|
시장보고서
상품코드
1690736
전기 추진 위성 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Electric Propulsion Satellites - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
■ 보고서에 따라 최신 정보로 업데이트하여 보내드립니다. 배송일정은 문의해 주시기 바랍니다.
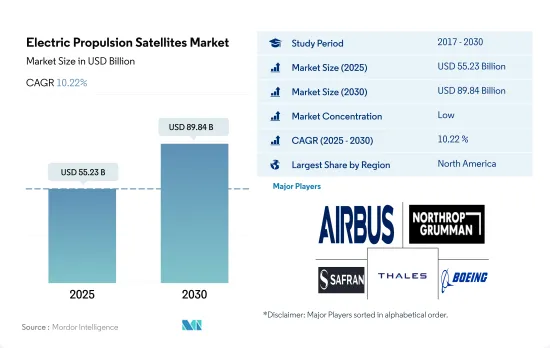
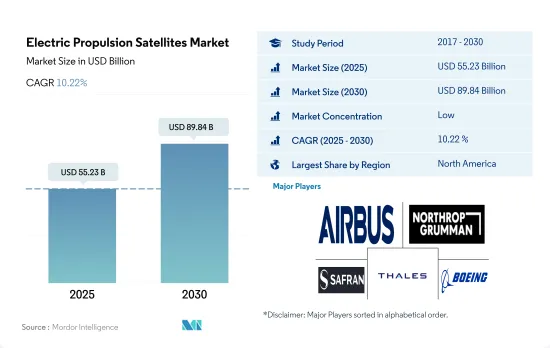
세계의 전기 추진 위성 시장 규모는 2025년 552억 3,000만 달러로 추정되며, 2030년에는 898억 4,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 예측 기간 중(2025-2030년) CAGR 10.22%로 성장할 전망입니다.
우주탐사에 대한 정부와 민간기업의 관심이 높아지면서 이 시장 확대에 박차를 가하고 있습니다.
- 전기 위성 추진 시스템 세계 시장은 다양한 분야에서 위성 배치 수요 증가에 견인되어 최근 몇 년간 강력한 성장을 이루고 있습니다. 북미는 NASA 등의 확립된 우주 기관이나 SpaceX, Blue Origin, Boeing 등의 비공개 회사의 존재 등에 의해 세계 우주 추진 시장의 지배적인 기업로서 대두해 왔습니다. 이러한 기업들은 야심찬 우주 임무와 위성 배치를 위해 노력하고 있으며, 선진 추진 시스템 수요를 견인하고 있습니다. NASA도 태양전기 추진 프로젝트를 진행하고 있으며, 야심찬 발견과 과학 미션의 기간과 능력의 연장을 목표로 하고 있습니다.
- 아시아태평양은 최근 우주 능력의 급속한 확대를 목격하고 있습니다. 중국, 인도, 일본과 같은 국가들은 우주 기술과 위성 제조에서 큰 진보를 이루고 있으며 세계 시장에서 강력한 기업으로서의 지위를 확립하고 있습니다. 2022년 5월 중국 위성전기 추진 회사인 Kongtian Dongli는 중국 위성 발사 계획이 급증하면서 수백만 위안의 엔젤 라운드 자금을 확보했습니다.
- 유럽에는 ESA와 같은 조직을 통한 우주 탐사에서 협력의 강한 전통이 있습니다. ESA와 여러 회원국 간의 파트너십은 우주 기술, 위성 제조 및 발사 능력에 큰 진보를 가져왔습니다. 2023년 2월 스페인을 기반으로 하는 우주 이동성 제공업체인 IENAI SPACE는 ATHENA(NAnotechnology를 동력원으로 하는 일렉트로스프레이 기반 적응 가능한 THruster) 추진 시스템을 성숙시키고 추가 개발하기 위해 일반 지원 기술 프로그램 내에서 2개의 ESA 계약을 획득했습니다.
세계의 전기 추진 위성 시장 동향
전기 추진 시스템에 대한 중점 증가는 관련 우주 프로그램에 대한 지출의 성장을 조장할 것으로 예상됩니다.
