
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1836702
비행 데이터 모니터링 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Flight Data Monitoring - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
비행 데이터 모니터링 시장 규모는 2025년에 58억 2,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 81억 8,000만 달러에 이를 전망이며, CAGR 7.06%로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다.

항공사와 운항사는 현재 비행 데이터를 전략적 자산으로 취급하고 있으며 예측 분석과 연비 효율 알고리즘을 통해 비용 절감을 실현하고 있습니다. ICAO의 실시간 조난 추적 규칙부터 FAA의 25시간 조종석 음성 레코더 의무화에 이르기까지 규제 조화는 표준화된 세계 기준선을 작성하면서 채용 일정을 압축합니다. 중앙 집중화된 클라우드 기반 분석으로의 이동은 항공기의 무게 패널티를 제거하고 고급 분석을 경제적으로 매력적으로 만드는 지상 플랫폼을 지원합니다. 기술 공급업체는 AI 지원 장치와 개방형 데이터 아키텍처를 지원하므로 운항사가 공통 인터페이스에서 성능, 유지보수 및 안전 대시보드를 통합할 수 있습니다. 북미는 확립된 데이터 공유 프레임워크를 통해 선행자 우위를 유지하고 있지만 아시아태평양은 항공 인프라의 규모가 확대되고 도시 지역의 항공 모빌리티 프로젝트가 기세를 늘릴수록 가장 빠른 확대를 기록하고 있습니다.
세계의 비행 데이터 모니터링 시장 동향 및 인사이트
온보드 비행 데이터 모니터링 시스템의 채택을 가속화하는 세계 규제
규제 기관은 성능과 기록의 기준을 조정하여 컴플라이언스를 다음부터 동기화된 세계 프레임워크로 변화시키고 있습니다. ICAO의 부속서 6에 대한 수정 조항 48은 2025년 1월 이후 27,000kg을 넘는 항공기에 조난 발생 시 매분 위치 데이터를 전송할 것을 의무화하고 있으며, 비행 기록과 실시간 연결을 융합시킨 업그레이드를 강요하고 있습니다. 이와 병행하여, 2024년 5월에 시행되는 FAA의 25시간 조종석 보이스 레코더 규칙은 항공사가 레거시 기체에 적합한 레코더를 장비함으로써 8억 달러의 리노베이션 파도를 만들었습니다. 이 하모나이제이션은 인증을 간소화하고, 1대 당 비용을 낮추며, 소규모 운항회사를 방관시켰던 지금까지의 지리적 장벽을 제거합니다. 제조업체는 단일 제품 라인을 대륙 전반에 걸쳐 확장할 수 있는 반면, 운항사는 임대, 재판매 및 국경을 넘어서는 습식리스 계약을 간소화하는 보편적으로 허용되는 안전 기준으로부터 이익을 얻을 수 있습니다.
운항 중단과 비용 절감을 위해 예지 보전을 우선하는 항공사
항공사는 부품의 마모를 예측하고 예정되지 않은 유지 보수 이벤트를 피하기 위해 다중 비행 데이터 세트를 적용하는 경우가 늘고 있습니다. NASA의 연구에 따르면, 컨디션 기반 유지보수는 인터벌 스케줄링에 비해 직접적인 유지 보수 비용을 최대 30% 절감할 수 있습니다. 록히드 마틴의 HercFusion 플랫폼은 약 300만 시간의 비행 시간을 기반으로 훈련되었으며 C-130 운영자의 임무 가동률을 3% 향상시키고 연료 소비를 15% 줄일 수 있음을 입증했습니다. 에어버스는 이 모델을 Skywise Fleet Performance 제품군으로 확장하여 이지 제트가 이전에 중단된 시스템 장애를 사전에 피할 수 있게 함으로써 수익과 승객의 신뢰를 보호합니다. 이러한 성능 향상으로 비행 데이터 모니터링은 비용 센터에서 전략적 이익의 테코로 변화하여 전사적 도입이 가속화됩니다.
높은 초기 도입 비용 및 통합 비용으로 소규모 항공사 채용 제한
차터편을 운항하는 회사나 지역 항공사는 이폭이 적고, 기체도 낡기 때문에 대규모의 개조가 필요한 경우가 많습니다. FAA는 Part135 SMS를 준수하는 데 매년 4,740만 달러의 비용이 소요될 것으로 예상되며, 소규모 항공사의 자본 부담의 크기를 돋보이게 합니다. 리노베이션에는 가동 중지 시간, 전문 노동력 및 인증 서류 작성이 필요하며 많은 소규모 운영자는 부득이한 경우에만 일정을 잡습니다. 그 결과 시장이 이분화됩니다. 대규모 운송 회사는 함대 전체의 예측 분석으로 향하지만, 소규모 사업자는 컴플라이언스 전용 모드에 머물러 하드웨어 가격이 하락하거나 임대 모델이 등장할 때까지 효율화의 이점을 놓치게 됩니다.
보고서에서 분석된 기타 촉진요인 및 억제요인
- UAV 및 소형 플랫폼용의 경량으로 클라우드 대응의 FDM 솔루션의 배치
- 성능 및 연료 최적화를 위한 AI 플랫폼에 실시간 FDM 데이터 통합
- 데이터 프라이버시 및 소유권에 대한 우려로 광범위한 채택 지연
부문 분석
온보드 디바이스는 2024년에 68.22%의 점유율을 유지했으며, 비행 데이터 모니터링 시장 규모를 비행 안전 요구의 핵심으로 삼고 있습니다. 파일럿과 디스패처에게 초과 경고와 같은 시간에 중요한 데이터를 제공합니다. 그러나 지상 플랫폼은 CAGR 8.10%로 성장하고 있습니다. 항공사는 항공기 전반에 걸쳐 다년간의 이력을 처리하는 중앙 집중식 클라우드를 선호하기 때문입니다. 이 아키텍처는 항공기의 무게를 줄이고 기내에서 호스팅하는 것이 현실적이지 않은 고급 AI를 가능하게 합니다. 사용 가능한 대역폭이 증가하고 안전한 위성 링크를 통해 터치다운 후 몇 분 후에 사후 검토를 위한 거의 실시간 다운링크가 가능합니다. 항공사는 여러 OEM 형식을 공통 데이터베이스에 통합하여 라이선스 비용을 줄이면서 교차형 벤치마킹을 개선합니다. 하니웰과 NXP의 협업은 고성능 온보드 프로세서와 클라우드 API를 결합하여 운항사가 항공기 또는 데이터센터에 있는 분석을 선택할 수 있습니다. 규제기관은 이 하이브리드 설계를 받아들여 혼재기의 인증을 가속화하고, 저렴한 항공사는 아비오닉스를 대폭 업그레이드하지 않고도 고급 애널리틱스에 액세스할 수 있도록 하고 있습니다. 지상 아키텍처는 하드웨어 라이프사이클을 연장하기 때문에 지속가능성 과제에도 부합합니다. 각 항공기가 새 알고리즘을 위해 개조하는 대신 항공사는 서버 측 소프트웨어를 업데이트하여 업그레이드 비용과 전자 폐기물을 줄입니다.
고정익기는 2024년 비행 데이터 모니터링 시장 규모의 59.92%를 차지했습니다. 이것은 이미 레코더와 빠른 액세스 장치를 갖춘 여객기와 화물기의 광범위한 세계 함대를 반영합니다. 이 설치 기반은 업그레이드를 계속 구매하지만, 성장은 시장 전체의 평균보다 낮습니다. 이와는 대조적으로 무인 항공기 부문은 CAGR 10.01%로 확대될 전망입니다. 이는 규제 당국이 검사, 물류 및 도시 공중 이동 임무를 위한 상용 통로를 여는 프레임워크를 최종 결정했기 때문입니다. 무인 항공기의 무게와 전력 소비 제한으로 인해 공급업체는 얇은 센서, 에지 프로세서, 셀룰러 또는 위성 데이터 파이프로 향합니다. 여기에서 배운 교훈은 현재 레거시 터보프롭 기계와 헬리콥터의 리노베이션 프로젝트에 영향을 미치고 역방향 기술 이전을 입증하고 있습니다. 응급 의료 서비스와 해외 에너지의 회전익 항공기는 틈새 시장이지만 꾸준히 채택되었습니다. GE 에어로스페이스와 크레이토스 디펜스와의 공동 개발은 비용에 민감한 무인 시스템용으로 개발된 기술 혁신이 유인 지역 제트용으로 재패키징되었음을 보여줍니다. 플랫폼 컨버전스는 하나의 기체 클래스에 대해 개발된 분석을 여러 기체 유형으로 이식할 수 있어 공급업체 생태계를 강화하고 운영자 전환 비용을 절감합니다.
UAV의 성장은 공급망도 재구성합니다. 왜냐하면 기존 항공사 이외의 기업(소프트웨어 신흥기업, 휴대전화 사업자, 물류 브랜드)은 하드웨어를 구입하는 것이 아니라 서비스로서 모니터링을 구입하기 때문입니다. 이 구독의 전망은 업데이트 주기를 압축하고 공급업체가 일회성 장비 판매에서 정기적인 분석 수익으로 전환하도록 촉구합니다. 이 추세는 고정 날개 기계 및 회전 날개 기계에 파급되는 알고리즘의 혁신을 촉진하기 때문에 궁극적으로 항공사에게 이익을 가져다줍니다. 각국 당국이 특정 카테고리의 운항 규칙을 발표하면 자율 비행이나 원격 조종의 상업 임무에 비행 데이터 모니터링을 의무화하는 경우가 많아 미래 수요를 둘러싸게 됩니다.
지역 분석
북미는 선진적인 규제와 운영 환경을 통해 리더십을 유지하며 2024년 지출액의 30.33%를 차지했습니다. 항공사는 성숙한 공급망과 FAA 안전 관리 시스템 규제의 혜택을 받아 항공사 전반에 걸쳐 종합적인 데이터 수집 및 벤치마킹을 장려합니다. 항공사는 배차의 신뢰성을 높이고 연료 소비를 줄이고 환경 공개를 요구하는 투자자를 만족시키기 위해 AI를 활용한 애널리틱스를 도입하고 있습니다. 이 지역의 레거시 플릿은 밀집되어 있기 때문에 항공사는 빠른 액세스 레코더를 연결 가능 장치로 교체하므로 강력한 복고풍 파이프라인도 보장됩니다. 항공 안전정보 분석 및 공유 프로그램과 같은 협력적인 틀은 매크로 레벨의 리스크 동향을 밝히는 것으로 추가된 각 데이터세트의 보상을 증폭시킵니다.
아시아태평양은 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 7.67%로 가장 빠르게 확대될 전망입니다. 이는 인도와 동남아시아의 연간 여객 수가 2자리 성장하는 것 외에도 중국이 도시의 항공 모빌리티에 전략적 투자를 하고 있는 것이 요인입니다. 각국 정부는 디지털 항공 샌드박스에 자금을 제공하고 표준화된 감시 장비를 갖춘 항공기의 인증 부담을 완화하고 있습니다. 이 지역의 저렴한 항공사는 연료 최적화 모듈을 사용하여 엄청난 마진을 보호합니다. 동시에 풀서비스 에어라인은 기체의 급속한 증비 중에 일정의 무결성을 유지하기 위해 예지보전을 도입하고 있습니다. 국가 비전 계획에서는 항공 운송량의 확대를 지속가능성 지표와 연결시키는 경우가 많으며, 이산화탄소 감축의 주장을 검증하는 데 있어서 비행 데이터 모니터링이 필수적인 역할을 담당하고 있습니다.
유럽에서는 EASA의 리스크 기반 모니터링 접근 방식이 꾸준히 도입되고 있습니다. 2024년 10월 Data4Safety의 확장으로 9개 회원국과 8개 공항이 추가 통합되어 범유럽의 안전 데이터 풀이 비약적으로 확대되었습니다. 항공사는 탄소에 가격을 붙여 연료 효율에 맞는 환경 정책과 감시 투자를 정합시킵니다. GDPR(EU 개인정보보호규정) 준수는 여전히 장애물이지만 벤더는 프라이버시 바이 디자인 아키텍처를 통해 이를 해결하고 보다 광범위한 참여를 촉진하고 있습니다. 국경을 넘어선 작업은 공통 기술 표준의 이점을 누리며, 저렴한 항공사는 하드 와이어 데이터 모듈을 재설계하지 않고 네트워크의 어느 곳에나 항공기를 할당할 수 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 온보드 비행 데이터 모니터링 시스템의 채용을 가속하는 세계 법령
- 운항 중단 및 비용을 줄이기 위한 항공사의 예지 보전 우선시
- UAV나 소형 플랫폼용의 경량으로 클라우드 대응의 FDM 솔루션 배치
- 실시간 FDM 데이터를 AI 플랫폼에 통합하여 성능과 연료 최적화
- 항공사에 FDM 프로그램의 채용을 촉구하는 보험 연동 인센티브
- 인시던트 발생 후의 투명성 및 인시던트 조사의 자동화 중시
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 높은 초기 도입 비용 및 통합 비용으로 인한 소규모 사업자의 도입 제한
- 데이터의 프라이버시나 소유권에 관한 우려로 보다 광범위한 채용 지연
- 항공기 플랫폼 및 어비오닉스 간의 한정적인 기술 표준화
- 실용적인 인사이트를 추출하기 위한 사내 분석 전문가의 부족
- 밸류체인 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술적 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자 및 소비자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계의 강도
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측 : 금액
- 설치 유형별
- 온보드
- 지상
- 플랫폼별
- 고정날개
- 회전날개
- 무인 항공기(UAV)
- 컴포넌트별
- 하드웨어
- 소프트웨어 및 분석
- 서비스
- 최종 사용자별
- 상용 항공사
- 화물 항공사
- 비즈니스 제트 및 오퍼레이터
- 헬리콥터 EMS 및 해양 서비스
- 방위 및 국토 안보
- UAV 서비스 제공업체
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 남미
- 브라질
- 기타 남미
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Teledyne Controls(Teledyne Technologies Incorporated)
- Honeywell International Inc.
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- Safran SA
- Curtiss-Wright Corporation
- Flight Data Systems
- FLYHT Aerospace Solutions Ltd.
- Metro Aviation
- Brazos Safety Systems, LLC
- Groupe NSE
- Gogo Business Aviation(Gogo Inc.)
- Airbus SE
- General Electric Company
- Collins Aerospace(RTX Corporation)
- Spidertracks Ltd.(Vellox Group)
- Scaled Analytics Inc.
- Aerobytes Ltd.
- Helinalysis Ltd.
- Leonardo SpA
제7장 시장 기회 및 전망
AJY 25.10.27The flight data monitoring market size is valued at USD 5.82 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to reach USD 8.18 billion by 2030, advancing at a 7.06% CAGR.
