
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1687454
내비게이션 위성 시스템 칩 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Global Navigation Satellite System Chip - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
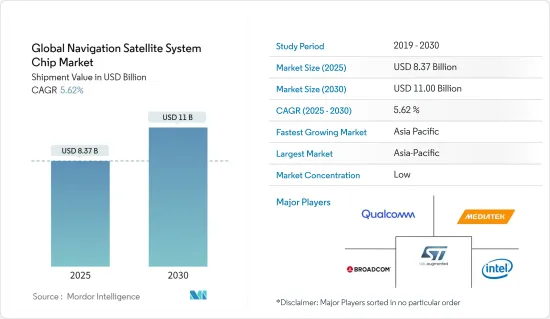
세계의 내비게이션 위성 시스템 칩 시장 규모(출하액 기준)는 2025년 83억 7,000만 달러에서 2030년에는 110억 달러로 성장하고, 예측 기간(2025-2030년)의 CAGR은 5.62%를 나타낼 것으로 예상됩니다.

COVID-19 팬데믹의 발생은 2020년 초기 단계에서 반도체공급 체인과 생산을 크게 혼란시켰습니다.
세계의 내비게이션 위성 시스템(GNSS) 칩은 기본적으로 우주로부터의 신호를 제공하고 측위와 데이터 타이밍을 GNSS 수신기로 전송하는 위성의 별자리를 가리킵니다.
이러한 칩의 정확성과 정확성은 주로 가시 범위의 위성에 달려 있으며, 그 결과 여러 국가가 더 나은 내비게이션과 매핑을 위해 지역적인 별자리를 열심히 전개하려고 합니다.
GNSS 사용자는 즉시 가까운 위치 공유 속도를 기대합니다. 최소한 4개의 위성을 식별하고 전체 데이터를 수신해야 하기 때문에 표준 포지셔닝에서는 불가능한 경우가 많습니다. 분, 몇 시간 또는 실패할 수도 있습니다. 그러나 GNSS 수신기 데이터를 모바일 네트워크 셀의 정보와 통합하면 성능을 향상시킬 수 있으며 IoT 업계의 많은 용도에 이익을 줄 수 있습니다.
2021년 1월, U-Blox는 저전력 광역(LPWA) 셀룰러 통신과 GNSS 기술을 시스템인 패키지에 통합한 ALEX-R5 모듈을 발표했습니다.
내비게이션과 측위 기능을 탑재한 가전제품 증가로 저소비전력 GNSS 칩 수요가 상당히 높아질 것으로 예상됩니다. Towatch와 같은 기술적으로 고급 웨어러블 장치를 사용합니다. GNSS 칩은 주로 이러한 장비에 내장되어 있습니다.
소니는 2020년 8월, IoT나 웨어러블 단말용의 고정밀 GNSS 수신 LSI를 발표했습니다.신규 LSI는 종래의 L1 밴드 수신과, 현재 GNSS 컨스텔레이션 사이에서 확장이 진행되고 있는 L5 밴드 수신에 대응하고 있어, 듀얼 밴드 측위에 적합합니다.
세계의 내비게이션 위성 시스템 칩 시장 동향
스마트폰 분야가 큰 시장 점유율을 차지할 전망
EU28, 북미, 중국 등의 성숙 시장은 상당히 포화되었음에도 불구하고 스마트폰 출하량은 GNSS 칩을 사용하는 장치를 상회하고 있습니다. 이 칩은 GPS, GLONASS, Galileo와 같은 일반적으로 사용 가능한 모든 위성 네트워크를 지원합니다.
게다가 스마트폰의 하드웨어 시장에서는 어느 정도의 독점 상태가 GNSS 칩의 탑재 범위를 제한하고 있었습니다.
유럽 위원회는 시장에 투입되는 새로운 스마트폰에 위성 및 Wi-Fi 위치 정보 서비스를 포함할 것을 의무화하는 규제를 승인했습니다.
