|
시장보고서
상품코드
1850209
농약 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Agrochemicals - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
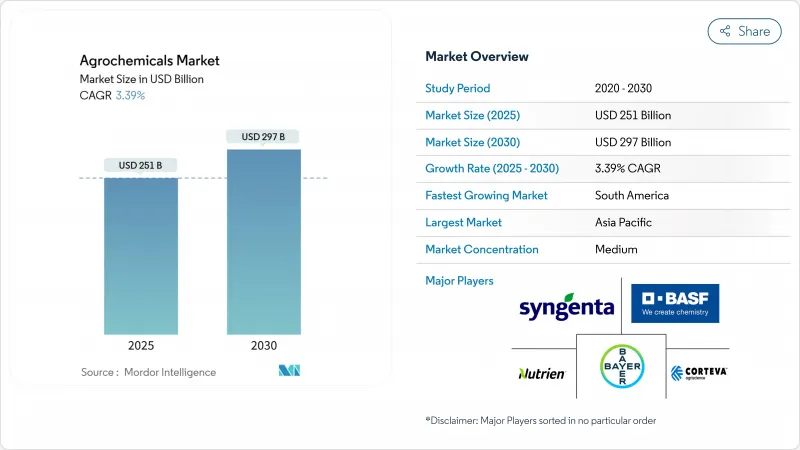
농약 시장은 2025년에 2,510억 달러, 2030년에는 2,970억 달러에 이르고, CAGR은 3.39%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

성장을 지원하는 것은 대규모 곡물 경제권에서 지속적인 비료 수요, 생물학적 작물 보호 제품의 급속한 보급, 투입 자재의 사용 효율을 높이는 정밀 농업 도구의 보급입니다. 동시에 2030년까지 화학농약 사용량을 반감시키는 EU의 Farm to Fork 지침, 중국의 정기적인 비료 수출 억제, 주요 수입 시장에서의 잔류 규제 강화로 생산자는 저독성 화학물질 및 디지털 자문 서비스로 포트폴리오 시프트를 가속화할 수밖에 없게 되었습니다. 생물학적 제제는 현재 30개국에서 실시되고 있는 농약세제와 브라질과 인도의 등록 경로의 합리화를 배경으로 급속히 규모를 확대하고 있는 한편, 신규 작용 모드를 가지는 고급 제초제는 비용이 많이 드는 내성 잡초 증가에 대처하고 있습니다. 제네릭 의약품이 성숙 분자의 마진을 침식하고 새로운 '인풋 아즈 어 서비스' 모델이 제품량보다 성과 기반 가격 설정에 보상함에 따라 경쟁의 치열성이 증가하고 있으며, 농약 시장에서 기술 통합과 지속가능성 증명에 의해 정의되는 10년의 무대가 갖추어지고 있습니다.
세계 농약 시장 동향과 통찰
제초제 내성 잡초 증가가 프리미엄 제초제 수요에 박차를 가한다.
제초제 저항성 잡초는 현재 전 세계적으로 2억 7,000만 에이커 이상으로 만연하고 있으며, 생산자는 새로운 작용 모드를 가진 프리미엄 제초제를 찾고 있습니다. FMC의 도다이렉스 액티브는 30년 만의 새로운 제초제 모드로 페루에서 처음 등록되어 벼의 저항성 벼과 잡초를 대상으로 하고 있으며 2025년 8월에 상업 판매가 시작될 예정입니다. 미국 환경보호청의 2024년 저항성 관리 프레임워크는 종합적인 잡초 관리 프로토콜을 강화하고 혁신적인 제형에 규제 지원을 제공합니다. 스미토모화학의 아르헨티나에서의 라피디실 등록은 불경기 시스템에 대응하기 위한 경쟁쟁을 지지하고, 보전경기 제초제에 의한 연간 매출 1,000억엔(6억 5,000만 달러)을 목표로 합니다. 저항성 잡초는 전 세계적으로 연간 150억 달러를 초과하는 수율 손실을 초래하기 때문에 생산자의 지불 의향은 여전히 강합니다.
AI를 활용한 Input Az A 서비스 비즈니스 모델의 융합
디지털 농업 플랫폼은 농학적 조언, 가변 속도 처방 및 성과 기반 보증을 번들로 하여 기존 제품만의 유통을 대체하고 있습니다. 바이엘의 CROPWISE 플랫폼은 현재 현장 센서, 기상 데이터 및 위성 이미지를 통합하고 살포 및 시비 일정을 미세 조정하고 있습니다. BASF와 Agmatix는 머신러닝 진단을 적용하여 대두 시스트 선충의 스트레스가 눈에 보이는 증상이 나타나기 전에 감지하고 수율을 보호하면서 약물 부하를 줄입니다. 신젠타와 타라니스의 제휴는 소매업체에게 AI를 활용한 스카우팅을 제공하고, 정확한 투입 자재의 배치를 촉진하고, 일회성 매출을 정기 수입으로 바꿉니다. 이러한 서비스를 통해 1에이커당 화학물질 사용량을 최대 20%까지 줄이고 농약 시장에서 지속가능성 요구와 수익성을 일치시킬 수 있습니다.
EU, 브라질, 중국에서 고독성 농약의 단계적 폐지 가속
규제당국은 독성이 지적된 유효성분의 유예기간을 단축하고, 제조업체에게 재고상각과 개량 파이프라인의 가속을 강요하고 있습니다. 유럽 연합(EU)의 최신 제안은 영향을 받기 쉬운 서식지에서 특정 유기 인산염을 제거하는 것으로, 브라질은 EU와 승인 기준을 합쳐 2026년까지 약 200개의 레거시 분자를 제거합니다. BASF는 2024년에 글루포시네이트 공장을 폐쇄하고 규제 강화 전망과 관련하여 손상차손을 기록했습니다. 중국 정책은 저독성 살균제와 바이오 농약을 우선시하며 2025년까지 9만 톤의 상업 생산량을 전망하고 있습니다.
부문 분석
농약 시장의 2024년 매출액의 46.0%를 비료가 차지했는데, 이는 곡물과 지방종자에 대영양소를 공급하는데 필수적인 역할을 하고 있음을 반영하고 있습니다. 그러나 불안정한 천연가스 가격은 암모니아 비용을 높여 질소 생산자의 마진을 압박하고 우레아제 억제제나 수율을 떨어뜨리지 않고 살포량을 15-25% 삭감하는 방출 제어형 코팅제 등의 효율화 기술로 축발을 옮기는 조짐을 보이고 있습니다. 비료의 농약 시장 규모는 신흥 경제 국가에서의 시용률의 두드림으로 인해 시장 전체보다 둔한 CAGR 2.3%로 확대될 것으로 예측됩니다. 따라서 생산자는 프리미엄 폴리머 코팅 제품과 탄소 크레딧에 연동된 제품 등 수량 이상의 가치를 획득할 수 있는 제품을 중시하고 있습니다.
미생물, 식물, 페로몬 및 생화학을 포함한 생물학적 부문은 2024년에 14.7% 성장했으며 2030년에는 250억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다. 그 중 바이오 살충제의 농약 시장 규모는 유럽의 잔류 규제 강화나 브라질의 패스트 트랙 등록에 밀려 CAGR 15.2%로 확대될 전망입니다. 그 결과, 병충해 종합 관리 프로그램은 화학 및 생물학적 기법을 1시즌마다 회전시켜 공급업체가 자체 계통과 보조제를 상호 판매할 수 있게 되었습니다. Syngenta Biologicals나 FMC 등 대기업은 이 분야에 적극적으로 전환하여 포트폴리오의 갭을 메우기 위해 M&A를 가속시키고 있습니다. 제초제, 살균제, 보조제 및 식물 성장 조절제는 여전히 중요하며, 이들을 합친 농약 시장 점유율은 생물학적 제제가 더 높은 마진을 얻으면서 물량을 잠식함에 따라 약간 감소할 것으로 예측됩니다.
지역 분석
아시아태평양은 2024년에 가장 높은 수익을 유지했으며 농약 시장의 48.5%를 차지했습니다. 중국은 세계의 활성성분 생산량의 50%를 생산하고 있지만, 국내 환경규제는 현재 저독성 라인을 우선하고 있으며, 바이오 농약 생산 능력에 대한 투자를 자극하고 있습니다. 인도의 계약 개발 및 제조 조직은 구미 파이프라인의 갭을 메우는 다년 계약을 획득하여 두 자리수의 매출 성장을 견인합니다. 일본은 배출량 목표를 달성하기 위해 방출제어비료의 채택을 가속화하고 호주는 비료 수요와 기후에 따른 가뭄 조정의 균형을 맞춥니다. 디지털 토양 검사와 균형 잡힌 영양 섭취를 추진하는 정부 보조금 프로그램은 기본적인 소비 패턴을 강화합니다.
남미는 가장 급성장하고 있는 지역으로 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 4.4%로 성장할 것으로 예상됩니다. 브라질의 바이오 시장은 2024년 50억 BRL(10억 달러)에 이르고 콩과 면화에 집중합니다. 물류 병목 현상은 여전히 남아 있으며, 브라질 농도의 62%가 최적의 품질보다 적기 때문에 비용이 상승하고 제제 공장의 지역화가 진행되고 있습니다. 아르헨티나의 불경기작 면적은 90%를 넘어 Rapididicil과 같은 잔사 대응 제초제 수요를 지지하고 있습니다. 기후 변화, 특히 가뭄은 미량 영양소와 수효율 제품의 판매를 끌어 올리고 농약 시장에서 적응 기술을 위한 탄력적인 비즈니스 케이스를 형성하고 있습니다.
북미와 유럽은 성숙하지만 여전히 혁신의 중심지입니다. 미국은 농가의 비용을 1톤당 100달러 상승시킬 수 있는 캐나다산 칼리의 관세 제안과 싸우고 있으며, 생물학적 질소 치환과 칼륨 가용화 미생물에 대한 관심을 촉구하고 있습니다. 캐나다는 4R 영양 관리 인증을 추진하고 대출 인센티브를 비료 모범 사례에 연결합니다. 유럽의 Farm to Fork 전략은 2030년까지 농약을 50% 절감할 의무가 있으며 생물학적 인증 가속화와 디지털 추적성 시스템을 추진하고 있습니다. 중동 및 아프리카는 각각 3.4%와 4.1%의 성장을 이루었는데, 이것은 소규모 기반에서인 것, 소블린에 의한 식량 안보에 대한 투자, 수경 재배의 채택, 사막의 재생 농법에 뒷받침된 것입니다. 종합적으로 볼 때, 이러한 역학 관계는 농약 시장을 점진적인 부피 성장의 경로로 유지하고 고부가가치 제품 대체를 통해 보완합니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 제초제 내성 잡초 증가가 고급 제초제 수요를 자극
- AI를 활용한 Input-as-a-Service 비즈니스 모델의 융합
- 농약세 제도에 의한 생물 제제의 급증
- 질소 효율 제품의 탄소 신용 수익화
- 완효성 비료의 주류화
- 수직 농장과 실내 농장에서의 작물의 다양화
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- EU, 브라질, 중국에 있어서의 고독성 활성 물질의 단계적 폐지의 가속
- 불안정한 글리포세이트 가격이 제조업체의 이익을 압박
- 규제 데이터 패키지 비용 상승
- 북미의 만성 액티비스트 소송 위험
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 제품 유형별
- 비료
- 질소
- 인산
- 칼륨
- 농약
- 제초제
- 살충제
- 살균제
- 바이오 농약
- 보조제
- 식물성장조정제
- 비료
- 용도별
- 작물 베이스
- 곡물
- 콩류 및 지방종자
- 과일 및 채소
- 비작물 베이스
- 잔디 및 관상용 잔디
- 기타 비작물 베이스
- 작물 베이스
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 기타 북미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 영국
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 중동
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 이집트
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Syngenta Group
- Bayer Crop Science AG
- BASF Agricultural Solutions
- Corteva Agriscience
- Nutrien Ltd
- Yara International ASA
- Mosaic Company
- CF Industries Holdings
- UPL Ltd
- FMC Corporation
- Sumitomo Chemical AgroSolutions
- Nufarm Ltd
- KS AG
- ICL Group
- OCP Group
- Albaugh LLC
- OCI Global
- RovensaNext
- Bharat Rasayan Ltd
- Helm AG
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
SHW 25.11.17The agrochemicals market reached USD 251 billion in 2025 and is forecast to rise to USD 297 billion by 2030, translating into a steady 3.39% CAGR.
Growth is supported by sustained fertilizer demand in large grain economies, rapid penetration of biological crop-protection products, and wider deployment of precision-agriculture tools that lift input-use efficiency. At the same time, the European Union's Farm to Fork mandate to halve chemical pesticide use by 2030, China's periodic fertilizer export curbs, and increasingly stringent residue limits in major import markets are forcing producers to accelerate portfolio shifts toward low-toxicity chemistries and digital advisory services. Biologicals are scaling quickly on the back of pesticide-tax regimes now active in 30 countries and streamlined Brazilian and Indian registration pathways, while premium herbicides with novel modes of action address the costly rise of resistant weeds. Competitive intensity is growing as generics erode margins on mature molecules and new "input-as-a-service" models reward outcome-based pricing over product volume, setting the stage for a decade defined by technology integration and sustainability credentials within the agrochemicals market.
Global Agrochemicals Market Trends and Insights
Escalating Herbicide-Resistant Weeds Spur Premium Herbicide Demand
Herbicide-resistant weeds now infest more than 270 million acres worldwide, pushing growers toward premium actives that deliver novel modes of action. FMC's Dodhylex active, the first new herbicide mode in three decades, secured its inaugural registration in Peru and targets resistant grass weeds in rice, with a commercial launch slated for August 2025. The United States Environmental Protection Agency's 2024 resistance-management framework reinforces integrated weed-management protocols, giving regulatory support to innovative formulations. Sumitomo Chemical's Rapidicil registration in Argentina underpins the competitive race to serve no-till systems, aiming for JPY 100 billion (USD 0.65 billion) in annual sales from conservation-tillage herbicides. Growers' willingness to pay remains strong because resistant weeds impose yearly global yield losses above USD 15 billion.
Convergence of AI-Enabled Input-as-a-Service Business Models
Digital farming platforms are displacing traditional product-only distribution by bundling agronomic advice, variable-rate prescriptions, and outcome-based guarantees. Bayer's CROPWISE platform now integrates field sensors, weather data, and satellite imagery to fine-tune spraying and fertilizing schedules. BASF and Agmatix apply machine-learning diagnostics to detect soybean cyst nematode stress before visual symptoms appear, protecting yields while cutting chemical load. Syngenta's tie-up with Taranis equips retailers with AI-powered scouting to drive precise input placement, converting one-time sales into subscription revenue. These services reduce chemical intensity per acre by up to 20%, aligning profitability with sustainability imperatives in the agrochemicals market.
Accelerating Phase-Outs of High-Toxicity Actives in EU, Brazil, and China
Regulators are shortening grace periods for active ingredients flagged for toxicity, forcing manufacturers to write off inventory and accelerate reformulation pipelines. The European Union's latest proposal eliminates certain organophosphates from sensitive habitats, while Brazil aligns approval criteria with the EU, removing nearly 200 legacy molecules by 2026. BASF shuttered its glufosinate plant in 2024, booking impairment charges linked to the tighter regulatory outlook. Chinese policies prioritize low-toxicity fungicides and biopesticides, expecting commercial volumes of 90,000 metric tons by 2025.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Surge in Biologicals Pushed by Pesticide-Tax Regimes
- Carbon-Credit Monetization of Nitrogen-Efficiency Products
- Volatile Glyphosate Pricing Squeezes Formulator Margins
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Fertilizers accounted for 46.0% of 2024 revenue inside the agrochemicals market, reflecting their indispensable role in macronutrient delivery to grains and oilseeds. Yet volatile natural gas prices inflated ammonia costs, squeezing margins for nitrogen producers and signaling a pivot toward efficiency technologies such as urease inhibitors and controlled-release coatings that reduce application rates by 15-25% without yield loss. The agrochemicals market size for fertilizers is forecast to expand at just 2.3% CAGR, slower than the overall market because of plateauing application rates in developed economies. Producers, therefore, emphasize premium polymer-coated lines and carbon-credit-linked offerings that capture value beyond volume.
The biological segment, encompassing microbials, botanicals, pheromones, and biochemicals, grew 14.7% in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 25 billion by 2030. Within that total, the agrochemicals market size for bio-insecticides is on track to advance at 15.2% CAGR, buoyed by European residue-limit tightening and Brazilian fast-track registrations. As a result, integrated pest-management programs now mix chemical and biological tools in single-season rotations, enabling suppliers to cross-sell proprietary strains and adjuvants. Major players such as Syngenta Biologicals and FMC pivot aggressively toward this space, accelerating mergers and acquisitions to fill portfolio gaps. Herbicides, fungicides, adjuvants, and plant growth regulators remain critical; and their combined share of the agrochemicals market is projected to decline slightly as biologicals cannibalize volume while fetching higher margins.
The Agrochemicals Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Fertilizers, Pesticides, Adjuvants, and Plant Growth Regulators), by Application (Crop-Based and Non-Crop-Based), and by Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East, and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific retained the highest regional revenue in 2024, accounting for 48.5% within the agrochemicals market, supported by intensive cultivation across China and India. China manufactures 50% of the worldwide active-ingredient output, yet domestic environmental rules now favor low-toxicity lines, stimulating investment in biopesticide capacity. India's contract development and manufacturing organizations secure multiyear deals that fill Western pipeline gaps, driving double-digit revenue growth. Japan accelerates the adoption of controlled-release fertilizers to meet emission targets, the Australia balances fertilizer demand with climate-induced drought adjustments. Government subsidy programs promoting digital soil testing and balanced nutrition enhance baseline consumption patterns.
South America is the fastest-growing territory, expanding by 4.4% CAGR through 2030. Brazil's biological market hit BRL 5 billion (USD 1 billion) in 2024, with uptake concentrated in soybean and cotton. Logistics bottlenecks persist; 62% of Brazilian agricultural roads are below optimal quality, raising costs and encouraging localized formulation plants. Argentina's no-till acreage exceeds 90%, underpinning demand for residue-compatible herbicides such as Rapidicil. Climate volatility, especially drought, boosts micronutrient and water-efficiency product sales, shaping a resilient business case for adaptive technologies within the agrochemicals market.
North America and Europe, though mature, remain innovation hubs. The United States contends with tariff proposals on Canadian potash that could raise farmer costs by USD 100 per ton, prompting interest in biological nitrogen replacement and potassium-solubilizing microbes. Canada promotes 4R nutrient-stewardship certification, linking lender incentives to fertilizer best practices. Europe's Farm to Fork strategy mandates 50% pesticide cuts by 2030, triggering accelerated biological approvals and digital traceability systems. The Middle East and Africa grew 3.4% and 4.1%, respectively, propelled by sovereign food-security investments, hydroponic adoption, and reclaimed desert farming, albeit from smaller bases. Collectively, these dynamics keep the agrochemicals market on a path of gradual volume growth complemented by higher-value product substitution.
- Syngenta Group
- Bayer Crop Science AG
- BASF Agricultural Solutions
- Corteva Agriscience
- Nutrien Ltd
- Yara International ASA
- Mosaic Company
- CF Industries Holdings
- UPL Ltd
- FMC Corporation
- Sumitomo Chemical AgroSolutions
- Nufarm Ltd
- K+S AG
- ICL Group
- OCP Group
- Albaugh LLC
- OCI Global
- RovensaNext
- Bharat Rasayan Ltd
- Helm AG
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating herbicide-resistant weeds spur premium herbicide demand
- 4.2.2 Convergence of AI-enabled Input-as-a-service business models
- 4.2.3 Surge in biologicals pushed by pesticide-tax regimes
- 4.2.4 Carbon-credit monetization of nitrogen-efficiency products
- 4.2.5 Mainstream expansion of controlled-release fertilizers
- 4.2.6 Crop diversification in vertical and indoor farms
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Accelerating phase-outs of high-toxicity actives in EU, Brazil and China
- 4.3.2 Volatile glyphosate pricing squeezes formulator margins
- 4.3.3 Rising Regulatory data-package costs
- 4.3.4 Chronic activist litigation risk in North America
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Fertilizers
- 5.1.1.1 Nitrogenous
- 5.1.1.2 Phosphatic
- 5.1.1.3 Potassic
- 5.1.2 Pesticides
- 5.1.2.1 Herbicides
- 5.1.2.2 Insecticides
- 5.1.2.3 Fungicides
- 5.1.2.4 Bio-pesticides
- 5.1.3 Adjuvants
- 5.1.4 Plant Growth Regulators
- 5.1.1 Fertilizers
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Crop-based
- 5.2.1.1 Grains and Cereals
- 5.2.1.2 Pulses and Oilseeds
- 5.2.1.3 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.2.2 Non-crop-based
- 5.2.2.1 Turf and Ornamental Grass
- 5.2.2.2 Other Non-crop-based
- 5.2.1 Crop-based
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Mexico
- 5.3.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.2.1 Germany
- 5.3.2.2 France
- 5.3.2.3 United Kingdom
- 5.3.2.4 Italy
- 5.3.2.5 Spain
- 5.3.2.6 Russia
- 5.3.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.3.1 China
- 5.3.3.2 India
- 5.3.3.3 Japan
- 5.3.3.4 Australia
- 5.3.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle East
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.3.6 Africa
- 5.3.6.1 South Africa
- 5.3.6.2 Egypt
- 5.3.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Syngenta Group
- 6.4.2 Bayer Crop Science AG
- 6.4.3 BASF Agricultural Solutions
- 6.4.4 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.5 Nutrien Ltd
- 6.4.6 Yara International ASA
- 6.4.7 Mosaic Company
- 6.4.8 CF Industries Holdings
- 6.4.9 UPL Ltd
- 6.4.10 FMC Corporation
- 6.4.11 Sumitomo Chemical AgroSolutions
- 6.4.12 Nufarm Ltd
- 6.4.13 K+S AG
- 6.4.14 ICL Group
- 6.4.15 OCP Group
- 6.4.16 Albaugh LLC
- 6.4.17 OCI Global
- 6.4.18 RovensaNext
- 6.4.19 Bharat Rasayan Ltd
- 6.4.20 Helm AG