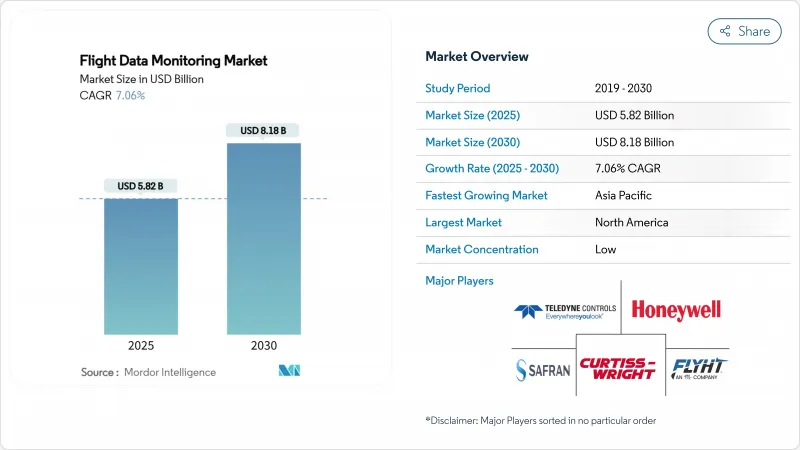
Airlines and operators now treat flight data as a strategic asset that unlocks cost savings through predictive analytics and fuel-efficiency algorithms. Regulatory harmonization-from ICAO's real-time distress tracking rule to the FAA's 25-hour cockpit voice recorder mandate-compresses adoption timelines while creating a standardized global baseline. The shift toward centralized, cloud-based analysis supports on-ground platforms that eliminate aircraft weight penalties and make advanced analytics economically attractive. Technology suppliers respond with AI-ready devices and open data architectures, enabling operators to integrate performance, maintenance, and safety dashboards on a common interface. North America retains first-mover advantage through established data-sharing frameworks, yet Asia-Pacific records the fastest expansion as its aviation infrastructure scales and urban air mobility projects gather momentum.
Global Flight Data Monitoring Market Trends and Insights
Global Mandates Accelerating Adoption of Onboard Flight Data Monitoring Systems
Regulatory bodies are aligning performance and recording standards, transforming compliance from a patchwork into a synchronized global framework. ICAO's Amendment 48 to Annex 6 obliges aircraft above 27,000 kg to transmit position data every minute during distress events beginning January 2025, forcing upgrades that blend flight recording and real-time connectivity. In parallel, the FAA's 25-hour cockpit voice recorder rule, effective May 2024, has created a USD 800 million retrofit wave as carriers outfit legacy fleets with compliant recorders. This harmonization simplifies certification, lowers per-unit costs, and removes the previous geographic barriers that had kept small operators on the sidelines. Manufacturers can scale single product lines across continents, while operators benefit from a universally accepted safety baseline that streamlines leasing, resale, and cross-border wet-lease arrangements.
Airlines Prioritizing Predictive Maintenance to Reduce Operational Disruptions and Costs
Operators increasingly apply multi-flight data sets to predict component wear and avert unscheduled maintenance events. NASA studies show that condition-based maintenance can cut direct maintenance costs by up to 30% compared with interval scheduling. Lockheed Martin's HercFusion platform, trained on roughly 3 million flight hours, demonstrated a 3% uptick in mission availability and a 15% cut in fuel burn for C-130 operators. Airbus extends the model with its Skywise Fleet Performance+ suite, which allows easyJet to pre-empt system failures that historically triggered cancellations, thereby protecting revenue and passenger trust. These performance gains turn flight data monitoring from a cost center into a strategic profit lever and accelerate enterprise-wide adoption.
High Upfront Installation and Integration Costs Limiting Adoption Among Smaller Operators
Charter firms and regional airlines often operate on slim margins and older airframes that require extensive modification. The FAA estimates Part 135 SMS compliance will cost the segment USD 47.4 million each year, highlighting the capital burden for small fleets. Retrofits demand downtime, specialized labor, and certification paperwork that many small operators schedule only when forced. The result is a market bifurcation: large carriers move toward fleet-wide predictive analytics, while smaller outfits stay in compliance-only mode, missing efficiency benefits until hardware prices decline or leasing models emerge.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Deployment of Lightweight, Cloud-Enabled FDM Solutions for UAVs and Smaller Platforms
- Integration of Real-Time FDM Data into AI Platforms for Performance and Fuel Optimization
- Data Privacy and Ownership Concerns Delaying Broader Adoption
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Onboard devices retained a 68.22% share in 2024, anchoring the flight data monitoring market size to core flight safety demands. They supply time-critical data such as exceedance alerts to pilots and dispatchers. Yet on-ground platforms are growing at an 8.10% CAGR because airlines prefer centralized clouds that process multi-year histories across fleets. This architecture removes weight from the aircraft and enables advanced AI that would be impractical to host onboard. Increasing bandwidth availability and secure satellite links allow near-real-time downlink for after-action review minutes after touchdown. Airlines consolidate multiple OEM formats into common databases, improving cross-type benchmarking while cutting licensing costs. Honeywell and NXP's collaboration couples high-performance onboard processors with cloud APIs so operators can choose which analytics reside in the aircraft versus the data center. Regulatory bodies accept this hybrid design, accelerating certification for mixed fleets and letting low-cost carriers access sophisticated analytics without heavy avionics upgrades. Ground architectures also align with sustainability agendas because they prolong hardware lifecycles. Rather than retrofitting each aircraft for new algorithms, airlines update server-side software, slashing upgrade expense and e-waste.
Fixed-wing aircraft contributed 59.92% of the flight data monitoring market size in 2024, reflecting the broad global fleet of passenger and cargo jets that already carry recorders and quick-access devices. This installed base continues to purchase incremental upgrades, but its growth sits below the overall market average. In contrast, the unmanned aerial vehicle segment is expanding at a 10.01% CAGR because regulators are finalizing frameworks that open commercial corridors for inspection, logistics, and urban-air-mobility missions. Weight and power limits on drones push suppliers toward low-profile sensors, edge processors, and cellular or satellite data pipes. Lessons learned here now influence retrofit projects in legacy turboprops and helicopters, demonstrating reverse technology transfer. Rotary-wing fleets in emergency medical services and offshore energy remain niche yet steady adopters, drawn by the need to monitor engine health and exceedances in high-cycle missions. GE Aerospace's collaboration with Kratos Defense illustrates cross-pollination: innovations developed initially for cost-sensitive unmanned systems are being repackaged for manned regional jets. Platform convergence ensures that analytics created for one airframe class are portable across multiple types, reinforcing vendor ecosystems and reducing operator switching costs.
UAV growth also reshapes supply chains because non-traditional aviation firms-software startups, cellular operators, and logistics brands-purchase monitoring as a service rather than buying hardware outright. This subscription outlook compresses refresh cycles, encouraging vendors to migrate from one-time equipment sales toward recurring analytics revenues. The trend ultimately benefits airlines because it finances faster algorithmic innovation that spills into fixed-wing and rotary-wing fleets. As national authorities publish specific-category operating rules, they often make flight data monitoring compulsory for autonomous or remotely piloted commercial missions, locking in future demand.
The Flight Data Monitoring Market Report is Segmented by Installation Type (On-Board and On-Ground), Platform (Fixed-Wing, Rotary-Wing, and More), Component (Hardware, Software and Analytics, and Services), End User (Commercial Airlines, Cargo and Freight Operators. Business Jet Operators, UAV Service Providers, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America sustains leadership through advanced regulatory and operational environments, accounting for 30.33% of 2024 spending. Operators benefit from mature supply chains and the FAA's Safety Management System regulations, which incentivize comprehensive data capture and benchmarking across carriers. Airlines deploy AI-augmented analytics to boost dispatch reliability, cut fuel burn, and satisfy investors requesting environmental disclosures. The region's dense legacy fleet also assures a strong retrofit pipeline as carriers swap quick-access recorders for connectivity-enabled units. Collaborative frameworks such as the Aviation Safety Information Analysis and Sharing program amplify the return on each additional data set by revealing macro-level risk trends.
