
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1687894
라틴아메리카의 폐기물 관리 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)South American Waste Management - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
라틴아메리카의 폐기물 관리 시장 규모는 2025년에 378억 4,000만 달러로 추정되고, 예측 기간(2025-2030년) 중 CAGR 7.4%를 넘을 전망이며, 2030년에는 540억 7,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.

이 지역의 폐기물 생산 증가가 시장을 견인하고 있습니다. 게다가 순환형 경제를 목표로 하는 폐기물 관리의 3R에 관한 의식 고조도 시장을 견인하고 있습니다.
라틴아메리카는 재활용업체에게 흥미로운 이용 사례가 됩니다. 이 지역은 몇 가지 폐기물 처리 문제에 직면해 있지만, 확실히 큰 가능성을 지닌 신흥 시장입니다. 재활용률은 일반적으로 10%를 넘지 않으며, 다수의 야외 쓰레기장이 가동되고 있습니다. 그 외의 문제로는 직장에 있어서 비정규직의 많음과 40%를 넘는 부적절한 폐기물 관리를 들 수 있습니다. 지속가능한 비즈니스 모델 및 간접적인 절약에 따른 법률이 요구되는 등, 새로운 변혁의 메가 동향에 의해, 이러한 문제의 해결책을 찾는 것이 급선무가 되고 있습니다. 라틴아메리카의 폐기물 처리에 대한 요망은 그 유효성을 촉진하고 민간 참여를 늘려 투자를 촉진하고 디지털 성과를 도입하려는 가운데 확대되고 있습니다. 전자제품의 재활용은 틈새 부문이며, 큰 서약을 보여줍니다. 그러나, 당 지역에서는, 적절한 회수 네트워크 및 환경 친화적인 사업소의 설치라고 하는 점에서, 스크랩 및 재활용의 기본에 아직 임하고 있지 않습니다. 라틴아메리카에서는 소규모 사업이나 수작업을 통한 분해가 아직 일반적이지만 브라질과 멕시코의 재활용 업체들은 보다 '세련된 기술'을 도입할 수 있게 됐다고 로살레스는 지적합니다. 이로 인해 예를 들어 플라스틱은 더 멀리까지 분해할 수 있게 되었습니다. 라틴아메리카 폐기물 처리 분야는 최근 몇 년 동안 꾸준히 성장하고 개발해 왔습니다.
라틴아메리카는 몇 가지 폐기물 처리 문제에 직면하고 있으며, 재활용률은 최대 10% 정도입니다. 이 문제에 대한 해결책을 찾는 것은 지속 가능성과 간접적 절약이라는 새로운 변혁적 메가 동향을 위해 필수적입니다. 라틴아메리카 폐기물 처리 시장은, 유효성의 향상, 투자를 촉진하기 위한 민간 참가의 증가, 디지털 성과의 도입을 모색하는 가운데 확대되고 있습니다. 유엔의 라틴아메리카 및 카리브해 경제 위원회 경제 개발부는, 개산으로 2030년까지 지역 전체에서 480만 명의 고용을 창출할 수 있다고 보고하고 있습니다. 유엔환경계획 보고서에 따르면 2050년까지 770만 명의 신규 일자리를 창출하고 연간 6210억 달러를 절약할 수 있다고 합니다. 예를 들어 칠레는 2040년까지 순환 경제에서 18만 명 이상의 정규직을 창출하겠다는 목표를 내걸고 있습니다. 2차적인 문제는 폐기물 선별업체를 체계화된 폐기물 처리 시스템에 통합하는 것입니다. 포괄적 재활용을 위한 지역 이니셔티브(Regional Initiative for Inclusive Recycling)에 따르면 인포멀 분야는 약 400만 명에 이릅니다. 이 분야는 이 지역 전체 외부 폐기물 수집량의 약 25-50%를 차지하고 있습니다.
이러한 상황에서 폐기물을 관리하는 것은 중요한 재료를 사용하는 절호의 기회입니다. 재사용이 제대로 이루어지지 않을 경우 귀중한 수단이 상실될 수 있습니다. 라틴아메리카에서는 폐기물을 생산하는 나라도 수입하는 나라도 있어 일반적으로 가이드라인의 가장자리에 존재하는 토착 수문을 형성하고 있습니다. 이 지역의 금융 개발과 강화의 위치가 급속히 진행되고 있기 때문에 폐기물 측정은 다른 지역보다 빨리 중요해지고 있습니다. 현재 진행형으로, 전자 폐기물은 라틴아메리카 전역의 공공 계획에서 매우 눈에 띄는 문제가 되고 있습니다. 민간 지역 단체나 일반 사회 단체도 폐기물 문제에 뛰어들려는 열의가 개발되고 있습니다. 이는 폐기물의 위험한 회랑에 대한 정치적 중압과 일반 시민의 우려 때문일 뿐만 아니라 폐기물 담당자가 제공하는 매력적인 산업의 가능성 때문이기도 합니다. 라틴아메리카 제국에서는 폐기물을 새로운 녹색 대처나 비즈니스의 창출원으로 간주하는 움직임이 진행되고 있습니다. 라틴아메리카에서 특히 우려되고 있는 것은 슬그머니 폐기물을 분별하고 파기하는 것입니다. 이러한 문제는 접근법과 가이드라인, 전자 폐기물 전문가, 건전한 백업 및 충분히 기능하고 있는 비즈니스 부문, 적절한 기술 혁신 및 역량, 매우 중요한 교육 및 인식을 가진 사회 질서, 분명하고 뛰어난 관찰, 관리, 인가 기관 등 올바른 틀을 설정함으로써 대처할 수 있습니다.
라틴아메리카의 폐기물 관리 시장 동향
재활용 수요 증가로 시장 견인
- 아르헨티나의 재활용업체인 Reciclar은 TOMRA의 지원으로 1회당 6억 개 이상의 페트병 처리 능력을 향상시켰습니다. TOMRA와 Reciclar는 라틴아메리카에서 귀중한 재원의 간접적인 처리를 가속화하는 모범을 보였습니다. 아르헨티나의 공장은 2만 2,000평방미터 이상의 면적을 가지고 있으며, TOMRA의 재활용 선별 장치와 부처의 최신 세대를 갖추고 있습니다. AUTOSORT(TM)와 AUTOSORT(TM) FLAKE에 의해 재활용 업자는 1회당 3만 톤 이상의 PET 홀더를 색과 재료 타입으로 선별 및 회수해, 데미타스, 그린, 라이트 블루의 PET 플레이크와, 다양한 사이즈 및 색의 HDPE 플레이크를 제조할 수 있습니다. 또, Reciclar는, 소비자용 PET병으로부터 식품용 PET 재활용품을 제조하고 있습니다.
- 순결한 상황이 달성된 덕분에, 재활용업체는 그것들을 한층 더 고품질의 PET나 HDPE 리사이클재에 재이용해, 재활용율을 높인 새로운 포장이나 병을 제조할 수 있습니다. 플라스틱 재활용 과제는 모든 사람이 관련된 세계의 문제이며 라틴아메리카에서는 이 과제가 결코 작은 것이 아닙니다.
- 이 때문에 재활용 부문의 중요한 기업인 TOMRA Recycling Sorting과 Reciclar, SA는 플라스틱의 라이프사이클을 연장하고, 이 지역의 환경 활동에 기여하기 위해 손을 잡아 왔습니다. 양사는 약속, 발명, 성실성을 통해 재생 플라스틱의 이용을 극대화하는 것을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 레시클라는 최근 아르헨티나의 재활용 과제에 대응하기 위해 새로운 TOMRA 설비를 도입했습니다. ECOPLAS 보고서에 따르면 2021년 재생 플라스틱 총량은 30만 7,000톤에 달했으며, 2020년 대비 11톤 증가했습니다.
- 마르셀리노 카셀라에 의해 혁신된 이 공장은 지난 28년간 폐기물 수집, 선별, 회수를 전문으로 해왔지만, 최근에 데미타스, 녹색 또는 하늘색 PET 플레이크와 다양한 크기와 색의 HDPE 플레이크를 제조하기 위해 새로운 AUTOSORT(TM) 플레이크 유닛을 2대 추가했습니다. TOMRA Recycling Sorting의 선진적인 PET병과 PET 포장의 선별 장치와 기술에 의해 아르헨티나 기업은 회당 6억 개의 페트병과 1만 8,000톤의 플라스틱 팔레트의 처리 능력을 달성해, PET 폐기물 처리에서 아르헨티나의 주요 기업이 되었습니다.
시장을 견인하는 폐기물 생산량 증가
- 라틴아메리카는 세계의 식량 생산에 있어 헤아릴 수 없는 존재입니다. 하지만 음식물 쓰레기 문제와는 무관하지 않습니다. 라틴아메리카는 세계 농수산물 수출의 약 4분의 1을 차지하고 있습니다. 경제협력개발기구(OECD) 데이터에 따르면 국토 면적의 38%가 농업에 사용되고 그 중 9.5%가 농작물, 28.5%가 목축에 사용되고 있습니다. 농업 부문은 라틴아메리카 생활에 있어서 지극히 중요하며, GDP의 4.7을 차지하고, 이 지역 인구의 적어도 14%를 고용하고 있습니다. 식량 손실과 폐기를 막는 것은 세계적으로 남은 가장 중요한 과제 중 하나입니다.
- 이 과제는 라틴아메리카에도 미치고 있습니다. FAO는 세계 식품 손실의 6%가 라틴아메리카와 카리브해 지역에서 발생하고 있다고 추정하고 있으며, 이 지역에서는 매회 식량의 약 15%가 손실되어 폐기되고 있습니다. 범미보건기구(PAN AMERICAN HEAL THORGANIZATION)는 2030년에 기아는 이 지역의 6,700만 명에게 영향을 미칠 것으로 전망됩니다. 또한 이 수치는 우크라이나 전쟁으로 인해 발생한 세계 식량 공급의 지연을 나타내고 있습니다. 그렇기 때문에 정말 수치스러운 기아의 데이터가 예상되는 것입니다.
라틴아메리카의 폐기물 관리 산업 개요
라틴아메리카의 폐기물 관리 시장은 단편적인 성질을 가지고 있으며, 많은 지역 및 지역 기업과 소수의 세계 참가 기업이 존재합니다. 주요 진입 기업으로는 RECYCLE S. DE R.L, Proactiva Medio Ambiente, Honduras Environmental Services, Capitol Environmental Services, Inc., The Trinidad and Tobago Solid Waste Management Company Limited (SWMCOL) 등입니다. 라틴아메리카의 폐기물 관리 시장은 경쟁이 치열하고 효과적인 폐기물 관리 및 더 나은 폐기물 재활용 이니셔티브 개발을 위해 정부에 의해 새로운 법률이 시행되고 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
- 분석 방법
- 조사 단계
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 역학
- 현재의 시장 시나리오
- 시장 개요
- 시장 역학
- 성장 촉진요인
- 라틴아메리카에서는 급속한 도시화 및 인구 증가로 도시 쓰레기 발생량 증가
- 매립지 사용량 삭감 및 클린 에너지 생성 필요성으로 폐기물 발전 시설에 대한 투자 진행
- 성장 억제요인
- 비공식 폐기물 분야
- 한정된 재원
- 기회
- 국제무역 및 폐기물 수출입
- 폐기물 관리 인프라 및 서비스에 대한 관민 파트너십과 민간 분야 투자로 증대하는 폐기물 관리 요구에 대응
- 성장 촉진요인
- 밸류체인 및 공급망 분석
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자 및 소비자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
- 라틴아메리카 폐기물 관리 산업에서의 물류 지원 및 개발에 관한 인사이트
- 라틴아메리카 폐기물 관리 산업에 진입하는 신흥 기업 전략에 관한 인사이트
- 효과적인 폐기물 관리에서 기술의 진보 및 혁신
제5장 시장 세분화
- 폐기물 유형별
- 산업 폐기물
- 도시 고형 폐기물
- 전자 폐기물
- 플라스틱 폐기물
- 의료 폐기물
- 처리 방법별
- 회수
- 매립처분
- 소각
- 재활용
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 기업 프로파일
- RECYCLE S. DE RL
- Proactiva Medio Ambiente
- Honduras Environmental Services
- The Trinidad and Tobago Solid Waste Management Company Limited(SWMCOL)
- Capitol Environmental Services, Inc
- Inciner8 Limited
- Casella Waste Systems, Inc.
- US Ecology, Inc.
- Waste Management, Inc
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- Republic Services, Inc*
제7장 라틴아메리카 폐기물 관리 산업의 장래 성장 전망
제8장 부록
- 도시 지역의 주에 의한 고형 폐기물 발생량 통계
- 라틴아메리카 인구 규모(백만명)
- 라틴아메리카 GDP
- 라틴아메리카 인플레이션율
- 라틴아메리카 소비자 물가 지수(절대치)
- 라틴아메리카 환율
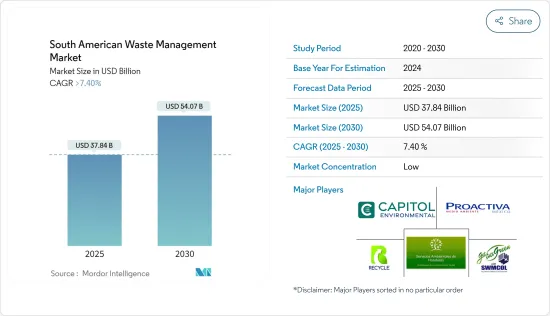
The South American Waste Management Market size is estimated at USD 37.84 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 54.07 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of greater than 7.4% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
The increasing waste production in the region drives the market. Furthermore, the market is driven by the increasing awareness about the 3 R's of waste management, which intends to create a circular economy.
Latin America presents an intriguing case study for recyclers. It's an emerging market with great eventuality, indeed, though the region is facing several waste operation problems. Recycling rates generally don't exceed 10, with numerous open-air dumps in operation. Other issues include high situations of informality in the workplace and further than 40 of inaptly managed waste. Finding a result of these problems is imperative due to new transformative megatrends, similar to calls for sustainable business models and legislation in line with indirect frugality. The waste operation request in Latin America is expanding as it seeks to facilitate effectiveness, increase private participation to boost investment and incorporate digital results. Electronics recycling is a niche showing a significant pledge. However, our region is still dealing with the basics of scrap recycling in terms of setting up proper collection networks and environmentally sound establishments. While small-scale operations and homemade disassembly are still common across Latin America, Rosales notes that recyclers in Brazil and Mexico have been able to install more ' sophisticated technology.' This allows farther bracket of plastics, for example. The waste operation sector in Latin America has been growing and developing steadily over the last many times.
Latin America faces several waste operation problems, with recycling rates that are at most 10, a large number of open-air dumps, high levels of informality in the plant, and further than 40 of inaptly managed waste. Finding a result to this problem is imperative due to new transformative Mega Trends, similar to sustainability and indirect frugality. The waste operation market in Latin America is expanding as it seeks to improve effectiveness, increase private participation to boost investment and incorporate digital results. At a rough estimate, better waste operation could produce up to 4.8 million jobs across the region by 2030, the UN's Economic Development Division of the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean reported. By 2050, it would be suitable to generate 7.7 million new jobs and save up to 621 billion US- Dollars annually, a UN Environment Programme report states. Chile, for example, has set a target of creating further than 180,000 formal jobs in the circular economy by 2040. A secondary problem is the integration of waste selectors into a systematized waste operation system. The informal sector consists of around four million people, according to the Regional Initiative for Inclusive Recycling. The sector contributes roughly 25 to 50 percent of all external waste collection in the region.
In the current situation, overseeing waste presents a faultless chance to use the important materials that can be set up in multitudinous kinds of inclined widgets. On the off chance that reusing is not meetly done, precious means can be lost. In Latin America, nations both produce and import-waste, shaping the indigenous sluice that exists generally on the edges of the guideline. Because of the locale's quickened financial development and position of enhancement, the measure of-waste is getting more important quicker than in other regions. On ongoing occasions, e-waste has become an extremely conspicuous issue in public plans across Latin America. Private area and common society associations also have a developing enthusiasm for diving into waste issues. This is not just because of political weight and public worries about the dangerous corridor of waste but also because of the appealing industry openings that waste directors offer. Progressively Latin American nations are seeing waste on the board as a creator of new green endeavours and business. Of specific solicitude in Latin America is the sneaking and casual assortment and destroying of waste, which prompts unreasonable contest and unusual pitfalls. These difficulties can be tended to by having the correct framework set up, including approaches and guidelines, e-waste specialist-ops, sound backing and meetly working business sectors, suitable innovation and abilities, social orders that are very important educated and aware, and obviously great observing, control, and authorization bodies.
South American Waste Management Market Trends
Increasing demand for recycling driving the market
- Argentinian recycler Reciclar has improved its capacity of over 600 million plastic bottles per time thanks to TOMRA's outfit. TOMRA and Reciclar set an example of accelerating an indirect treatment of precious coffers in Latin America. The Argentinian factory, with a face area of further than 22,000 m2, features the rearmost generation of TOMRA Recycling Sorting outfit and ministry. AUTOSORT (TM) and AUTOSORT (TM) FLAKE allow the recycler business to sort and recover further than 30,000 tons/ time of PET holders by color and material type and produce demitasse, green, or light blue PET flakes and HDPE flakes of different sizes and colors. Also, Reciclar produces food-grade PET recyclates from post-consumer PET bottles.
- Thanks to the chastity situations achieved, recyclers can further reuse them into high-quality PET and HDPE recyclates for the product of new packaging and bottles with increased recycled content, thus supporting an environmentally friendly resource operation and product in Argentina. The plastic recycling challenge is a global problem in which all are involved, and in Latin America, the task isn't a minor bone.
- For this reason, TOMRA Recycling Sorting and Reciclar, S.A., two important companies in the recycling sector, are joining forces to contribute to environmental conduct in the region to extend the life cycle of plastics. Both companies seek to maximize the use of recycled plastic through commitment, invention, and fidelity. According to this charge, Reciclar recently installed fresh TOMRA outfits to meet the recycling challenges in Argentina. An ECOPLAS report estimates that the total volume of plastic reclaimed in 2021 amounted to 307,000 tonnes of plastics, an increase of 11 compared to 2020.
- The factory innovated by Marcelino Casella, which has specialized in collecting, sorting, and recovering waste for the last 28 times, only recently added 2 new AUTOSORT (TM) FLAKE units to its operation to produce demitasse, green or light blue PET flakes and HDPE flakes of different sizes and colors. Thanks to TOMRA Recycling Sorting's advanced PET bottle and PET packaging sorting outfit and technology, the Argentinean company has reached a processing capacity of 600 million plastic bottles and a product of 18,000 tons of plastic pallets per time, becoming the leading company in Argentina in PET waste processing.
Increasing waste production driving the market
- Latin America is inestimable for global food production. Yet it's no stranger to the food waste issue. Latin America accounts for about a quarter of global exports in agricultural and fisheries products. According to the OECD data, 38 of its available area is used for agriculture, out of which 9.5 is devoted to crops and 28.5 to pasturage. The agricultural sector is crucial for Latin American livelihoods, contributing to a normal of 4.7 of GDP and employing at least 14 of the region's population. Precluding food loss and waste is one of the topmost remaining global challenges.
- This challenges enterprises also Latin America. The FAO estimates that 6 of global food losses occur in Latin America and the Caribbean, and the region loses and/ or wastes each time about 15 of its food each. The Pan American Health Organization estimates that " in 2030, hunger will affect 67 million people in the region, a figure that doesn't take into account the impacts of the COVID-19 epidemic ". In addition, this figure represents the global food supply lapses caused by the war in Ukraine. So, indeed, advanced shameful hunger data are anticipated.
South American Waste Management Industry Overview
The South American waste management market is fragmented in nature, with a lot of regional and local players and a few global players. Some of the major players include RECYCLE S. DE R.L, Proactiva Medio Ambiente, Honduras Environmental Services, Capitol Environmental Services, Inc., The Trinidad and Tobago Solid Waste Management Company Limited (SWMCOL), and many more. The South American waste management market is highly competitive, with newer laws being implemented by the governments for effective waste management and the development of better waste recycling initiatives.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Method
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Overview
- 4.3 Market Dynamics
- 4.3.1 Drivers
- 4.3.1.1 The rapid urbanization and population growth in South America have led to increased municipal waste generation.
- 4.3.1.2 The need to reduce landfill usage and generate clean energy has led to investments in waste-to-energy facilities.
- 4.3.2 Restraints
- 4.3.2.1 Informal Waste Sector
- 4.3.2.2 Limited Financial Resources
- 4.3.3 Opportunities
- 4.3.3.1 International Trade and Waste Import/Export
- 4.3.3.2 Public-private partnerships and private sector investments in waste management infrastructure and services are helping to address the growing waste management needs
- 4.3.1 Drivers
- 4.4 Value Chain / Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.6 Insights on the Logisitcs support and development in the waste management industry in Latin America
- 4.7 Insights on the strategies of the rising startups venturing into the Latin American waste management industry
- 4.8 Technological advancement and innovation in the effective waste management
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Waste type
- 5.1.1 Industrial waste
- 5.1.2 Municipal solid waste
- 5.1.3 E-waste
- 5.1.4 Plastic waste
- 5.1.5 Bio-medical waste
- 5.2 By Disposal methods
- 5.2.1 Collection
- 5.2.2 Landfill
- 5.2.3 Incineration
- 5.2.4 Recycling
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Overview (Market Concentration and Major Players)
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 RECYCLE S. DE R.L
- 6.2.2 Proactiva Medio Ambiente
- 6.2.3 Honduras Environmental Services
- 6.2.4 The Trinidad and Tobago Solid Waste Management Company Limited (SWMCOL)
- 6.2.5 Capitol Environmental Services, Inc
- 6.2.6 Inciner8 Limited
- 6.2.7 Casella Waste Systems, Inc.
- 6.2.8 US Ecology, Inc.
- 6.2.9 Waste Management, Inc:
- 6.2.10 Covanta Holding Corporation
- 6.2.11 Republic Services, Inc*
7 FUTURE GROWTH PROSPECTS OF LATIN AMERICAN WASTE MANAGEMENT INDUSTRY
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Statistics on the state-wise solid waste generation in urban areas
- 8.2 Latin America size of population (million)
- 8.3 Latin America GDP
- 8.4 Latin America inflation
- 8.5 Latin America Consumer Price Index (absolute)
- 8.6 Latin America exchange rate



















