의무화가 반영되고 있습니다. 인플레이션 억제법에 근거한 연방세액 공제는 국가적 무결성을 강화하는 반면, 캘리포니아의 2025년 건축 기준 사이클에서는 제품 함유 탄소량의 한계가 더욱 강화될 전망입니다. 캐나다의 '보다 환경 친화적인 주택 이니셔티브'는 저금리 대출을 보수 공사로 이끌고 셀룰로오스 및 미네랄 모직 단열재에 대한 수요를 자극합니다.
유럽에서는 건축물의 에너지 성능 지령과 도입 예정인 탄소 국경 조정 메커니즘에 의해 고탄소 수입품의 비용 상승과 국내 저탄소 생산의 촉진이 결합되어 높은 도입 기반이 유지되고 있습니다. 스칸디나비아 국가에서는 이미 모든 대형 건축물에 대해 라이프사이클 탄소 평가를 의무화하고 있어 디지털 여권과 매스 팀버(대규모 목조) 수요를 가속시키고 있습니다. 독일과 프랑스는 공공 부문의 저탄소 콘크리트 조달을 주도하고 영국에서는 도시 해체 공사에서 재사용 가능한 자재를 회수하는 순환형 건설 허브의 시험 운용을 진행하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 급속한 도시화 및 진화하는 그린 빌딩 기준이 결합되어 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 10.95%로 확대될 것으로 예측되고 있습니다. 중국에서는 2025년까지 모든 신규 프로젝트가 최저라도 기본 등급의 그린 인증을 취득하는 것이 의무화되어 있어, 복수의 성에서는 제조시 탄소 배출량의 기준치가 도입되고 있습니다. 인도의 에너지 절약 건축 기준과 인도네시아의 그린 빌딩 평의회 평가 시스템이 조기 도입을 추진하고 있지만, 지자체별 시행 상황이 변동하고 있기 때문에 단기적인 수요 증가에는 억제적인 요소가 있습니다. 이미 성숙한 호주와 싱가포르는 지역 전체에 전문 지식을 수출하고 있으며 공급망의 현지화 및 지역 인증 기준의 강화를 촉진하고 있습니다.
남미, 중동 및 아프리카는 여전히 개발 도상이며 인프라 투자의 확대에 따라 매력적인 시장입니다. 브라질의 'Procel Edifica' 라벨 시스템과 아랍에미리트(UAE)의 'Estidama Pearl' 평가 시스템은 기후 특성에 따른 성능 요구 사항을 충족하기 위해 자재 공급업체에게 현지 생산을 촉구합니다. 자금 조달은 여전히 주요 장벽이지만, 다자간 은행에 의한 그린 본드의 이러한 시장으로의 유입이 증가하고 있으며, 차기 계획 사이클에서의 보급 가속의 기반이 갖추어지고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 애널리스트에 의한 3개월간의 지원
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 의무화된 에너지 절약 기준 강화
- 정부의 인센티브 및 인증 제도
- 기업의 넷 제로 목표, 함유 탄소 조달
- 노후화된 건축 스톡에 대한 개수 붐
- 디지털 재료 여권에 의한 사용한 가치의 수익화
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 인증 재료의 높은 초기 비용
- 지역별 인증 및 성능의 복잡성
- 2027년 이후의 바이오 베이스 원료 공급 압박
- 밸류체인 분석
- Porter's Five Forces
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁정도
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 소재 유형별
- 저탄소 콘크리트 및 시멘트
- 재생 금속
- 가공 목재 및 재생 목재
- 광물 울 단열재
- 셀룰로오스 및 바이오폼 단열재
- 재활용 플라스틱 복합재
- 용도별
- 틀
- 단열재
- 지붕재
- 외장용 사이딩
- 인테리어 마무리
- 기타 용도
- 최종 사용자 업계별
- 주택용
- 상업용
- 산업 및 공공 시설용
- 인프라
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 사우디아라비아
- 남아프리카
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율(%) 및 순위 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- BASF
- Binderholz GmbH
- Cemex SAB de CV
- Coromandel International Ltd.
- DuPont
- Heidelberg Materials
- Holcim Ltd
- Interface Inc.
- Kingspan Group
- Owens Corning
- PPG Industries Inc
- Rockwool A/S
- Saint-Gobain
- Sika AG
- SmartLam
- Steico SE
- Weyerhaeuser Company
제7장 시장 기회 및 장래 전망
AJY 26.01.26The Green Building Materials Market is expected to grow from USD 298.52 million in 2025 to USD 327.25 million in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 518.64 million by 2031 at 9.62% CAGR over 2026-2031.