Asia-Pacific posts the fastest expansion at 7.67% CAGR through 2030, fueled by double-digit annual passenger growth in India and Southeast Asia alongside China's strategic investments in urban air mobility. Governments fund digital-aviation sandboxes, easing the certification burden for aircraft with standardized monitoring devices. Low-cost carriers in the region use fuel-optimization modules to defend razor-thin margins. At the same time, full-service airlines deploy predictive maintenance to preserve schedule integrity during rapid fleet ramp-ups. National vision plans often tie air-traffic expansion to sustainability metrics, giving flight data monitoring an essential role in validating carbon-reduction claims.
Europe maintains steady uptake due to EASA's risk-based oversight approach. The Data4Safety expansion in October 2024 integrated nine additional member states and eight airports, dramatically enlarging the pan-European safety data pool. Airlines align monitoring investments with environmental policies that price carbon and reward fuel efficiency. GDPR compliance remains a hurdle, but vendors address this through privacy-by-design architectures, encouraging broader participation. Cross-border operations benefit from common technical standards, allowing low-cost carriers to allocate aircraft anywhere in their networks without reengineering hard-wired data modules.
- Teledyne Controls (Teledyne Technologies Incorporated)
- Honeywell International Inc.
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- Safran SA
- Curtiss-Wright Corporation
- Flight Data Systems
- FLYHT Aerospace Solutions Ltd.
- Metro Aviation
- Brazos Safety Systems, LLC
- Groupe NSE
- Gogo Business Aviation (Gogo Inc.)
- Airbus SE
- General Electric Company
- Collins Aerospace (RTX Corporation)
- Spidertracks Ltd. (Vellox Group)
- Scaled Analytics Inc.
- Aerobytes Ltd.
- Helinalysis Ltd.
- Leonardo S.p.A
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Global mandates accelerating adoption of onboard flight data monitoring systems
- 4.2.2 Airlines prioritizing predictive maintenance to reduce operational disruptions and costs
- 4.2.3 Deployment of lightweight, cloud-enabled FDM solutions for UAVs and smaller platforms
- 4.2.4 Integration of real-time FDM data into AI platforms for performance and fuel optimization
- 4.2.5 Insurance-linked incentives encouraging airlines to adopt FDM programs
- 4.2.6 Growing emphasis on post-incident transparency and automated incident investigation
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront installation and integration costs limiting adoption among smaller operators
- 4.3.2 Data privacy and ownership concerns delaying broader adoption
- 4.3.3 Limited technical standardization across aircraft platforms and avionics
- 4.3.4 Lack of in-house analytics expertise to extract actionable insights
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Installation Type
- 5.1.1 Onboard
- 5.1.2 On-ground
- 5.2 By Platform
- 5.2.1 Fixed-wing
- 5.2.2 Rotary-wing
- 5.2.3 Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV)
- 5.3 By Component
- 5.3.1 Hardware
- 5.3.2 Software and Analytics
- 5.3.3 Services
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Commercial Airlines
- 5.4.2 Cargo and Freight Operators
- 5.4.3 Business Jet Operators
- 5.4.4 Helicopter EMS and Offshore Services
- 5.4.5 Defense and Homeland Security
- 5.4.6 UAV Service Providers
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Russia
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Teledyne Controls (Teledyne Technologies Incorporated)
- 6.4.2 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.3 L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.4 Safran SA
- 6.4.5 Curtiss-Wright Corporation
- 6.4.6 Flight Data Systems
- 6.4.7 FLYHT Aerospace Solutions Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Metro Aviation
- 6.4.9 Brazos Safety Systems, LLC
- 6.4.10 Groupe NSE
- 6.4.11 Gogo Business Aviation (Gogo Inc.)
- 6.4.12 Airbus SE
- 6.4.13 General Electric Company
- 6.4.14 Collins Aerospace (RTX Corporation)
- 6.4.15 Spidertracks Ltd. (Vellox Group)
- 6.4.16 Scaled Analytics Inc.
- 6.4.17 Aerobytes Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Helinalysis Ltd.
- 6.4.19 Leonardo S.p.A
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment










