
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1849914
데이터센터 건설 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Data Center Construction - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
데이터센터 건설 시장 규모는 2025년에 2,813억 4,000만 달러, 2030년에는 4,001억 6,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 2025-2030년 CAGR은 7.30%를 나타낼 것으로 예상됩니다.

이 확대는 AI 대응 용량에 대한 수요의 급증, 클라우드 마이그레이션의 보급, 디지털 인프라를 사용자에게 접근하는 에지 전개를 반영하고 있습니다. 하이퍼스케일 운영자의 설비 투자는 크게 급증하고 표준화된 반복 가능한 구축 모델을 선호하는 견고한 세계 구축 파이프라인으로 전환되고 있습니다. 그러나 변압기와 배전반 공급망의 혼란은 납품 리드타임을 120주 이상으로 늘리고 일정의 확실성을 위협하고 프로젝트의 위험을 높입니다. 에너지 효율에 대한 규제의 압력과 병행하여, 소유자는 프로젝트의 초기 단계부터 현장 재생에너지와 열 회수 시스템을 통합할 필요가 있어 설계의 복잡성이 증가하는 한편, 급성장하고 있는 그린본드 파이낸스에의 액세스도 어려워지고 있습니다.
세계의 데이터센터 건설 시장 동향과 인사이트
클라우드 애플리케이션, AI, 빅 데이터 워크로드 확대
고밀도 AI 랙에서는 랙당 50-100kW의 전력이 요구되고 설계 개요가 근본적으로 변화하여 기존의 공냉 시스템보다 액냉이 선호되도록 되어 있습니다. 마이크로소프트사만으로도 2025년 AI 인프라에 CAPEX에 800억 달러를 기록, 중복 400kV 급전과 현장 변전소를 갖춘 기가와트 스케일 캠퍼스를 설계하는 빌더에 박차를 가하고 있습니다. 이러한 설비에 대한 구리 수요는 이미 기존 클라우드 설비의 6배 수준에 달하고 있으며, 고급 열 관리 설비를 위한 전문업체의 성장 분야를 지원하고 있습니다. 텍사스에 있는 크루소의 1.2GW 캠퍼스와 같은 프로젝트는 데이터센터 건설 시장이 전통적인 건설 기법을 늘리고 있는 방법을 보여주며, 모듈식 블록, 메가와트급 침지 탱크, AI 컴퓨팅 로드맵에 보조를 맞춘 빠른 허가 전략이 필요합니다.
하이퍼스케일 설비 도입 가속
하이퍼스케일 시설의 수용 능력은 2030년까지 3배가 될 것으로 예측되고 있으며, 전 세계적으로 증가하는 면적의 대부분을 차지합니다. 터너 컨스트럭션이 오하이오주에 건설한 192MW의 IT 파워를 갖춘 20억 달러의 밴티지 시설은 대량 조달과 조립식 스키드를 통해 단가를 낮추는 표준화된 반복 빌드 접근법의 전형입니다. 이 모델은 규모의 경제를 확보하는 한편, 전력이 풍부한 시장에 활동을 집중시키고, 노동력 공급력을 희박시키고, 버지니아 북부와 더블린 등 지역에서는 임금 프리미엄을 20% 이상으로 밀어 올립니다. 재무구조는 수십억 달러 규모의 전력구매계약에 의존하고 있으며, 전력회사의 상호연결 대기행렬과 청정에너지 목표가 종종 건설단계를 결정하게 됩니다.
부동산, 설치, 유지 보수 비용 상승
노동력 부족은 버지니아주 북부의 3.5GW 클러스터 전체에서 전기기사와 배관공 임금에 20%의 프리미엄을 올리고 계약자의 가동률을 제약하며 프로젝트 일정을 연장하고 있습니다. 개발자들은 토지와 전력이 비교적 저렴한 피닉스와 마드리드와 같은 2차 도시를 찾게 되었습니다. 철골 뿌리와 개폐 장치의 대량 구매 계약과 구리의 장기 헤지가 DPR 구조와 같은 비용 제어 전략을 지원합니다. 기존의 콘크리트 쉘이 67-110만 달러인 반면 철골 프레임은 20년간의 라이프사이클 비용이 35만 달러로 여전히 비용면에서 유리합니다.