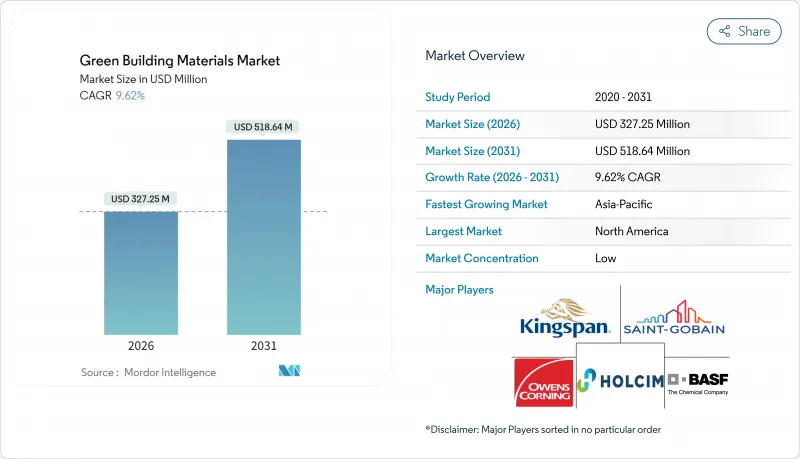
The outlook reflects sustained policy pressure for zero-emission construction, rising corporate net-zero commitments and rapid scaling of low-carbon material technologies. Regulatory alignment between the European Union, the United States and other major economies is eliminating historical fragmentation, enabling global manufacturers to capture scale efficiencies and accelerate product innovation. Demand is further supported by financial incentives that narrow the price gap with conventional products, while digital material-tracking tools are beginning to monetise end-of-life value streams. Together, these forces are triggering the fastest adoption cycle the green building materials market has experienced to date.
Global Green Building Materials Market Trends and Insights
Mandatory Energy-Efficiency Codes Tightening
Worldwide building codes are shifting from voluntary guidelines to binding performance standards. In Europe, the revised Energy Performance of Buildings Directive requires all new buildings to achieve zero on-site fossil-fuel emissions by 2030, and existing residential stock must upgrade to at least an E rating by the same year. The United States is following with the 2024 International Energy Conservation Code, which streamlines state adoption and adds life-cycle carbon provisions. Stricter codes boost demand for high-performance insulation, low-carbon concrete and advanced facades, rewarding suppliers that can verify product sustainability through digital compliance platforms. Enhanced enforcement further raises compliance costs for traditional materials, creating durable competitive advantages for certified alternatives.
Government Incentives and Certification Schemes
Tax credits, green bonds and preferential financing are transforming project economics. The US Inflation Reduction Act's Section 45L offers up to USD 5,000 per qualifying housing unit, and the 179D deduction now covers larger commercial upgrades. Canada has earmarked CAD 10 billion for clean-energy infrastructure, funnelling capital toward certified materials. With programs such as LEED, WELL and ENERGY STAR now linked to discounted financing, developers can offset the 15-25% price premium associated with advanced products. These incentives accelerate adoption in cost-sensitive segments and create reliable revenue streams for manufacturers that maintain up-to-date certification portfolios.
High Upfront Cost of Certified Materials
Certified products typically command 15-25% price premiums owing to testing, specialised processing and smaller production runs. The premium is most acute in residential construction, where buyers focus on first-cost and may overlook lifecycle savings. Novel products such as carbon-negative concrete or bio-based insulation also carry R&D amortisation charges. While declining as volumes rise and carbon pricing narrows cost differentials, elevated upfront expense remains a near-term adoption barrier, particularly in developing regions without robust incentive programs.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Corporate Net-Zero, Embodied-Carbon Procurement
- Retrofit Wave for Ageing Building Stock
- Certification and Performance Complexity Across Regions
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Low-carbon concrete and cement captured 24.17% of green building materials market share in 2025, underscoring industry urgency to abate the 8% of global greenhouse-gas emissions linked to conventional cement. Breakthrough technologies such as mineral-carbonation processes that sequester 45% CO2 while preserving strength have transitioned from pilot to limited commercial scale. Heidelberg Materials' Lengfurt project will capture 70,000 t of CO2 per year, signalling mainstream viability. Recycled metals retain reliable demand as structural steel routinely contains 93% scrap content and achieves 98% recovery rates at end-of-life. Engineered wood products, notably cross-laminated timber, are expanding as developers capitalise on faster assembly, lighter foundations and on-site carbon storage. Mineral-wool insulation remains a staple thanks to new non-combustible product lines, while cellulose and bio-foam insulation is progressing at a 10.17% CAGR, supported by renewable feedstocks and high thermal performance. Recycled-plastic composites are growing more selectively as lifecycle assessments raise concerns over micro-plastic shedding, although wood-polymer boards continue to penetrate exterior decking and facade niches.
Growth prospects vary across materials. Low-carbon binders benefit from inflight carbon-capture subsidies and will accelerate once carbon pricing regimes scale. Mass-timber markets hinge on expanded certified forestry capacity and revisions to height limits in building codes. Cellulose's trajectory depends on securing sufficient post-consumer paper streams and scaling enzymatic treatment plants. Overall, material innovation reinforces competitive differentiation, compelling incumbents to integrate circular-economy features, verified carbon footprints and digital passports into every product line.
The Green Building Materials Market Report is Segmented by Material Type (Low-Carbon Concrete and Cement, Recycled Metals, and More), Application (Framing, Insulation, and More), End-Use Industry (Residential, Commercial, Industrial and Institutional, and Infrastructure), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle-East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America accounted for 40.35% of the green building materials market size in 2025, reflecting long-standing ENERGY STAR and LEED programmes and state-level zero-energy-ready building mandates. Federal tax credits under the Inflation Reduction Act strengthen national alignment, while California's 2025 code cycle is expected to tighten embodied-carbon limits further. Canada's Greener Homes Initiative funnels low-interest loans into retrofit upgrades, stimulating demand for cellulose and mineral-wool insulation.
Europe maintains a high adoption baseline due to the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive and the forthcoming Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, which together raise the cost of high-carbon imports and incentivise domestic low-carbon production. Scandinavian countries have already mandated whole-life-carbon assessments for all large buildings, accelerating demand for digital passports and mass timber. Germany and France lead public-sector procurement of low-carbon concrete, while the United Kingdom pilots circular-construction hubs to harvest reusable materials from urban demolition.
Asia-Pacific is forecast to expand at an 10.95% CAGR through 2031 as rapid urbanisation meets evolving green-building codes. China requires all new projects to achieve at least Basic Grade green certification by 2025, while several provinces have introduced embodied-carbon benchmarks. India's Energy Conservation Building Code and Indonesia's Green Building Council rating system are driving early adoption, though fragmented municipal enforcement tempers near-term volumes. Australia and Singapore, already mature, are exporting expertise across the region, reinforcing supply-chain localisation and regional certification standards.
South America and the Middle East and Africa remain nascent but attractive as infrastructure investment expands. Brazil's Procel Edifica labelling system and the United Arab Emirates' Estidama Pearl Rating System are encouraging material suppliers to localise production to meet climate-specific performance needs. Financing remains the principal hurdle; however, multilateral banks increasingly channel green bonds into these markets, setting the stage for accelerated uptake during the next planning cycle.
- BASF
- Binderholz GmbH
- Cemex S.A.B. de C.V.
- Coromandel International Ltd.
- DuPont
- Heidelberg Materials
- Holcim Ltd
- Interface Inc.
- Kingspan Group
- Owens Corning
- PPG Industries Inc
- Rockwool A/S
- Saint-Gobain
- Sika AG
- SmartLam
- Steico SE
- Weyerhaeuser Company
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Mandatory Energy-Efficiency Codes Tightening
- 4.2.2 Government Incentives and Certification Schemes
- 4.2.3 Corporate Net-Zero, Embodied-Carbon Procurement
- 4.2.4 Retrofit Wave for Ageing Building Stock
- 4.2.5 Digital Material Passports Monetising End-Of-Life Value
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Upfront Cost of Certified Materials
- 4.3.2 Certification And Performance Complexity Across Regions
- 4.3.3 Bio-Based Feedstock Supply Crunch Post-2027
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Material Type
- 5.1.1 Low-carbon Concrete and Cement
- 5.1.2 Recycled Metals
- 5.1.3 Engineered / Reclaimed Wood
- 5.1.4 Mineral-wool Insulation
- 5.1.5 Cellulose and Bio-foam Insulation
- 5.1.6 Recycled-plastic Composites
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Framing
- 5.2.2 Insulation
- 5.2.3 Roofing
- 5.2.4 Exterior Siding
- 5.2.5 Interior Finishing
- 5.2.6 Other Applications
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 Residential
- 5.3.2 Commercial
- 5.3.3 Industrial and Institutional
- 5.3.4 Infrastructure
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 South Korea
- 5.4.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share(%)/ Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Info, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 BASF
- 6.4.2 Binderholz GmbH
- 6.4.3 Cemex S.A.B. de C.V.
- 6.4.4 Coromandel International Ltd.
- 6.4.5 DuPont
- 6.4.6 Heidelberg Materials
- 6.4.7 Holcim Ltd
- 6.4.8 Interface Inc.
- 6.4.9 Kingspan Group
- 6.4.10 Owens Corning
- 6.4.11 PPG Industries Inc
- 6.4.12 Rockwool A/S
- 6.4.13 Saint-Gobain
- 6.4.14 Sika AG
- 6.4.15 SmartLam
- 6.4.16 Steico SE
- 6.4.17 Weyerhaeuser Company
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment


















