
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1842444
농업용 항균제 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Agricultural Antibacterials - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
농업용 항균제 시장 규모는 2025년에 117억 달러, 2030년에는 147억 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되며 CAGR은 4.70%를 나타낼 전망입니다.
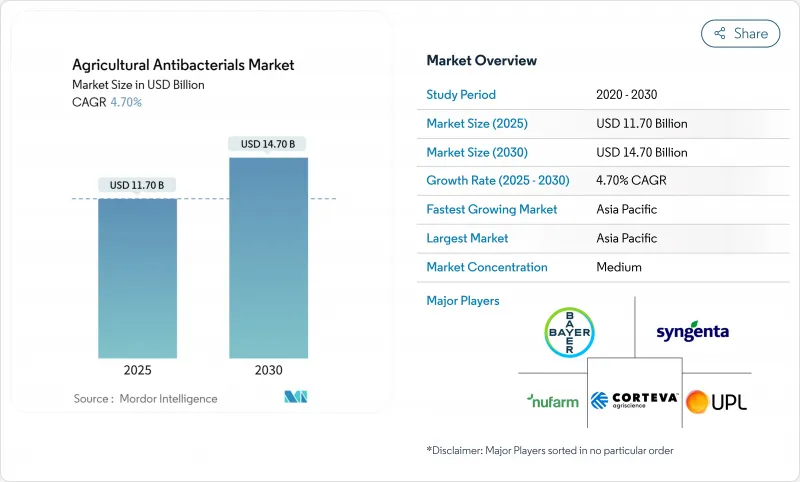
시장 확대의 배경은 기후와 관련된 박테리아 병압의 격화, 보호 작물 재배 증가, 나노 구리 및 생물학적 살균제의 기술 진보가 있습니다. 구리 기반 제품은 시장의 이점을 유지하지만, 규제 요건과 소매업체의 지속가능성에 대한 요구가 숙주에 특화된 생물학적 솔루션과 정밀 분산 시스템의 채택을 가속화하고 있습니다. 아시아태평양이 주요 수요지임에 변화는 없지만, 북미와 유럽은 2030년까지 시장 개척을 좌우하는 규제 프레임워크와 기술 기준을 확립하고 있습니다. 주요 공급업체는 생물학적 및 디지털 솔루션을 위해 전략적으로 포트폴리오를 다양화하고 있으며, IoT 지원 용도 타이밍, 박테리오파지 상용화 및 적은 분산량으로 최적의 효능을 발휘하는 나노 분산 제제를 통해 시장 기회를 창출하고 있습니다.
세계의 농업용 항균제 시장 동향과 인사이트
음식 공급 압력의 급상승
세계적인 식량 안보의 필요성으로부터 2050년까지 식량 생산량을 50% 증가시킬 필요가 있지만, 한편 세균성 병원체는 현재 연간 600억 달러를 넘는 작물 손실을 가져오고 있습니다. 아시아태평양의 농업 생산자는 체계적인 항균 프로그램을 실시하고 있으며, 중국은 2025년까지 연간 24만-25만 톤의 농약 소비량을 유지하고, 그 중에는 9만 톤 이상의 생물학적 제제도 포함됩니다. 수출 지향 과일 및 채소 생산자는 엄격한 잔류 농약 제로 요건을 준수하고 있으며 최적의 작물 수율과 시장 접근을 보장하는 프리미엄 항균 솔루션에 대한 수요가 지속되고 있습니다.
보호작물 면적 확대
북미 및 유럽의 온실 및 터널 재배는 연간 8-12%의 성장을 보이며, 그 결과 박테리아 성장에 적합한 온습도 프로파일을 가진 조밀한 식물 캐노피가 형성됩니다. 네덜란드 및 캐나다 토마토 및 오이 시설에서는 노지 재배에 비해 항균제의 살포 빈도가 20% 높다고 보고되었습니다. 네덜란드나 캐나다 토마토와 오이 시설에서는 노지 재배에 비해 항균제의 살포 빈도가 20% 높다고 보고되었습니다. 이에 대응하기 위해 공급업체는 수경 재배의 양액 순환을 보호하는 나노 분산액과 저 식물 독성 제제의 개발에 주력하고 있습니다.
