
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1687111
우주 이용 C4ISR 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Space-based C4ISR - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
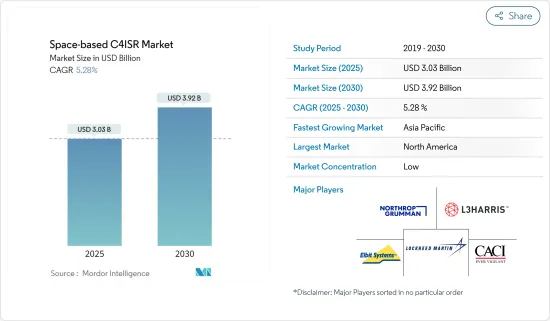
우주 이용 C4ISR 시장 규모는 2025년에 30억 3,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 39억 2,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 예측 기간 중 2025년부터 2030년까지 CAGR 5.28%로 성장할 전망입니다.

첩보, 감시 및 정찰(ISR)은 국가의 전략적 방위에서 매우 중요한 역할을 합니다. 많은 국가들은 상황 인식을 강화하고 통신 속도를 높이고 위협 감지 능력을 강화하기 위해 우주 이용 시스템에 주목하고 있습니다. 세계 각국은 현재 및 미래의 안전 보장 요구를 충족시키기 위해 데이터 수집부터 발신에 이르기까지 모든 측면에서 ISR 시스템을 활용하고 있습니다. 또한 많은 국가들이 우주 기반 강력한 이미지 정보(IMINT)를 무기고로 강화하고 우주 공간에서 원활한 군사 작전을 위해 이러한 능력을 적극적으로 강화하고 있습니다.
지리 공간 시스템의 보급과 마이크로 일렉트로닉스의 발전은 정교한 우주 이용 C4ISR 시스템을 구축하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 이러한 시스템은 고급 기능을 자랑하는 동시에 관련 연구개발 비용을 낮추고 있습니다. 그러나 우주 이용 C4ISR에 대한 수요의 급증은 사이버 보안과 잠재적인 우주 이용 무기 공격에 대한 우려 증가를 가져왔습니다. 게다가 규제적 제약과 기술적 한계는 우주 이용 C4ISR 시스템의 설계와 진보에 어려움을 야기하여 앞으로 수년간 시장 성장을 방해할 수 있습니다.
우주 이용 C4ISR 시장 동향
예측기간 동안 ISR 분야가 시장을 독점할 전망
우주 이용 C4ISR 시장에서의 첩보, 감시 및 정찰(ISR) 능력은 현대 방위 전략의 눈이 되고 귀가 됩니다. 우주에서 ISR 기술은 고급 위성 시스템, 원격 감지, 데이터 분석을 포함하여 정확하고 시기 적절한 정보 수집, 전략적 모니터링 및 정찰을 가능하게 합니다. 하이브리드 시나리오로 이동하는 전쟁의 양상 변화는 공동 작전에 의해 지원되고 효과적인 작전을 가능하게 하는 상호 운용성을 필요로 합니다.
이러한 궤도는 GEO보다 데이터 전송 속도가 빠르기 때문에 몇 가지 장점이 있기 때문에 여러 국가가 다양한 ISR 위성을 LEO 및 MEO 위성 별자리로 출시합니다. 또한 LEO 위성은 추진력과 전력이 적어 소형화할 수 있어 데이터 지연도 줄어듭니다. 따라서 다양한 국가들이 ISR 위성을 우주로 발사하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 2024년 1월, 미쓰비시중공업의 H2A 로켓이 일본의 ISR 위성을 궤도에 올려 북한의 군사 거점의 움직임 등의 데이터를 수집했습니다. 마찬가지로 2023년 12월 인도는 AI를 탑재한 50대의 감시 위성을 개발하고, 포착한 데이터를 분석하여 실시간으로 최신 정보를 제공하며 인도의 국경 감시를 강화할 계획을 발표했습니다. 게다가 2024년 5월, 스페이스 X사의 팔콘 9로켓이, 정보 수집 용도의 정부판 스타링크 위성을 발사했습니다. 미국은 향후 수년간 수백기의 위성을 궤도에 발사할 계획입니다.
이와 같이 첨단 ISR 시스템의 연구개발, 조달을 위해 많은 투자가 이루어지고 있어 시장의 성장을 견인할 가능성이 있습니다. 기술 진보, 우주 지배권 획득 경쟁, 군용 위성에 대한 예산 배분 증가는 예측 기간 동안 이 부문의 성장을 더욱 촉진할 것으로 예상됩니다.
아시아태평양이 예측 기간 동안 가장 높은 성장을 기록할 전망
아시아태평양의 인프라 투자는 우주 이용 C4ISR 시스템의 성장을 가속화하고 있습니다. 중국은 첨단 능력, 급증하는 발사 로켓, 강력한 BeiDou 위성 네비게이션 프로그램으로 두드러집니다. 2015년에 전략 지원군을 결성한 후 중국은 48위성의 BeiDou 컨스텔레이션을 완성하여 지구동기궤도(GEO)와 저궤도(LEO)의 통신위성과 ISR위성을 강화한 것입니다. 이것은 특히 LEO에서 우주 능력의 확대와 함께 중국의 C4ISR 네트워크를 강화하고 있습니다.
한편 인도는 군사통신 인프라를 대폭 강화하고 있어 운용 가능한 3기의 군사통신 전용 위성과 다목적 위성군을 자랑하고 있습니다. 최근 인도 국방부의 전기 광학 위성 승인에 주목받은 이러한 자산은 우주 기반 정보 능력을 강화하는 인도의 헌신을 강조합니다. 게다가 ISRO는 향후 5년간 50대의 지리정보위성을 발사할 야심찬 계획을 세우고 있으며, 부대의 움직임을 감시하고 광대한 지형을 파악할 수 있습니다.
우주 이용 C4ISR 산업 개요
우주 이용 C4ISR 시장은 단편화되어 있으며, 일부 국제 및 지역 기업들이 세계 군 수요를 지원합니다. 이 시장에서 유명한 기업으로는 Northrop Grumman Corporation, Lockheed Martin Corporation, L3Harris Technologies Inc., CACI International Inc., Elbit Systems Ltd. 등이 있습니다.
시장 기업들은 지역 간의 도달범위를 넓히고 군로부터 추가 계약을 확보하기 위해 새로운 전략을 반영합니다. 새로운 지역에서의 발판을 굳히기 위해, 현지 제조업체와의 제휴나 합작 사업도 늘고 있습니다. 게다가, 특히 우주 이용 C4ISR 시스템을 진보시키기 위한 연구개발에 대한 투자 증가는 AI와 양자 네트워킹 등의 최첨단 기술과 함께 예측 기간 동안 새로운 고객을 유치하고 시장 점유율을 강화하는 자세입니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 전제조건
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 역학
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 산업의 매력-Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 구매자 및 소비자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
제5장 시장 세분화
- 목적별
- C4
- ISR
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 유럽
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 세계 기타 지역
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 벤더의 시장 점유율
- 기업 프로파일
- Elbit Systems Ltd
- General Dynamics Corporation
- Maxar Technologies Ltd
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- BAE Systems PLC
- CACI International Inc.
- Kratos Defense & Security Solutions Inc.
- The Boeing Company
- L3Harris Technologies Inc.
- Defence Research and Development Organisation
- Hanwha Systems Co. Ltd
제7장 시장 기회 및 향후 동향
AJY 25.04.04The Space-based C4ISR Market size is estimated at USD 3.03 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 3.92 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.28% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) play a pivotal role in a nation's strategic defense. Many countries are turning to space-based systems to bolster their situational awareness, enhance communication speeds, and fortify their threat detection capabilities. Globally, countries are leveraging ISR systems across the board, from data collection to dissemination, to meet current and future security demands. Furthermore, many nations have bolstered their arsenals with potent space-based image intelligence (IMINT) and are actively enhancing these capabilities for smoother military operations in space.
The rise in geospatial system adoption and advancements in microelectronics have been instrumental in crafting sophisticated space-based C4ISR systems. These systems boast advanced features while simultaneously driving down associated R&D costs. However, the surge in demand for space-based C4ISR has brought about heightened concerns regarding cybersecurity and potential space-based weapon attacks. Additionally, regulatory constraints and technological limitations pose challenges to the design and advancement of space-based C4ISR systems, potentially impeding the market's growth in the coming years.