유럽 GNSS청에 따르면 브로드콤, 퀄컴, 미디어 테크 등 스마트폰용 칩셋의 각종 제조업체를 포함해 위성 내비게이션 칩셋 공급 시장의 95% 이상이 신제품으로 갈릴레오를 지원하고 있습니다. 팝셋 제공업체가 Galileo 지원 칩셋을 제조하고 세계 스마트폰 브랜드가 이미 이러한 칩셋을 최신 스마트폰 모델에 통합했기 때문에 예측 기간 동안 이 시장에는 추가 성장 기회가 예상됩니다.
또한, 새로운 세대의 안드로이드 스마트폰에는 2주파 멀티 컨스텔레이션 데이터를 추적할 수 있는 고성능의 세계의 내비게이션 위성 시스템(GNSS) 칩이 탑재되어 있습니다. Point Positioning) 알고리즘의 적용이 보다 즐거워졌습니다. S8과 비교하면 2주파 데이터를 취득하는 장점이 강조됩니다.
아시아태평양이 큰 시장 점유율을 차지할 전망
BeiDou는 2000년에 처음으로 발사되었으며, 중국 국가 우주국(CNSA)에 의해 운영되고 있습니다. B1C(1575.42MHz), B2a(1175.42MHz), B2I와 B2b(1207.14MHz), B3I 등이 BeiDou 위성으로부터 전송되는 신호입니다(1268.52MHz).
중국의 GNSS에 대한 자세는 유럽과는 다릅니다. 유럽에서는 소비자용 제품부터 중요한 인프라에 이르기까지 11개의 GNSS 대응 기술 그룹이 널리 인지되어 있지만, 중국의 상황은 훨씬 복잡합니다.
2021년 3월 11일, 중국은 제14차 5개년 계획을 발표했습니다. 향후 5년간의 개발의 모든 측면에 접해, 중국의 2035년 비전을 제시할 계획입니다. u시스템의 보급과 이용의 심화, 업계의 고품질 성장 촉진은 중요한 국가 전략 프로젝트로서 계획의 정책 지침으로 제창되고 있습니다.
게다가 한국우주기술위원회에 따르면 2021년까지 지상시험을, 2022년까지 위성항법기초기술을 2024년까지 실제 위성제조를 구축했습니다.
2021년 2월 과학정보통신부는 인공위성, 로켓 및 기타 중요한 장비의 제조 능력을 향상시키기 위해 우주 활동에 6,150억 원(5억 5,310만 달러)의 예산을 기록할 것이라고 발표했습니다.
내비게이션 위성 시스템 칩 산업 개요
세계의 내비게이션 위성 시스템 칩 시장은 여러 기업으로 구성되어 있습니다. 시장 점유율은 어떤 기업도 시장을 독점하고 있지 않습니다.
- 2021년 12월 - MediaTek은 차세대 플래그십 스마트폰용 5G 스마트폰 칩 'Dimensity 9000'에 대해 OPPO, Vivo, Xiaomi, Honor를 비롯한 여러 스마트폰 브랜드에서 디바이스 제조업체로 수락하고 동의했다고 발표했습니다. 9000을 탑재한 최초의 플래그쉽 스마트폰은 2022년 1분기에 시장에 투입될 예정입니다.