부문 분석
2024년 데이터센터 건설 시장 점유율의 58.2%를 Tier 3 자산이 차지하고, 균형 잡힌 중복성과 설비 투자 프로파일을 통해 사실상 기업 표준으로서의 역할을 강화했습니다. 한편, 은행, 증권거래소, 공공기관의 클라우드 지령이 99.995%의 업타임에 프리미엄을 지불하기 때문에 티어 4 수요는 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 7.8%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다. 티어 4 프로젝트에서는 유틸리티 이중화, 2N 파워트레인, 구획화된 방화 구역 등 건설의 복잡성이 2배가 되는 경우가 많으며, Tier 2 설계도에 비해 예산이 최대 70% 증가합니다. 터너 컨스트럭션이 노스캐롤라이나주에서 실시한 모듈식 Tier4 프로젝트에서는 공장에서 테스트한 파워 포드를 사용하여 시운전에 걸리는 시간을 15% 단축했습니다.
개발자는 또한 라이프사이클의 경제성을 중요시합니다. 따라서 데이터센터 건설 시장에서는 기계, 전기, 제어를 통합하고 최초 전원 투입 시 Tier4 인증을 받는 설계 시공 컨소시엄이 증가하고 있습니다. 조립식 냉동기 및 컨테이너형 UPS는 Tier4 준수를 희생하지 않고 규모를 확장할 수 있어 수요 증가에 적합한 지출을 가능하게 하는 다단계 전개를 지원합니다.
코로케이션은 2024년 매출의 54.3%를 유지하며 멀티테넌트의 유연성과 시장 투입 속도의 가치 제안을 강조했습니다. 하지만 자사의 하이퍼스케일러는 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 8.5%를 나타내 클라우드 대기업이 핵심 인프라를 소유하는 전략적 움직임을 반영하고 있습니다. 100억 달러를 들여 건설된 메타 루이지애나 캠퍼스는 400만 평방 피트의 레이아웃을 AI 트레이닝 클러스터 전용으로 사용하고 있으며, 600MW의 태양광 발전 PPA에 지원되고 있습니다. 코로케이션 사업자는 빌드 투 슈트 홀이나 액냉 대응 플로어를 제공하는 것으로 대응해, 하이퍼스케일인 확장 중에서도 관련성을 유지하고 있습니다.
건설 형태는 다양화되고 있습니다. 코로케이션 홀은 유연한 케이지 레이아웃, 핫 아일 봉쇄 및 다양한 테넌트 밀도를 지원하는 공유 미트 미룸을 필요로 합니다. 하이퍼스케일러는 MW당 설비 투자액을 20% 줄이기 위해 12MW 블록을 쿠키 커터 방식으로 복제하는 것을 선호합니다. 공장에서 조립된 구조용 강철은 미리 용접된 상태로 현장에 도착하기 때문에 30MW 건물의 건설 기간은 3주로 단축됩니다. 그 결과 데이터센터 건설 시장은 EPC 공급업체를 하이퍼스케일러를 위한 수십억 달러 규모의 세계 프레임워크 계약과 에지 및 엔터프라이즈 수요를 위한 지역 프레임워크로 점차 세분화하고 있습니다.
데이터센터 건설 시장은 티어유형(Tier 1과 Tier 2, Tier 3과 티어4), 데이터센터 유형(코로케이션, 자작 하이퍼스케일러(CSP), 엔터프라이즈, 엣지), 인프라(전기 인프라, 기계 인프라), 지역별로 구분됩니다. 시장 예측은 금액(달러)으로 제공됩니다.
지역별 분석
독일은 유럽 데이터센터 건설 시장의 핵심이며 2024년에는 세계 데이터센터 건설 시장 규모의 약 6%를 차지했습니다. 특히 프랑크푸르트, 베를린, 함부르크 등 주요 거점에 집중하는 견고한 디지털 인프라는 세계의 기술 대기업으로부터 많은 투자를 유치하고 있습니다. 이 나라의 지속가능한 데이터센터 개발에 대한 노력은 엄격한 에너지 효율 규제와 신재생에너지 채택 확대를 통해 분명합니다. 특히 프랑크푸르트는 유럽 중심의 위치와 광범위한 광섬유 연결의 혜택을 받아 중요한 디지털 허브로 등장합니다. 첨단 기술 생태계, 숙련된 노동력, 안정된 정치 환경이 독일 데이터센터를 더욱 강화하고 있습니다. 독일의 데이터센터는 혁신적인 냉각 기술과 지속 가능한 건설 기술에 점점 더 중점을 두고 업계의 환경 책임에 대한 새로운 기준을 세우고 있습니다.
