
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1851882
POC(Point of Care) 분자진단 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향, 통계, 성장 예측(2025-2030년)Point-of-Care Molecular Diagnostics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
POC 분자진단 시장은 2025년에 39억 8,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 60억 8,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 2025-2030년 CAGR 8.77%로 성장할 전망입니다.

이 견조한 성장 궤도는 중앙 집중식 실험실에서 중합효소 연쇄반응 등급의 감도를 침대 옆에서 30분 이내에 제공하는 컴팩트한 플랫폼으로 업계 전반의 전환을 강조하고 있습니다. 성장의 원동력으로는 호흡기, 소화기, 성병, 종양 검사 메뉴 확대, 진단 회복력에 대한 강력한 공공 투자, 임상의가 결과를 거의 즉시 검색, 해석 및 저장할 수 있는 클라우드 기반 데이터 관리의 신속한 통합 등이 있습니다.
한편, 아시아태평양은 중국과 인도가 항균제 스튜어드십 및 고정밀 종양학을 지원하기 위한 분산형 검사에 투자하고 있기 때문에 볼륨 엔진으로 대두되고 있습니다. 기존 기업은 열 사이클러를 소형화하고, 신규 참가 기업은 온도 사이클을 생략한 등온 시스템을 상품화하며, 양 그룹은 산재하는 기기를 통합 진단 네트워크에 연결하는 소프트웨어 대시보드를 전개하기 때문에 경쟁이 격화되고 있습니다. 그럼에도 불구하고, 상환의 모호함, 검사실이 개발한 검사의 규제 준수에 드는 비용 상승, 시약 유통을 위한 콜드체인 인프라의 갭 등이 특정 환경, 특히 열대 지역과 자원이 부족한 지역 등, 가장 혜택을 받을 수 있는 지역에서의 보급을 지연시킬 우려가 있습니다.
세계의 POC(Point of Care) 분자진단 시장 동향 및 인사이트
분산형 및 신속한 호흡기 감염 검사에 대한 수요 증가
20분 미만의 호흡기 패널이 임상적으로 널리 채용됨에 따라 응급실의 대기 시간이 단축되고 경험적 약물의 사용이 줄어들어 불필요한 입원이 제한되었습니다. 의료 시스템의 보고에 따르면, 포인트 오브 케어의 분자 검사 결과는 대부분의 진찰에서 치료 계획을 변경하고, 항균제 스튜어드십을 향상시키며, 입원 기간을 단축하고 있습니다. 연결 모듈은 HL7 또는 FHIR을 사용하여 전자 의료 기록에 데이터를 푸시하고 감염 제어 팀에 이전에 몇 시간 후에 도착했던 데이터를 거의 실시간으로 시각화합니다. 이러한 명확한 운영상의 이점은 인플루엔자와 코로나 바이러스의 계절에 대량의 카트리지를 공급하는 원동력이 되어 POC 분자진단 시장의 제조업체에게 안정적인 경상 수익을 보장합니다.
POC 분자진단제 도입에 대한 정부 및 프로그램에 따른 지원
National Institutes of Health Point-of-Care Technologies Research Network는 2024년에 6가지 목표를 모은 자금 모집을 시작하여 종양학, 감염, 만성 질환 모니터링에서 프로토타입 개발을 가속화합니다. 미국 식품의약국은 2024년 6월에 최초의 요점 C형 간염 RNA를 허가하여 만성적으로 감염된 수백만 명의 미국인에 대한 당일 진단 및 치료를 가능하게 합니다. 유럽과 일본의 유사한 개념은 미래의 아웃 브레이크에 대한 의료 시스템의 준비를 강화하기 위해 플랫폼 전개에 여러 해 예산을 할당합니다. 예측 가능한 공공 부문의 지원은 일시적인 수요 곡선이 아닌 구조적인 수요 곡선을 보여주며 POC 분자진단 시장에서 경쟁하는 기업의 자본 계획을 개선하는 것입니다.
세분화된 불투명한 진료 보상 체계
중앙 실험실용으로 설계된 코딩 프레임워크는 반드시 니어 페이센트 플랫폼에 적용되는 것은 아니며, 공급자는 지불률에 대해 확신하지 않습니다. 2024년에 FDA가 결정한 검사실이 개발한 검사 시행 재량권의 단계적 폐지는 벤더가 공정한 환불을 요구해 지불자에게 일하는 한편, 새로운 컴플라이언스 및 문서화의 비용을 부과하게 됩니다. 종양학 및 다발성 암의 조기 발견 패널은 규제 당국의 허가가 떨어질 때까지 적용 범위의 결정이 늦어지고 임상적 유용성이 분명함에도 불구하고 보급이 늦어져 더욱 큰 불확실성에 직면하고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 서포트
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 분산형으로 신속한 호흡기 감염증 검사 수요 증가
- POC 분자진단제 도입을 위한 정부 및 프로그램에 의한 지원
- 새로운 용도를 가능하게 하는 기술의 진보(예 : 종양, 항균 스튜어드십)
- POC MDx의 비 기존 세팅(예 : 의원, 소매 약국)으로의 확대
- 미국 의원에서의 CLIA 면제 멀티플렉스 PCR 플랫폼의 채용 상황
- 마이크로유체 카트리지의 혁신이 아시아에서의 종양 유전자 패널 촉진
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 세분화되어 불투명한 보험 상환 상황
- 높은 규제 및 전환 비용
- 열대 저소득 지역의 동결 건조 시약의 콜드체인 갭
- 아이소서멀 NAAT의 위양성에 의한 임상의의 회의심
- 규제 전망
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업 간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측
- 제품 및 서비스별
- 어세이 및 키트
- 계기 및 분석 장치
- 소프트웨어 및 디지털 서비스
- 용도별
- 감염증
- 종양학
- 혈액학
- 출생 전 검사 및 신생아 검사
- 내분비학
- 파마코유전체학 및 컴패니언 Dx
- 기타 용도
- 기술별
- PCR 베이스
- INAAT
- 기타 기술
- 최종 사용자별
- 병원
- 홈케어
- 기타 최종 사용자
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 독일
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 이탈리아
- 스페인
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 일본
- 인도
- 한국
- 호주
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 중동 및 아프리카
- GCC
- 남아프리카
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Abbott
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- Danaher
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- BioMerieux SA
- Siemens Healthineers AG
- Becton, Dickinson and Company
- Hologic Inc.
- Qiagen NV
- QuidelOrtho Corporation
- Visby Medical Inc.
- OraSure Technologies Inc.
- Meridian Bioscience Inc.
- Co-Diagnostics Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- T2 Biosystems Inc.
- Genedrive plc
- Binx Health, Inc.
제7장 시장 기회 및 향후 전망
AJY 25.11.19The point of care molecular diagnostics market is valued at USD 3.98 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 6.08 billion in 2030, reflecting an 8.77% CAGR over 2025-2030.
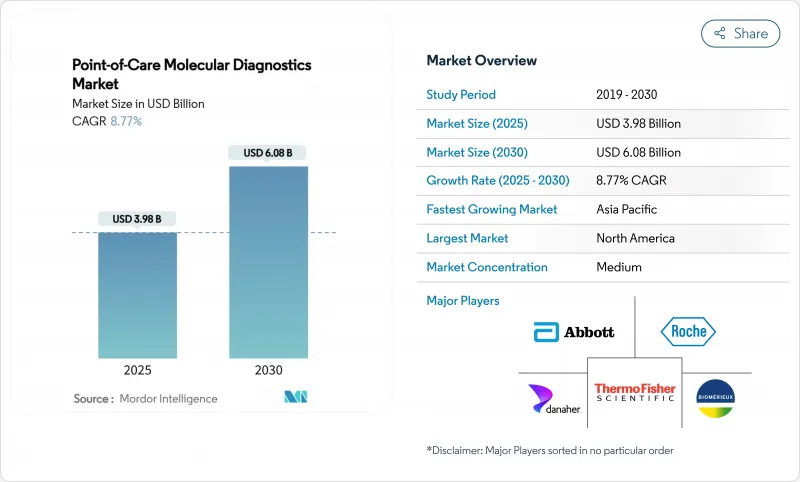
This solid upward path underscores an industry-wide transition from centralized laboratories to compact platforms that deliver polymerase chain reaction-grade sensitivity in less than 30 minutes at the bedside. Growth drivers include the widening menu of respiratory, gastrointestinal, sexually transmitted, and oncology assays, strong public investment in diagnostic resilience, and the rapid integration of cloud-based data management that allows clinicians to retrieve, interpret, and archive results almost instantly.
North America remains the largest regional contributor, benefitting from an extensive installed base, early regulatory approvals, and relatively predictable payer frameworks, while Asia Pacific is emerging as the volume engine as China and India invest in decentralized testing to support antimicrobial stewardship and precision oncology. Competitive intensity is building as incumbents miniaturize thermal cyclers, newcomers commercialize isothermal systems that omit temperature cycling, and both groups deploy software dashboards that knit scattered devices into unified diagnostic networks. Even so, reimbursement ambiguity, the rising cost of regulatory compliance for laboratory-developed tests, and gaps in cold-chain infrastructure for reagent distribution threaten to slow uptake in certain settings, particularly tropical or resource-constrained regions that stand to benefit most.
Global Point-of-Care Molecular Diagnostics Market Trends and Insights
Increased Demand for Decentralized and Rapid Respiratory Infection Testing
Widespread clinical adoption of sub-20-minute respiratory panels has trimmed emergency department wait times, reduced empiric drug use, and limited unnecessary admissions. Health systems report that point-of-care molecular results shift therapeutic plans in the majority of encounters, which improves antimicrobial stewardship and shortens length of stay. Connectivity modules use HL7 or FHIR to push data into electronic health records, giving infection-control teams near real-time visibility that previously arrived hours later. These clear operational wins fuel high cartridge volumes during influenza and coronavirus seasons, which in turn secure stable recurring revenue for manufacturers within the point of care molecular diagnostics market.
Government and Programmatic Support for POC Molecular Diagnostics Adoption
The National Institutes of Health Point-of-Care Technologies Research Network opened six targeted funding calls in 2024, accelerating prototype development across oncology, infectious disease, and chronic condition monitoring. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted the first point-of-care hepatitis C RNA authorization in June 2024, enabling same-visit diagnosis and treatment for millions of chronically infected Americans. Comparable initiatives in Europe and Japan allocate multi-year budgets for platform deployment to shore up health-system preparedness against future outbreaks. Predictable public-sector support signals a structural rather than episodic demand curve, which improves capital planning for firms competing in the point of care molecular diagnostics market.
Fragmented and Uncertain Reimbursement Landscapes
Coding frameworks designed for central laboratories do not always translate to near-patient platforms, leaving providers unsure of payment rates. The 2024 FDA decision to phase out enforcement discretion for laboratory-developed tests imposes fresh compliance and documentation costs just as vendors lobby payers for equitable reimbursement. Oncology and multi-cancer early detection panels face even greater uncertainty because coverage determinations lag behind regulatory clearances, slowing uptake despite evident clinical benefit.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Technological Advancements Enabling New Applications in Oncology and Antimicrobial Stewardship
- Expansion of POC MDx into Non-Traditional Settings
- Cold-Chain Gaps for Lyophilized Reagents in Tropical Low-Income Regions
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Abbott Laboratories
- Roche
- Danaher
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- bioMerieux
- Siemens Healthineers
- Beckton Dickinson
- Hologic
- QIAGEN
- QuidelOrtho
- Visby Medical Inc.
- Orasure Technologies
- Meridian Bioscience
- Co-Diagnostics
- Pfizer
- T2 Biosystems
- Genedrive plc
- Binx Health, Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increased Demand for Decentralized and Rapid Respiratory Infection Testing
- 4.2.2 Government and Programmatic Support for POC Molecular Diagnostics Adoption
- 4.2.3 Technological Advancements Enabling New Applications (e.g., Oncology, Antimicrobial Stewardship)
- 4.2.4 Expansion of POC MDx into Non-Traditional Settings (e.g., Physician Offices, Retail Pharmacies)
- 4.2.5 CLIA-waived Multiplex PCR Platforms Adoption in U.S. Physician Offices
- 4.2.6 Microfluidic Cartridge Innovation Catalyzing Oncology Gene Panels in Asia
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Fragmented and Uncertain Reimbursement Landscapes
- 4.3.2 High Regulatory and Transition Costs
- 4.3.3 Cold-Chain Gaps for Lyophilized Reagents in Tropical Low-Income Regions
- 4.3.4 Clinician Skepticism due to False-Positives in Isothermal NAAT
- 4.4 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value/Volume)
- 5.1 By Product & Service
- 5.1.1 Assays & Kits
- 5.1.2 Instruments / Analyzers
- 5.1.3 Software & Digital Services
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Infectious Diseases
- 5.2.2 Oncology
- 5.2.3 Hematology
- 5.2.4 Prenatal & Neonatal Testing
- 5.2.5 Endocrinology
- 5.2.6 Pharmacogenomics & Companion Dx
- 5.2.7 Other Applications
- 5.3 By Technology
- 5.3.1 PCR-based
- 5.3.2 INAAT
- 5.3.3 Other Technologies
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Hospitals
- 5.4.2 Homecare Settings
- 5.4.3 Other End Users
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Australia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Abbott
- 6.4.2 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- 6.4.3 Danaher
- 6.4.4 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.4.5 BioMerieux SA
- 6.4.6 Siemens Healthineers AG
- 6.4.7 Becton, Dickinson and Company
- 6.4.8 Hologic Inc.
- 6.4.9 Qiagen N.V.
- 6.4.10 QuidelOrtho Corporation
- 6.4.11 Visby Medical Inc.
- 6.4.12 OraSure Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.13 Meridian Bioscience Inc.
- 6.4.14 Co-Diagnostics Inc.
- 6.4.15 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.4.16 T2 Biosystems Inc.
- 6.4.17 Genedrive plc
- 6.4.18 Binx Health, Inc.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment

















