
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1851456
IoNT(Internet Of Nano Things) 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Internet Of Nano Things - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
세계의 IoNT(Internet Of Nano Things) 시장 규모는 2025년 229억 9,000만 달러로 추정되며, 예측 기간 중(2025-2030년) CAGR은 25.60%로 확대되어, 2030년에는 718억 8,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.

이 급증은 테라헤르츠 밴드 나노 안테나 설계의 상업화, 초저전력 탄소나노튜브 센서의 전개, 나노스케일 통신 프로토콜의 주류 무선 네트워크에의 급속한 수렴을 반영하고 있습니다. 정부는 나노 센서를 기반으로 한 유행 감시 프레임 워크에 자금을 제공하고 민간 투자는 분자 수준의 데이터를 실용적인 통찰력으로 변환하는 AI 주도 오케스트레이션 플랫폼을 가속화하고 있습니다. 하드웨어는 전체 지출의 거의 절반을 차지하지만 기업이 기기보다 분석을 선호하기 때문에 소프트웨어 플랫폼은 현저하게 빠른 속도로 확대되고 있습니다. 지역별로는 북미가 연방 연구 보조금과 초기 테라헤르츠 주파수 할당으로 선도하고 있지만, 아시아태평양은 반도체 허브가 나노센서 네트워크를 인더스트리 4.0 로드맵에 통합하고 있기 때문에 가장 강한 성장을 보이고 있습니다. 반도체 메이저가 기존 공장을 활용하는 한편, 신흥기업이 파괴적인 분자통신 스택을 도입하기 때문에 경쟁 압력은 강해지고 있지만, 높은 제조 비용과 단편적인 주파수 정책이 현저한 역풍으로 남아 있습니다.
세계의 IoNT(Internet Of Nano Things) 시장 동향과 통찰
초저전력 센서를 가능하게 하는 나노기술의 급속한 발전
탄소나노튜브를 기반으로 한 장치는 주변 에너지를 활용하여 기존 배터리의 제약이 없어지고 유지보수 사이클이 단축됩니다. 매사추세츠공과대학(MIT)의 엔지니어들은 광합성에 의해 자기발전하는 식물 발전 나노센서를 입증하여 원격지 배치를 위한 에너지 자율성을 검증했습니다. 질화붕소 나노튜브 섬유는 열화 없이 가혹한 산업 환경을 견딜 수 있는 내열 네트워크를 제공합니다. Materials Nexus의 희토류가 없는 영구 자석의 획기적인 혁신으로 대표되는 바와 같이, AI에 의해 가속화된 재료 발견과 함께, 기술 혁신의 사이클은 수년에서 수개월로 단축되었습니다. 이러한 진보로 정밀농업부터 위험환경 모니터링에 이르기까지 폭넓은 응용이 가능하게 되어 나노 사물인터넷(IoNT) 시장의 장기적인 성장을 지원하고 있습니다.
실시간 건강 모니터링 웨어러블 수요 증가
Nanowear의 나노 센서 심장 패치의 FDA 승인은 나노 대응 의료기기에 대한 규제의 타당성을 강조합니다. 탄소나노튜브 필름으로 만들어진 지속적인 포도당 모니터는 눈에 띄지 않는 피부 패치의 폼 팩터를 유지하면서 실험실의 정확도와 비교할 수 있습니다. 다항목 분석 패치는 전해질, 젖산 및 코티솔을 동시에 추적하고 만성 질환 비용을 낮추는 예방 케어 모델을 지원합니다. 이러한 장치를 도입한 헬스케어 병원에서는 패혈증의 조기 발견과 ICU 체류기간의 단축이 보고되어 IoNT(Internet Of Nano Things) 시장 확대에 대한 헬스케어의 공헌이 강화되고 있습니다. 이 분야의 2024년 매출 점유율은 30.3%에 달하여 다른 업계가 과제해야 하는 수요가 정착하고 있음을 나타냅니다.
