
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1848321
탄닌 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Tannin - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
탄닌 시장 규모는 2025년 29억 8,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 2030년에 41억 4,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 예측 기간 동안 CAGR은 6.80%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

이러한 상승세는 가죽, 와인, 목재 복합재, 특수 영양제 등 분야에서 천연 원료 사용이 증가하는 추세에 크게 힘입고 있습니다. 규제가 강화되고 소비자들이 지속가능하고 친환경적인 제품을 점점 더 요구함에 따라 합성 첨가제 사용이 현저히 줄어들고 있습니다. 특히 농업 폐기물, 나무껍질, 해조류 등 원료 조달 방식의 혁신은 공급망 회복탄력성을 강화하고 순환경제 목표와 부합합니다. 이러한 진전은 기존 원자재 의존도를 낮출 뿐만 아니라 환경적 지속가능성을 주도합니다. 더불어 크롬 프리 가죽, 유기농 와인 기준, 포름알데히드 무첨가 목재 접착제의 신속한 도입은 산업 및 소비자 영역 모두에서 바이오 기반 폴리페놀에 대한 수요가 급증하고 있음을 보여줍니다. 시장 경쟁은 여전히 완만하지만, 추출 기술에서 우위를 점하고 수직적 통합을 추구하는 기업들은 독보적인 경쟁력을 확보하고 있습니다. 이러한 선도 기업들은 운영 효율성을 높일 뿐만 아니라 프리미엄 계약을 체결하고 시장 입지를 공고히 하고 있습니다. 이러한 추세는 혁신, 지속가능성, 변화하는 소비자 취향에 힘입어 탄닌 시장에 대한 낙관적인 장기 전망을 제시합니다.
세계의 탄닌 시장 동향 및 인사이트
가죽 산업에서 자연적이고 환경 친화적 무두질제에 대한 높은 수요
가죽 산업이 지속 가능한 무두질 방식으로 전환함에 따라, 기존 크롬 기반 화학 물질의 친환경 대안으로 여겨지는 식물성 탄닌 수요가 눈에 띄게 증가하고 있습니다. 유럽연합(EU)의 REACH 규제로 인해 가죽 가공 과정에서 유해 화학 물질에 대한 제한이 강화되면서 제조업체들은 천연 대체재로 눈을 돌리고 있습니다. 북미에서는 미국 환경보호청(EPA)이 특정 크롬 화합물을 발암성 물질로 지정하면서 식물성 무두질제로의 전환이 가속화되었습니다. 보고서에 따르면 식물성 무두질 가죽은 럭셔리 시장에서 프리미엄 가격을 형성할 뿐만 아니라 주요 패션 브랜드의 지속가능성 철학과도 부합합니다. 이들 브랜드는 이제 소비자 선호도와 규제 요구를 모두 충족시키기 위해 크롬 프리 소재를 조달 정책의 최우선 순위로 삼고 있습니다. 또한 첨단 바이오 마감 시스템의 등장으로 가죽 가공 방식이 변화하고 있으며, 생분해성 솔루션을 통해 내구성과 미적 매력을 높이는 동시에 지속가능성 기준을 충족시키고 있습니다. 이러한 산업 전반의 변화는 친환경 제품에 대한 소비자 수요 증가와 산업용 화학물질 사용 제한을 위한 규제 압박에 대한 대응을 보여줍니다. 자동차 시트, 고급 가죽 제품, 신발 등 주요 분야가 이 변화를 주도하며 지속가능하고 고품질 소재에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. 또한 순환 경제 원칙에 대한 강조가 증가하면서 가죽 산업은 폐기물 최소화와 자원 효율성으로 방향을 전환하고 있으며, 이는 지속 가능한 태닝으로의 움직임을 강화하고 있습니다.
와인과 음료 생산에 탄닌 사용 증가
와인 제조업자들이 색상 안정성 향상, 입안감 개선, 숙성 특성 최적화를 목표로 하면서 동시에 변화하는 규제 요건을 준수하기 위해 노력함에 따라 와인 제조용 탄닌에 대한 수요가 크게 증가하고 있습니다. 미국에서는 주류·담배세무국(TTB)이 정확한 사용 한도를 설정하여 레드 와인의 경우 1000갤런당 최대 24파운드(약 10.9kg), 화이트 와인의 경우 1000갤런당 6.4 GAE(갈란당 탄닌산량)까지 허용하고 있습니다. 이러한 표준화된 지침은 업계 전반에 걸쳐 일관된 채택을 촉진하고 있습니다. 유럽에서는 유럽 식품안전청(EFSA)이 동물 사료에 탄닌산을 최대 15mg/kg 농도로 사용하도록 승인하여 전통적인 와인 생산을 넘어 응용 범위를 확대했습니다. 전 세계적으로 국제포도원·와인기구(OIV)는 호두갈, 밤나무, 참나무, 포도씨 등 식물성 원료의 품질 기준을 정의함으로써 와인 제조용 탄닌 사용을 합법화했습니다. 또한 FDA의 특정 탄닌 화합물에 대한 GRAS(일반적으로 안전하다고 인정됨) 지정이 식품 및 음료 분야의 광범위한 적용을 촉진했습니다. 유기농 인증 프로그램은 천연 유래 탄닌에 대한 프리미엄 기회를 창출함으로써 시장 세분화에 기여하고 있습니다.
복잡한 추출 공정이 상업적 확장을 제한
탄닌 추출 공정의 기술적 복잡성과 자본 요구로 인해 시장 확장은 장벽에 직면해 있으며, 소규모 생산자와 신규 진입자들이 어려움을 겪고 있습니다. 미국 특허청에 등록된 200건 이상의 탄닌 추출 방법 특허는 효율적 생산에 필요한 기술적 정교함을 강조합니다. 국제표준화기구(ISO)는 탄닌 제품에 대한 엄격한 품질 기준을 설정하여 추출 매개변수에 대한 세심한 통제를 요구합니다. 이는 첨단 장비를 보유하지 않은 기업들에게 도전 과제를 제시합니다. 한편 유럽의약품청(EMA)의 의약품 등급 탄닌에 대한 우수제조관리기준(GMP)은 선진적인 품질 관리와 검증된 추출 방법을 요구합니다. 마찬가지로 미국 식품의약국(FDA)의 건강기능식품에 대한 현행 우수제조관리기준(cGMP)은 상세한 식물 추출 요건을 규정하여 규정 준수 비용을 증가시키고 기술적 난제를 가중시킵니다. 이러한 규제 및 기술적 장벽은 시장 진입을 지연시킬 뿐만 아니라 생산 비용을 상승시킵니다. 이는 가격에 민감한 부문과 신흥 시장에서 특히 합성 제품 대비 탄닌 기반 제품의 경쟁력을 저해할 수 있습니다.
부문 분석
2024년 기준 식물성 탄닌이 82.43%의 시장 점유율로 우위를 점하고 있으며, 이는 수십 년간 정교해진 추출 기술과 안정적인 공급망의 결과입니다. 이러한 탄닌은 케브라초, 아카시아, 밤나무, 참나무 등 전통적으로 선호되는 원료에서 추출됩니다. 견고한 농업 관행과 가공 시설을 바탕으로 한 시장 주도력은 최상급 품질과 안정적인 공급을 보장합니다. 미국 농무부 산림청은 국내 산림에서 나무껍질 탄닌을 추출하는 심층 연구를 수행하여 견고한 공급망 구축의 토대를 마련했습니다. 한편 유럽 산림 연구소는 산림 활력과 탄닌 원료 수요 간의 균형을 맞추는 지속 가능한 나무껍질 수확 지침을 발표했습니다. 이러한 전통적 원료는 광범위한 규제 승인을 받고 있으며, FDA는 특정 식물 유래 탄닌을 식품 사용에 안전하다고 인정합니다. 또한 국제산림연구기구연합(IUFRO)은 환경 기준을 저해하지 않으면서 탄닌의 안정적 공급을 보장하는 지속가능한 조달 관행을 주도하고 있습니다.