식물 병원성 박테리아의 항생제 내성 증가
Erwinia amylovora와 Xanthomonas 균주는 5-7 시즌 이내에 스트렙토마이신 치료에 대한 내성을 획득합니다. 내성 문제는 사과와 감귤류와 같은 다년생 작물에서 특히 심각하며, 박테리아 집단은 성장 단계를 넘어 지속되고 수평 이동에 의해 내성 유전자를 축적합니다. 과수원에서는 여러 유효성분을 로테이션으로 사용하고 비용이 많이 드는 모니터링 시스템을 도입해야 하므로 투입 비용이 25-40% 높아집니다. 파지 블렌드와 구리와 아연의 하이브리드는 대체 솔루션을 제공하지만 이러한 채택에는 운영자 훈련과 특수 살포 장비가 필요합니다.
보고서에서 분석된 기타 성장 촉진요인 및 억제요인
- 기후 관련 세균발생률 상승
- 디지털 질병 예측과 IoT 센서의 급속한 보급
- 규제 요건 강화는 새로운 항생제 등록 위험
부문 분석
농업용 항균제 시장에서는 구리 화합물이 2024년 매출의 61%를 차지하고 확립된 멀티사이트 화학에 대한 지속적인 의존성을 입증했습니다. 나노구리 디스퍼전과 하이브리드 Cu/Zn 블렌드는 CAGR 13.6%를 나타낼 것으로 예상되며, 투여량과 잔류 수준의 저감을 요구하는 농업 수요에 힘입어지고 있습니다. 생물학적 제제 시장 점유율은 작지만 생물 농약 부문의 74%를 차지하며 강력한 성장률을 유지하고 있습니다. 유럽 연합이 2025년에 계획한 구리의 단계적 폐지는 지배적인 구리 부문에 큰 위험을 초래하여 박테리오파지 및 합성 펩티드로의 전환을 가속화시킬 수 있습니다.
내성 박테리아는 여러 돌연변이를 동시에 일으켜야 하기 때문에 멀티사이트 접근법은 여전히 효과적입니다. 그러나 환경 축적에 대한 우려와 소매 정책은 미래의 지속가능성에 도전하고 있습니다. 디티오카르바메이트와 아미드는 구리가 식물 독성을 일으키는 특수한 용도로 사용되는 반면, 기존의 항생제는 항균제 내성 정책에 의해 쇠퇴해 갑니다. 나노화된 전달 시스템은 40-60%의 금속 함량 감소로 동등한 현장 성능을 달성할 수 있어 생물학적 대체물질이 완전히 상업화될 때까지의 과도적인 해결책이 됩니다.
멀티사이트 세포벽 파괴제는 2024년 농업용 항균제 시장에서 43%의 압도적 점유율을 유지했습니다. 나노입자 캐리어 시스템에 의해 강화된 산화 스트레스 유도제는 병변 제어의 개선과 식물 독성의 저감을 나타내는 시험 데이터에 지지되어 연률 11.1%의 성장을 나타내고 있습니다. 단백질 합성 억제제는 특히 과수원에서의 사용에 있어서, 내성균의 개발이나 인간의 건강에의 응용과 공통의 메커니즘에 대한 우려로부터, 규제상의 제한에 직면하고 있습니다. DNA/RNA 억제제는 전신활성이 미관의 요구에 부합하는 온실에서의 관상용도로 고가로 거래되고 있지만, 승인된 용도가 한정되어 있기 때문에 농업에서의 광범위한 채용은 제한되고 있습니다.
이러한 메커니즘의 분포는 새로운 단일 표적 항생제에 대한 긴 등록 과정을 피하고 환경 요구 사항을 충족하면서 저항성과 싸우는 광역 스펙트럼의 화학 물질로 시장 변화를 반영합니다. 제품 유형은 기존의 구리 기반 제품에 산화 나노 제제와 생물학적 제제를 추가하고 여러 작물 유형에 걸쳐 종합적인 병해 방제를 실시했습니다.
