
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1850159
헬스케어 IT 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Healthcare IT - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
헬스케어 IT 시장 규모는 2025년에 4,131억 4,000만 달러, 2030년에는 8,396억 7,000만 달러에 이르고, 예측 기간(2025-2030년)의 CAGR은 15.24%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

지속적인 기세는 헬스케어 산업이 지금 의료비 억제와 질 향상의 과제의 중심임을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 거래 정보 공개에 따르면 구매자는 클라우드 기반 분석 플랫폼에 일관되게 최대의 자금을 투입하고 있으며 동시에 독립형 On-Premise 소프트웨어 예산이 줄어들고 있습니다. 헬스케어 인포메이션 테크놀로지 업계는 원격 서비스에 대한 지불자의 상환 코드 확대로부터 이익을 얻고 있어, 이것은 보수적인 프로바이더도 디지털 프론트 도어에 향하게 하는 정책의 움직임입니다. 워크플로 재설계 및 사이버 보안 보장을 번들로 제공하는 구현 파트너는 Time-to-Value를 단축합니다. 투자자 전화 회의에서는 이사회가 IT 투자를 승인할 때 임상의의 불타는 증후군보다 공급망의 취약성을 강조하는 것으로 밝혀졌고, 간접적으로 AI 기반 자동화가 전략적 로드맵의 최상위 수준으로 꼽힙니다.
세계 헬스케어 IT - 시장 동향 및 통찰력
AI 주도의 임상 판단 지원: 진단 정확도 재정의
2025년 말까지 약 10개 시설 중 9개 시설이 조기 진단 및 원격 모니터링을 위해 AI의 실용화를 계획하고 있습니다. 문서화를 자동화하면 사무처리 시간이 이미 3분의 2 가까이 단축되고, 임상의는 환자와의 직접적인 관계에 시간을 할애할 수 있습니다. 방사선학이 최전선에 있으며 AI 지원 감지 도구는 이전에는 두 번째 판독이 필요했던 미묘한 병변을 포착하여 치료 경로의 측정 가능한 개선으로 이어졌습니다. 그러나 미국 의료 시스템의 53%만이 이러한 모델을 감독하는 전문 거버넌스 팀을 보유하고 있으며 감시되지 않는 성능 드리프트의 위험을 높이는 감독 갭이 있습니다. 실시간 바이어스 대시보드를 제공하는 공급업체는 업데이트율이 높아지고 투명성이 중요한 구매 기준으로 부상하고 있음을 시사합니다. 포인트 오브 케어에서 모델 설명 가능성 큐를 받은 임상의는 AI가 생성한 권장 사항에 대한 신뢰성이 더 높다고 보고하고 보다 깊은 워크플로우를 통합하도록 촉구합니다.
원격의료의 급속한 보급 : 지방 접근 혁명
원격의료는 2030년까지 농촌의 의사수가 더욱 23% 감소할 것으로 예측되는 가운데 의료가 미치지 못한 지역의 추정 20억명을 위한 거리 기반 케어 갭을 메우는 중요한 진보입니다. 공동 원격 ICU 네트워크에서는 사실상 가능한 범위 내에서 전문의의 감시를 저 긴급 병원으로 확대한 결과 사망률이 최대 40% 감소했습니다. 인프라 법안에 근거한 광대역 컨소시엄은 연결 비용을 낮추고 1차 케어 클리닉이 비디오 트리아지를 시험적으로 도입하여 응급실외의 진찰 시간을 몇 분 단축할 수 있게 했습니다. 의료기관의 CFO(최고재무책임자)는 선택적 치료로 인한 이익률이 떨어지는 것을 보완하기 위해 원격의료로 인한 수입을 꼽는 경우가 많습니다. 또한 원격진료에 익숙한 의사가 디지털 상처치료와 같은 인접한 혁신의 변혁 챔피언이 되어 보다 광범위한 변혁을 유기적으로 가속시킨다는 새로운 움직임도 나오고 있습니다.
복잡한 규제 : 컴플라이언스 부담 증가
630개가 넘는 헬스케어 규칙이 있으며 최근에는 20개가 넘는 규칙이 업데이트됨에 따라 기업은 임상 이외의 규정 준수에 연간 약 390억 달러를 지출해야 했습니다. 소규모 병원에서는 오버헤드 중 문서화 팀에 비해 비율이 불균형하고 환자를 위한 기술에 대한 자금이 압박되고 있습니다. 중앙 집중식 규칙 매핑 엔진에 투자한 의료기관은 워크플로 경고를 실시간으로 수신할 수 있어 신속한 개선과 감사를 통해 처벌을 줄일 수 있습니다. 그럼에도 불구하고 AI에 특화된 법률이 가까이 다가오고 있기 때문에 개발자는 모델 카드 공개를 발표하도록 요청받고 있습니다. 컴플라이언스 컨설턴트는 초기 코딩 단계에서 프라이버시 바이 디자인 원칙을 통합하여 향후 리엔지니어링 비용을 줄일 수 있다고 보고합니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- AI 주도의 임상 의사 결정 지원의 도입
- 지방에서의 원격 의료의 급속한 보급
- 종이 없는 기술에 대한 수요 증가
- 헬스케어 서비스와 인프라에 대한 정부 자금의 증액
- 고령화가 원격 환자 모니터링의 도입을 추진
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 규제의 복잡성
- 숙련된 의료 IT 인력의 부족
- 중소규모의 의료시설에 있어서의 자본 예산의 제약
- 공급망 분석
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 용도별
- 전자건강기록(EHR)
- 이미지 아카이브 및 통신 시스템(PACS)
- 의료 영상 정보 시스템(RIS)
- 실험실 정보 시스템(LIS)
- 전산화된 의사 주문 항목(CPOE)
- 임상 의사결정 지원 시스템(CDSS)
- 원격 의료 솔루션
- 원격 환자 모니터링
- 수익주기 관리(RCM)
- 약국 정보 시스템(PIS)
- 임상 정보 시스템
- 디지털 헬스케어 공급망 관리 시스템
- 고객관계관리(CRM)
- 헬스케어 보험자용 솔루션
- 부정 행위 탐지 및 지불 무결성 관리
- 기타
- 구성요소별
- 소프트웨어
- 하드웨어
- 서비스
- 배송 방법별
- On-Premise
- 클라우드 기반
- 최종 사용자별
- 병원과 의료 시스템
- 진단 및 영상 센터
- 기타
- 지역
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 호주
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- GCC
- 남아프리카
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Epic Systems Corp.
- Oracle Health(Cerner)
- McKesson Corp.
- Philips Healthcare
- GE HealthCare
- Siemens Healthineers
- Allscripts(Altera Digital Health)
- athenahealth
- IBM Watson Health
- Optum Inc.
- Teladoc Health
- Amwell
- InterSystems Corp.
- MEDITECH
- Change Healthcare
- R1 RCM Inc.
- Accenture Health
- Cognizant Digital Health
- Tata Consultancy Services(TCS)
- Wipro HealthEdge
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
SHW 25.11.07The Healthcare IT Market size is estimated at USD 413.14 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 839.67 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 15.24% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
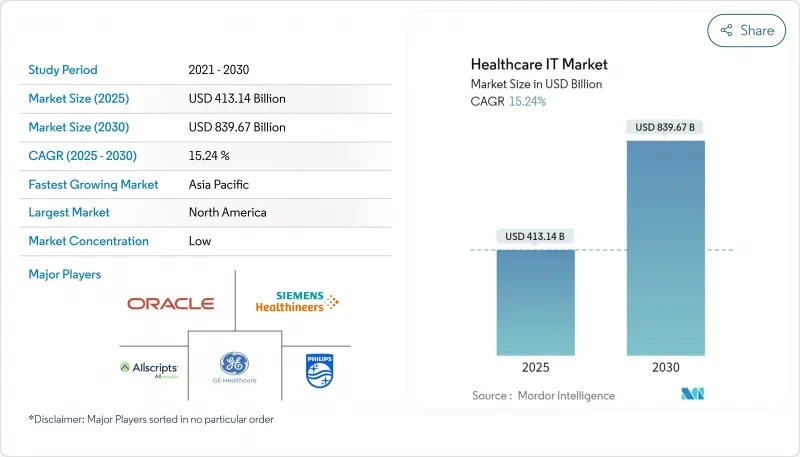
Sustained momentum confirms that the industry is now central to healthcare cost-containment and quality-improvement agendas. Transaction disclosures show that buyers consistently channel the highest capital into cloud-ready analytics platforms, while simultaneously paring budgets for stand-alone on-premise software. The Healthcare Information Technology industry benefits from payers' expanded reimbursement codes for remote services, a policy move that is nudging even conservative providers toward digital front doors. Implementation partners that can bundle workflow redesign with cybersecurity assurances are shortening time-to-value, a pattern that explains the services component's out-sized Healthcare Information Technology market share. Investor calls reveal that boards are weighing supply-chain fragility less heavily than clinician burnout when green-lighting IT spend, indirectly elevating AI-based automation to the top of strategic roadmaps.
Global Healthcare IT Market Trends and Insights
AI-Driven Clinical Decision Support: Redefining Diagnostic Precision
Hospitals are moving decisively into algorithm-enabled care: by end-2025, roughly nine in ten institutions plan to operationalize AI for early diagnosis and remote monitoring. Automated documentation already cuts paperwork time by close to two-thirds, freeing clinicians for direct patient engagement. Radiology is at the vanguard; AI-assisted detection tools are catching subtle lesions that once required second reads, leading to measurable improvements in treatment pathways. Yet only 53 % of U.S. health systems have dedicated governance teams overseeing these models, an oversight gap that raises the risk of unmonitored performance drift. Vendors that include real-time bias dashboards in their offerings are seeing higher renewal rates, suggesting that transparency is emerging as a key buying criterion. Clinicians who receive model-explainability cues at the point of care report greater confidence in AI-generated recommendations, encouraging deeper workflow embedding.
Rapid Telehealth Uptake: Rural Access Revolution
Telehealth is closing distance-based care gaps for an estimated two billion people in under-served geographies, a critical advancement as rural doctor numbers are projected to fall another 23 % by 2030. Collaborative tele-ICU networks show up to 40 % reductions in mortality after virtually enabled coverage extends specialist oversight to low-acuity hospitals. Broadband consortia funded under infrastructure bills have lowered connectivity costs, enabling primary-care clinics to pilot video triage that shaves minutes off emergency-department boarding times. Provider CFOs increasingly cite telehealth revenue as an offset to declining elective-procedure margins, signalling that virtual visits have matured into a durable line of business. An emerging behavior is that physicians seasoned in remote consults become change champions for adjacent innovations such as digital wound care, organically accelerating broader transformation.
Complexity of Regulations: Compliance Burden Intensifies
More than 630 active healthcare rules-and over twenty recent updates-force organizations to pour roughly USD 39 billion a year into non-clinical compliance. Smaller hospitals allocate a disproportionate share of overhead to documentation teams, crowding out funds for patient-facing technologies. Providers that invested in centralized rule-mapping engines now receive real-time workflow alerts, enabling faster remediation and reducing audit penalties. Nevertheless, looming AI-specific legislation is prompting developers to publish model-card disclosures, extending product cycles but enhancing buyer trust. Compliance consultants report that integrating privacy-by-design principles at early coding stages trims future re-engineering costs, a lesson gradually reflected in procurement scorecards.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rise in Demand for Paper-less Technology: Data-Driven Care Transformation
- Increased Government Funding: Policy-Driven Market Acceleration
- Shortage of Skilled Health-IT Workforce: Implementation Bottleneck
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Epic Systems Corp.
- Oracle Health (Cerner)
- McKesson Corp.
- Koninklijke Philips
- GE Healthcare
- Siemens Healthineers
- Allscripts (Altera Digital Health)
- athenahealth
- IBM
- Optum
- Teladoc Health
- Amwell
- InterSystems Corp.
- Meditech
- Change Healthcare
- R1 RCM
- Accenture Health
- Cognizant Digital Health
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)
- Wipro HealthEdge
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 AI-Driven Clinical Decision Support Adoption
- 4.2.2 Rapid Telehealth Uptake in Rural Areas
- 4.2.3 Rise in the Demand for Paper-less Technology
- 4.2.4 Increased Government Funding on Healthcare Services and Infrastructure
- 4.2.5 Aging Population Driving Remote Patient-Monitoring Deployment
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Complexity of Regulations
- 4.3.2 Shortage of Skilled Health-IT Workforce
- 4.3.3 Capital-Budget Constaint in Small and Medium sized Healthcare facilities
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Application
- 5.1.1 Electronic Health Records (EHR)
- 5.1.2 Picture Archiving & Communication Systems (PACS)
- 5.1.3 Medical Imaging Information Systems (RIS)
- 5.1.4 Laboratory Information Systems (LIS)
- 5.1.5 Computerized Physician Order Entry (CPOE)
- 5.1.6 Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
- 5.1.7 Telehealth Solutions
- 5.1.8 Remote Patient Monitoring
- 5.1.9 Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)
- 5.1.10 Pharmacy Information Systems (PIS)
- 5.1.11 Clinical Information systems
- 5.1.12 Digital Healthcare Supply chain management systems
- 5.1.13 Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- 5.1.14 Healthcare Payer Solutions
- 5.1.15 Fraud Detection & Payment Integrity
- 5.1.16 Others
- 5.2 By Component
- 5.2.1 Software
- 5.2.2 Hardware
- 5.2.3 Services
- 5.3 By Delivery Mode
- 5.3.1 On-Premise
- 5.3.2 Cloud-Based
- 5.4 By End-User
- 5.4.1 Hospitals & Health Systems
- 5.4.2 Diagnostic & Imaging Centers
- 5.4.3 Others
- 5.5 Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Epic Systems Corp.
- 6.3.2 Oracle Health (Cerner)
- 6.3.3 McKesson Corp.
- 6.3.4 Philips Healthcare
- 6.3.5 GE HealthCare
- 6.3.6 Siemens Healthineers
- 6.3.7 Allscripts (Altera Digital Health)
- 6.3.8 athenahealth
- 6.3.9 IBM Watson Health
- 6.3.10 Optum Inc.
- 6.3.11 Teladoc Health
- 6.3.12 Amwell
- 6.3.13 InterSystems Corp.
- 6.3.14 MEDITECH
- 6.3.15 Change Healthcare
- 6.3.16 R1 RCM Inc.
- 6.3.17 Accenture Health
- 6.3.18 Cognizant Digital Health
- 6.3.19 Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)
- 6.3.20 Wipro HealthEdge
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment

