갈조류는 가장 급성장하는 공급원으로 떠오르고 있으며, 2030년까지의 예측 CAGR은 8.04%를 자랑합니다. 이 급성장은 갈조류의 우수한 플로로탄닌 생리활성과 의약품으로서의 역할의 급성장에 기인합니다. 미국 해양 대기청은 갈조류 양식을 환경에 해를 끼치지 않고 수확할 수 있는 지속 가능한 해양 자원이라고 합니다. 이를 뒷받침하기 위해 유럽 해양 어업 기금(European Maritime and Fisheries Fund)은 해양 생명공학 연구에 자금을 제공하고 의약품과 영양 보충제 모두에 적용할 수 있는 플로로탄닌 추출에 스포트라이트를 적용하고 있습니다. 일본에서는 해양 연구 개발 기구가 선진적인 양식 방법을 개척해, 갈조류로부터 연간을 통해 안정적으로 플로로탄닌을 얻을 수 있도록 하고 있습니다. 국제 해조 협회는 이러한 해양 유래 탄닌의 품질 기준을 설정하여 고급 용도로의 통합을 촉진하고 있습니다. 이러한 진보로 갈조류는 틈새 응용 분야에서 요구되는 공급원이되었을뿐만 아니라 육상 식물의 수확과 관련된 지속가능성 문제를 해결합니다.
지역 분석
2024년 유럽은 엄격한 환경 규제와 천연 탄닌 응용을 주도하는 견고한 산업 인프라를 바탕으로 34.11%의 압도적 시장 점유율을 차지할 전망입니다. 유럽 식품안전청(EFSA)은 식품, 사료 및 산업용 탄닌에 대한 명확한 안전 프로토콜을 수립하여 규제 확실성을 조성함으로써 투자를 유치하고 있습니다. 한편 유럽의약품청(EMA)은 특정 탄닌 화합물의 의약품 사용을 승인하여 수익성 높은 틈새 시장을 창출했습니다. EU의 REACH 규정은 산업 내 유해 화학물질을 제한하며 탄닌과 같은 안전하고 자연적인 대체재로의 전환을 의무화합니다. 유럽위원회의 순환경제 실행계획은 농림 폐기물을 바이오 기반 화학물질로 전환하는 것을 주창하며 해당 지역의 의지를 더욱 강조합니다. 재정 측면에서는 유럽투자은행이 탄닌 추출 및 가공을 포함한 지속가능한 기술 벤처 기업을 지원하며 지역 인프라를 강화하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양 지역은 급속한 산업화와 천연 제품 사용을 장려하는 진화하는 규제에 힘입어 2030년까지 연평균 7.74%의 성장률을 기록할 것으로 전망되며 급속히 부상하고 있습니다. 중국 국가발전개혁위원회가 주도하는 전략적 개발 계획은 이제 바이오 기반 화학 물질을 중점으로 삼아 탄닌 생산의 길을 열고 있습니다. 인도 화학비료부는 생산 연계 인센티브를 시행하여 농산물 부산물로부터의 탄닌 추출을 비롯한 천연 제품 제조를 지원하고 있습니다. 일본 후생노동성은 기능성 식품의 지평을 넓혀 다양한 형태의 탄닌 기반 원료를 수용하고 있습니다. 동남아시아 국가연합(ASEAN)은 천연 제품에 대한 지역 표준을 마련하여 탄닌 소재 무역을 간소화하고 있습니다. 호주 농림부는 유기농 인증 프로그램을 시작하여 천연 유래 탄닌의 프리미엄 시장 진출을 지원함으로써 지역 시장 구조를 다각화하고 있습니다.
북미는 합성 대체재보다 천연 대체재를 장려하는 규제 조치에 힘입어 꾸준한 성장 궤도를 그리고 있습니다. 미국 식품의약국(FDA)의 탄닌 화합물 GRAS(일반적으로 안전하다고 인정되는 물질) 지정이 식품·음료 분야 진출의 길을 열었습니다. 미국 환경보호청(EPA)의 포름알데히드 배출 기준은 목재 제조용 탄닌 기반 접착제의 활용 근거를 강화했습니다. 한편, 주류·담배세무국(TTB)은 와인 처리 재료 규정을 개선하여 탄닌 사용에 대한 명확한 지침과 한계를 설정함으로써 혁신과 안전 사이의 균형을 맞추고 있습니다. 원료 공급원이 풍부한 남미에서는 브라질이 지속 가능한 산림 경영에 대한 투자를 주도하며 탄닌 공급망을 강화하고 있습니다. 중동 및 아프리카 지역에서는 농업 폐기물 가치화 촉진 국제 프로그램과 순환 경제 원칙에 대한 인식 제고로 인해 관심이 급증하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 가죽 산업에서 천연 및 친환경 태닝 에이전트에 대한 높은 수요
- 와인이나 음료 제조에 탄닌 사용 증가
- 식품 산업에서 지속 가능하고 천연 원료 선호
- 목재 접착제 및 파티클보드 산업 성장
- 농업 폐기물 및 나무껍질 추출물로부터의 지속 가능한 조달
- 탄닌의 항산화 및 기타 특성으로 인한 기능성 식품에서 활용 증가
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 복잡한 추출 공정이 상업 규모 확대를 제한
- 지역별 추출 수율 변동성
- 엄격한 FDA 및 EU 규제로 인한 준수 비용 증가
- 합성 대체재와의 경쟁
- 공급망 분석
- 규제 전망
- Porter's Five Forces
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력/소비자
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 원료별
- 식물
- 갈조류
- 용도별
- 식품 및 음료
- 의약품 및 영양보조식품
- 가죽 산업
- 목재 산업
- 기타
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 기타 북미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 이탈리아
- 프랑스
- 스페인
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 랭킹 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Sodra Skogsagarna
- Ajinomoto Co., Inc
- Silvateam Group
- Laffort Holding
- TANAC
- Ulrich Holding GmbH
- Esseco Group Srl
- Tanin dd Sevnica
- Tannin Corporation
- NTE Company(Pty)Limited
- Gallotannin Co. Ltd
- Forestal Quebracho SA
- Polson Ltd.
- UCL Company(Pty) Ltd
- Silvateam group
- Xi'an Prius Biological Engineering Co.,Ltd
- Forestal Mimosa Limited
- ChemFaces Biochemical Co., Ltd.
- Glentham Life Sciences Limited
- FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
HBR 25.11.12The tannin market size reached USD 2.98 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 4.14 billion by 2030, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.80% during the forecast period.
