
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1687710
전장 엑솜 분석(WES) 시장(2025-2030년) : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측Whole Exome Sequencing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
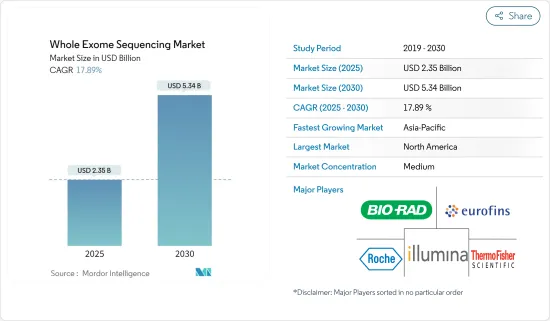
전장 엑솜 분석(WES) 시장 규모는 2025년 23억 5,000만 달러에서 예측 기간(2025-2030년) 동안 CAGR 17.89%로 성장하여 2030년에는 53억 4,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.

세계의 전장 엑솜 분석(WES) 시장을 견인하는 주요 요인으로는 임상 진단에서의 용도 확대, 희소 질환의 진단 수요 증가, 유전체학과 차세대 분석의 연구 개발 노력 강화, 맞춤형 의료에 대한 요구 증가 등이 있습니다. 예를 들어, 2022년 3월 British Medical Journal에 게재된 논문에서는 전장 엑솜 분석이 어렸을 때 희귀 유전병을 진단받은 일부 환자 그룹에 대해 일상적으로 이용 가능하다고 강조합니다. 이 기사는 차세대 시퀀서가 수백에서 수천 개의 유전자 서열을 신속하고 현저히 낮은 비용으로 분석할 수 있다고 강조합니다. 이러한 장점을 감안할 때, 전장 엑솜 분석(WES) 시장은 향후 몇 년 동안 성장할 전망입니다.
또한, 전장 엑솜 분석은 HIV, 암, COVID-19와 같은 질병과 관련된 바이러스의 유전체를 검사하는 데 매우 중요한 역할을 합니다. 이러한 질병의 유병률이 증가함에 따라 전장 엑솜 분석에 대한 수요도 증가하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 세계보건기구(WHO)의 HIV Statistics에 따르면 2023년에는 세계에서 약 3,990만 명이 HIV를 보유했습니다. 이러한 유전체 분석 방법은 질병으로 이어질 수 있는 유전자 돌연변이를 해명하여 RNA 분석 수요를 더욱 증폭시킵니다.
게다가 유전체학과 차세대 시퀀서의 R&D의 급증은 시장 성장을 가속하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 2022년 5월, NanoString Technologies Inc.는 Illumina NextSeq 1000, NextSeq 2000 분석 시스템, GeoMx Digital Spatial Profiler 사용자를 위한 공간 데이터 분석을 강화하도록 설계된 클라우드 기반 워크플로우를 발표했습니다. 이 기술 혁신은 사용자 친화적인 통합 런 계획 도구를 통해 프로테옴 분석과 동시에 모든 트랜스크립트의 공간 분석을 간소화합니다. 이러한 진보는 시장을 더욱 강화할 것으로 예상됩니다.
결론적으로 앞서 언급한 요인은 시장의 견조한 성장 궤도를 보여줍니다. 하지만 이 기술의 복잡한 성질, 숙련된 전문가의 높은 필요성, 전장 엑솜 분석을 둘러싼 법적 및 윤리적 딜레마가 시장의 확대를 억제할 가능성이 있습니다.
전장 엑솜 분석(WES) 시장 동향
개인화된 의료 부문은 예측 기간 동안 상당한 성장이 예상됩니다.
개인화된 의료는 질병의 분자적 특성을 기반으로 개별 환자에게 맞는 치료법을 제공합니다. 이 접근법은 최근 몇 년 동안 인기를 끌고 있습니다. 종종 "맞춤형 의료"라고 불리는 정밀 의료는 각 환자의 명확한 유전자 프로파일을 중시하는 면에서 전통적인 방법과 구별됩니다. 유전학이 진보하고 인간의 유전적 체질이 특히 건강, 발육, 약물 반응에 어떤 영향을 미치는지에 대한 이해가 깊어짐에 따라, 의료 전문가는 무수한 건강 상태에 대해 보다 안전하고 효과적인 치료법을 개발하기 위해 노력합니다. 정밀 의료의 이점은 다양하며 건강과 헬스케어를 모두 향상시킵니다.