지역 분석
아시아태평양은 2024년에 농업용 항균제 시장 점유율의 33%를 차지했고 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 8.2%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다. 중국의 농약 총 소비량은 25만 톤을 유지하고 있으며, 녹색 개발 정책에 따라 생물학적 제제가 9만 톤을 차지하고 있습니다. 인도의 농약 시장은 활성화되고 있으며, 정부의 주도로 2,600만 헥타르의 유기농업이 목표로 되고 있습니다. 이 지역은 열대 습윤지대이기 때문에 벼나 감귤류의 칸키츠에 지속적인 세균성 병해가 발생해, 연간을 통한 살포 프로그램이 필요하게 됩니다. 일본과 호주는 고가치의 신선한 식품 수출에 중점을 두고 있으며, 국제 잔류 요건을 준수하기 위해 나노 구리 분산액을 도입하고 있습니다.
북미는 기술 진보로 성숙한 시장을 유지하고 있습니다. 미국과 캐나다에서는 보호 재배가 꾸준히 성장하고 있으며, 순환 시스템에서 점적 주입형 항균제의 필요성이 높아지고 있습니다. EPA(미국 환경보호국)에 의한 농업용 항생제의 평가는 파지 기반 대체품 및 디지털 지원 시스템의 개발을 추진하는 한편 시장 불확실성을 창출하고 있습니다. 멕시코는 야채 수출 확대를 계속하고 있지만 미국의 수입 규제를 준수하기 위해 높은 살균제 사용량을 유지하고 있습니다.
유럽은 2030년까지 화학농약을 50% 절감해야 하는 유럽 그린딜이라는 규제 과제에 직면하고 있습니다. 2025년 구리 규제가 만료됨에 따라 생산자는 미생물에 의한 대안을 지향하고 연구는 합성 펩티드와 RNA 기반 살균제에 주력하고 있습니다. 독일, 프랑스, 스페인은 생물학적 농약의 도입을 선도하고 있으며, 중유럽과 동유럽의 생산자는 전환 기간 동안에도 효능을 유지하기 위해 나노 구리 솔루션을 평가했습니다. 영국은 EU 규정의 무결성을 유지하면서 환경 보호와 작물 안보 사이의 균형을 맞추기 위해 새로운 생물학적 제제의 합리화된 승인을 개발합니다. 러시아는 곡물 생산 면적을 늘리고 효율적인 구리 제제가 필요합니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 식량 공급압력의 급상승
- 보호작물작업면적 확대
- 기후 관련 세균발생률 상승
- 디지털 질병 예측과 IoT 센서의 급속한 보급
- 박테리오파지 기반 제품의 상업화
- 순환형 무비료 재배 시스템의 성장
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 식물 병원성 세균에서의 항생제 내성 증가
- 규제 요건 강화에 따른 신규 항생제 등록 위험
- 생물학적 살균제에 대한 짧은 유통 기한과 콜드체인 요건
- 중금속계 살균제의 ESG 및 소매업체의 상장 폐지
- 규제 상황
- 기술적 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계의 강도
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측(금액, 달러)
- 제품 유형별
- 구리 기반
- 디티오카르바메이트
- 아미드
- 나노 구리 및 하이브리드 구리/아연
- 항생제
- 생물학적 제제
- 기타 합성 유형
- 작용 방식별
- 다중 표적 세포벽 파괴제
- 단백질 합성 억제제
- 산화 스트레스 유도제
- DNA/RNA 합성 차단제
- 제형별
- 액상 현탁액
- 액상 분산성 과립(WDG)
- 습윤성 분말
- 나노 분산체 및 캡슐화 제제
- 적용 방법별
- 엽면 살포
- 종자/모종 처리
- 토양 주입
- 관개 시스템 및 점적 관개 주입
- 작물 유형별
- 곡물 및 잡곡
- 지방종자 및 콩류
- 과일 및 야채
- 상업용 현금작물
- 온실작물
- 잔디 및 관상용 작물
- 유통 채널별
- 제조업체 직접 판매
- 농업 소매/협동조합
- 온라인 및 전자상거래 플랫폼
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 기타 북미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 스페인
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 호주
- 뉴질랜드
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 중동
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 사우디아라비아
- 튀르키예
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Bayer AG
- Syngenta AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- Nufarm
- Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
- AMVAC Chemical Corporation
- UPL
- Albaugh LLC
- Gowan Company, LLC
- Certis Biologicals(A Subsidiary of Mitsui & Co., Ltd.)
- Koppert
- BioWorks Inc.(Biobest)
- BioSafe Systems, LLC
- Phagelux AgriHealth, Inc
- Parijat Industries(India) Pvt. Ltd.
제7장 시장 기회와 전망
KTH 25.10.28The agricultural antibacterials market size is valued at USD 11.70 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 14.70 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 4.70%.
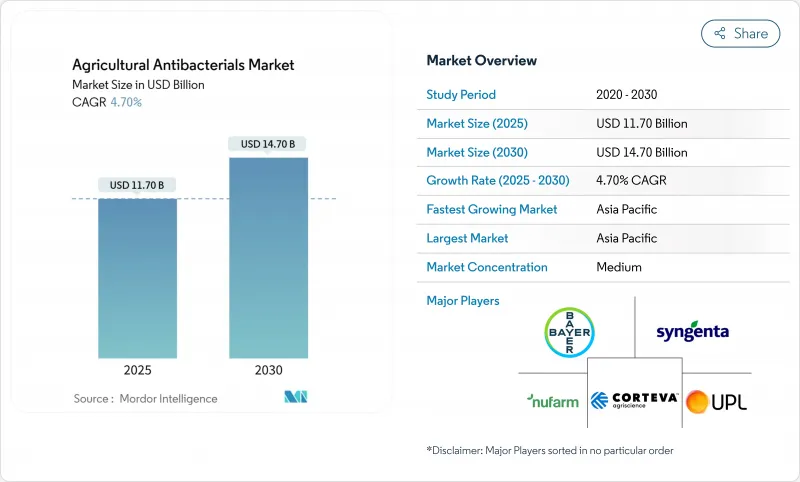
The market expansion is attributed to intensifying climate-related bacterial disease pressure, increased protected-crop cultivation, and technological advancements in nano-copper and biological bactericides. Although copper-based products maintain market dominance, regulatory requirements and retailer sustainability mandates are accelerating the adoption of host-specific biological solutions and precision application systems. The Asia-Pacific region remains the primary demand center, while North America and Europe establish regulatory frameworks and technological standards that will influence market development through 2030. Key suppliers are strategically diversifying their portfolios toward biological and digital solutions, generating market opportunities through IoT-enabled application timing, bacteriophage commercialization, and nano-dispersion formulations that deliver optimal efficacy at reduced application rates.
Global Agricultural Antibacterials Market Trends and Insights
Surging Food-Supply Pressure
Global food security requirements necessitate a 50% increase in food production by 2050, while bacterial pathogens currently generate annual crop losses exceeding USD 60 billion. Agricultural producers in the Asia-Pacific region implement systematic antibacterial programs, with China maintaining pesticide consumption at 240,000-250,000 metric tons annually through 2025, including over 90,000 metric tons of biologicals. Export-oriented fruit and vegetable producers comply with stringent zero-tolerance residue requirements, sustaining demand for premium antibacterial solutions that ensure optimal crop yields and market accessibility.
Expansion of Protected-Crop Acreage
Greenhouse and tunnel operations in North America and Europe experience 8-12% annual growth, resulting in dense plant canopies with temperature-humidity profiles conducive to bacterial growth.Tomato and cucumber facilities in the Netherlands and Canada report 20% higher antibacterial application frequencies compared to open-field operations. This increase drives demand for water-system compatible formulations. In response, suppliers focus on developing nano-dispersions and low-phytotoxic formulations to protect recirculating hydroponic nutrient streams.