- 2021년 1월 Qualcomm Technologies Inc.와 Alps Alpine은 차선 수준의 차량 절대 측위를 지원하는 카메라 기반 센싱 및 측위 장치 "ViewPose"를 발표했습니다. Positioning(VEPP) 소프트웨어를 처리하기 위한 Snapdragon Automotive Cockpit Platform과 같은 Qualcomm Technology의 여러 솔루션을 활용하여 전동 프론트 미러, 리어 미러, 사이드 미러, 고화질 맵 클라우드 소싱, 셀룰러 Vehicle-to-Everything(C-V2X)용 차선 레벨 내비게이션, 선진 운전 지원 시스템(ADAS) 및 자율 주행 용도를 위한 차선 레벨
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 인사이트
- 시장 개요
- 업계의 매력도 - Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 소비자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
- 업계 밸류체인 분석
- COVID-19 팬데믹 시장에 대한 영향 평가
제5장 시장 역학
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 환경 친화적인 운송 솔루션, 지속 가능한 농업, 기상 모니터링 채택
- 정확한 실시간 데이터에 대한 수요 증가
- 새로운 신호나 주파수의 출현 등 GNSS 인프라의 진화
- 시장의 과제
- 정확한 지하, 수중, 실내 내비게이션을 제공하는 GNSS의 무력함
- 높은 소비 전력에 관한 복잡성
제6장 GNSS의 주요 통계
- GNSS 수신기 출하 대수, 가격 카테고리별
- 하이엔드 수신기 출하 대수, 가격 카테고리별
- GNSS 디바이스 출하 대수, 궤도 하위 부문별
- GNSS 기기 설치 대수, 최종 사용자별
제7장 시장 세분화
- 디바이스 유형
- 스마트폰
- 태블릿 및 웨어러블 기기
- 개인 추적 장치
- 저전력 자산 추적기
- 차량 내 시스템
- 드론
- 기타 디바이스 유형
- 최종 사용자 산업
- 자동차
- 소비자 가전
- 항공
- 기타 최종 사용자 산업
- 지역
- 북미
- 미국
- 유럽
- 러시아
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 한국
- 라틴아메리카
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 북미
제8장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 프로파일
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Mediatek Inc.
- STMicroelectronics NV
- Broadcom Inc.
- Intel Corporation
- U-blox Holdings AG
- Thales Group
- Quectel Wireless Solutions Co. Ltd
- Skyworks Solutions Inc.
- Furuno Electric Co. Ltd
- Hemisphere GNSS
- Trimble Inc.
- Sony Group Corporation
제9장 투자 분석
제10장 시장의 미래
KTH 25.05.07The Global Navigation Satellite System Chip Market size in terms of shipment value is expected to grow from USD 8.37 billion in 2025 to USD 11.00 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.62% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted the supply chain and production of semiconductors in the initial phase of 2020. For multiple chipmakers, the impact was more severe. Due to labor shortages, many packages and testing plants in the Asia-Pacific region reduced or even suspended operations. This also created a bottleneck for end-product companies that depend on semiconductors.
Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) essentially refers to the constellation of satellites that provide signals from space, transmit positioning, and data timing to the GNSS receivers. The receivers then use such data to determine various factors, such as location, speed, and altitude, combined with several sensors.
The precision and accuracy of such chips are primarily dependent on the satellites in the visibility range. As a result, multiple countries are eagerly trying to deploy regional constellations for better navigation and mapping. However, in the market, only five countries (China, Russia, the United States, India, and Japan) and the European Union have their GNSS systems.
GNSS users expect near-instantaneous position sharing speeds. This is often impossible with standard positioning as at least four satellites must be identified, and their complete data should be received. In adverse signal conditions or harsh environments, transmitting and receiving data can take minutes, hours, or even fail. However, the performance can be improved by integrating the GNSS receiver data with information from mobile network cells to benefit numerous applications in the IoT industry.
In January 2021, U-Blox announced its ALEX - R5 module, which integrates low-power wide-area (LPWA) cellular communication and GNSS technology into the system-in-package. The two key elements are the company's UBX - R5 LTE - M/NB-IoT chipset with a secure cloud functionality and the U-Blox M8 GNSS chip for adequate location accuracy for healthcare applications.
The increasing volume of consumer electronics equipped with navigation and positioning features is expected to create a considerable demand for low-power GNSS chips. Technologically advanced wearable devices are in the demand trend currently. At present, almost 50% of the global population has been using tech-advanced wearable devices, such as fitness bands and smartwatches. GNSS chips are majorly being integrated into these devices to give precise locations to the user even while running, walking, or driving, allowing them to stay connected with their close ones.
