
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1851820
커넥티드 선박 시장 : 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Connected Ship - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
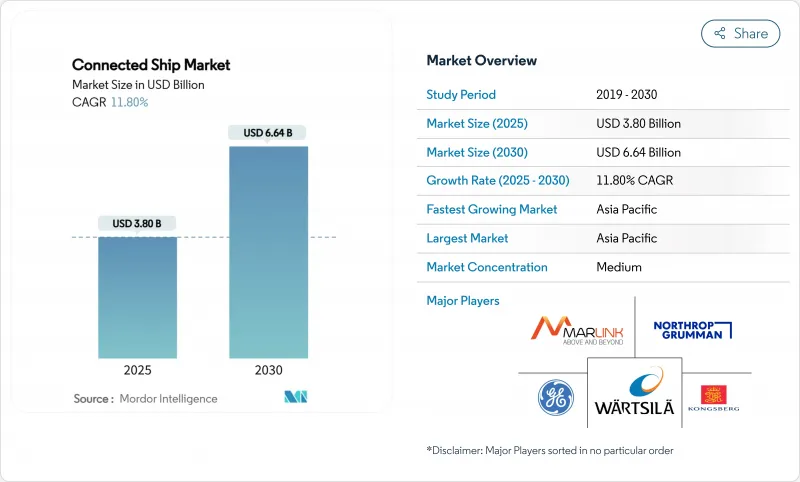
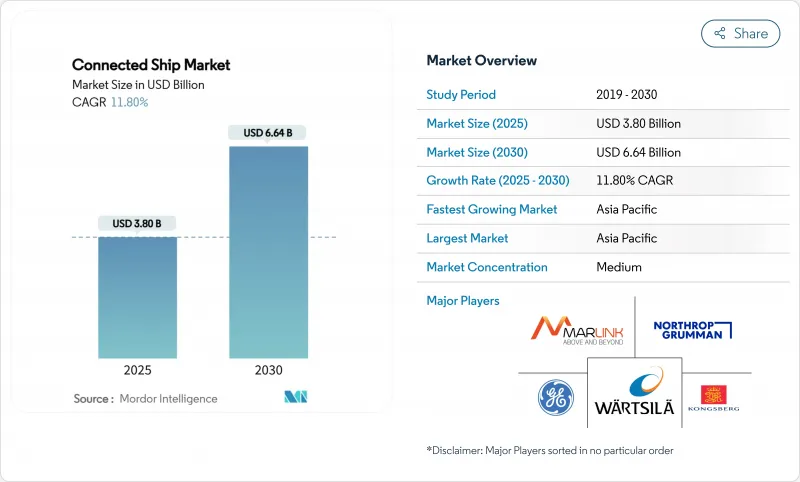
세계의 커넥티드 선박 시장 규모는 2025년 38억 달러, 2030년까지 66억 4,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 추정되며, 예측 기간 중(2025-2030년) CAGR은 11.80%로 예상됩니다.
국제해사기관(IMO)의 e-navigation 및 탄소집약도 보고에 관한 요구사항의 시행이 증가하고, 데이터 접속은 옵션의 추가에서 운용상의 필수조건으로 변화하고 있습니다. 상업선대의 소유자는 연료 사용량 감소, 배출량 감소, 컴플라이언스 유지를 위해 운항의 디지털화를 진행하고 있는 반면, 방위기관은 상황인식과 승무원의 복리후생을 위해 채용을 가속화하고 있습니다. 위성의 기술 혁신, 특히 저궤도 별자리는 대역폭 비용을 줄이고 소규모 사업자의 접근을 확대했습니다. 2024년 공급망 충격은 하드웨어 취약성을 드러내고 제조업체에게 니어 쇼어 생산을 요구하도록 촉구했지만 규제 확실성과 기술 성숙은 모든 선박 클래스에서 수요를 계속 강화하고 있습니다.
세계의 커넥티드 선박 시장 동향과 통찰
IMO e-navigation과 CII의 의무화
지속적인 데이터 보고가 정기적인 로그에 따를 대신 선박은 브리지, 기관실, 육상 사무소를 연결하는 실시간 연결의 통합을 강요하고 있습니다. 2024년 1월부터 시작된 Maritime Single Window는 항구에 표준화된 전자 데이터를 제출하도록 의무화하여 전 세계 연결 요구 사항을 높였습니다. 2025년부터 운영이 시작되는 새로운 수로 기준 S-100은 자율 내비게이션에 사용되는 디지털 트윈에 공급하는 세밀한 수심층을 추가합니다. 2025년에 채택된 선원의 전자 증명서는 승무원 관리를 더욱 디지털화하여 관리 시간 지연을 줄입니다.
ICT와 IoT의 선상에 도입이 진행됨
선대 관리자는 현재 수천 개의 저전력 센서를 배치하고 예측 분석 엔진에 공급하여 유지 보수 팀이 고장 전에 부품을 수리할 수 있도록 하고 있습니다. Maersk와 Onomondo의 협업은 세계 셀룰러와 위성 링크를 통해 컨테이너를 연결하고 대규모 운송 회사가 일정의 신뢰성을 높이기 위해 IoT를 활용하는 방법을 보여줍니다. NB-IoT 및 BLE 메쉬 디바이스는 박스 내의 습도, 진동 및 충격을 추적하여 지속적인 종단 간화물을 시각화합니다. 엣지 컴퓨팅 모듈은 위성 대역폭 사용을 줄이고 지연에 민감한 기능을 유지하기 위해 로컬로 데이터를 처리합니다. 한국과 일본의 항만 사업자는 선박이 접안할 때 데이터를 백홀하는 선박간 5G 네트워크를 지원하고 정보의 루프를 닫고 있습니다.
광대역 접속의 높은 CAPEX/OPEX
하드웨어, 설치, 통신 시간, 승무원의 훈련이 함께, 특히 소규모 부정기 선박 운항 회사의 경우 선주의 예산을 압박합니다. 미국 해안 경비대의 사이버 규칙은 연간 1억 3,870만 달러의 컴플라이언스 비용을 추가하여 디지털 업그레이드의 장애물을 높이고 있습니다. 반도체 부족은 2024년 내내 전자기기의 가격을 인상했으며, 중국제 부품에 대한 관세는 제조비용에 추가로 25% 상승했습니다. 많은 선주들은 가동 중지 시간을 최소화하기 위해 선박이 건독에 들어갈 때까지 라인 핏 프로젝트를 늦추지만 이 방법은 투자 회수 기간을 장기화합니다. 자본 부담을 줄이기 위해 임대 모델과 서비스형 대역폭 계획이 상승하고 있지만 채용은 여전히 신중합니다.
부문 분석
2024년 커넥티드 선박 시장 매출의 85%를 차지하는 것은 상용 부문이며, 이는 많은 상선 수와 규제 준수 비용의 상승을 반영하고 있습니다. 상선의 커넥티드 선박 시장 규모는 CAGR 11.4%를 보일 것으로 예측되고 있으며, 연료 최적화, 화물 시각화, 승무원 연결에 대한 투자를 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 방위 용도는 해군이 자율적인 초계기, 안전한 통신, 통합 전역 인식을 추구함에 따라 CAGR 13.5%로 확대되고 있습니다. 인도 태평양에서의 지정학적 긴장 증가와 합동 연습이 방위 수요를 더욱 뒷받침하고 있지만, 예산 사이클에 의한 조달의 지연이 당면의 수량을 억제하고 있습니다. 민간 항공사는 메쉬 네트워킹과 강화된 사이버 보안 등 비용 효율적인 민간 스핀오프를 위한 방어 혁신에 주목하고 있습니다.
상업 분야에서 선대의 디지털화는 연료 소비량 감소와 기항 효율화를 통해 투자에 대한 재무적 수익을 보장합니다. 한편, 국방 구매자는 대역폭 가격보다 이중화된 위성 통신 링크와 전자기파 내성에 가치를 두고 있으며, 이 차이가 벤더의 로드맵을 형성하고 있습니다. 소프트웨어 정의 라디오의 크기와 비용이 감소함에 따라 무역 회사, 해안 경비대 및 해군 고객에게 최소한의 하드웨어 차이로 서비스를 제공하는 부문 횡단 플랫폼이 나타납니다. 이 수렴은 개발주기를 단축하고 R&D 비용을 보다 광범위한 볼륨 기반으로 분산시켜 사이버 보안에 특화된 공급업체의 틈새 시장을 열면서 기존 공급업체를 강화합니다.
커넥티드 선박시장은 선박 유형별(상업, 방위, 연안경비), 용도 유형별(선박 교통관리, 선대운용, 선대건강 모니터링), 적합성별(라인핏, 레트로핏), 지역별로 구분됩니다.
지역 분석
아시아태평양은 2024년 커넥티드 선박 시장 점유율 35%로 세계를 선도해 2030년까지 성장률은 21.6%로 예상됩니다. 중국의 녹색 조선 행동 계획은 2025년까지 제로 카본 선박의 점유율 50%를 목표로 하고 있으며, 조선소는 연료전지, 배터리, 대체 연료를 감시하는 디지털 시스템의 통합을 추진하고 있습니다. 일본의 Society 5.0 프로그램은 선박간 데이터 교환 및 해상자율형 수상선 연구에 자금을 제공하여 내수를 강화하고 있습니다. 한국의 수출 신용 지원은 신조선 입찰 시 광대역 위성 통신을 지정하도록 선단에 장려하여 LEO 대응 하이브리드 네트워크로의 조기 이행을 확실히 하고 있습니다.
북미는 엄격한 사이버 보안 규정과 예지 보전을 매력적으로 만드는 높은 인건비로 매출 2위를 차지하고 있습니다. 미국 해안 경비대는 2025년 7월부터 사이버 보안 강화를 의무화해 존스 법률 선대의 사이버 보안 개수를 가속화하고 있습니다. 캐나다 사업자는 북극권의 항해보고를 준수하고 육상 인프라가 원격 기술 지원을 가능하게 하기 위해 연결성을 활용하고 있습니다.
유럽은 성숙한 도입 수준에 있지만 환경 법제로 인해 성장 관련성을 유지하고 있습니다. FuelEU Maritime과 EU 배출량 거래 시스템에 대한 해운 참여는 연결된 플랫폼만 제공할 수 있는 세분화된 데이터 보고를 요구합니다. 스칸디나비아, 네덜란드, 스페인의 항만은 현재 디지털로 검증된 이산화탄소 삭감에 대한 항만 사용료의 감액을 제공하여 비즈니스 사례를 강화하고 있습니다. EU 지역의 근해 사업자는 연안 지역에서도 일정한 데이터 흐름을 유지하기 위해 셀룰러 백홀과 결합된 저전력 단말기에 투자하고 있습니다. 이러한 요인이 상반되어 2030년까지 유럽의 선대 전환은 꾸준히 진행되고 있습니다.
기타 혜택:
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 해상무역량 증가
- ICT 및 IoT의 차재화
- 해상 관광과 크루즈 교통의 확대
- IMO의 e-네비게이션과 CII의 데이터 보고 의무화
- LEO 콘스텔레이션의 급속한 전개에 의한 광대역 비용 저하
- 데이터 주도 항해 최적화를 추진하는 탄소 강도 목표
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 광대역 접속의 높은 CAPEX/OPEX
- 높아지는 사이버 리스크와 보험료
- OEM간 데이터 소유권/상호운용성의 격차
- 디지털 기술을 익힌 선원이나 육상 스탭의 부족
- 가치/공급망 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁의 격렬함
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 선박 유형별
- 상업
- 방위 및 해안 경비
- 용도별
- 선박 교통관리
- 플릿 오퍼레이션
- 함대 건강 모니터링
- 피트별
- 레트로 핏
- LINE-FIT
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 유럽
- 영국
- 독일
- 프랑스
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 남미
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Northrop Grumman Corp.
- General Electric Co.
- Wartsila Oyj Abp
- Kongsberg Gruppen ASA
- Marlink AS
- Synectics Ltd.
- Atos SE
- Inmarsat(Viasat)
- Iridium Communications
- Navis(Navis LLC)
- DNV(Veracity)
- ABS Wavesight
- ABB Marine and Ports
- Thales Group
- Cobham Satcom
- KVH Industries
- Furuno Electric
- Samsung Heavy Industries
- Raytheon Technologies
- Starlink(SpaceX)
- OneWeb(Eutelsat)
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
JHS 25.11.25The Connected Ship Market size is estimated at USD 3.80 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 6.64 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 11.80% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Rising enforcement of International Maritime Organization requirements for e-navigation and carbon intensity reporting has moved data connectivity from an optional add-on to an operational prerequisite. Commercial fleet owners are digitizing operations to trim fuel use, cut emissions, and maintain compliance, while defense agencies accelerate adoption for situational awareness and crew welfare. Satellite innovations, especially Low Earth Orbit constellations, have slashed bandwidth costs, widening access for small operators. Supply-chain shocks in 2024 exposed hardware vulnerabilities and prompted manufacturers to seek near-shore production, yet regulatory certainty and maturing technology continue to reinforce demand across all vessel classes.
Global Connected Ship Market Trends and Insights
IMO e-navigation and CII mandates
Continuous data reporting now replaces periodic logs, forcing vessels to integrate real-time connectivity that links bridge, engine room, and shore offices. The Maritime Single Window, live since January 2024, obliges ports to accept standardized electronic submissions, which raises baseline connectivity requirements worldwide. New S-100 hydrographic standards, operational from 2025, add granular bathymetric layers that feed digital twins used for autonomous navigation. The revised International Maritime Organization strategy targets a 40% cut in CO2 intensity by 2030, so ship owners equip sensors that validate progress and avoid penalties.Electronic certificates for seafarers, adopted in 2025, further digitize crew management and reduce administrative lags.
Growing incorporation of ICT and IoT on board
Fleet managers now deploy thousands of low-power sensors that feed predictive analytics engines, allowing maintenance teams to fix components before failure. Maersk's collaboration with Onomondo connects containers through global cellular and satellite links, showing how large carriers exploit IoT to raise schedule reliability. NB-IoT and BLE Mesh devices track humidity, vibration, and shock inside boxes, creating continuous end-to-end cargo visibility. Edge computing modules process data locally to lower satellite bandwidth use and preserve latency-sensitive functions. Port operators in South Korea and Japan support ship-to-shore 5 G networks that backhaul the data once vessels berth, closing the information loop.
High CAPEX / OPEX of broadband connectivity
Hardware, installation, airtime, and crew training together stretch shipowner budgets, especially for smaller tramp operators. The United States Coast Guard cyber rules add USD 138.7 million per year in compliance costs, raising the hurdle for digital upgrades. Semiconductor scarcity lifted electronics pricing throughout 2024, and tariffs on Chinese components added a further 25% to production costs. Many owners delay line-fit projects until vessels dry-dock to minimize downtime, yet this approach prolongs payback periods. Leasing models and bandwidth-as-a-service plans are emerging to ease capital strain, though adoption remains cautious.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid roll-out of LEO constellations
- Carbon-intensity targets driving data-driven voyage optimization
- Escalating cyber-risk and insurance premiums
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The commercial segment generated 85% of the connected ship market revenue in 2024, reflecting the sheer number of merchant hulls and rising regulatory compliance costs. The connected ship market size for commercial vessels is projected to grow at an 11.4% CAGR, underpinning investments in fuel optimisation, cargo visibility, and crew connectivity. Defense applications are expanding at 13.5% CAGR as navies pursue autonomous patrol craft, secure communications, and integrated battlespace awareness. Growing geopolitical tensions and joint exercises in the Indo-Pacific further drive defense demand, yet budget cycles introduce procurement delays that temper near-term volumes. Commercial carriers look to defense innovations-such as mesh networking and hardened cybersecurity-for cost-effective civilian spin-offs.
Fleet digitization in the commercial arena anchors financial return on investment through lower fuel burn and port call efficiency. Meanwhile, defense buyers value redundant satcom links and electromagnetic resilience over bandwidth price, a distinction that shapes vendor roadmaps. As software-defined radios shrink in size and cost, cross-segment platforms emerge that serve merchants, coast guard, and naval customers with minimal hardware variance. The convergence shortens development cycles and spreads R&D cost across a wider volume base, reinforcing incumbent yet open niches for specialized cybersecurity vendors.
The Connected Ship Market is Segmented by Ship Type (Commercial, Defence, and Coast-Guard), by Application Type (Vessel Traffic Management, Fleet Operations, Fleet Health Monitoring), by Fit (Line Fit, Retrofit), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific leads global adoption with 35% connected ship market share in 2024 and a 21.6% growth trajectory to 2030. China's green shipbuilding action plan, targeting 50% share in zero-carbon vessels by 2025, pushes yards to integrate digital systems that monitor fuel cells, batteries, and alternative fuels. Japan's Society 5.0 program funds research on ship-to-shore data exchange and maritime autonomous surface ships, reinforcing domestic demand. South Korea's export credit support encourages fleets to specify high-bandwidth satcom during newbuild tenders, ensuring early migration to LEO-enabled hybrid networks.
North America ranks second by revenue, driven by strict cybersecurity regulations and high labor costs that make predictive maintenance attractive. The United States Coast Guard mandate, effective July 2025, accelerates cyber-secure retrofits on Jones Act fleets, while offshore energy operators view connected drilling vessels as essential for safety and uptime. Canadian operators leverage connectivity to comply with Arctic voyage reporting and to enable remote technical assistance amid sparse shore infrastructure.
Europe commands mature adoption levels but remains growth-relevant due to environmental legislation. FuelEU Maritime and inclusion of shipping in the EU Emissions Trading System demand granular data reporting that only connected platforms can deliver. Ports across Scandinavia, the Netherlands, and Spain now offer reduced harbour dues for digitally verified carbon reductions, reinforcing the business case. Intra-EU short-sea operators invest in low-power terminals paired with cellular backhaul to maintain constant data flow even within coastal zones. Together, these factors underpin steady European fleet conversions through 2030.
- Northrop Grumman Corp.
- General Electric Co.
- Wartsila Oyj Abp
- Kongsberg Gruppen ASA
- Marlink AS
- Synectics Ltd.
- Atos SE
- Inmarsat (Viasat)
- Iridium Communications
- Navis (Navis LLC)
- DNV (Veracity)
- ABS Wavesight
- ABB Marine and Ports
- Thales Group
- Cobham Satcom
- KVH Industries
- Furuno Electric
- Samsung Heavy Industries
- Raytheon Technologies
- Starlink (SpaceX)
- OneWeb (Eutelsat)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing seaborne trade volumes
- 4.2.2 Growing incorporation of ICT and IoT on-board
- 4.2.3 Expanding maritime tourism and cruise traffic
- 4.2.4 IMO e-navigation and CII data-reporting mandates
- 4.2.5 Rapid roll-out of LEO constellations lowering broadband cost
- 4.2.6 Carbon-intensity targets driving data-driven voyage optimisation
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High CAPEX / OPEX of broadband connectivity
- 4.3.2 Escalating cyber-risk and insurance premiums
- 4.3.3 Data-ownership / interoperability gaps among OEMs
- 4.3.4 Shortage of digitally-skilled seafarers and shore staff
- 4.4 Value/Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Ship Type
- 5.1.1 Commercial
- 5.1.2 Defence and Coast-Guard
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Vessel Traffic Management
- 5.2.2 Fleet Operations
- 5.2.3 Fleet Health Monitoring
- 5.3 By Fit
- 5.3.1 Retrofit
- 5.3.2 Line-fit
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.2 Germany
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 South Korea
- 5.4.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5 South America
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Info, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Northrop Grumman Corp.
- 6.4.2 General Electric Co.
- 6.4.3 Wartsila Oyj Abp
- 6.4.4 Kongsberg Gruppen ASA
- 6.4.5 Marlink AS
- 6.4.6 Synectics Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Atos SE
- 6.4.8 Inmarsat (Viasat)
- 6.4.9 Iridium Communications
- 6.4.10 Navis (Navis LLC)
- 6.4.11 DNV (Veracity)
- 6.4.12 ABS Wavesight
- 6.4.13 ABB Marine and Ports
- 6.4.14 Thales Group
- 6.4.15 Cobham Satcom
- 6.4.16 KVH Industries
- 6.4.17 Furuno Electric
- 6.4.18 Samsung Heavy Industries
- 6.4.19 Raytheon Technologies
- 6.4.20 Starlink (SpaceX)
- 6.4.21 OneWeb (Eutelsat)
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment












