
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1849989
농업용 효소 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Agricultural Enzymes - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
농업용 효소 시장 규모는 2025년에 6억 달러로 평가되었고, 2030년에 9억 200만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 예측 기간 중 CAGR은 8.5%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

이러한 성장은 합성 화학물질에 대한 규제 강화, 잔류물 없는 식품에 대한 소비자 수요 증가, 효소 제형 및 전달 기술의 꾸준한 발전을 반영합니다. 성숙 시장의 상업적 재배자들은 기존 투입재의 일부를 효소 기반 생물학적 제제로 대체하고 있으며, 아시아태평양 지역의 소규모 농가들은 대상별 보조금 프로그램의 지원을 받아 수확량 증대형 생물학적 제제로 전환하고 있습니다. 정밀 발효 및 AI 기반 단백질 설계 분야의 병행 발전으로 제품 개발 주기가 단축되고 있으며, 장기 탄소 크레딧 프로그램은 재생형 효소 솔루션을 도입하는 농민들에게 새로운 수익원을 창출하고 있습니다. 농화학 대기업들이 파트너십과 인수를 통해 생물학적 포트폴리오를 강화하고, 전문 생명공학 기업들이 차세대 다중 효소 칵테일 상용화를 서두르면서 경쟁 강도가 높아지고 있습니다.
세계의 농업용 효소 시장 동향 및 인사이트
유기농 및 잔류물 없는 식품 수요
소매업체들이 잔류물 허용 기준을 강화하고, EU의 '농장에서 식탁까지 전략'이 2030년까지 화학 농약 사용을 50% 감축하도록 의무화함에 따라 전 세계 유기농 농산물 지출이 증가하고 있습니다. 농가들은 인증 유기농 유통 채널에서 20-30%의 가격 프리미엄을 얻어, 화학 잔류물 없이 영양분을 동원하는 효소 도입의 전환 비용을 상쇄합니다. 효소 기반 프로그램은 인·질소 가용성 향상, 식물 방어 경로 강화, 토양 미생물군집 균형 개선을 통해 유기농 시스템의 수확량 격차 해소에 기여합니다. 스페인의 상업적 과수원 운영자들은 2024년 인산염 비료에서 인산분해효소-요소분해효소 혼합 과립제로 전환한 후 9%의 수확량 증가를 보고하며 뚜렷한 경제적 효과를 입증했습니다. 이와 유사한 성과가 현재 캐나다 전역의 온실 채소 재배에서도 확산을 주도하고 있으며, 액상 셀룰라아제 혼합제는 작물 회전 사이의 바이오매스 분해를 개선하여 재배 주기를 단축시킵니다.
생물학적 투입재 채택 급증
브라질은 현재 경작지의 60% 이상에 생물학적 작물 보호 솔루션을 적용하고 있으며, 이는 EU 및 미국의 채택률을 크게 앞지릅니다. 합성 제초제 및 살균제에 대한 내성 증가로 새로운 작용 방식에 대한 탐구가 가속화되면서, 농업용 효소가 생물학적 방제 미생물과 시너지 효과를 내는 동반자로 자리매김하고 있습니다. 마투그로소 주의 밭작물 재배자들은 2024-2025 시즌에 리파아제와 만난나아제 효소가 포함된 종자 처리 혼합제를 도입한 후 옥수수 연속 재배 수확량이 4.6% 증가했습니다. 인도에서도 유사한 추세가 전개되고 있으며, 주 차원의 보조금 프로그램이 효소 투입 비용의 최대 30%를 지원하여 소규모 농가의 도입을 촉진하고 두 자릿수 시장 성장을 이끌고 있습니다.
분산된 규제 승인 체계
생물학적 투입재 개발사들은 여전히 상이한 승인 일정을 헤쳐나가야 합니다. EU는 제품 분류에 따라 여러 서류 제출을 요구합니다. 미국의 신규 통합 바이오기술 규제 웹사이트는 국내 투명성을 개선했으나 글로벌 조화는 여전히 요원합니다. 지연으로 평균 상용화 주기가 18-24개월 연장되며 규정 준수 비용이 증가하고, 일부 기업은 소수 고가치 시장 선점을 선택합니다. 소규모 혁신 기업들이 가장 큰 어려움을 겪으며, 규제 지원을 위해 대형 농화학 기업과 협력하는 경우가 많아 독립적인 시장 진출 전략이 제한될 수 있습니다.
부문 분석
인산분해효소는 고정화된 토양 인을 활성화하여 2024년 농업용 효소 시장의 37%를 점유했습니다. 이 인은 적용된 비료의 80%에 달하는 양입니다. 비료 가격이 변동성을 유지함에 따라, 곡물 및 유채종자 전반에 걸쳐 인 활성화 솔루션에 대한 수요는 여전히 강세를 보입니다. 따라서 인산분해효소 분야의 농업용 효소 시장 규모는 2030년까지도 지배적인 매출 위치를 유지할 전망입니다. 셀룰라아제는 셀오시(CelOCE) 및 관련 혁신 기술의 추진으로 13.8%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 성장률 1위를 기록했습니다. 이 효소들은 작물 잔여물을 분해하여 유익한 미생물의 에너지원이 되는 당류를 방출하고 토양 구조를 개선합니다. 요소분해효소, 지방분해효소, 단백질분해효소가 포트폴리오를 완성하며, 복합적인 현장 조건에 대응하기 위해 상호 보완적인 활성을 결합한 칵테일 제품이 점차 증가하고 있습니다.
고부가가치 원예 분야에서는 단일 작업으로 정밀한 영양분 동원과 스트레스 대응 강화가 요구되면서 다중 효소 혼합물로의 전환이 두드러집니다. 신생 기업들은 유통기한 문제와 비용 절감을 위해 농장에서 직접 신선한 셀룰라아제 풍부 혼합물을 제조할 수 있는 현장 발효 키트를 개발 중입니다. 대형 업체들은 인산분해효소-요소분해효소 시너지 효과를 통합해 질소 이용 효율을 개선하고 논밭에서 휘발을 완화하며, 농업용 효소 시장 내 솔루션 세트의 확대를 반영하고 있습니다.
액상 제품은 기존 살포 장비와의 호환성과 효율적인 엽면 흡수로 인해 2024년 농업용 효소 시장 규모의 46.2%를 유지했습니다. 그러나 물류 비용과 콜드체인 의존도는 제품 관리자들이 더 높은 내온성 기술을 선택하도록 유도하고 있습니다. 연평균 12.4% 성장률을 보이는 과립 제품은 이제 ‘과립 내 바이오리액터’ 구조를 적용하여 효소를 최대 24개월간 안정화시키면서 토양 접촉 후 시간 조절 방출을 가능하게 합니다.
분말 제형은 비용 효율적인 중간 지점을 차지하지만 전용 혼합 장비가 필요합니다. 하이브리드 수분산성 과립은 이러한 경계를 모호하게 하여 액체와 같은 편의성과 과립의 내구성을 동시에 제공합니다. 특히 콜드체인 격차가 지속되는 아시아태평양 및 아프리카 열대 지역에서 성장을 추구하는 기업들의 경우, 제형의 다용도성이 경쟁 차별화의 핵심이 될 것으로 예상됩니다.
지역 분석
2024년 농업용 효소 시장의 약 35%를 차지하는 북미는 강력한 유통 인프라와 생물학적 투입물에 대한 신속한 규제 승인의 혜택을 받고 있습니다. 캐나다 농가는 지난 시즌 1,180만 헥타르의 유전자 조작 작물을 재배하여 보완적 효소 프로그램에 유리한 환경을 조성했습니다. 미국 생장촉진제 부문도 마찬가지로 활기차며, 효소가 함유된 엽면 살포제가 아몬드 및 토마토 생산자들 사이에서 주목받고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 가장 빠르게 성장하는 지역으로, 2030년까지 연평균 10%의 성장률을 기록할 전망입니다. 인도의 바이오농업 부문은 2023년 124억 달러 규모에 달했으며, 현재 국가 보조금이 효소 비용의 최대 30%를 지원하여 소규모 농가의 도입을 가속화하고 있습니다. 콜드체인 격차는 여전히 주요 장애물로 남아 있습니다. 인도 낙농 산업 전반에 필요한 용량의 80%가 여전히 부족하여 제조사들이 입상 제품에 주력하도록 촉구하고 있습니다. 중국의 토지 이전 개혁은 대규모 농장 단위를 장려하여, 대규모 적용이 가능한 효소 기술의 사업성을 개선하고 있습니다.
유럽은 그린딜(Green Deal) 하의 엄격한 농약 감축 목표 덕분에 강력한 입지를 유지하고 있습니다. 생물학적 방제 활성 물질은 2011년 120종에서 2022년 거의 220종으로 증가했으며, 해당 기간 동안 매출은 두 배 증가한 15억 4,900만 유로를 기록했습니다. 브라질의 선도적인 60% 생물학적 채택률을 앞세운 남미는 특히 대두와 옥수수용 효소 강화 종자 처리 분야에서 성숙하면서도 확장 중인 시장입니다. 중동 및 아프리카는 규제 명확성과 콜드체인 투자에 성장이 좌우되지만 신흥 시장으로서의 가능성을 보이고 있으며, 남아프리카공화국과 걸프 국가들이 초기 도입을 주도하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 유기농 및 잔류물 없는 식품 수요
- 생물학적 투입재 채택 급증
- 연구개발과 제품 혁신 강화
- 종자 코팅 미세 투여 기술
- 재생농업 탄소 크레딧 프로그램
- 농장 내 효소 발효 장치
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 분산된 규제 승인 체계
- 토양과 기후에 따른 성능 변동
- 열대 지역의 콜드체인 격차
- 화학비료 대비 단기 ROI의 불투명성
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 효소 유형별
- 인산분해효소
- 탈수소효소
- 요소분해효소
- 단백질분해효소
- 지방분해효소
- 셀룰라아제
- 기타 효소 유형
- 제형별
- 액상
- 분말
- 입상
- 용도별
- 농작물 보호
- 비옥도 향상
- 식물 성장 제어
- 적용 모드별
- 종자 처리
- 엽면 처리
- 토양 처리
- 작물 유형별
- 곡물
- 유지종자 및 콩류
- 과일 및 채소
- 잔디 및 관상용 식물
- 기타 작물
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 기타 북미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 중동
- 사우디아라비아
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 튀르키예
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 케냐
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Novonesis
- Elemental Enzymes
- Enzyme Solutions Inc.
- Bioworks Inc.
- Infinita Biotech Pvt. Ltd.
- Biocatalysts Ltd
- Enzyme Development Corporation
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
HBR 25.11.14The Agricultural Enzymes Market size is estimated at USD 600 million in 2025, and is anticipated to reach USD 902 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 8.5% during the forecast period.
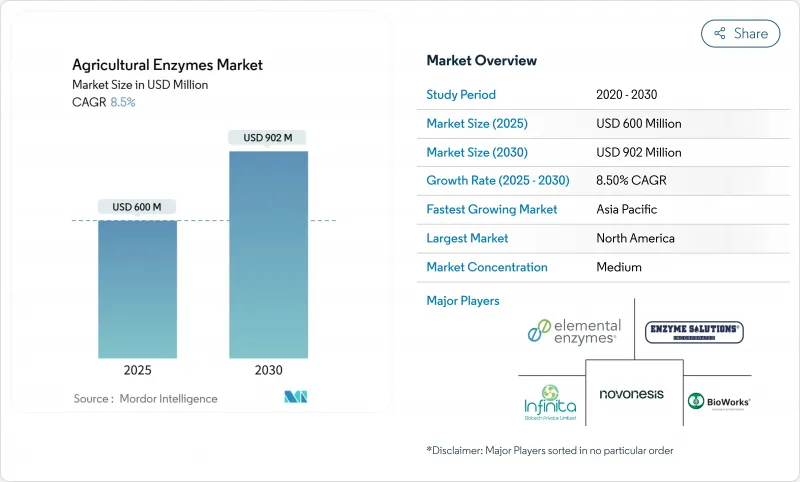
This growth reflects the tightening of regulations on synthetic chemicals, a greater consumer appetite for residue-free food, and steady advances in enzyme formulation and delivery technologies. Commercial growers in mature markets are replacing a share of conventional inputs with enzyme-based biologicals, while smallholders in Asia-Pacific are moving toward yield-boosting biologicals supported by targeted subsidy programs. Parallel advances in precision fermentation and AI-driven protein design are reducing product-development cycles, while long-term carbon-credit programs are generating new revenue streams for farmers who deploy regenerative enzyme solutions. Competitive intensity is rising as agrochemical majors strengthen biological portfolios through partnerships and acquisitions, and specialized biotechnology firms race to commercialize next-generation multi-enzyme cocktails.
Global Agricultural Enzymes Market Trends and Insights
Organic and Residue-free Food Demand
Global spending on organic produce is climbing as retailers tighten residue thresholds, and the EU Farm to Fork Strategy mandates a 50% cut in chemical pesticide use by 2030. Farmers gain 20-30% price premiums in certified organic channels, offsetting the transition costs of adopting enzymes that mobilize nutrients without chemical residues. Enzyme-embedded programs help close yield gaps in organic systems by enhancing phosphorus and nitrogen availability, fortifying plant defense pathways, and improving soil microbiome balance. Commercial orchard operators in Spain reported a 9% yield uplift after switching from phosphate fertilizers to a blended phosphatase-urease granule in 2024, demonstrating clear economic returns. Similar outcomes are now driving uptake in greenhouse vegetables across Canada, where liquid cellulase blends shorten crop cycles by improving biomass breakdown between rotations.
Biological Input Adoption Surge
Brazil now applies biological crop-protection solutions on more than 60% of cultivated land, significantly ahead of adoption rates in the EU and USA. Mounting resistance to synthetic herbicides and fungicides is accelerating the search for new modes of action, positioning agricultural enzymes as synergistic companions to biocontrol microbes. Row-crop growers in Mato Grosso logged a 4.6% corn-on-corn yield gain in the 2024/25 season after integrating a seed-treatment cocktail containing lipase and mannanase enzymes. Similar momentum is unfolding in India, where state-level subsidy programs cover up to 30% of enzyme input costs, catalyzing smallholder adoption and fueling double-digit market growth.
Fragmented Regulatory Approvals
Biological input developers still navigate divergent approval timelines, with the EU requiring multiple dossiers depending on product classification. The new US Unified Website for Biotechnology Regulation improves domestic transparency, yet global harmonization remains distant.Delays add 18-24 months to average commercialization cycles, inflating compliance costs and prompting some firms to prioritize fewer, high-value markets. Smaller innovators struggle most, often partnering with larger agrochemical companies for regulatory support, which can limit independent go-to-market strategies.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Intensified Research and Development, and Product Innovation
- Seed-coating Micro-dose Delivery
- Cold-chain Gaps in Tropical Regions
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Phosphatases captured 37% of the agricultural enzymes market in 2024 by unlocking immobilized soil phosphorus that otherwise reaches 80% of applied fertilizer. As fertilizer prices remain volatile, demand for phosphorus-mobilizing solutions stays strong across cereals and oilseeds. The agricultural enzymes market size for phosphatases is, therefore, set to maintain a dominant revenue position through 2030. Cellulases, propelled by CelOCE and related innovations, top the growth chart at a 13.8% CAGR. These enzymes deconstruct crop residues, releasing sugars that fuel beneficial microbes and improve soil structure. Ureases, lyases, and proteases round out the portfolio, with cocktail products increasingly combining complementary activities to match complex field conditions.
The shift toward multi-enzyme blends is pronounced in high-value horticulture, where growers demand precise nutrient mobilization and stress-response enhancement in one pass. Start-ups are developing on-farm fermentation kits that allow growers to brew fresh cellulase-rich mixes, avoiding shelf-life concerns and reducing costs. Larger players integrate phosphatase-urease synergies to improve nitrogen use efficiency and mitigate volatilization in paddy fields, reflecting a broadening solution set within the agricultural enzymes market.
Liquid products retained 46.2% of the agricultural enzymes market size in 2024, primarily due to their compatibility with existing spraying equipment and efficient foliar absorption. Yet logistics costs and cold-chain dependency are steering product managers toward more temperature-tolerant technologies. Granular products, advancing at 12.4% CAGR, now embed "bioreactor-in-a-granule" architectures that stabilize enzymes for up to 24 months while enabling timed release after soil contact.
Powder formulations occupy a cost-efficient middle ground, but require dedicated mixing equipment. Hybrid water-dispersible granules blur these lines, providing liquid-like convenience with granular durability. Expect competitive differentiation to hinge on formulation versatility, particularly for companies pursuing growth in the Asia-Pacific and African tropics where cold-chain gaps persist.
The Agricultural Enzymes Market is Segmented by Enzyme Type (Phosphatases and More), by Formulation (Liquid and More), by Application (Crop Protection and More), by Mode of Application (Seed Treatment and More), by Crop Type (Cereals and Grains, Oil Seeds and Pulses, and More), and by Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East, and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America, holding about 35% of the agricultural enzymes market in 2024, benefits from robust distribution infrastructure and rapid regulatory clearance for biological inputs. Canadian growers planted 11.8 million hectare of genetically engineered crops last season, creating a receptive environment for complementary enzyme programs. The US biostimulant segment is equally vibrant, with enzyme-infused foliar sprays gaining traction among almond and tomato producers.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, on track for a 10% CAGR through 2030. India's BioAgri segment reached USD 12.4 billion in 2023, and state subsidies now cover up to 30% of enzyme costs, accelerating adoption among smallholders. Cold-chain gaps remain a material hurdle; 80% of the required capacity is still absent across India's dairy sector, prompting manufacturers to emphasize granular products. China's land-transfer reforms encourage larger farm units, improving the business case for enzyme technologies that can be applied at scale.
Europe retains a strong foothold thanks to stringent pesticide-reduction goals under the Green Deal. Biocontrol active substances climbed from 120 in 2011 to almost 220 in 2022, doubling revenue to EUR 1.549 billion in that period. South America, led by Brazil's trail-blazing 60% biological adoption, remains a mature yet expanding arena, particularly for enzyme-enhanced seed treatments in soy and corn. The Middle East and Africa show emerging promise, though growth hinges on regulatory clarity and cold-chain investment, with South Africa and the Gulf states spearheading early adoption.
- Novonesis
- Elemental Enzymes
- Enzyme Solutions Inc.
- Bioworks Inc.
- Infinita Biotech Pvt. Ltd.
- Biocatalysts Ltd
- Enzyme Development Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Organic and Residue-free Food Demand
- 4.2.2 Biological Input Adoption Surge
- 4.2.3 Intensified Research and Development, and Product Innovation
- 4.2.4 Seed-coating Micro-dose Delivery
- 4.2.5 Regenerative-Ag Carbon-Credit Programs
- 4.2.6 On-farm Enzyme Fermentation Units
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Fragmented Regulatory Approvals
- 4.3.2 Soil and Climate based Performance Variability
- 4.3.3 Cold-chain Gaps in Tropical Regions
- 4.3.4 Invisible Short-term ROI vs Chemicals
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porters Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Enzyme Type
- 5.1.1 Phosphatases
- 5.1.2 Dehydrogenases
- 5.1.3 Ureases
- 5.1.4 Proteases
- 5.1.5 Lyases
- 5.1.6 Cellulases
- 5.1.7 Other Enzyme Types
- 5.2 By Formulation
- 5.2.1 Liquid
- 5.2.2 Powder
- 5.2.3 Granular
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Crop Protection
- 5.3.2 Fertility Enhancement
- 5.3.3 Plant Growth Regulation
- 5.4 By Mode of Application
- 5.4.1 Seed Treatment
- 5.4.2 Foliar Spray
- 5.4.3 Soil Treatment
- 5.5 By Crop Type
- 5.5.1 Cereals and Grains
- 5.5.2 Oilseeds and Pulses
- 5.5.3 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.5.4 Turf and Ornamentals
- 5.5.5 Other Crops
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Russia
- 5.6.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 Australia
- 5.6.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Argentina
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.6 Africa
- 5.6.6.1 South Africa
- 5.6.6.2 Kenya
- 5.6.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Novonesis
- 6.4.2 Elemental Enzymes
- 6.4.3 Enzyme Solutions Inc.
- 6.4.4 Bioworks Inc.
- 6.4.5 Infinita Biotech Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Biocatalysts Ltd
- 6.4.7 Enzyme Development Corporation



