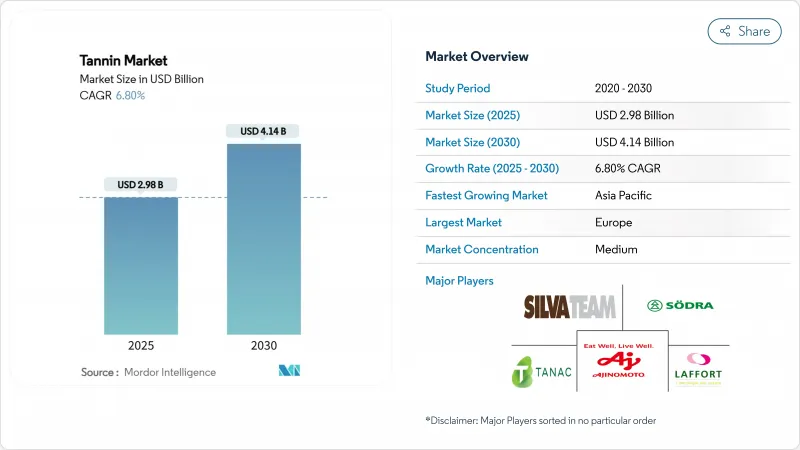
This upswing is largely fueled by a rising inclination towards natural inputs in sectors like leather, wine, wood composites, and specialty nutrition. As regulations tighten and consumers increasingly demand sustainable, eco-friendly products, there's a pronounced shift away from synthetic additives. Innovations in sourcing, especially with agro-waste, bark, and seaweed, bolster supply chain resilience and resonate with circular economy goals. Such strides not only lessen reliance on conventional raw materials but also champion environmental sustainability. Furthermore, the swift embrace of chrome-free leather, organic wine standards, and formaldehyde-free wood adhesives underscores the burgeoning appetite for bio-based polyphenols in both industrial and consumer realms. While market competition remains moderate, firms excelling in extraction technology and pursuing vertical integration are carving out a distinct advantage. These pioneers are not only enhancing operational efficiencies but also clinching premium contracts and solidifying their market stance. This trajectory paints a bullish long-term outlook for the tannin market, propelled by innovation, sustainability, and shifting consumer tastes.
Global Tannin Market Trends and Insights
High demand for natural and eco-friendly tanning agents in leather industry
As the leather industry pivots towards sustainable tanning, there's a notable surge in demand for vegetable tannins, seen as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional chromium-based chemicals. Stricter limitations on hazardous chemicals in leather processing, driven by the European Union's REACH regulation, are pushing manufacturers towards natural substitutes. In North America, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's designation of certain chromium compounds as carcinogenic has hastened the shift to plant-based tanning agents. Reports highlight that vegetable-tanned leather not only fetches a premium in luxury markets but also resonates with the sustainability ethos of leading fashion brands. These brands are now prioritizing chrome-free materials in their sourcing policies, aligning with both consumer preferences and regulatory demands. Moreover, the advent of advanced bio-finishing systems is transforming leather processing, offering biodegradable solutions that boost durability and aesthetic appeal while meeting sustainability benchmarks. This industry-wide shift underscores a response to heightened consumer demand for eco-friendly products and regulatory pushes to curtail industrial chemical use. Key sectors championing this change include automotive upholstery, luxury leather goods, and footwear, all witnessing a rising appetite for sustainable, high-quality materials. Furthermore, a growing emphasis on circular economy principles is steering the leather industry towards waste minimization and resource efficiency, bolstering the move to sustainable tanning.
Increasing use of tannins in wine and beverage production
The demand for oenological tannins is witnessing significant growth as winemakers aim to improve color stability, enhance mouthfeel, and optimize aging characteristics, all while adhering to evolving regulatory requirements. In the United States, the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) has established precise usage limits, allowing up to 24 pounds of tannins per 1000 gallons in red wine and 6.4 GAE per 1000 gallons in white wine. These standardized guidelines are driving consistent adoption across the industry. In Europe, the European Food Safety Authority has approved tannic acid for use in animal feed at concentrations up to 15 mg/kg, thereby expanding its applications beyond traditional wine production. Globally, the International Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV) has legitimized the use of oenological tannins by defining quality standards for botanical sources such as nutgalls, chestnut, oak, and grape seeds. Additionally, the FDA's GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) designation for specific tannin compounds has facilitated their integration into broader food and beverage applications. Organic certification programs further contribute to market segmentation by creating premium opportunities for naturally sourced tannins.
Complex extraction processes limit commercial scaling
Market expansion faces hurdles due to the technical intricacies and capital demands of tannin extraction processes, with smaller producers and newcomers feeling the pinch. Over 200 patents on tannin extraction methods, recorded by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, underscore the technological finesse needed for efficient production. The International Organization for Standardization has set stringent quality benchmarks for tannin products, necessitating meticulous control over extraction parameters. This poses challenges for firms without cutting-edge equipment. Meanwhile, the European Medicines Agency's Good Manufacturing Practice mandates for pharmaceutical-grade tannins call for advanced quality control and validated extraction methods. Similarly, the FDA's Current Good Manufacturing Practice guidelines for dietary supplements stipulate detailed botanical extraction requirements, driving up compliance costs and adding to technical challenges. Such regulatory and technical hurdles not only decelerate market entry but also inflate production expenses. This could hinder the competitiveness of tannin-based products, especially against synthetic counterparts, in price-sensitive sectors and emerging markets.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Tannin's antioxidant and other properties drives its use in nutraceuticals
- Growth in the wood adhesive and particleboard industry
- Variability in extraction yiels across geography
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2024, plant-based tannins dominate the market with an 82.43% share, a testament to decades of refined extraction methods and dependable supply chains. These tannins are sourced from traditional favorites like quebracho, acacia, chestnut, and oak. This market leadership is bolstered by robust agricultural practices and processing facilities, ensuring top-notch quality and dependable supply. The U.S. Department of Agriculture's Forest Service has conducted in-depth studies on extracting bark tannins from the nation's forests, paving the way for a solid supply chain. Meanwhile, the European Forest Institute has rolled out sustainable bark harvesting guidelines, balancing forest vitality with the demand for tannin raw materials. These traditional sources enjoy broad regulatory acceptance, with the FDA deeming specific plant-derived tannins safe for food use. Furthermore, the International Union of Forest Research Organizations champions sustainable sourcing practices, ensuring a steady supply of tannins without compromising environmental standards.
Brown algae is emerging as the fastest-growing source, boasting an 8.04% CAGR projected through 2030. This surge is attributed to the algae's superior phlorotannin bioactivity and its burgeoning role in pharmaceuticals. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration vouches for brown algae cultivation, deeming it a sustainable marine resource that can be harvested without harming the environment. Backing this, the European Maritime and Fisheries Fund is funding research into marine biotechnologies, spotlighting phlorotannin extraction for both pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications. In Japan, the Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology has pioneered advanced cultivation methods, ensuring brown algae consistently yield phlorotannins year-round. The International Seaweed Association has set quality benchmarks for these marine-derived tannins, facilitating their integration into premium applications. Such advancements not only elevate brown algae as a sought-after source for niche applications but also address the sustainability challenges tied to harvesting terrestrial plants.
The Tannin Market Report is Segmented by Source (Plant and Brown Algae); Application (Food and Beverage, Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical, Leather Industry, Wood Industry, and Others); and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
In 2024, Europe commands a dominant 34.11% market share, bolstered by stringent environmental regulations and a robust industrial framework that champions natural tannin applications. The European Food Safety Authority has set forth definitive safety protocols for tannins in food, feed, and industrial uses, fostering a climate of regulatory certainty that attracts investments. Meanwhile, the European Medicines Agency has greenlit specific tannin compounds for pharmaceutical use, carving out lucrative market niches. The EU's REACH regulation curbs hazardous chemicals in industries, mandating a shift towards safer, natural alternatives like tannins. Further underscoring the region's commitment, the European Commission's Circular Economy Action Plan champions the transformation of agricultural and forestry waste into bio-based chemicals. On the financial front, the European Investment Bank is backing sustainable tech ventures, including tannin extraction and processing, bolstering the region's infrastructure.
Asia-Pacific is on a rapid ascent, projected to grow at a 7.74% CAGR through 2030, fueled by swift industrialization and evolving regulations that endorse natural product uses. China's strategic development plans, spearheaded by the National Development and Reform Commission, now spotlight bio-based chemicals, paving the way for tannin production. In India, the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers rolls out production-linked incentives, bolstering the manufacturing of natural products, notably tannin extraction from agricultural byproducts. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare broadens the horizon for functional foods, now embracing tannin-based ingredients in varied formats. The Association of Southeast Asian Nations sets the stage with regional standards for natural products, streamlining trade for tannin materials. Down under, Australia's Department of Agriculture launches organic certification programs, paving the way for a premium market for naturally sourced tannins, thus diversifying the regional market landscape.
North America charts a steady growth trajectory, driven by regulatory measures that champion natural substitutes over synthetic ones. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration's GRAS determinations for tannin compounds pave their way into the food and beverage sector. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's standards on formaldehyde emissions bolster the case for tannin-based adhesives in wood manufacturing. Meanwhile, the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau refines regulations on wine treating materials, setting clear guidelines and limits for tannin use, balancing innovation with safety. South America, with its rich tapestry of raw material sources, sees Brazil spearheading investments in sustainable forestry, fortifying tannin supply chains. In the Middle East and Africa, there's a burgeoning interest, spurred by international programs advocating agricultural waste valorization and a rising consciousness of circular economy tenets.
- Sodra Skogsagarna
- Ajinomoto Co., Inc
- Silvateam Group
- Laffort Holding
- TANAC
- Ulrich Holding GmbH
- Esseco Group Srl
- Tanin d.d. Sevnica
- Tannin Corporation
- NTE Company (Pty) Limited
- Gallotannin Co. Ltd
- Forestal Quebracho S.A.
- Polson Ltd.
- UCL Company (Pty) Ltd
- Silvateam group
- Xi'an Prius Biological Engineering Co.,Ltd
- Forestal Mimosa Limited
- ChemFaces Biochemical Co., Ltd.
- Glentham Life Sciences Limited
- FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 High Demand for Natural and Eco-Friendly Tanning Agents in Leather Industry
- 4.2.2 Increasing Use of Tannins in Wine and Beverage Production
- 4.2.3 Preference of Sustainable, And Natural Ingredients in Food Industry
- 4.2.4 Growth in the Wood Adhesive and Particleboard Industry
- 4.2.5 Sustainable Sourcing from Agro-Waste and Bark Extracts
- 4.2.6 Tannin's Antioxidant and Other Properties Drives Its Use in Nutraceuticals
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Complex Extraction Processes Limit Commercial Scaling
- 4.3.2 Variability In Extraction Yield Across Geography
- 4.3.3 Stringent FDA And EU Regulation Increase Compliance Costs
- 4.3.4 Competition From Synthetic Alternatives
- 4.4 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Source
- 5.1.1 Plant
- 5.1.2 Brown Algae
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Food and Beverage
- 5.2.2 Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical
- 5.2.3 Leather Industry
- 5.2.4 Wood Industry
- 5.2.5 Others
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Mexico
- 5.3.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.2.1 Germany
- 5.3.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.2.3 Italy
- 5.3.2.4 France
- 5.3.2.5 Spain
- 5.3.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.3.1 China
- 5.3.3.2 India
- 5.3.3.3 Japan
- 5.3.3.4 Australia
- 5.3.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 South Africa
- 5.3.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.3 United Arab Emirates
- 5.3.5.4 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials (if available), Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Sodra Skogsagarna
- 6.4.2 Ajinomoto Co., Inc
- 6.4.3 Silvateam Group
- 6.4.4 Laffort Holding
- 6.4.5 TANAC
- 6.4.6 Ulrich Holding GmbH
- 6.4.7 Esseco Group Srl
- 6.4.8 Tanin d.d. Sevnica
- 6.4.9 Tannin Corporation
- 6.4.10 NTE Company (Pty) Limited
- 6.4.11 Gallotannin Co. Ltd
- 6.4.12 Forestal Quebracho S.A.
- 6.4.13 Polson Ltd.
- 6.4.14 UCL Company (Pty) Ltd
- 6.4.15 Silvateam group
- 6.4.16 Xi'an Prius Biological Engineering Co.,Ltd
- 6.4.17 Forestal Mimosa Limited
- 6.4.18 ChemFaces Biochemical Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.19 Glentham Life Sciences Limited
- 6.4.20 FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation



