Escalating Antibiotic Resistance in Plant-Pathogenic Bacteria
Erwinia amylovora and Xanthomonas strains develop resistance to streptomycin treatments within five to seven seasons. The resistance issue is particularly severe in perennial crops such as apples and citrus, where bacterial populations persist across growing seasons and accumulate resistance genes through horizontal transfer. Orchards face 25-40% higher input costs as growers must rotate multiple active ingredients and implement costly monitoring systems. While phage blends and copper-zinc hybrids offer alternative solutions, their adoption requires operator training and specialized spray equipment.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Climate-Linked Rise in Bacterial Incidence
- Rapid Uptake of Digital Disease Forecast and IoT Sensor
- Tightening Regulatory Requirements Create Registration Risk for New Antibiotics
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Copper compounds generated 61% of 2024 revenue in the agricultural antibacterial market, demonstrating the continued reliance on established multi-site chemistry. Nano-copper dispersions and hybrid Cu/Zn blends are experiencing growth at a 13.6% CAGR, driven by agricultural demands for reduced dosage and residue levels. While biologicals represent a smaller market share, they account for 74% of the biopesticide segment and maintain strong growth rates. The European Union's planned copper phase-out in 2025 presents a significant risk to the dominant copper segment and may accelerate the transition to bacteriophages and synthetic peptides.
The multi-site approach remains effective as bacterial resistance requires multiple simultaneous mutations. However, environmental accumulation concerns and retail policies challenge its future sustainability. Dithiocarbamates and amides serve specific applications where copper causes plant toxicity, while traditional antibiotics decline due to antimicrobial resistance policies. Investment flows toward nano-enabled delivery systems that achieve comparable field performance with 40-60% less metallic content, serving as transitional solutions until biological alternatives reach full commercial development.
Multi-site cell-wall disruptors maintain a dominant 43% share of the 2024 agricultural antibacterials market. Oxidative-stress inducers, enhanced by nano-particle carrier systems, demonstrate an 11.1% annual growth rate, supported by trial data showing improved lesion control and reduced phytotoxicity. Protein-synthesis inhibitors face regulatory restrictions due to resistance development and concerns over shared mechanisms with human health applications, particularly in orchard use. DNA/RNA blockers command higher prices in greenhouse ornamental applications where systemic activity meets aesthetic requirements, though limited approved uses restrict broader agricultural adoption.
The distribution of mechanisms reflects a market shift toward broad-spectrum chemistries that combat resistance while meeting environmental requirements, avoiding lengthy registration processes associated with new single-target antibiotics. Companies are integrating traditional copper-based products with oxidative nano-formulations and biological products to provide comprehensive disease control across multiple crop types.
The Agricultural Antibacterials Market is Segmented by Product Type (Copper-Based, and More), Mode of Action (Protein-Synthesis Inhibitors and More), Formulation Form (Liquid Suspensions and More), Application Method (Foliar Spray and More), Crop Type (Cereals and Grains, and More), Distribution Channel (Manufacturer Direct and More), and Geography (North America and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific holds 33% of the agricultural antibacterials market share in 2024 and is projected to grow at an 8.2% CAGR through 2030. China maintains its total pesticide consumption at 250,000 metric tons, with biologicals accounting for 90,000 metric tons due to green-development policies. India's agrochemical market is boosting, with government initiatives targeting 26 million hectares for organic farming. The region's tropical humidity creates persistent bacterial blight in rice and citrus canker, necessitating year-round application programs. Japan and Australia focus on high-value fresh produce exports, implementing nano-copper dispersions to comply with international residue requirements.
North America maintains a mature market with technological advancement. The United States and Canada show steady growth in protected cultivation, increasing the need for drip-injected antibacterials in recirculating systems. EPA evaluations of agricultural antibiotics create market uncertainty while driving development in phage-based alternatives and digital support systems. Mexico continues to expand its vegetable exports, maintaining high bactericide usage to comply with United States import regulations.
Europe faces regulatory challenges with the European Green Deal mandating a 50% reduction in chemical pesticides by 2030. The 2025 copper regulation expiration drives growers toward microbial alternatives, while research focuses on synthetic peptides and RNA-based bactericides. Germany, France, and Spain lead biological adoption, while Central and Eastern European producers evaluate nano-copper solutions to maintain efficacy during transition periods. The United Kingdom maintains EU regulatory alignment while developing streamlined approvals for new biologicals to balance environmental protection with crop security. Russia increases grain production area, requiring efficient copper formulations, though Western supplier access remains limited by geopolitical factors.
- Bayer AG
- Syngenta AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- Nufarm
- Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
- AMVAC Chemical Corporation
- UPL
- Albaugh LLC
- Gowan Company, L.L.C.