맞춤형 의료 분야를 추진하는 요인으로는 다양한 암의 유병률의 상승, 암이나 기타 질환에 대한 맞춤형 치료의 저렴한 가격, 맞춤형 치료에 의한 부작용의 경감, 선진국 시장에서의 광범위한 채용, 혁신적인 약제의 출현 등을 들 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, 2022년 8월 의료기기 혁신 컨소시엄은 Somatic Reference Sample(SRS) 이니셔티브의 파일럿 프로젝트를 시작했습니다. 이 프로젝트는 차세대 분석(NGS)을 이용한 암 진단 약물의 검증 및 규제 심사 과정을 개선하기 위한 것입니다. NGS는 진단과 치료의 새로운 길을 열어주는 혁신적인 기술로 두드러집니다. 그러나 이러한 진단 검사가 임상적으로 실행 가능하기 위해서는 엄격한 검증을 받아야 하며, 이 과정은 참조 샘플에 크게 의존합니다.
게다가 시장 각사는 제휴, 합병, 인수, 제품 발매 등의 전략에 임하고 있어 이들 모두가 이 분야의 확대에 박차를 가할 것으로 예상됩니다. 예를 들어, 2023년 11월, Illumina는 저소득 및 중소득국에서 병원체 분석을 목표로 한 Global Health Access Initiative를 발표했습니다. 이 이니셔티브에서는 다양한 분석 애플리케이션을 할인된 가격으로 제공합니다. 여기에는 결핵의 약물 내성 프로파일링, 진화 및 재발 바이러스를 감시하기 위한 전장 유전체 분석, 인플루엔자 유사 질환 감시를 위한 호흡기 병원체 검출, 병원체를 추적하기 위한 환경 모니터링(폐수 분석 등), 집단 수준의 항균제 내성 모니터링 등이 포함됩니다.
이러한 역학을 고려하면, 개인화된 의료 분야는 향후 몇 년 동안 크게 성장할 수 있습니다.
북미는 예측 기간 중 상당한 성장이 예상됩니다.
북미는 수익 측면에서 주요 지역 시장으로 두드러집니다. 전장 엑솜 분석(WES) 시장의 성장을 가속하는 주요 요인으로는 암 등의 유전성 질환과 만성 질환의 유병률 상승, 고령화, 표적 의료 및 맞춤형 의료에 대한 수요 증가, 정부의 지원책 등을 들 수 있습니다. 2022년 10월 HIV.gov의 보고에 따르면 미국에서는 약 120만 명이 HIV에 감염되었습니다. 이는 전염병 부담이 증가하고 있음을 뒷받침하고 진단제에 대한 수요 증가가 예측되어 예측 기간 동안 시장 성장을 뒷받침할 것으로 보입니다.
주요 기업 간의 합병, 인수, 제품 출시, 제휴는 이 지역 시장 역학을 더욱 활성화시킵니다. 주목할만한 예는 QIAGEN이 2023년 1월 캘리포니아에 본사를 둔 인구 유전체학의 선도기업인 Helix사와 독점적 전략 제휴를 맺은 것입니다. 이 제휴는 유전성 질환 동반 진단의 개발을 촉진하는 것입니다. 첨단 NGS 및 PCR 기술을 활용한 통합 서비스는 신속한 환자 모집, 실제 임상 증거 및 종합적인 진단 솔루션을 약속합니다.
감염증의 유병률 상승이나 적극적인 제품 출시 등, 이러한 역학을 고려하면 북미 시장은 향후 수년에 큰 성장이 예상됩니다.
전장 엑솜 분석 업계 개요
전장 엑솜 분석(WES) 시장은 세계 및 지역적으로 사업을 전개하는 기업이 여러 회사 존재하기 때문에 그 성격상 적당히 통합되어 있습니다. 경쟁 구도에는 Eurofins Scientific Group, Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, illumine Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Konica Minolta Inc.(Ambry Genetics), Beijing Genomics Institute, Azenta Inc., Psomagen Inc.(Macrogen Inc.), PerkinElmer Inc., GENEYX GENOMEX, CD Genomics, QIAGEN Inc. 등 시장 점유율을 보유한 지명도가 높은 국내외 기업의 분석이 포함됩니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 역학
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 임상 진단에서의 응용 증가와 희귀 질환의 진단 수요 증가
- 유전체학 및 차세대 시퀀서 분야에서의 연구 개발 증가
- 맞춤형 의료에 대한 수요 증가
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 기술의 복잡성과 숙련자의 부족
- 전장 엑솜 분석과 관련된 법적 및 윤리적 문제
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자/소비자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
제5장 시장 세분화
- 제품 유형별
- 시스템
- 키트
- 서비스
- 기술별
- 2세대 분석
- 합성에 의한 분석(SBS)
- 하이브리드화 및 라이게이션에 의한 분석(SBL)
- 제3세대 분석
- 2세대 분석
- 용도별
- 진단
- 신약 발견 및 개발
- 맞춤형 의료
- 기타 용도(농업, 동물 연구 등)
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 호주
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- GCC
- 남아프리카
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 프로파일
- Konica Minolta Inc.(Ambry Genetics)
- Beijing Genomics Institute
- Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.
- Eurofins Scientific Group
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- Azenta, Inc.
- Illumina Inc.
- Psomagen Inc.(Macrogen Inc.)
- PerkinElmer Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- GENEYX GENOMEX
- CD Genomics
- QIAGEN Inc.
제7장 시장 기회와 앞으로의 동향
CSM 25.04.07The Whole Exome Sequencing Market size is estimated at USD 2.35 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 5.34 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 17.89% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Key factors propelling the global whole exome sequencing market include its rising applications in clinical diagnostics, heightened demand for rare disease diagnoses, intensified R&D efforts in genomics and next-generation sequencing, and an increasing appetite for personalized medicine. For example, a March 2022 article in the British Medical Journal highlighted that whole exome sequencing is routinely available for a select group of patients diagnosed with rare childhood genetic diseases. The article further emphasized that next-generation sequencing can rapidly sequence hundreds or even thousands of genes at a significantly reduced cost. Given these advantages, the market for whole exome sequencing is poised for growth in the coming years.
Additionally, whole exome sequencing plays a pivotal role in testing the genomes of viruses linked to diseases like HIV, cancer, and COVID-19. As the prevalence of these diseases rises, so does the demand for whole-exome sequencing. For instance, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) HIV Statistics, around 39.9 million people globally were living with HIV in 2023. Such genomic sequencing methods shed light on genetic variants that may lead to diseases, further amplifying the demand for RNA sequencing.
Moreover, the surge in R&D within genomics and next-generation sequencing is fueling market growth. For instance, in May 2022, NanoString Technologies Inc. unveiled a cloud-based workflow designed to enhance spatial data analysis for users of the Illumina NextSeq 1000, NextSeq 2000 sequencing systems, and the GeoMx Digital Spatial Profiler. This innovation streamlines the spatial analysis of whole transcriptomes in tandem with proteome analytes due to its integrated, user-friendly run planning tool. Such advancements are expected to bolster the market further.
In conclusion, the aforementioned factors indicate a robust growth trajectory for the market. The intricate nature of the technique, a pressing need for skilled professionals, and the legal and ethical dilemmas surrounding whole exome sequencing may restrain the market's expansion.
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Trends
Personalized Medicine Segment is Expected to Witness Significant Growth Over the Forecast Period
Personalized medicine tailors therapies to individual patients based on the molecular underpinnings of their diseases. This approach has gained traction in recent years. Often referred to as "individualized medicine," precision medicine diverges from traditional methods by emphasizing each patient's distinct genetic profile. With advancements in genetics and a deeper comprehension of human genetic makeup, especially how it influences health, development, and drug responses, medical professionals are crafting safer, more effective treatments for a myriad of health conditions. The benefits of precision medicine are manifold, enhancing both health and healthcare.
Factors propelling the personalized medicine segment include the rising prevalence of various cancers, the affordability of personalized therapies for cancer and other diseases, reduced side effects from tailored treatments, widespread adoption in developed markets, and the emergence of innovative drugs.
For example, in August 2022, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium initiated a pilot project under its Somatic Reference Sample (SRS) Initiative. This project aims to refine the validation and regulatory review processes for cancer diagnostics utilizing next-generation sequencing (NGS). NGS stands out as a transformative technology, unlocking new avenues in diagnostics and therapeutics. However, for these diagnostic tests to be clinically viable, they must undergo rigorous validation, a process heavily reliant on reference samples.