기타 혜택
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 클라우드 애플리케이션, AI, 빅 데이터 워크로드 증가
- 하이퍼스케일 시설의 도입을 가속
- 인구밀집지 부근에서의 엣지 컴퓨팅의 구축 증가
- 재생에너지의 의무화가 시설 설계를 형성
- 조립식/모듈식 빌드에 의해 시장 투입까지의 시간을 단축
- ESG 연동형 그린 본드 대출이 설비 투자를 활성화
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 부동산, 설치, 유지 보수 비용 상승
- 보다 엄격한 에너지 소비와 탄소 규제의 제한
- 고급 액체 냉각을 위한 숙련 노동자 부족
- 고용량 파워 기어 공급 체인의 불안정성
- 공급망 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술 전망
- Porter's Five Forces
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 소비자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
- 주요 데이터센터 통계
- 지역 수준의 종합적인 데이터센터 운영자(MW 단위)
- 다양한 지역에 있어서의 향후의 주요 데이터센터 프로젝트 일람(2025-2030년)
- 데이터센터 건설의 CAPEX와 OPEX
- 데이터센터의 전력 흡수 용량(MW), 지역(2023년 및 2024년)
- 다양한 지역에 있어서 데이터센터 건설에의 인공지능(AI) 임베디드
- 규제 및 컴플라이언스의 틀
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 티어 유형별
- Tier 1 및 Tier 2
- Tier 3
- Tier 4
- 데이터센터 유형별
- 코로케이션
- 자체 구축 하이퍼스케일러(CSP)
- 엔터프라이즈 및 엣지
- 인프라별
- 전기 인프라별
- 전력 분배 솔루션
- 전력 백업 솔루션
- 기계 인프라별
- 냉각 시스템
- 랙 및 캐비닛
- 서버 및 스토리지
- 기타 기계 인프라
- 일반 건설
- 서비스 - 설계 및 컨설팅, 통합, 지원 및 유지보수
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 호주 및 뉴질랜드
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 걸프 협력 회의 국가
- 튀르키예
- 이스라엘
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 이집트
- 나이지리아
- 기타 아프리카
- Tier 1 및 Tier 2
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 메가와트(MW) 용량 기준 데이터센터 인프라 투자(2024년 대 2030년)
- 데이터센터 건설 현황(주요 공급업체 목록)
- 기업 프로파일
- AECOM
- Turner Construction Co.
- DPR Construction
- Jacobs Solutions Inc.
- Skanska AB
- Balfour Beatty plc
- Whiting-Turner Contracting Co.
- Hensel Phelps
- Fortis Construction Inc.
- Goodman Group
- PT Jaya Obayashi
- Hibiya Engineering Ltd.
- Fluor Corporation
- Keppel Data Centres Holding
- NTT Global Data Centers
- Equinix Inc.
- Digital Realty Trust Inc.
- QTS Realty Trust LLC
- China State Construction Engineering Corp.
- Larsen and Toubro Ltd.(LandT Construction)
- Bouygues Construction SA
- Vinci Energies(Actemium)
- Samsung CandT Corporation
- Collen Construction Ltd.
- Corgan
- 데이터센터 건설 기업 목록
제7장 시장 기회와 향후 전망
KTH 25.11.03The data center construction market size is expected to be valued at USD 281.34 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 400.16 billion by 2030, advancing at a 7.30% CAGR during 2025-2030.