- 연구 투자에 대한 보조금은 북미 위성 발사 로켓 시장의 혁신과 성장의 주요 원동력이 되었습니다. 이는 위성 발사 비용을 크게 줄일 수 있는 재사용 로켓과 같은 신기술 개발에 자금을 제공하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 2023년, 2022-2027년 대통령 예산 요구 요약에 따르면 NASA는 태양전기 추진 개발에 9,800만 달러를 받을 전망입니다. 2021년 3월, NASA는 Maxar Technologies 및 Busek Co.와 함께 6킬로와트(kW)의 태양 전기 추진 서브시스템을 성공적으로 테스트했습니다.
- 또한 2022년 11월 ESA는 우주 프로젝트에서 유럽의 리드를 유지하기 위해 향후 3년간 우주 자금을 25% 증액할 것을 제안했다고 발표했습니다. ESA는 22개국에 2023년부터 2025년까지 185억 유로의 예산을 지지할 것을 요구하고 있습니다. 2023년 4월, Dawn Aerospace는 DLR(독일항공우주센터)과 공동으로 인공위성 및 심우주 미션을 위한 아산화질소 기반의 녹색추진제의 성능을 높이기 위한 실현가능성 조사를 실시하는 계약을 체결했습니다.
- 아시아태평양에서는 우주 계획 증가로 우주 추진제에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. 2022년 5월 중국 위성전기 추진 회사인 Kongtian Dongli는 중국의 별자리 계획이 급증하면서 수백만 위안의 엔젤 라운드 자금을 확보했다고 발표했습니다. 이 회사의 주요 제품은 홀 추진기와 마이크로파 전기 추진 시스템입니다. 마찬가지로 2023년 2월 인도 정부는 ISRO가 액체 추진 시스템 센터(LPSC)와 ISRO 추진 복합 시설의 개발을 포함한 다양한 우주 관련 활동을 위해 20억 달러를 받을 전망이라고 발표했습니다.
전기 추진 위성 산업 개요
전기 추진 위성 시장은 세분화되어 있으며 상위 5개사가 23%를 차지하고 있습니다. 이 시장 주요 기업은 Airbus SE, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Safran SA, Thales, The Boeing Company입니다(알파벳순).
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 주요 요약과 주요 조사 결과
제2장 보고서 제안
제3장 소개
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
- 조사 방법
제4장 주요 산업 동향
- 우주 개발에 대한 지출
- 규제 프레임워크
- 세계
- 호주
- 브라질
- 캐나다
- 중국
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 인도
- 이란
- 일본
- 뉴질랜드
- 러시아
- 싱가포르
- 한국
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 영국
- 미국
- 밸류체인과 유통채널 분석
제5장 시장 세분화
- 추진 유형
- 완전 전동
- 하이브리드
- 최종 사용자
- 상업
- 군용
- 지역
- 아시아태평양
- 유럽
- 북미
- 세계 기타 지역
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 주요 전략 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 상황
- 기업 프로파일
- Accion Systems Inc.
- Ad Astra Rocket Company
- Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings, Inc
- Airbus SE
- Busek Co. Inc.
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Safran SA
- Sitael SpA
- Thales
- The Boeing Company
제7장 CEO에 대한 주요 전략적 질문
제8장 부록
- 세계 개요
- 개요
- Porter's Five Forces 분석 프레임워크
- 세계의 밸류체인 분석
- 시장 역학(DROs)
- 정보원과 참고문헌
- 도표 일람
- 주요 인사이트
- 데이터 팩
- 용어집
The Electric Propulsion Satellites Market size is estimated at 55.23 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 89.84 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 10.22% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
The growing interest of governments and private players in space exploration have fueled the expansion of this market
- The global market for electric satellite propulsion systems witnessed robust growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for satellite deployments across various sectors. North America has emerged as a dominant player in the global space propulsion market, mainly due to the presence of established space agencies such as NASA and private companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Boeing. These entities have undertaken ambitious space missions and satellite deployments, driving the demand for advanced propulsion systems. NASA is also working on the Solar Electric Propulsion project, which aims to extend the duration and capabilities of ambitious discoveries and science missions.
- Asia-Pacific has witnessed a rapid expansion of its space capabilities in recent years. Countries like China, India, and Japan have made significant strides in space technology and satellite manufacturing, positioning themselves as formidable players in the global market. In May 2022, Kongtian Dongli, a Chinese satellite electric propulsion company, secured multi-million yuan angel round financing amid a proliferation of Chinese constellation plans.
- Europe has a strong tradition of collaboration in space exploration through organizations like the ESA. ESA's partnerships with multiple member states have resulted in significant advancements in space technology, satellite manufacturing, and launch capabilities. In February 2023, IENAI SPACE, an in-space mobility provider based in Spain, received two ESA contracts within the General Support Technology Program to mature and further develop ATHENA (Adaptable THruster based on Electrospray powered by NAnotechnology) propulsion systems.
Global Electric Propulsion Satellites Market Trends
The increased emphasis on electric propulsion system is expected to aid in the growth of spending on its related space programs
- The grant for research and investment has been a major driver of innovation and growth in the North American satellite launch vehicle market. It has helped to fund the development of new technologies, such as reusable launch vehicles, which have the potential to significantly reduce the cost of satellite launches. In FY2023, according to the President's budget request summary from FY2022 to FY2027, NASA is expected to receive USD 98 million for the development of Solar Electric Propulsion. In March 2021, NASA, along with Maxar Technologies and Busek Co., successfully completed a test of the 6-kilowatt (kW) solar electric propulsion subsystem
- Additionally, in November 2022, ESA announced that it had proposed a 25% boost in space funding over the next three years to maintain Europe's lead in space projects. The ESA is asking its 22 nations to back a budget of EUR 18.5 billion for 2023-2025. In April 2023, Dawn Aerospace was awarded a contract to conduct a feasibility study with DLR (German Aerospace Center) to increase the performance of a nitrous-oxide-based green propellant for satellites and deep-space missions.
- In Asia-Pacific, the demand for space propulsion is driven by increasing space programs. In May 2022, Kongtian Dongli, a Chinese satellite electric propulsion company, announced that it had secured multi-million yuan angel round financing amid a proliferation of Chinese constellation plans. The company's main products are hall thrusters and microwave electric propulsion systems. Likewise, in February 2023, the Indian government announced that ISRO is expected to receive USD 2 billion for various space-related activities, including the development of the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) and ISRO Propulsion Complex.
Electric Propulsion Satellites Industry Overview
The Electric Propulsion Satellites Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 23%. The major players in this market are Airbus SE, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Safran SA, Thales and The Boeing Company (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.2 Regulatory Framework
- 4.2.1 Global
- 4.2.2 Australia
- 4.2.3 Brazil
- 4.2.4 Canada
- 4.2.5 China
- 4.2.6 France
- 4.2.7 Germany
- 4.2.8 India
- 4.2.9 Iran
- 4.2.10 Japan
- 4.2.11 New Zealand
- 4.2.12 Russia
- 4.2.13 Singapore
- 4.2.14 South Korea
- 4.2.15 United Arab Emirates
- 4.2.16 United Kingdom
- 4.2.17 United States
- 4.3 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Propulsion Type
- 5.1.1 Full Electric
- 5.1.2 Hybrid
- 5.2 End User
- 5.2.1 Commercial
- 5.2.2 Military
- 5.3 Region
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.3 North America
- 5.3.4 Rest of World
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Accion Systems Inc.
- 6.4.2 Ad Astra Rocket Company
- 6.4.3 Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings, Inc
- 6.4.4 Airbus SE
- 6.4.5 Busek Co. Inc.
- 6.4.6 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.7 Safran SA
- 6.4.8 Sitael S.p.A.
- 6.4.9 Thales
- 6.4.10 The Boeing Company
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
샘플 요청 목록