Furthermore, market players are engaging in strategic maneuvers like partnerships, mergers, acquisitions, and product launches, all of which are expected to fuel the segment's expansion. For instance, in November 2023, Illumina unveiled its Global Health Access Initiative, targeting pathogen sequencing in low- and middle-income countries. This initiative offers discounted rates on a range of sequencing applications. These include drug resistance profiling for tuberculosis, whole-genome sequencing to monitor evolving and reemerging viruses, respiratory pathogen detection for influenza-like illness surveillance, environmental monitoring (like wastewater analysis) to track pathogens, and overseeing population-level antimicrobial resistance.
Given these dynamics, the personalized medicine segment is poised for substantial growth in the coming years.
North America is Expected to Witness a Significant Growth Over the Forecast Period
North America stands out as a leading regional market in terms of revenue. Key drivers fueling the growth of the whole-exome sequencing market include the rising prevalence of genetic and chronic disorders like cancer, an aging population, an increasing demand for targeted and personalized medicine, and supportive government initiatives. As reported by HIV.gov in October 2022, approximately 1.2 million individuals in the United States were affected by HIV. This underscores a rising burden of infectious diseases, which is expected to register a heightened demand for diagnostics and bolster market growth during the forecast period.
Mergers, acquisitions, product launches, and partnerships among key players further energize market dynamics in the region. A notable example is QIAGEN's exclusive strategic partnership with California-based Helix, a population genomics leader established in January 2023. This collaboration is set to advance the development of companion diagnostics for hereditary diseases. The integrated services, powered by advanced NGS and PCR technologies, promise rapid patient recruitment, real-world evidence, and comprehensive diagnostic solutions.
Given these dynamics, including the rising prevalence of infectious diseases and active product launches, the North American market is poised for substantial growth in the coming years.
Whole Exome Sequencing Industry Overview
The whole exome sequencing market is moderately consolidated in nature due to the presence of a few companies operating globally as well as regionally. The competitive landscape includes an analysis of some international and domestic companies that hold market shares and are well known, including Eurofins Scientific Group, Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, illumine Inc., and Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. Konica Minolta Inc. (Ambry Genetics), Beijing Genomics Institute, Azenta Inc., Psomagen Inc. (Macrogen Inc.), PerkinElmer Inc., GENEYX GENOMEX, and CD Genomics, QIAGEN Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumption and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Applications in the Clinical Diagnosis and Growing Demand for the Diagnosis of Rare Diseases
- 4.2.2 Increasing R&D in the Field of Genomics and Next-generation Sequencing
- 4.2.3 Increasing Demand for Personalized Medicine
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Complexity of Technique and Lack of Skilled Personnel
- 4.3.2 Legal and Ethical Issues Associated with Whole Exome Sequencing
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (Market Size by Value in USD)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 System
- 5.1.2 Kits
- 5.1.3 Services
- 5.2 By Technology
- 5.2.1 Second-Generation Sequencing
- 5.2.1.1 Sequencing by Synthesis (SBS)
- 5.2.1.2 Sequencing by Hybridization and Ligation (SBL)
- 5.2.2 Third-generation Sequencing
- 5.2.1 Second-Generation Sequencing
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Diagnostics
- 5.3.2 Drug Discovery and Development
- 5.3.3 Personalized Medicine
- 5.3.4 Other Applications (Agriculture, Animal Research, etc.)
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 South Korea
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.4.1 GCC
- 5.4.4.2 South Africa
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5 South America
- 5.4.5.1 Brazil
- 5.4.5.2 Argentina
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Company Profiles
- 6.1.1 Konica Minolta Inc. (Ambry Genetics)
- 6.1.2 Beijing Genomics Institute
- 6.1.3 Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.
- 6.1.4 Eurofins Scientific Group
- 6.1.5 F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- 6.1.6 Azenta, Inc.
- 6.1.7 Illumina Inc.
- 6.1.8 Psomagen Inc. (Macrogen Inc.)
- 6.1.9 PerkinElmer Inc.
- 6.1.10 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.1.11 GENEYX GENOMEX
- 6.1.12 CD Genomics
- 6.1.13 QIAGEN Inc.

