Space-based C4ISR Market Trends
The ISR Segment is Expected to Dominate the Market During the Forecast Period
Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities in the space-based C4ISR market represent the eyes and ears of modern defense strategies. ISR technologies in space encompass advanced satellite systems, remote sensing, and data analytics, enabling precise and timely intelligence gathering, strategic surveillance, and reconnaissance, which are crucial for informed decision-making in national security. The changing face of warfare moving toward hybrid scenarios will be underpinned by joint operations and require interoperability to allow effective operation.
Several countries are launching various ISR satellites into LEO and MEO satellite constellations as these orbits have several advantages over GEO, such as faster data transfer. In addition, LEO satellites are smaller because they require less propulsion and less power, and the data latency is reduced. So, various countries are launching ISR satellites into space. For instance, in January 2024, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Limited's H2A rocket carried a Japanese ISR satellite into orbit to gather data on movements at North Korean military sites and for other applications. Similarly, in December 2023, India announced that it plans to develop 50 AI-enabled surveillance satellites to analyze the captured data to provide real-time updates and bolster India's border surveillance. Furthermore, in May 2024, SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket launched government versions of Starlink satellites for intelligence-gathering applications. The US plans to launch hundreds of these satellites into orbit in the upcoming years.
Thus, many investments are being made to research, develop, and procure advanced ISR systems that may drive the market's growth. Technological advancement, the race to gain space dominance, and increased budget allocations on military satellites are further expected to drive the growth of this segment during the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific is Expected to Register the Highest Growth During the Forecast Period
Infrastructure investments in Asia-Pacific are accelerating the growth of space-based C4ISR systems. China is a standout with its advanced capabilities, a burgeoning fleet of launch vehicles, and a robust BeiDou satellite navigation program. Notably, after forming the Strategic Support Force in 2015, China completed its 48-satellite BeiDou constellation, bolstering its communication and ISR satellites in geosynchronous-earth orbit (GEO) and low-earth orbit (LEO). This, coupled with its expanding space capabilities, especially in LEO, has fortified China's C4ISR network.
Meanwhile, India is significantly enhancing its military communication infrastructure, boasting three operational dedicated military communication satellites and a fleet of dual-purpose ones. These assets, highlighted by the recent approval of an electro-optical satellite by the Indian Ministry of Defense, underscore India's commitment to bolstering its space-based intelligence capabilities. Additionally, ISRO's ambitious plan to launch 50 geo-intelligence satellites over the next five years, capable of monitoring troop movements and capturing vast swathes of terrain, further solidifies the increasing demand for C4ISR systems in the region.
Space-based C4ISR Industry Overview
The space-based C4ISR market is fragmented, with several international and regional players supporting the demand from the global armed forces. Some prominent players in the market are Northrop Grumman Corporation, Lockheed Martin Corporation, L3Harris Technologies Inc., CACI International Inc., and Elbit Systems Ltd.
Market players are crafting fresh strategies to broaden their reach across regions and secure additional contracts from the armed forces. They are increasingly forging partnerships and joint ventures with local manufacturers to bolster their foothold in new territories. Moreover, heightened investments in R&D, particularly for advancing space-based C4ISR systems, coupled with cutting-edge technologies such as AI and quantum networking, are poised to entice new clientele and bolster their market share during the forecast period.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Purpose
- 5.1.1 C4
- 5.1.2 ISR
- 5.2 Geography
- 5.2.1 North America
- 5.2.1.1 United States
- 5.2.1.2 Canada
- 5.2.2 Europe
- 5.2.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.2.2.2 France
- 5.2.2.3 Germany
- 5.2.2.4 Russia
- 5.2.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.2.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.2.3.1 China
- 5.2.3.2 India
- 5.2.3.3 Japan
- 5.2.3.4 South Korea
- 5.2.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.2.4 Rest of the World
- 5.2.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Vendor Market Share
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Elbit Systems Ltd
- 6.2.2 General Dynamics Corporation
- 6.2.3 Maxar Technologies Ltd
- 6.2.4 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.2.5 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.2.6 BAE Systems PLC
- 6.2.7 CACI International Inc.
- 6.2.8 Kratos Defense & Security Solutions Inc.
- 6.2.9 The Boeing Company
- 6.2.10 L3Harris Technologies Inc.
- 6.2.11 Defence Research and Development Organisation
- 6.2.12 Hanwha Systems Co. Ltd

