나노 규모의 심각한 데이터 보안 및 개인 정보 보호 위험
나노센서는 전통적인 암호화를 위한 컴퓨팅 헤드룸이 없기 때문에 병원, 공장, 지자체의 네트워크를 위험에 빠뜨릴 수 있는 공격 표면이 노출되어 있습니다. 이식 가능한 의료용 나노센서는 특히 취약하며, 납치된 포도당 모니터는 측정값을 변조하여 환자를 위험에 빠뜨릴 수 있습니다. GDPR(EU 개인정보보호규정)은 나노센서 데이터를 고위험으로 취급하고 자율적인 서브mm 디바이스에 구현하기 어려운 명시적 동의를 의무화하고 있습니다. 양자 내성 경량 암호는 아직 개념 실증 단계에 있으며, 보안 격차를 넓혀 나노물질 인터넷 시장 예측 CAGR에 부정적인 4.3%의 영향을 미칩니다.
부문 분석
하드웨어는 2024년 매출의 47.6%를 차지했으며, 나노 사물인터넷(IoNT) 시장은 필수 물리 디바이스, 안테나, 게이트웨이에 집중하고 있습니다. 그러나 분석 플랫폼이 분자 데이터의 분류를 이용하기 때문에 소프트웨어 부문은 CAGR 28.6%로 약진하고 있습니다. 서비스는 아직 시작되었지만 기업이 나노 디바이스와 레거시 시스템을 통합하기 위해 컨설팅 전문 지식이 필요하기 때문에 두 자리 성장을 기록하고 있습니다. Dow와 Carbice의 열 인터페이스 재료에 관한 협업은 전문적인 노하우가 얼마나 이익률이 높은 서비스 라인으로 변화하는지를 보여줍니다.
소프트웨어 붐이 가치 획득을 재정의합니다. 상품화로 인해 하드웨어 금리가 줄어들지만 수십억 개의 엔드포인트를 관리하는 오케스트레이션 스택은 프리미엄 라이선스를 요구합니다. 클라우드 벤더는 나노 디바이스 API를 통합하여 개발자를 보안, AI 및 라이프사이클 관리를 번들로 제공하는 통합 플랫폼으로 끌어들입니다. 예측 기간 동안, 소프트웨어 수익과 연동하는 IoNT(Internet Of Nano Things) 시장 규모는 하드웨어와의 차이를 줄이고 생태계 전체의 경쟁 전략을 재조정할 것으로 예측됩니다.
헬스케어는 2024년 매출액의 30.3%를 차지했으며, 가장 큰 채용 기업으로 생체연속 모니터링, 임플란트 모니터링, 스마트 약물전달에 나노센서를 활용하고 있습니다. 한편 스마트시티 프로그램은 지자체가 대기질 분석, 누수 감지, 지능형 교통 제어를 위한 나노 센서 메쉬를 도입하기 때문에 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 27.6%로 확대합니다. 제조업에서는 생산 라인에 내장된 나노센서가 실시간 분자 데이터를 예측 유지보수 엔진에 보내고, 물류 기업은 나노센서를 컨테이너 내에 설치하여 콜드체인의 컴플라이언스를 검증합니다.
환경기관은 고전적인 센서에 없는 10억분의 1 분해능으로 오염물질을 검출하는 나노센서 부표를 채용합니다. 농업 관련 기업은 영양 부족을 조기에 알리는 식물 조직 나노 센서를 살포하여 비료 사용과 물 낭비를 줄입니다. 이러한 전개는 수직적 다양화가 엔터프라이즈 경제 전체로 IoNT(Internet Of Nano Things) 시장 침투를 가속화하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
IoNT(Internet Of Nano Things) 시장은 컴포넌트별(하드웨어, 소프트웨어, 서비스), 최종 사용자별(헬스케어, 물류 및 운수, 방위 및 항공우주, 제조, 기타), 통신기술별(전자파, 분자통신, 나노 RFID/NFC, 기타), 전개 모델별(On-Premise, 클라우드, 하이브리드), 지역별로 분류되어 있습니다. 시장 예측은 금액(달러)으로 제공됩니다.
지역 분석
북미는 2024년 38.6%의 매출 점유율을 유지했으며, 연방 정부의 보조금, 테라헤르츠대 조기 할당, 나노 클래스 생산이 가능한 반도체 공장 정착이 뒷받침됐습니다. NIST의 IoT 자문위원회는 표준 표준을 명확히하고 상업 조종사를 가속화합니다. 그러나 높은 인건비와 자본 지출은 금리를 압박하고, 인재 파이프라인은 나노제조 기술자공급에 고전하고 있습니다. 미국은 방위, 항공우주, 첨단 건강 관리 임플란트에 주력하고 캐나다는 천연 자원 관리를 위한 환경 모니터링에 자원을 투입합니다.
아시아태평양의 CAGR은 2030년까지 28.1%가 되어, 인더스트리 4.0에의 적극적인 대처, 일렉트로닉스공급 체인의 충실, 5G의 풋프린트 확대가 반영됩니다. 중국은 수율과 안전성을 높이기 위해 제조 공장과 화학 플랜트에 나노 센서를 통합하여 제조업에의 흡수를 추진하고, 일본의 의료 기술 기업은 생체 적합성 나노 임플란트를 개척합니다. 한국은 전기통신사업에서 리더십을 발휘해 6G 대응 나노메시 네트워크를 시험적으로 구축하고 있습니다. 지역 정부는 나노의 연구 개발에 보조금을 내는 것으로, 시장 투입까지의 시간을 단축해, 경쟁을 격화시키고 있습니다. 그 결과, 규모의 우위성이 태어나 10년 후까지는 아시아태평양과 북미의 나노물의 인터넷 시장 규모의 차이가 줄어듭니다.
유럽은 세계 규범을 형성하는 데이터 프라이버시와 지속가능성의 틀을 지지하고 영향력을 유지하고 있습니다. Horizon Europe는 에지 AI와 IoT 연구에 1억 유로를 기록했으며, 그 중 일부는 나노 디바이스의 상호 운용성에 할당되었습니다. 독일은 정밀 제조에 나노 센서를 도입하고 영국은 그래핀 기반 건강 패치를 테스트하고 있습니다. 남미와 중동, 아프리카의 신흥지역은 환경과 인프라 모니터링에 선택적으로 투자하여 라이프사이클 비용을 억제하면서 높은 입도를 실현하는 나노센서의 능력을 활용하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택:
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 상정과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 초저전력 센서를 가능하게 하는 나노기술의 급속한 진보
- 실시간 건강 모니터링 웨어러블 수요 증가
- 인더스트리 4.0과 스마트 매뉴팩처링의 채용 확대
- 5G 및 6G와 엣지 컴퓨팅 인프라의 보급
- 신호 감쇠를 저감하는 테라헤르츠 밴드 나노 안테나의 브레이크스루 등장
- 나노 센서를 활용한 정부 출자 유행 감시 네트워크
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 나노 규모의 심각한 데이터 보안 및 개인 정보 보호 위험
- 높은 자본 비용과 나노 가공의 복잡성
- 생체 적합성과 장기적인 세포 독성이 우려되는 인체에 대한 전개
- 표준화된 테라헤르츠 주파수 규제의 부족으로 보급을 지연
- 업계 밸류체인 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- 업계의 매력 Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
- 거시경제 요인이 시장에 미치는 영향
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 컴포넌트별
- 하드웨어
- 소프트웨어
- 서비스
- 최종 사용자별
- 헬스케어
- 물류 및 운송
- 방위 및 항공우주
- 제조업
- 에너지 및 전력
- 환경 모니터링
- 소매
- 농업
- 스마트 시티 및 인프라
- 기타 최종 사용자
- 커뮤니케이션 테크놀로지별
- 전자
- 분자 커뮤니케이션
- 나노 RFID/NFC
- 나노센서 네트워크
- 나노위성 통신
- 기타
- 전개 모델별
- On-Premise
- 클라우드
- 하이브리드
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 칠레
- 기타 남미
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 싱가포르
- 말레이시아
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 중동
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 사우디아라비아
- 튀르키예
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 나이지리아
- 이집트
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- IBM Corporation
- Intel Corporation
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- SAP SE
- Juniper Networks, Inc.
- Nokia Corporation
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Analog Devices, Inc.
- STMicroelectronics NV
- Nanoscale Components, Inc.
- NanoSensors, Inc.
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- TeraSense Group, Inc.
- Graphenea, Inc.
- Litmus Automation, Inc.
- ON Semiconductor Corporation
- Microchip Technology Inc.
- Camtek Ltd.
- NeuraLace Medical, Inc.
- Nanolike SAS
- Ambiq Micro, Inc.
- Synapse Wireless, Inc.
제7장 투자 분석
제8장 시장 기회와 앞으로의 동향
- 화이트 스페이스와 미충족 요구 평가
The Internet of Nano Things Market size is estimated at USD 22.99 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 71.88 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 25.60% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
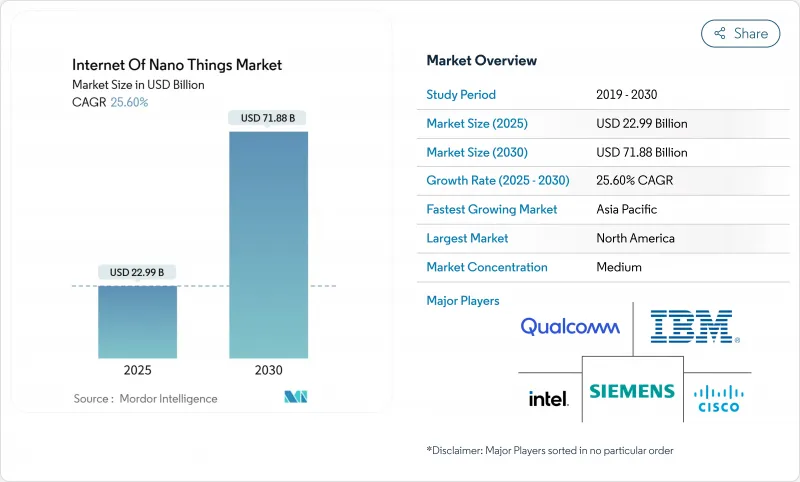
The surge reflects the commercialisation of terahertz-band nano-antenna designs, the roll-out of ultra-low power carbon-nanotube sensors, and the rapid convergence of nanoscale communication protocols with mainstream wireless networks. Governments are funding pandemic surveillance frameworks built on nanosensors, while private investment is accelerating AI-driven orchestration platforms that translate molecular-level data into actionable insight. Hardware continues to account for almost half of all spending, but software platforms are expanding at a markedly faster pace as enterprises prioritise analytics over devices. Regionally, North America leads on account of federal research grants and early terahertz spectrum allocation, yet Asia-Pacific exhibits the strongest growth as semiconductor hubs embed nanosensor networks into Industry 4.0 roadmaps. Competitive pressure is intensifying as semiconductor majors leverage existing fabs while start-ups introduce disruptive molecular communication stacks, but steep fabrication costs and fragmented spectrum policies remain notable headwinds.
Global Internet Of Nano Things Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Advancements in Nanotechnology Enabling Ultra-Low Power Sensors
Carbon-nanotube-based devices now harvest ambient energy, removing conventional battery constraints and slashing maintenance cycles. MIT engineers demonstrated plant-powered nanosensors that self-energize through photosynthesis, validating energy autonomy for remote deployments. Boron nitride nanotube fibres provide heat-tolerant networks that withstand harsh industrial settings without degradation. Coupled with AI-accelerated materials discovery, exemplified by Materials Nexus' rare-earth-free permanent magnet breakthrough, innovation cycles have shrunk from years to months. These advances unlock applications ranging from precision agriculture to hazardous-environment monitoring, underpinning the long-term growth of the Internet of Nano Things market.
Growing Demand for Real-Time Health Monitoring Wearables
FDA clearance of Nanowear's nanosensor cardiac patch underscores regulatory validation for nano-enabled medical devices. Continuous glucose monitors built on carbon-nanotube films now rival laboratory accuracy while retaining discreet, skin-patch form factors. Multi-analyte patches track electrolytes, lactate, and cortisol simultaneously, supporting preventive care models that lower chronic-disease costs. Hospitals integrating these devices report earlier sepsis detection and shorter ICU stays, reinforcing healthcare's contribution to the Internet of Nano Things market expansion. The sector's 30.3% revenue share in 2024 signals entrenched demand that other verticals must challenge.