In August 2020, Sony Corporation announced the release of high-precision GNSS receiver LSIs for IoT and wearable devices. The new LSIs support the conventional L1 band reception and L5 band reception, which are currently being expanded across GNSS constellations, making them suitable for dual-band positioning.
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Chip Market Trends
The Smartphones Segment is Expected to Hold a Significant Market Share
Despite considerable saturation of mature markets, such as EU28, North America, and China, the shipments of smartphones still outnumber devices using GNSS chips. Smartphones have been using GNSS chips for a considerable time. In most cases, these chips support all publicly available satellite networks, such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, etc. However, compared to dedicated navigation devices, these solutions were less accurate.
Additionally, a degree of monopoly in the smartphone hardware market limited the scope for GNSS chip installations. Most of the time, Qualcomm hardware does not include Broadcom GNNS chips and vice versa, as they are prime competitors. However, in recent years, this scenario has been changing.
The European Commission has approved a regulation mandating that new smartphones launched in the market will have to include satellite and Wi-Fi location services. According to the regulation, chipsets enabled with the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) capabilities are likely to have access to the EU's satellite system Galileo, which provides accurate positioning and timing information. Eight EU countries have been following this regulation and are using Galileo-compatible chipsets.
According to the European GNSS Agency, over 95% of the satellite navigation chipset supply market supports Galileo in new products, including various manufacturers of smartphone chipsets like Broadcom, Qualcomm, and Mediatek. With leading GNSS chipset providers producing Galileo-ready chipsets and global smartphone brands already integrating these chipsets in their latest smartphone models, the market is expected to have further growth opportunities during the forecast period.
Further, the new generation of Android smartphones is equipped with high-performance global navigation satellite system (GNSS) chips capable of tracking dual-frequency multi-constellation data. Starting from Android version 9, users can disable the duty cycle power-saving option; thus, better quality pseudo-range and carrier phase raw data are available. Also, the application of the Precise Point Positioning (PPP) algorithm has become more enjoyable. This work aims to assess the PPP performance of the first dual-frequency GNSS smartphone produced by Xiaomi equipped with a Broadcom BCM47755. The advantage of acquiring dual-frequency data is highlighted by comparing the performance obtained by Xiaomi with that of a single-frequency smartphone, the Samsung S8. The vertical and horizontal accuracy achieved by Xiaomi is 0.51 m and 6 m, respectively, while those achieved by Samsung is 5.64 m for 15 m for horizontal and vertical.
Asia-Pacific is Expected to Account for a Significant Market Share
BeiDou, first launched in 2000 and operated by the China National Space Administration, is based in China (CNSA). BeiDou has 48 satellites in orbit after 20 years. B1I (1561.098 MHz), B1C (1575.42 MHz), B2a (1175.42 MHz), B2I and B2b (1207.14 MHz), and B3I are among the signals being transmitted by BeiDou satellites (1268.52 MHz).
China's attitude to GNSS differs from that of Europe. While there are 11 widely acknowledged GNSS-enabled technical groupings in Europe, ranging from consumer products to vital infrastructure, the situation in China is far more complicated. There were three broad sectors - industrial market, mass consumer market, and specific market.
On March 11, 2021, China rolled out its 14th five-year plan. It is a plan that touches on all aspects of development over the next five years and presents China's 2035 vision. The 14th Five-Year Plan's persistent emphasis on R&D and innovation substantially impacts China's GNSS industry. "Deepen the promotion and use of BeiDou systems; Promote the industry's high-quality growth" is advocated as a policy guideline in the plan as an important national strategic project. The strategy is expected to signify a boost in the GNSS industry's research and development, promote BeiDou's industrial application and accelerate significant core technology advancements.
Further, the Korean Committee of Space Technology hopes to build a ground test by 2021, fundamental satellite navigation technology by 2022, and actual satellite manufacturing by 2024, according to the Korean Committee of Space Technology. Three satellites will be put in the geostationary orbit above the Korean Peninsula, making the KPS a seven-satellite constellation.
In February 2021, the Ministry of Science and ICT announced a budget of KRW 615 billion (USD 553.1 million) for space activities to increase the country's capacity to create satellites, rockets, and other critical equipment.
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Chip Industry Overview
The GNSS chip market consists of several players. In terms of market share, none of the players dominate the market. Significant players include Qualcomm Technologies Inc., Mediatek Inc., and STMicroelectronics NV, among others. The market players are considering strategic partnerships and collaborations to expand their market shares. Some of the recent developments in the market are:
- December 2021 - MediaTek announced device maker acceptance and endorsements from some smartphone brands, including OPPO, Vivo, Xiaomi, and Honor, for its Dimensity 9000 5G smartphone chip for next-generation flagship smartphones. The first flagship smartphones powered by the Dimensity 9000 will hit the market in the first quarter of 2022. Since the processor supports the newest Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and GNSS standards, smartphone users can experience seamless communication.
- January 2021 - Qualcomm Technologies Inc. and Alps Alpine Co. Ltd announced a camera-based sensing and positioning device called ViewPose to support absolute lane-level vehicle positioning. Alps Alpine is leveraging multiple solutions from Qualcomm Technologies like the Qualcomm Snapdragon Automotive 5G platform, which supports Multi-Frequency GNSS and a Snapdragon Automotive Cockpit Platform for processing multiple camera images and Vision Enhanced Precise Positioning (VEPP) software. This provides a cost-effective solution to lane-level accuracy for the electric front, rear- and side-view mirrors, high-definition map crowdsourcing, lane-level navigation for cellular vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X), and advanced driving assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving applications.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.2.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.2.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.2.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.3 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Assessment of the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Adoption of Environment-friendly Transport Solutions, Sustainable Agriculture, and Meteorological Monitoring
- 5.1.2 Increasing Demand for Accurate Real-time Data
- 5.1.3 Evolution of GNSS Infrastructure, such as the Appearance of New Signals and Frequencies
- 5.2 Market Challenges
- 5.2.1 Inability of GNSS to Offer Accurate Underground, Underwater, and Indoor Navigation
- 5.2.2 Complexity Regarding High Power Consumption
6 KEY GNSS STATISTICS
- 6.1 GNSS Receiver Shipments (in billion units), by Price Categories
- 6.2 High-end Receiver Shipments (in million units), by Price Categories
- 6.3 Shipment of GNSS Devices (in thousand units), by Orbital Sub-segment
- 6.4 Installed Base of GNSS Devices (in billion Units) by End User
7 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 7.1 Device Type
- 7.1.1 Smartphones
- 7.1.2 Tablets and Wearables
- 7.1.3 Personal Tracking Devices
- 7.1.4 Low-power Asset Trackers
- 7.1.5 In-vehicle Systems
- 7.1.6 Drones
- 7.1.7 Other Device Types
- 7.2 End-user Industry
- 7.2.1 Automotive
- 7.2.2 Consumer Electronics
- 7.2.3 Aviation
- 7.2.4 Other End-user Industries
- 7.3 Geography
- 7.3.1 North America
- 7.3.1.1 United States
- 7.3.2 Europe
- 7.3.2.1 Russia
- 7.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 7.3.3.1 China
- 7.3.3.2 Japan
- 7.3.3.3 South Korea
- 7.3.4 Latin America
- 7.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 7.3.1 North America
8 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 8.1 Company Profiles
- 8.1.1 Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- 8.1.2 Mediatek Inc.
- 8.1.3 STMicroelectronics NV
- 8.1.4 Broadcom Inc.
- 8.1.5 Intel Corporation
- 8.1.6 U-blox Holdings AG
- 8.1.7 Thales Group
- 8.1.8 Quectel Wireless Solutions Co. Ltd
- 8.1.9 Skyworks Solutions Inc.
- 8.1.10 Furuno Electric Co. Ltd
- 8.1.11 Hemisphere GNSS
- 8.1.12 Trimble Inc.
- 8.1.13 Sony Group Corporation



















