
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1906232
인도네시아의 전자상거래 물류 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 업계 동향과 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Indonesia E-Commerce Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
인도네시아의 전자상거래 물류 시장 규모는 2026년에는 57억 1,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다. 이는 2025년 52억 7,000만 달러에서 성장한 수치이며, 2031년에는 85억 6,000만 달러에 이를 전망입니다. 2026-2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 8.42%로 성장할 것으로 보입니다.

2024년 디지털 주문량은 35% 증가했으며, 지방 물류 허브와 국가 플랫폼을 연결하는 정부 프로그램이 네트워크 통합을 지속적으로 효율화하고 있습니다. 도로, 항만, 자동 분류 센터에 대한 투자는 배송 주기를 단축시키는 반면, 도시 소비자들은 당일 및 익일 배송 옵션 확대를 공급업체에 요구하고 있습니다. 분산된 경쟁 구조는 가격을 낮게 유지하지만 이익 마진을 압박하여 운송업체들이 AI 기반 경로 계획 및 창고 로봇 기술을 업그레이드하도록 촉진하고 있습니다. 한편, 1,500달러 미만 소포에 대한 규제 개혁으로 국경 간 규정 준수가 완화되어 소규모 수출업체에게 새로운 수익 채널이 열렸다.
인도네시아의 전자상거래 물류시장 동향 및 인사이트
지방도시에서 소포 취급량 급증
4G 커버리지 개선과 스마트폰 가격 하락이 대도시 외곽 지역에서의 온라인 쇼핑을 촉진하며, 세마랑, 말랑 등 2선 도시의 소포 물량을 끌어올리고 있습니다. 서비스 제공업체들은 지역 물류센터와 도시 단위 소형 물류센터를 결합해 저밀도 지역을 비용 효율적으로 서비스할 수 있도록 네트워크를 재설계해야 합니다. 토코피디아 나우(Tokopedia Now)와 같은 퀵커머스 업체들은 인근에 다중 픽업 지점을 늘려 운송사들이 더 넓은 지역에서 신속한 픽업-포장-배송 흐름을 조율하도록 하고 있습니다. 국가 물류 생태계 프로그램은 지방 물류센터와 전국 운송사를 연결하는 공통 데이터 레일을 제공하여 중소 업체들의 진입 장벽을 낮춥니다.
물류 비용 대 GDP 비율을 8%로 줄이는 정부의 이니셔티브
인도네시아의 2025-2029년 국가중기계획(RPJMN)은 물류 효율성을 경제 회복력의 핵심 축으로 규정했습니다. 각 부처는 도로, 항만, ICT 인프라 개선을 조율하여 빈 화물 운송과 행정 지연을 줄이고 있습니다. 신설 예정인 국가물류청 법안은 정책을 중앙집중화하여 2024년 2만 6,415개 컨테이너가 발이 묶인 사태와 같은 항만 혼잡을 방지할 계획입니다. 통신정보부(Kominfo)는 중립적 데이터 통합 기관으로 지정되어 운송사들이 화물 가시성과 동적 슬롯 예약을 가능하게 하는 API 피드 공개를 장려합니다.
인도네시아의 섬 지형이 라스트마일 배송 비용을 상승
17,500개 섬을 서비스하는 운송사들은 추가 해상 운송 구간, 기상 위험, 귀환 화물 부족으로 인해 자바 기준보다 40-60% 높은 배송 비용을 부담합니다. 얕은 항구와 중복된 해상 규정으로 인해 근해 운송은 여전히 미흡한 상태이며, 몬순 시즌은 일정과 재고 예측을 뒤흔든다. 해상 통행료 보조금이 도움이 되지만, 말루쿠나 파푸아로의 안정적인 항해를 위한 비용 프리미엄은 여전히 상업적 공급업체가 부담합니다.
부문 분석
2025년 인도네시아의 전자상거래 물류 시장 규모에서 운송 부문이 76.35%를 차지했습니다. 이는 도로망이 자바 섬 내 대량 화물 운송을 담당하고 해상 화물이 군도 지역을 연결하기 때문입니다. 그러나 라벨링 및 키팅을 중심으로 한 부가가치 서비스는 연평균 6.98% 성장할 것으로 예상되며, 이는 브랜드의 맞춤형 포장 수요를 충족시킬 것입니다. 운영사들은 정확도 향상과 체류 시간 단축을 위해 로봇 팔과 RFID 게이트를 점점 더 많이 도입하고 있습니다. 트럭 운송, 보관, 맞춤화를 결합한 통합 설비가 대형 마켓플레이스 계약을 따내고 있습니다.