- Certis Biologicals (A Subsidiary of Mitsui & Co., Ltd.)
- Koppert
- BioWorks Inc. (Biobest)
- BioSafe Systems, LLC
- Phagelux AgriHealth, Inc
- Parijat Industries (India) Pvt. Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surging Food-Supply Pressure
- 4.2.2 Expansion of Protected-Crop Acreage
- 4.2.3 Climate-Linked Rise in Bacterial Incidence
- 4.2.4 Rapid Uptake of Digital Disease Forecast and IoT Sensor
- 4.2.5 Commercialisation of Bacteriophage-Based Products
- 4.2.6 Growth of Recirculating Soilless Systems
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Escalating Antibiotic Resistance in Plant-Pathogenic Bacteria
- 4.3.2 Tightening Regulatory Requirements Creates Registration Risk for New Antibiotics
- 4.3.3 Short Shelf Life and Cold-Chain Requirements for Biological Bactericides
- 4.3.4 ESG and Retailer De-listing of Heavy-Metal Bactericides
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Copper-Based
- 5.1.2 Dithiocarbamates
- 5.1.3 Amides
- 5.1.4 Nano Copper and Hybrid Cu/Zn
- 5.1.5 Antibiotics
- 5.1.6 Biologicals
- 5.1.7 Other Synthetic Types
- 5.2 By Mode of Action
- 5.2.1 Multi-site Cell-wall Disruptors
- 5.2.2 Protein-Synthesis Inhibitors
- 5.2.3 Oxidative Stress Inducers
- 5.2.4 DNA/RNA Synthesis Blockers
- 5.3 By Formulation Form
- 5.3.1 Liquid Suspensions
- 5.3.2 Liquid-Dispersible Granules (WDG)
- 5.3.3 Wettable Powders
- 5.3.4 Nano-dispersions and Encapsulates
- 5.4 By Application Method
- 5.4.1 Foliar Spray
- 5.4.2 Seed/Transplant Treatment
- 5.4.3 Soil Injection
- 5.4.4 Water-System and Drip-Irrigation Injection
- 5.5 By Crop Type
- 5.5.1 Cereals and Grains
- 5.5.2 Oilseeds and Pulses
- 5.5.3 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.5.4 Commercial Cash Crops
- 5.5.5 Greenhouse Crops
- 5.5.6 Turf and Ornamentals
- 5.6 By Distribution Channel
- 5.6.1 Manufacturer Direct
- 5.6.2 Ag-Retail/Co-ops
- 5.6.3 Online and E-commerce Platforms
- 5.7 By Geography
- 5.7.1 North America
- 5.7.1.1 United States
- 5.7.1.2 Canada
- 5.7.1.3 Mexico
- 5.7.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.7.2 Europe
- 5.7.2.1 Germany
- 5.7.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.7.2.3 France
- 5.7.2.4 Spain
- 5.7.2.5 Russia
- 5.7.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.7.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.3.1 China
- 5.7.3.2 India
- 5.7.3.3 Japan
- 5.7.3.4 Australia
- 5.7.3.5 New Zealand
- 5.7.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.4 South America
- 5.7.4.1 Brazil
- 5.7.4.2 Argentina
- 5.7.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.7.5 Middle East
- 5.7.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.7.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.7.5.3 Turkey
- 5.7.5.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.7.6 Africa
- 5.7.6.1 South Africa
- 5.7.6.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.7.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Bayer AG
- 6.4.2 Syngenta AG
- 6.4.3 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.4 Nufarm
- 6.4.5 Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.6 AMVAC Chemical Corporation
- 6.4.7 UPL
- 6.4.8 Albaugh LLC
- 6.4.9 Gowan Company, L.L.C.
- 6.4.10 Certis Biologicals (A Subsidiary of Mitsui & Co., Ltd.)
- 6.4.11 Koppert
- 6.4.12 BioWorks Inc. (Biobest)
- 6.4.13 BioSafe Systems, LLC
- 6.4.14 Phagelux AgriHealth, Inc
- 6.4.15 Parijat Industries (India) Pvt. Ltd.



















