
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1850396
5G 인프라 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)5G Infrastructure - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
5G 인프라 시장은 2025년에 155억 5,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 540억 6,000만 달러에 이를 전망입니다.

현재의 확장은 네트워크 슬라이싱, 엣지 컴퓨팅 및 사설 네트워크 구축을 지원하는 완전히 프로그래밍 가능한 독립형 플랫폼을 통해 운영자가 이전의 비독립형 롤아웃을 대체하는 것에 축을 두고 있습니다. 자본은 순수한 커버리지에서 서비스 시작 사이클을 단축하고, 자동화를 개선하며, 평생 운영 비용을 줄이는 소프트웨어 정의 기능으로 이동합니다. 고속 광대역을 지역으로 확장하는 고정 무선 액세스(FWA)의 전개와 함께 제조업, 이동성, 에너지 등의 사설망에 대한 관심으로 수요가 강화되고 있습니다. 반면에 주파수 정책은 미드밴드 대역의 새로운 용량을 확보하고 공급업체의 로드맵은 통신 사업자가 단일 공급업체에 대한 의존성을 피하고 API를 보다 신속하게 수익화할 수 있는 클라우드 네이티브 Open RAN 설계를 중심으로 수렴하고 있습니다.
세계의 5G 인프라 시장 동향 및 인사이트
M2M 및 IoT 디바이스 밀도 증가
독립형 5G에서는 각 셀 사이트가 50,000대의 연결 장치를 처리할 수 있게 되어, 인더스트리 4.0의 생산 라인이나 거대한 센서 그리드의 전제조건이 됩니다. 현대자동차의 RedCap 지원 공장 네트워크는 저용량 장치라면 커버리지를 잃지 않고 전력 예산을 줄일 수 있음을 입증했습니다. 엣지 컴퓨팅은 컴퓨팅 리소스를 머신 근처로 이동시켜 로봇 엔지니어링 및 예측 유지보수 방식에 필요한 밀리초 단위의 대기 시간을 유지합니다. 자동차, 헬스케어, 중공업에서 사설 네트워크를 입증하면 소비자 핸드셋이 아닌 장치가 밀집된 환경에서 발생하는 수익의 상승을 검증하고 있습니다. 예측 기간 동안 스몰셀과 엣지 데이터센터에 대한 지속적인 지출은 이 원동력에 의해 지원됩니다.
모바일 데이터 소비 급증
클라우드 게임, 증강현실 비디오, AI 강화 스트리밍이 일관된 멀티기가비트 링크를 요구하기 때문에 월별 모바일 트래픽은 최고치를 계속 업데이트하고 있습니다. 영국 Three는 2024년 말 피크가 2Tbit/s를 초과한 후 백본 처리량을 9Tbit/s로 늘렸습니다. 중국에서는 규제 당국이 2030년까지 국내 트래픽이 4배가 될 것으로 예상하고 있으며, 사업자는 하루 종일 부하가 걸리는 상황에서도 효율성을 유지할 수 있는 용량 아키텍처로 이행하고 있습니다. 실시간 원격 초음파 진단의 입증 실험을 포함한 헬스케어 파일럿은 미션 크리티컬 이미지에 대한 업링크 용량의 가치를 강조합니다. 또한 인도와 미국에서는 FWA가 널리 사용되고 있으며 트래픽은 스마트폰에서 CPE 장치로 리디렉션되며, 경력은 홈퍼스트 비디오 습관을 위해 백홀의 재설계를 강요하고 있습니다.
RAN의 고밀도화 및 파이버 백홀의 초기 비용
스몰셀에서는 1만 달러에서 5만 달러, 매크로셀에서는 사이트당 20만 달러에 이르기 때문에 특히 mmWave가 의무화된 경우 고밀도 5G 실적은 자본 부담이 커집니다. 파이버 백홀은 프로젝트 예산에 30%를 올릴 수 있으며 교외 회랑에서는 굴착량이 적기 때문에 홈 파기 일정이 지연됩니다. 2023년 세계의 통신 CAPEX는 2017년 이후 처음으로 침체되었고, CFO는 롤아웃 가속에 신중해지고 있습니다. 네트워크 공유 계약은 최대 40%를 절약할 수 있지만 각 파트너의 프리미엄 차별화 마케팅 능력은 떨어집니다. 사업자당 10억 달러를 초과하는 스펙트럼 라이선스 수수료는 밸런스 시트 헤드룸을 더욱 압박합니다.
부문 분석
RAN 기기는 5G 인프라 시장에서 가장 큰 비율을 차지하고 있으며, 통신 사업자가 고밀도의 매크로셀 그리드와 스몰셀 그리드를 전개했기 때문에 2024년에는 37%의 매출을 계상했습니다. 이 최초의 하드웨어 파도는 RAN의 중요성을 유지하지만, 소프트웨어 정의 제어가 미래의 수익화를 결정하기 때문에 코어 네트워크는 32.36%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 다른 레이어를 상회합니다. 코어 플랫폼의 5G 인프라 시장 규모는 사용자 플레인과 컨트롤 플레인의 기능을 가상화하는 듀얼 모드 패킷 코어가 독립형으로 전개됨에 따라 급격히 확대됩니다. Vodafone Spain과 Three UK는 클라우드 네이티브 코어를 통해 통신 사업자가 엣지, 보안 및 퀄리티 온 디맨드 제품의 API를 공개할 수 있음을 강조합니다.
10년의 후반부에, 통신 사업자는 컨버지드 코어를 사설 네트워크 슬라이스, 저지연 산업 서비스, 실시간 애널리틱스 엔진으로 간주하고 있습니다. RAN에 대한 지출은 커버리지의 이정표가 달성됨에 따라 축소되는 반면, 라이프사이클 리프레시와 기능 애드온으로 인해 코어 청구가 계속 증가합니다. 또한 분산 장치가 회선 속도 트래픽을 데이터센터의 코어에 공급해야 하므로 전송 및 xHaul 예산도 증가합니다. 그 결과, 옵티컬 벤더와 라우팅 벤더가, 전술적인 파트너가 아닌 전략적인 파트너로서 스스로를 자리잡게 됩니다.
미드밴드가 2024년 5G 인프라 시장 점유율의 46%를 차지한 이유는 전파 도달 거리와 매시브 MIMO 어레이를 지원하는 수백 MHz 대역폭이 융합되어 있기 때문입니다. 시카고에서 베를린에 이르는 통신 사업자는 3.5GHz 대역의 무선을 사용하여 셀에 과도한 비용을 들이지 않고 교외 링을 커버합니다. 이 궤적은 특히 미국, 일본, 한국에서 mmWave 라디오, 중계기, 선진 빔포밍 실리콘과 관련된 5G 인프라 시장 규모가 급속히 상승한다는 것을 의미합니다.
1GHz 이하의 로우밴드는 광역 IoT 커버리지에는 필수이지만, 기가비트의 타겟에서는 고전을 강요받아 주역이 아니라 보완에 그칩니다. 미드밴드 및 하이밴드 블록을 동일한 면허 라운드로 번들하는 규제 당국은 캐리어가 차별화된 서비스 계층에 주파수 믹스를 맞추는 것을 돕습니다.
5G 인프라 시장은 통신 인프라별(5G 무선 액세스 네트워크, 5G 코어 네트워크, 전송/XHaul(Front, Mid, Back-Haul), 기타), 스펙트럼 밴드별(로우밴드, 미드밴드 등), 네트워크 아키텍처별(Non-Standalone(NSA), 기타), 코어 네트워크 기술별(Software-Defined Networking(SDN), 기타), Electronics, 기타), 지역별로 구분됩니다.
지역 분석
아시아태평양은 2024년 5G 인프라 시장 점유율의 24%를 차지했으며, 중국의 440만 기지국과 인도가 2027년까지 3,000만 FWA 가입자 연결을 목표로 하는 경쟁에 의해 견인됩니다. 이 지역은 한국이 97%의 인구 커버율을 유지하고 일본이 교외의 고밀도화를 진행함으로써 CAGR 32.27%로 확대됩니다. 인도네시아, 베트남, 필리핀의 농촌 지역에서는 공유 타워 모델에 기울이고, 호주에서는 원격지에서의 채굴 작업을 위해 위성과 5G의 하이브리드 백업이 진행됩니다.
북미에서는 커버리지의 성숙도가 80%를 넘고 있지만, 2023년의 침체를 거쳐 2025년에는 지출이 활성화됩니다. 에릭슨은 2024년 4분기에 지역별로 전년 대비 54%의 성장세를 기록했으며, 독립형 코어, 엣지존, 대기업 안건 예산이 다시 움직이기 시작한 것으로 나타났습니다. 미국의 통신사업자는 FWA를 광섬유와 번들해 서비스가 충분하지 않은 교외를 획득하고, 캐나다는 새로운 미드밴드 주파수대를 할당해 토착의 커뮤니티 접속을 가속시킵니다.
유럽은 단독 보급률로 지연을 겪고 있지만, 규제 조화로 인해 2030년까지 1,640억 유로의 경제 상승을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 독일의 보급률 96%는 정리된 상의 성과를 나타내고 있지만, 영국은 벤더 금지로 기기 교환이 지연되었기 때문에 퍼포먼스의 재조정이 필요합니다. 라틴아메리카에서는 29개 사업자가 상용 단계에 있습니다. 주파수 이용료가 하락하고 클라우드 기업이 중립 호스트 타워에 자금을 제공하게 되면 2030년까지 이 지역의 접속 수는 4억 2,500만에 이를 것으로 보입니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트 첨부
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 머신 투 머신과 IoT 디바이스의 밀도 향상
- 모바일 데이터 소비의 급증
- 정부의 주파수 경매가 중대역의 전개 가속
- 통신사업자의 설비 투자는 클라우드 네이티브 오픈 RAN 아키텍처로 전환
- 브라운필드 공업단지에서의 프라이빗 5G 수요 증가
- 농촌 시장에서 광섬유의 대체가 되는 고정 무선 액세스(FWA)
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- RAN의 고밀도화 및 파이버 백홀의 높은 초기 비용
- 네트워크 슬라이싱 수익화의 표준화 지연
- 중국 벤더에 대한 국가안보상의 제한
- mm파 도입에서 숙련 노동자의 부족
- 밸류체인 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- 투자 및 자금조달 동향
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
- 대체품의 위협
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 통신 인프라별
- 5G 무선 액세스 네트워크(RAN)
- 수송/xHaul(프런트홀, 미드홀, 백홀)
- 코어 네트워크(클라우드 네이티브 5GC)
- 스펙트럼 밴드별
- 저대역(1GHz 미만)
- 중대역(1-6GHz)
- 고대역 및 밀리파(24GHz 이상)
- 네트워크 아키텍처별
- 비독립형(NSA)
- 독립형(SA)
- 코어 네트워크 기술별
- 소프트웨어 정의 네트워크(SDN)
- 네트워크 기능 가상화(NFV)
- 멀티 액세스 엣지 컴퓨팅(MEC)
- 네트워크 슬라이싱
- 최종 사용자별
- 소비자 일렉트로닉스
- 자동차 및 이동성
- 공업제조업
- 헬스케어 및 생명과학
- 에너지 및 유틸리티
- 공공 안전 및 방위
- 스마트 시티 및 인프라
- 기타 산업(소매, 미디어, 농업)
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 한국
- 인도
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 튀르키예
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 나이지리아
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- AT&T Inc.
- Casa Systems Inc.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- CommScope Holding Company Inc.
- Corning Inc.
- Dell Technologies Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Fujitsu Limited
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- Intel Corporation
- Juniper Networks Inc.
- Mavenir Systems Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Nokia Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- Parallel Wireless Inc.
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Qucell Networks Co. Ltd.
- Rakuten Symphony Inc.
- Ribbon Communications Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- ZTE Corporation
제7장 시장 기회 및 향후 전망
AJY 25.11.19The 5G infrastructure market reached USD 15.55 billion in 2025 and is on course to attain USD 54.06 billion by 2030, translating into a 28.30% CAGR.
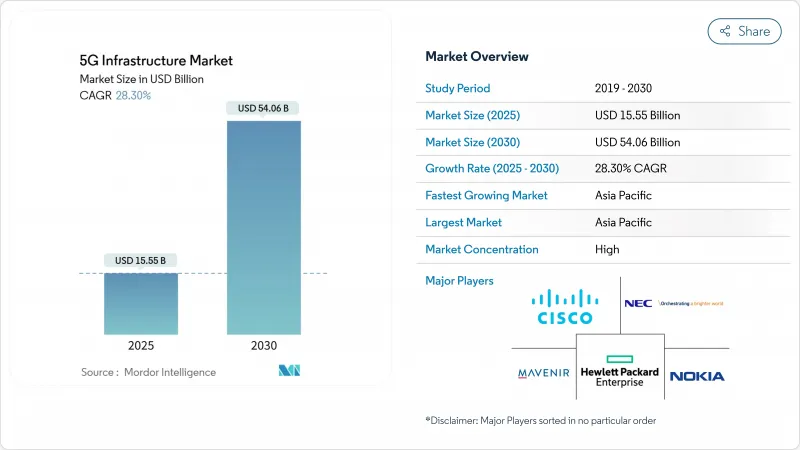
The current expansion pivots on operators replacing earlier non-standalone rollouts with fully programmable standalone platforms that support network slicing, edge computing and private network creation. Capital is shifting from pure coverage toward software-defined functions that shorten service launch cycles, improve automation and lower lifetime operating costs. Demand is reinforced by private-network interest from manufacturing, mobility and energy, alongside fixed-wireless access (FWA) deployments that extend high-speed broadband into rural zones. Meanwhile, spectrum policy is unlocking fresh mid-band capacity, and vendor road maps are converging around cloud-native Open RAN designs that let carriers avoid single-supplier dependence and monetize APIs more quickly.
Global 5G Infrastructure Market Trends and Insights
Increasing Machine-to-Machine and IoT Device Density
Standalone 5G allows each cell site to handle as many as 50,000 connected devices, a prerequisite for Industry 4.0 production lines and massive sensor grids. Hyundai Motor's RedCap-enabled factory network proved that reduced-capability devices can lower power budgets without losing coverage. Edge computing is moving compute resources closer to machines, keeping latency within millisecond windows that robotics and predictive-maintenance schemes require. Private-network proofs in automotive, healthcare, and heavy industry validate the revenue upside that comes from device-dense environments rather than consumer handsets. This driver underpins sustained spending on small cells and edge data centers over the forecast window.
Surge in Mobile Data Consumption
Monthly mobile traffic continues to set new highs as cloud gaming, extended-reality video, and AI-enhanced streaming demand consistent multi-gigabit links. Three UK boosted backbone throughput to 9 Tbit/s after end-2024 peaks surpassed 2 Tbit/s. In China, regulators expect national traffic to quadruple by 2030, moving operators toward capacity architectures that remain efficient under day-long loads. Healthcare pilots, such as real-time tele-ultrasound demonstrations, underline the value of uplink capacity for mission-critical imagery. FWA uptake in India and the United States is also redirecting traffic from smartphones to CPE units, pushing carriers to redesign backhaul for home-first video habits.
High Upfront RAN Densification and Fiber Back-Haul Costs
Small-cell bills from USD 10,000 to USD 50,000 and macro-cell outlays that reach USD 200,000 per site make dense 5G footprints capital heavy, especially where mmWave is mandated. Fiber back-haul can add 30% to project budgets, and scarce digs in suburban corridors slow trenching schedules. Global telecom CAPEX dipped in 2023, the first drop since 2017, making CFOs cautious about accelerated rollouts. Network-sharing deals deliver up to 40% savings but reduce each partner's ability to market premium differentiation. Spectrum licence fees above USD 1 billion per operator further compress balance sheet headroom.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Spectrum Auctions Accelerating Mid-Band Rollouts
- Telco Capex Pivot to Cloud-Native Open RAN Architectures
- Delayed Standardisation for Network-Slicing Monetisation
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
RAN equipment generated the largest slice of the 5G infrastructure market, delivering 37% revenue in 2024 as carriers rolled out dense macro and small-cell grids. That initial hardware wave will keep RAN important, yet core networks outpace other layers with a 32.36% CAGR because software-defined control decides future monetisation. The 5G infrastructure market size for core platforms is set to increase sharply as standalone rollouts mandate dual-mode packet cores that virtualise user plane and control plane functions. Vodafone Spain and Three UK highlight how cloud-native cores let operators expose APIs for edge, security and quality-on-demand products
In the second half of the decade, operators view the converged core as the engine for private-network slices, low-latency industrial services, and real-time analytics. RAN spend will taper as coverage milestones are met, whereas lifecycle refresh and feature add-ons keep core invoices growing. Transport and xHaul budgets also rise because distributed units must feed line-rate traffic into data-centre cores. Consequently, the 5G infrastructure market will witness supplier jockeying where optical and routing vendors position themselves as strategic rather than tactical partners.
Mid-band commanded 46% of 5G infrastructure market share in 2024 because it blends propagation reach with multi-hundred-MHz bandwidth that supports massive MIMO arrays. Operators from Chicago to Berlin use 3.5 GHz radios to cover suburban rings without overspending on cells. mmWave, however, shows the fastest 33.58% CAGR by serving FWA households and event venues. This trajectory means the 5G infrastructure market size linked to mmWave radios, repeaters and advanced beamforming silicon will climb quickly, especially in the United States, Japan and South Korea.
Low-band below 1 GHz stays vital for wide-area IoT coverage but struggles with gigabit targets, keeping it a supplement, not a star. mmWave deployment faces line-of-sight and foliage loss, yet high-gain antennas and AI-aided beam steering are closing some gaps. Regulators that bundle mid-band and high-band blocks in the same licence round help carriers align the spectrum mix with differentiated service tiers.
The 5G Infrastructure Market is Segmented by Communication Infrastructure (5G Radio Access Networks, 5G Core Networks, Transport / XHaul [Front, Mid, Back-Haul], and More), Spectrum Band (Low-Band, Mid-Band, and More), Network Architecture (Non-Standalone [NSA] and More), Core Network Technology (Software-Defined Networking [SDN] and More), End-User Vertical (Consumer Electronics, and More), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific held 24% of 5G infrastructure market share in 2024, driven by China's 4.4 million base stations and India's race to connect 30 million FWA subscribers by 2027. The region will expand at a 32.27% CAGR as South Korea sustains 97% population coverage and Japan adds suburban densification. Rural programmes in Indonesia, Vietnam, and the Philippines will lean on shared-tower models, while Australia advances with hybrid satellite-5G back-ups for remote mining operations.
North America shows coverage maturity above 80% of people yet reinvigorated spending in 2025 after a 2023 dip. Ericsson logged 54% year-over-year regional growth in Q4 2024, signalling that standalone cores, edge zones, and large enterprise deals are moving budgets again. US carriers bundle FWA with fibre to capture underserved suburbs, and Canada allocates fresh mid-band spectrum to accelerate indigenous-community connectivity.
Europe trails on standalone penetration but targets a EUR 164 billion economic boost by 2030 from harmonised regulation. Germany's 96% coverage illustrates what cohesive awards achieve, whereas the United Kingdom must rebuild performance after vendor bans slowed equipment swaps. Latin America steps into commercial phase with 29 operators live; regional connections should reach 425 million by 2030 as spectrum fees fall and cloud players finance neutral-host towers.
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- AT&T Inc.
- Casa Systems Inc.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- CommScope Holding Company Inc.
- Corning Inc.
- Dell Technologies Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Fujitsu Limited
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- Intel Corporation
- Juniper Networks Inc.
- Mavenir Systems Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Nokia Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- Parallel Wireless Inc.
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Qucell Networks Co. Ltd.
- Rakuten Symphony Inc.
- Ribbon Communications Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- ZTE Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing machine-to-machine and IoT device density
- 4.2.2 Surge in mobile data consumption
- 4.2.3 Government spectrum auctions accelerating mid-band rollouts
- 4.2.4 Telco capex pivot to cloud-native open RAN architectures
- 4.2.5 Emerging demand for private 5G in brownfield industrial sites
- 4.2.6 Fixed-wireless access (FWA) substituting fiber in rural markets
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront RAN densification and fiber back-haul costs
- 4.3.2 Delayed standardization for network-slicing monetization
- 4.3.3 National-security restrictions on Chinese vendors
- 4.3.4 Skilled-labor shortages for mmWave deployment
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Investment and Funding Trends
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8.5 Threat of Substitute Products
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Communication Infrastructure
- 5.1.1 5G Radio Access Network (RAN)
- 5.1.2 Transport / xHaul (Front-, Mid-, Back-haul)
- 5.1.3 Core Network (Cloud-native 5GC)
- 5.2 By Spectrum Band
- 5.2.1 Low-Band (less than 1 GHz)
- 5.2.2 Mid-Band (1-6 GHz)
- 5.2.3 High-Band / mmWave (above 24 GHz)
- 5.3 By Network Architecture
- 5.3.1 Non-Standalone (NSA)
- 5.3.2 Standalone (SA)
- 5.4 By Core Network Technology
- 5.4.1 Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
- 5.4.2 Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- 5.4.3 Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC)
- 5.4.4 Network Slicing
- 5.5 By End-user Vertical
- 5.5.1 Consumer Electronics
- 5.5.2 Automotive and Mobility
- 5.5.3 Industrial Manufacturing
- 5.5.4 Healthcare and Life Sciences
- 5.5.5 Energy and Utilities
- 5.5.6 Public Safety and Defense
- 5.5.7 Smart Cities and Infrastructure
- 5.5.8 Other Verticals (Retail, Media, Agriculture)
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Spain
- 5.6.3.6 Russia
- 5.6.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 APAC
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 Japan
- 5.6.4.3 South Korea
- 5.6.4.4 India
- 5.6.4.5 Australia
- 5.6.4.6 Rest of APAC
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Airspan Networks Inc.
- 6.4.2 AT&T Inc.
- 6.4.3 Casa Systems Inc.
- 6.4.4 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 6.4.5 CommScope Holding Company Inc.
- 6.4.6 Corning Inc.
- 6.4.7 Dell Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.8 Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- 6.4.9 Fujitsu Limited
- 6.4.10 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- 6.4.11 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Intel Corporation
- 6.4.13 Juniper Networks Inc.
- 6.4.14 Mavenir Systems Inc.
- 6.4.15 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.16 Nokia Corporation
- 6.4.17 Oracle Corporation
- 6.4.18 Parallel Wireless Inc.
- 6.4.19 Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.20 Qucell Networks Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.21 Rakuten Symphony Inc.
- 6.4.22 Ribbon Communications Inc.
- 6.4.23 Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.24 Verizon Communications Inc.
- 6.4.25 ZTE Corporation
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment



