지속적인 인프라 개선으로 도로 신뢰도는 높아지지만, 상승하는 유가와 환경 목표는 운송사들로 하여금 경로 최적화와 전기 밴 시험 운행을 촉진하고 있습니다. 창고 수요는 자카르타와 수라바야 항구 인근에 집중되어 자동화 허브를 위한 맞춤형 임대 수요가 급증하고 있습니다. 싱글스 데이나 라마단 같은 계절적 성수기에 유연하게 처리 능력을 조정할 수 있는 풀필먼트 업체들은 주요 플랫폼과 고마진 계약을 확보하고 있습니다.
B2C는 마켓플레이스 규모와 도시 고객 밀집도를 바탕으로 2025년 인도네시아 전자상거래 물류 시장 점유율 73.40%를 유지했습니다. 가격 민감도로 인해 운송사들은 비용 절감을 위해 최종 배송 단계에서 일괄 배송과 크라우드소싱 라이더를 활용합니다. B2B는 제조업체의 디지털 조달 전환과 JIT(정시 공급) 보충 수요로 인해 연평균 6.59% 성장할 전망입니다. 공장 라인을 겨냥한 공급업체들은 재고 감사, 품질 검사, 공급업체 관리 재고(VMS)를 추가해 고객 충성도를 높이고 있습니다.
C2C는 틈새 시장으로 남아 있지만 중고 패션 및 공예품을 거래하는 소셜커머스 플랫폼의 성장에 힘입어 상승세를 보입니다. 여기서 진품 인증과 저비용 반품 프로세스가 서비스 차별화 요소입니다. 마켓플레이스 주도 네트워크는 B2C와 B2B 장거리 운송을 통합한 하이브리드 모델을 도입해 트럭 활용도를 높이고 독립 운송업체의 마진을 압박할 수 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 애널리스트의 3개월간 지원
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장의 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 지방 도시(제2 및 제3급 도시)로부터의 소포 취급량의 급증
- 물류비 GDP 대비 비중을 8%로 낮추기 위한 정부의 추진
- 당일/익일 배송 옵션의 급속한 확산
- 인도네시아의 400조 루피아 규모 인프라 투자가 전자상거래 배송망의 확대를 촉진
- 인프라 투자(신규 유료도로, 항만, 공항)로 배송 소요 시간 단축 및 2/3선 도시 시장 개방
- 수도 이전(누산타라)으로 물류 허브 재편
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 군도 지형으로 인한 섬 간 라스트마일 비용 증가
- 분산된 CEP 업체 간 가격 경쟁으로 공급업체 마진 악화
- 인도네시아의 섬 지형이 라스트마일 배송 비용을 상승
- 현대 등급 A 창고의 숙련 노동자 부족
- 가치/공급망 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- 수요 및 공급 분석
- 업계의 매력도 - Five Forces 분석
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 구매자의 협상력
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
- 리버스/반품 물류에 관한 통찰
- 지정학적 이벤트가 공급망의 변천에 미치는 영향
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 서비스별
- 운송
- 도로
- 철도
- 항공
- 해상
- 창고 보관 및 풀필먼트
- 부가가치 서비스(라벨링, 포장, 키트화)
- 운송
- 비즈니스 모델별
- B2C
- B2B
- C2C
- 배송지별
- 국내
- 국경 간(국제)
- 배송 속도별
- 당일(24시간 이내)
- 익일(24-48시간)
- 표준(3-5일)
- 기타(5일 이상)
- 제품 카테고리별
- 식품 및 음료
- 퍼스널케어 및 가정용품
- 패션 & 라이프 스타일(액세서리, 의류, 양말)
- 가구
- 가전제품 및 가정용 전자제품
- 기타 제품
- 도시 레벨별
- 1선 도시
- 2선 도시
- 3선 도시 이하
- 주별
- 중부자바주
- 동자바주
- 서자바주
- 자카르타
- 반텐주
- 기타 주
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- JNE Express
- J&T Express
- SiCepat Ekspres
- Ninja Xpress
- Lion Parcel
- Wahana Express
- TIKI
- Pos Indonesia
- Paxel
- DHL Express
- UPS
- FedEx
- GoSend(Gojek)
- Grab Express
- Shipper
- Shopee Express
- Lazada eLogistics
- Kuehne Nagel
- DSV
- Kerry Logistics
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
HBR 26.01.26Indonesia E-Commerce Logistics Market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 5.71 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 5.27 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 8.56 billion, growing at 8.42% CAGR over 2026-2031.