Severe Data Security and Privacy Risks at Nanoscale
Nanosensors lack the compute headroom for traditional encryption, exposing attack surfaces that could compromise hospital, factory, or municipal networks. Implantable medical nanosensors are especially vulnerable; a hijacked glucose monitor can falsify readings, endangering patients. GDPR treats nanosensor data as high-risk, mandating explicit consent that is difficult to implement on autonomous sub-millimetre devices. Quantum-resistant lightweight ciphers remain at proof-of-concept stages, widening the security gap and exerting a negative 4.3% pull on forecast CAGR for the Internet of Nano Things market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Increasing Adoption of Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
- Proliferation of 5G/6G and Edge Computing Infrastructure
- High Capital Costs and Complexity of Nano-Fabrication
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Hardware generated 47.6% of 2024 revenue, anchoring the Internet of Nano Things market in essential physical devices, antennas, and gateways. Yet the software segment is racing ahead at a 28.6% CAGR as analytics platforms capitalise on torrents of molecular data. Services remain nascent but record double-digit growth because enterprises require consulting expertise to integrate nano-devices with legacy systems. Dow's collaboration with Carbice on thermal interface materials shows how specialised know-how is turning into high-margin service lines.
The software boom is redefining value capture: hardware margins compress as commoditisation sets in, while orchestration stacks that manage billions of endpoints command premium licences. Cloud vendors embed nano-device APIs, drawing developers into unified platforms that bundle security, AI, and lifecycle management. Over the forecast horizon, the Internet of Nano Things market size linked to software revenues is projected to narrow the gap on hardware, recalibrating competitive strategies across the ecosystem.
Healthcare contributed 30.3% of 2024 revenue and remains the largest adopter, leveraging nanosensors for continuous vitals monitoring, implant surveillance, and smart drug delivery. Smart-city programmes, however, will expand at 27.6% CAGR to 2030 as municipalities deploy nanosensor meshes for air-quality analytics, water-leak detection, and intelligent traffic control. In manufacturing, nanosensors embedded on production lines feed real-time molecular data into predictive-maintenance engines, while logistics firms fit nanosensors inside containers to verify cold-chain compliance.
Environmental agencies adopt nanosensor buoys that detect pollutants at parts-per-billion resolution, a capability classical sensors lack. Agriculture outfits scatter plant-tissue nanosensors that signal nutrient deficits early, cutting fertiliser usage and water waste. These deployments illustrate how vertical diversification is accelerating overall Internet of Nano Things market penetration across the real economy.
Internet of Nano Things Market is Segmented by Component (Hardware, Software, and Services), End-User (Healthcare, Logistics and Transportation, Defense and Aerospace, Manufacturing, and More), Communication Technology (Electromagnetic, Molecular Communication, Nano RFID/NFC, and More), Deployment Model (On-Premise, Cloud, and Hybrid), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained 38.6% revenue share in 2024, buoyed by federal grants, early terahertz spectrum allocation, and entrenched semiconductor fabs capable of nano-class production. The NIST IoT Advisory Board provides clarity around standards, accelerating commercial pilots. However, high labour costs and capital outlays squeeze margins, and the talent pipeline struggles to supply nano-manufacturing technicians. The United States focuses on defence, aerospace, and advanced healthcare implants, while Canada channels resources into environmental monitoring for natural-resource stewardship.
Asia-Pacific will post a 28.1% CAGR to 2030, reflecting aggressive Industry 4.0 incentives, deep electronics supply chains, and expansive 5G footprints. China drives manufacturing uptake, embedding nanosensors inside fabs and chemical plants to boost yield and safety, while Japan's med-tech firms pioneer bio-compatible nano implants. South Korea exploits telecom leadership to pilot 6G-ready nano-mesh networks. Regional governments subsidise nano R&D, compressing time-to-market and intensifying competition. The resulting scale advantages will narrow the Internet of Nano Things market size gap between Asia-Pacific and North America by decade end.
Europe remains influential, championing data privacy and sustainability frameworks that shape global norms. Horizon Europe has earmarked EUR 100 million for edge-AI and IoT research, with part allocated to nano-device interoperability. Germany deploys nanosensors in precision manufacturing, and the United Kingdom tests graphene-based health patches. Emerging regions in South America and the Middle East, and Africa invest selectively in environmental and infrastructure monitoring, capitalising on nanosensors' ability to deliver high granularity at lower lifecycle costs.
- IBM Corporation
- Intel Corporation
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- SAP SE
- Juniper Networks, Inc.
- Nokia Corporation
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Analog Devices, Inc.
- STMicroelectronics N.V.
- Nanoscale Components, Inc.
- NanoSensors, Inc.
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- TeraSense Group, Inc.
- Graphenea, Inc.
- Litmus Automation, Inc.
- ON Semiconductor Corporation
- Microchip Technology Inc.
- Camtek Ltd.
- NeuraLace Medical, Inc.
- Nanolike SAS
- Ambiq Micro, Inc.
- Synapse Wireless, Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumption and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid advancements in nanotechnology enabling ultra-low power sensors
- 4.2.2 Growing demand for real-time health monitoring wearables
- 4.2.3 Increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing
- 4.2.4 Proliferation of 5G/6G and edge computing infrastructure
- 4.2.5 Emerging terahertz-band nano-antenna breakthroughs reducing signal attenuation
- 4.2.6 Government-funded pandemic surveillance networks leveraging nanosensors
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Severe data security and privacy risks at nanoscale
- 4.3.2 High capital costs and complexity of nano-fabrication
- 4.3.3 Biocompatibility and long-term cytotoxicity concerns in human body deployments
- 4.3.4 Lack of standardized terahertz spectrum regulations causing deployment delays
- 4.4 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors on the Market
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUES)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.2 Software
- 5.1.3 Services
- 5.2 By End-user
- 5.2.1 Healthcare
- 5.2.2 Logistics and Transportation
- 5.2.3 Defense and Aerospace
- 5.2.4 Manufacturing
- 5.2.5 Energy and Power
- 5.2.6 Environmental Monitoring
- 5.2.7 Retail
- 5.2.8 Agriculture
- 5.2.9 Smart Cities and Infrastructure
- 5.2.10 Other End-users
- 5.3 By Communication Technology
- 5.3.1 Electromagnetic
- 5.3.2 Molecular Communication
- 5.3.3 Nano RFID/NFC
- 5.3.4 Nano Sensor Networks
- 5.3.5 Nano Satellite Communication
- 5.3.6 Others
- 5.4 By Deployment Model
- 5.4.1 On-Premise
- 5.4.2 Cloud
- 5.4.3 Hybrid
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Chile
- 5.5.2.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 Russia
- 5.5.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 Singapore
- 5.5.4.6 Malaysia
- 5.5.4.7 Australia
- 5.5.4.8 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.2.3 Egypt
- 5.5.5.2.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 IBM Corporation
- 6.4.2 Intel Corporation
- 6.4.3 Cisco Systems, Inc.
- 6.4.4 Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.5 Siemens AG
- 6.4.6 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.7 SAP SE
- 6.4.8 Juniper Networks, Inc.
- 6.4.9 Nokia Corporation
- 6.4.10 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.11 Analog Devices, Inc.
- 6.4.12 STMicroelectronics N.V.
- 6.4.13 Nanoscale Components, Inc.
- 6.4.14 NanoSensors, Inc.
- 6.4.15 Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.16 TeraSense Group, Inc.
- 6.4.17 Graphenea, Inc.
- 6.4.18 Litmus Automation, Inc.
- 6.4.19 ON Semiconductor Corporation
- 6.4.20 Microchip Technology Inc.
- 6.4.21 Camtek Ltd.
- 6.4.22 NeuraLace Medical, Inc.
- 6.4.23 Nanolike SAS
- 6.4.24 Ambiq Micro, Inc.
- 6.4.25 Synapse Wireless, Inc.
7 INVESTMENT ANALYSIS
8 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
- 8.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment