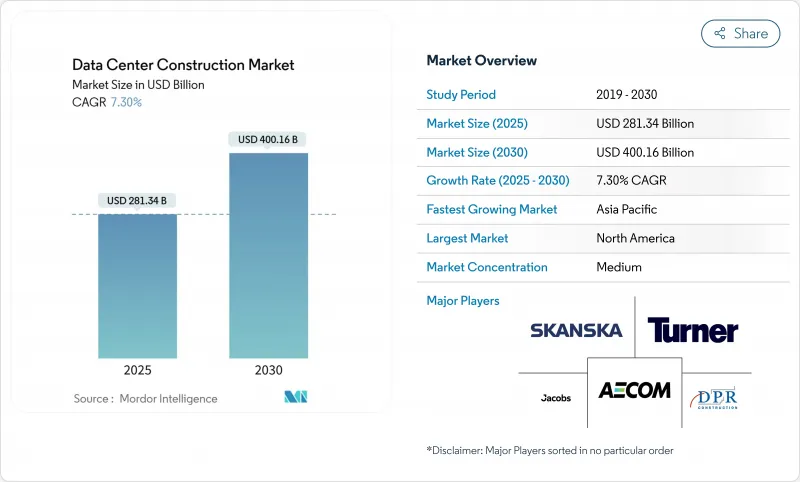
The expansion reflects surging demand for AI-ready capacity, widespread cloud migration, and edge deployments that place digital infrastructure closer to users. Capital spending by hyperscale operators has surged significantly, translating into a robust global construction pipeline that favors standardized, repeatable build models. Yet supply-chain disruptions in transformers and switchgear lengthen delivery lead times to more than 120 weeks, threatening schedule certainty and elevating project risk. Parallel regulatory pressure on energy efficiency pushes owners to integrate on-site renewables and heat-recovery systems from project inception, adding design complexity but also unlocking access to fast-growing pools of green-bond financing.
Global Data Center Construction Market Trends and Insights
Growing Cloud Applications, AI and Big Data Workloads
High-density AI racks now demand 50-100 kW per rack, fundamentally changing design briefs and favoring liquid cooling over legacy air systems. Microsoft alone has earmarked USD 80 billion in 2025 CAPEX for AI infrastructure, spurring builders to engineer gigawatt-scale campuses with redundant 400 kV feeds and on-site substations. Copper demand for these builds is already six times the level of conventional cloud facilities, which supports a growing specialty trade segment for advanced thermal-management installation. Projects such as Crusoe's 1.2 GW campus in Texas illustrate how the data center construction market is stretching traditional construction practices, requiring modular blocks, megawatt-class immersion tanks, and rapid permitting strategies that keep pace with AI compute roadmaps.
Accelerating Adoption of Hyperscale Facilities
Hyperscale capacity is forecast to triple by 2030, accounting for most incremental square footage added worldwide. Turner Construction's USD 2 billion Vantage facility in Ohio, with 192 MW of IT power, typifies the standardized, repeat-build approach that lowers unit costs via bulk procurement and prefabricated skids. While the model secures economies of scale, it concentrates activity in power-rich markets, tightening labor availability and driving wage premiums above 20% in regions such as Northern Virginia and Dublin. Financial structures depend on multibillion-dollar power-purchase agreements, meaning utility interconnection queues and clean-energy targets often dictate construction phasing.
Escalating Real-Estate, Installation and Maintenance Costs
Labor shortages layered on a 20% wage premium for electricians and pipefitters across Northern Virginia's 3.5 GW cluster, constraining contractor availability and extending project schedules. Developers increasingly scout secondary metros such as Phoenix and Madrid, where land and power remain comparatively inexpensive. Bulk-buy agreements for steel joists and switchgear plus long-term hedges on copper now underpin cost-control strategies at firms like DPR Construction, which completed a 100 MW campus in Texas on a fixed-price basis despite volatile commodity inputs. Steel framing remains cost-advantaged, with 20-year lifecycle outlays of USD 350,000 compared to USD 670,000-1.1 million for traditional concrete shells.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Edge-Computing Build-outs Near Population Hubs
- Renewable-Energy Mandates Shaping Facility Design
- Supply-Chain Volatility in High-Capacity Power Gear
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Tier 3 assets retained 58.2% of the data center construction market share in 2024, reinforcing their role as the de facto enterprise standard thanks to balanced redundancy and capex profiles. Meanwhile, Tier 4 demand is projected to grow at 7.8% CAGR through 2030 as banks, stock exchanges, and public-sector cloud mandates pay premiums for 99.995% uptime. Tier 4 projects often double construction complexity: dual utility feeds, 2N power trains, and compartmentalized fire zones inflate budgets by up to 70% over Tier 2 blueprints. Turner Construction's modular Tier 4 build in North Carolina cut commissioning time by 15% using factory-tested power pods, illustrating how innovation tempers cost escalation.
Developers also weigh lifecycle economics. The data center construction market therefore, sees rising design-build consortiums that integrate mechanical, electrical, and controls to certify Tier 4 on first power-up. Prefabricated chillers and containerized UPS segments enable scale without sacrificing Tier 4 compliance, supporting multi-phase rollouts that align spend with demand growth.
Colocation retained 54.3% of 2024 revenue, underlining its value proposition of multi-tenant flexibility and speed-to-market. However, self-built hyperscalers will widen at 8.5% CAGR through 2030, reflecting strategic moves by cloud giants to own core infrastructure. The USD 10 billion Meta Louisiana campus uses a 4 million-square-foot layout dedicated to AI training clusters and backed by a 600 MW solar PPA, underscoring how scale economics tilt toward owner-operator models. Colocation operators respond by offering build-to-suit halls and liquid-cooling-ready floors, preserving relevance amid hyperscale expansion.
Construction modalities diverge. Colocation halls require flexible cage layouts, hot-aisle containment, and shared meet-me rooms that accommodate diverse tenant densities. Hyperscalers instead prefer 12 MW blocks replicated in cookie-cutter fashion to cut capex per MW by 20%. Factory-assembled structural steel frames arrive on site pre-welded, slashing erection times to three weeks for a 30-MW building. As a result, the data center construction market is increasingly segmenting EPC suppliers into multi-billion-dollar global framework agreements for hyperscalers and regional frameworks for edge and enterprise demand.
Data Center Construction Market is Segmented by Tier Type (Tier 1 and 2, Tier 3 and Tier 4), Data Center Type(Colocation, Self-Built Hyperscalers (CSPs), Enterprise, and Edge), and Infrastructure (Electrical Infrastructure, Mechanical Infrastructure), and by Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Germany stands as the cornerstone of Europe's data center construction market, commanding approximately 6% of the global data center construction market size in 2024. The country's robust digital infrastructure, particularly concentrated in major hubs like Frankfurt, Berlin, and Hamburg, continues to attract significant investments from global technology giants. The nation's commitment to sustainable data center development is evident through strict energy efficiency regulations and the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources. Frankfurt, in particular, has emerged as a critical digital hub, benefiting from its central European location and extensive fiber connectivity. The country's data center landscape is further strengthened by its advanced technological ecosystem, skilled workforce, and stable political environment. German data centers are increasingly focusing on innovative cooling technologies and sustainable construction practices, setting new standards for environmental responsibility in the industry.
- AECOM
- Turner Construction Co.
- DPR Construction
- Jacobs Solutions Inc.
- Skanska AB
- Balfour Beatty plc
- Whiting-Turner Contracting Co.
- Hensel Phelps
- Fortis Construction Inc.
- Goodman Group
- PT Jaya Obayashi
- Hibiya Engineering Ltd.
- Fluor Corporation
- Keppel Data Centres Holding
- NTT Global Data Centers
- Equinix Inc.
- Digital Realty Trust Inc.
- QTS Realty Trust LLC
- China State Construction Engineering Corp.
- Larsen and Toubro Ltd. (LandT Construction)
- Bouygues Construction SA
- Vinci Energies (Actemium)
- Samsung CandT Corporation
- Collen Construction Ltd.
- Corgan
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing cloud applications, AI and big data workloads
- 4.2.2 Accelerating adoption of hyperscale facilities
- 4.2.3 Rising edge-computing build-outs near population hubs
- 4.2.4 Renewable-energy mandates shaping facility design
- 4.2.5 Prefabricated / modular builds shrinking time-to-market
- 4.2.6 ESG-linked green-bond financing unlocking capex
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Escalating real-estate, installation and maintenance cost
- 4.3.2 Stricter energy-consumption and carbon-compliance limits
- 4.3.3 Shortage of skilled labor for advanced liquid cooling
- 4.3.4 Supply-chain volatility in high-capacity power gear
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Key Data Center Statistics
- 4.8.1 Exhaustive Data Center Operators on Regional Level (in MW)
- 4.8.2 List of Major Upcoming Data Center Projects across various regions(2025-2030)
- 4.8.3 CAPEX and OPEX For Data Center Construction
- 4.8.4 Data Center Power Capacity Absorption In MW, regions, 2023 and 2024
- 4.9 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Inclusion in Data Center Construction across Various Regions
- 4.10 Regulatory and Compliance Framework
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Tier Type
- 5.1.1 Tier 1 and 2
- 5.1.1.1 Tier 3
- 5.1.1.2 Tier 4
- 5.1.2 By Data Center Type
- 5.1.2.1 Colocation
- 5.1.2.2 Self-build Hyperscalers (CSPs)
- 5.1.2.3 Enterprise and Edge
- 5.1.3 By Infrastructure
- 5.1.3.1 By Electrical Infrastructure
- 5.1.3.1.1 Power Distribution Solution
- 5.1.3.1.2 Power Backup Solutions
- 5.1.3.2 By Mechanical Infrastructure
- 5.1.3.2.1 Cooling Systems
- 5.1.3.2.2 Racks and Cabinets
- 5.1.3.2.3 Servers and Storage
- 5.1.3.2.4 Other Mechanical Infrastructure
- 5.1.3.3 General Construction
- 5.1.3.4 Service - Design and Consulting, Integration, Support and Maintenance
- 5.1.4 By Geography
- 5.1.4.1 North America
- 5.1.4.1.1 United States
- 5.1.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.1.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.1.4.2 South America
- 5.1.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.1.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.1.4.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.1.4.3 Europe
- 5.1.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.1.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.1.4.3.3 France
- 5.1.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.1.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.1.4.3.6 Russia
- 5.1.4.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.1.4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.1.4.4.1 China
- 5.1.4.4.2 Japan
- 5.1.4.4.3 India
- 5.1.4.4.4 South Korea
- 5.1.4.4.5 Australia and New Zealand
- 5.1.4.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.1.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.1.4.5.1 Middle East
- 5.1.4.5.1.1 Gulf Corporation Countries
- 5.1.4.5.1.2 Turkey
- 5.1.4.5.1.3 Israel
- 5.1.4.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.1.4.5.2 Africa
- 5.1.4.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.1.4.5.2.2 Egypt
- 5.1.4.5.2.3 Nigeria
- 5.1.4.5.2.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.1.1 Tier 1 and 2
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Data Center Infrastructure Investment Based on Megawatt (MW) Capacity, 2024 vs 2030
- 6.5 Data Center Construction Landscape (Key Vendors Listings)
- 6.6 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.6.1 AECOM
- 6.6.2 Turner Construction Co.
- 6.6.3 DPR Construction
- 6.6.4 Jacobs Solutions Inc.
- 6.6.5 Skanska AB
- 6.6.6 Balfour Beatty plc
- 6.6.7 Whiting-Turner Contracting Co.
- 6.6.8 Hensel Phelps
- 6.6.9 Fortis Construction Inc.
- 6.6.10 Goodman Group
- 6.6.11 PT Jaya Obayashi
- 6.6.12 Hibiya Engineering Ltd.
- 6.6.13 Fluor Corporation
- 6.6.14 Keppel Data Centres Holding
- 6.6.15 NTT Global Data Centers
- 6.6.16 Equinix Inc.
- 6.6.17 Digital Realty Trust Inc.
- 6.6.18 QTS Realty Trust LLC
- 6.6.19 China State Construction Engineering Corp.
- 6.6.20 Larsen and Toubro Ltd. (LandT Construction)
- 6.6.21 Bouygues Construction SA
- 6.6.22 Vinci Energies (Actemium)
- 6.6.23 Samsung CandT Corporation
- 6.6.24 Collen Construction Ltd.
- 6.6.25 Corgan
- 6.7 List of Data Center Construction Companies
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES and FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment



