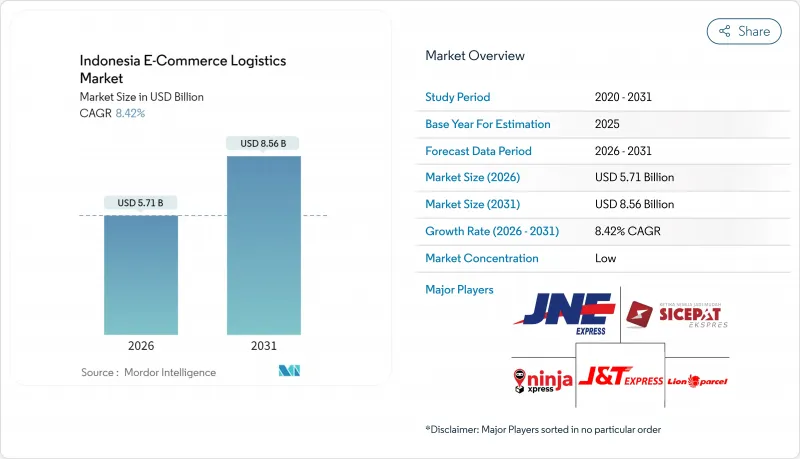
Digital ordering volumes climbed 35% in 2024, and government programs that connect provincial logistics hubs with national platforms continue to streamline network integration. Investments in roads, ports, and automated sortation centers shorten delivery cycles, while urban consumers push providers to accelerate same-day and next-day options. Fragmented competition keeps prices low but pressures profit margins, prompting carriers to upgrade AI-driven route planning and warehouse robotics. Meanwhile, regulatory reforms for parcels below USD 1,500 ease cross-border compliance, opening new revenue channels for small exporters.
Indonesia E-Commerce Logistics Market Trends and Insights
Explosive Parcel-Volume Surge from Tier-2/3 Cities
Improved 4G coverage and smartphone affordability are propelling online shopping outside metropolitan cores, lifting parcel counts in Semarang, Malang, and other secondary markets. Providers must redesign networks to serve lower-density zones cost-effectively, blending regional depots with city-level micro-fulfillment points. Quick-commerce operators such as Tokopedia Now increasingly stock multiple pick points nearby, forcing carriers to orchestrate rapid pick-pack-ship flows across a wider geography. The National Logistics Ecosystem program supplies common data rails that link provincial warehouses to national carriers, lowering onboarding barriers for smaller players.
Government Push to Cut Logistics Cost-to-GDP to 8%
Indonesia's RPJMN 2025-2029 embeds logistics efficiency as a pillar of economic resilience. Ministries coordinate road, port, and ICT upgrades to shrink empty backhauls and administrative delays. A new National Logistics Agency bill aims to centralize policy, preventing port congestion episodes such as the 2024 container backlog that stranded 26,415 boxes. Kominfo has been assigned as a neutral data integrator, incentivizing carriers to expose API feeds that enable shipment visibility and dynamic slot booking.
Archipelagic Geography Inflates Inter-Island Last-Mile Costs
Serving 17,500 islands saddles carriers with extra sea legs, weather risks, and scarce return loads that push delivery costs 40-60% above Java norms. Short sea shipping remains underserved due to shallow ports and overlapping maritime rules, while monsoon seasons upend schedules and inventory forecasts. The Sea Toll subsidy helps, yet commercial providers still shoulder cost premiums for reliable sailings to Maluku or Papua.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid Uptake of Same-Day/Next-Day Delivery Options
- IDR 400 Trillion Infrastructure Investment
- Fragmented CEP Price War Eroding Provider Margins
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Transportation captured 76.35% of the Indonesia e-commerce logistics market size in 2025 as road networks carry bulk intra-Java traffic and sea freight stitches together the archipelago. Yet value-added services, led by labeling and kitting, are projected to grow 6.98% CAGR, feeding brands' need for curated packaging. Operators increasingly embed robotic arms and RFID gates to elevate accuracy and shrink dwell times. Integrated setups that blend trucking, storage, and customization win large marketplace contracts.
Ongoing infrastructure upgrades enhance road reliability, but rising fuel prices and environmental targets nudge carriers to optimize routing and test electric vans. Warehousing demand clusters near Jakarta and Surabaya ports, prompting a surge in build-to-suit leases for automated hubs. Fulfillment players that can flex capacity around seasonal peaks, such as Singles Day or Ramadan, secure higher-margin slots with leading platforms.
B2C retained 73.40% of Indonesia e-commerce logistics market share in 2025 on the back of marketplace scale and urban customer density. Price sensitivity compels carriers to strip costs, spurring batch deliveries and crowdsourced riders for the final mile. B2B, forecast to rise 6.59% CAGR, benefits from manufacturers' digitizing procurement and demanding just-in-time replenishment. Providers targeting factory lines add inventory audit, quality checks, and vendor-managed stock to deepen client stickiness.
C2C stays niche but receives lift from social-commerce platforms that trade preloved fashion and crafts. Here, authentication and low-cost return loops differentiate service propositions. Marketplace-controlled networks could roll out hybrid models that pool B2C and B2B line-haul to boost truck utilization, compressing independent forwarders' margins.
The Indonesia E-Commerce Logistics Market Report is Segmented by Service (Transportation, Warehousing & Fulfilment, and Value-Added Services), Business Model (B2C, B2B, and C2C), Destination (Domestic and Cross-Border), Delivery Speed (Same-Day, and More), Product Category (Foods & Beverages, and More), City Tier (Tier 1, 2, and More), and Province (Jakarta, and More). Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- JNE Express
- J&T Express
- SiCepat Ekspres
- Ninja Xpress
- Lion Parcel
- Wahana Express
- TIKI
- Pos Indonesia
- Paxel
- DHL Express
- UPS
- FedEx
- GoSend (Gojek)
- Grab Express
- Shipper
- Shopee Express
- Lazada eLogistics
- Kuehne + Nagel
- DSV
- Kerry Logistics
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Explosive parcel-volume surge from tier-2/3 cities
- 4.2.2 Government push to cut logistics cost-to-GDP to 8 %
- 4.2.3 Rapid uptake of same-day / next-day delivery options
- 4.2.4 Indonesia's IDR 400 Trillion Infrastructure Investment Set to Boost E-Commerce Delivery Reach
- 4.2.5 Infrastructure Investments (new toll roads, ports, airports) is shrinking delivery transit times and opening tier-2/3 markets
- 4.2.6 National-capital move to Nusantara redrawing fulfilment hubs
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Archipelagic geography inflates inter-island last-mile costs
- 4.3.2 Fragmented CEP price war eroding provider margins
- 4.3.3 Indonesia's Island Geography Drives Up Last-Mile Delivery Costs
- 4.3.4 Skilled-labour gap in modern Grade-A warehouses
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Demand & Supply Analysis
- 4.8 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces
- 4.8.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.9 Reverse / Return Logistics Insights
- 4.10 Impact of Geo-Political Events on Supply Chain Shifts
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Transportation
- 5.1.1.1 Road
- 5.1.1.2 Rail
- 5.1.1.3 Air
- 5.1.1.4 Sea
- 5.1.2 Warehousing & Fulfilment
- 5.1.3 Value-Added Services (Labelling, Packaging, Kitting)
- 5.1.1 Transportation
- 5.2 By Business Model
- 5.2.1 B2C
- 5.2.2 B2B
- 5.2.3 C2C
- 5.3 By Destination
- 5.3.1 Domestic
- 5.3.2 Cross-border (international)
- 5.4 By Delivery Speed
- 5.4.1 Same-day (less than 24 h)
- 5.4.2 Next-day (24-48 h)
- 5.4.3 Standard (3-5 days)
- 5.4.4 Others (more than 5 days)
- 5.5 By Product Category
- 5.5.1 Foods & Beverages
- 5.5.2 Personal & Household Care
- 5.5.3 Fashion & Lifestyle (accessories, apparel, footwear)
- 5.5.4 Furniture
- 5.5.5 Consumer Electronics & Household Appliances
- 5.5.6 Other Products
- 5.6 By City Tier
- 5.6.1 Tier 1
- 5.6.2 Tier 2
- 5.6.3 Tier 3 and Below
- 5.7 By Provinces
- 5.7.1 Central Java
- 5.7.2 East Java
- 5.7.3 West Java
- 5.7.4 Jakarta
- 5.7.5 Banten
- 5.7.6 Rest of Provinces
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 JNE Express
- 6.4.2 J&T Express
- 6.4.3 SiCepat Ekspres
- 6.4.4 Ninja Xpress
- 6.4.5 Lion Parcel
- 6.4.6 Wahana Express
- 6.4.7 TIKI
- 6.4.8 Pos Indonesia
- 6.4.9 Paxel
- 6.4.10 DHL Express
- 6.4.11 UPS
- 6.4.12 FedEx
- 6.4.13 GoSend (Gojek)
- 6.4.14 Grab Express
- 6.4.15 Shipper
- 6.4.16 Shopee Express
- 6.4.17 Lazada eLogistics
- 6.4.18 Kuehne + Nagel
- 6.4.19 DSV
- 6.4.20 Kerry Logistics
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment


















