
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1910678
원자력 발전 : 시장 점유율 분석, 업계 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Nuclear Power - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
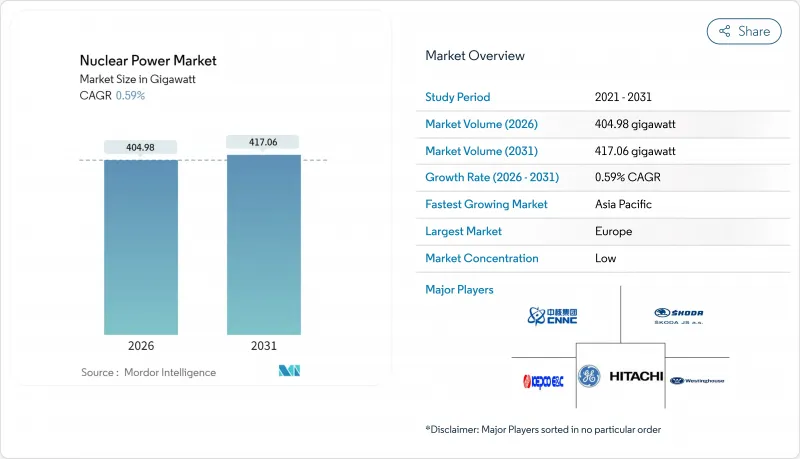
원자력 발전 시장은 2025년 402.60기가와트에서 2026년에는 404.98기가와트로 성장하고 2026년에서 2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 0.59%를 나타낼 전망입니다. 2031년까지 417.06기가와트에 달할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.

지속적인 설비 용량 증가는 여전히 완만한 수준에 머물고 있지만, 이 분야에서는 구조적인 전환이 진행되고 있습니다. 소형 모듈로(SMR)가 개발 단계에서 상업 전개로 이행하는 한편, 수명 연장 프로그램이 기존의 베이스 로드 발전을 지원한다는 구조입니다. 개발 사업자는 건설 리스크를 줄이기 위해 공장 생산 모듈에 주력하는 한편, 기존의 기가와트급 프로젝트는 상승하는 자본 비용, 장기화하는 리드 타임, 엄격화하는 자금 조달 룰에 직면하고 있습니다. 지역별 동향으로는 유럽의 방대한 기존 설비, 아시아태평양의 급속한 건설 페이스, 북미의 운전 기간 연장에 대한 주력이 특징입니다. 또, 산업 탈탄소화의 요구로부터도 기회가 탄생하고 있습니다. 고온 원자력 공정 열을 이용하면 철강, 시멘트, 화학 산업에서 석탄과 천연 가스 보일러를 대체할 수 있습니다.
세계의 원자력 발전 시장 동향과 전망
깨끗한 베이스로드 전력에 대한 수요 증가
전력부문의 탈탄소화 목표는 계속 엄격화되고 있으며, 계통운용자는 신뢰성을 손상시키지 않고 변동성 재생가능 에너지원을 대량으로 통합하는 데 어려움을 겪고 있습니다. 그 때문에 정부는 특히 전력 사용량이 연간 15-20% 증가하는 데이터센터 집적지용으로 24시간 365일 가동하는 탄소 프리 전원으로서 원자력을 재검토하고 있습니다. 한때 원자력발전의 단계적 폐지를 계획하고 있던 일본이나 한국 등 여러 경제권에서는 에너지 안보를 확보하기 위해 방침을 전환하고 있습니다. 용량 가치 지불과 부대 서비스 수익이 원자력 사업 계획에 통합되어 태양광과 풍력과의 현저한 비용 차이가 줄어들고 있습니다. 이에 따라 원자력 발전 시장은 스팟전력가격이 계속 변동하는 상황에서도 정책적인 지원을 확보하고 있습니다. 동시에, 규제 당국은 보다 엄격한 안전 마진을 요구하고 있으며, 이에 따라 라이선싱 심사 기간이 연장되는 한편, 공중의 수용성도 강화되고 있습니다.
운전기간 연장·출력 향상 프로그램
사업자는 40년 경과한 원자로를 60년, 심지어 80년 가동시키는 비용이 1kW당 500-1,000달러인 반면, 신규 건설에는 1kW당 6,000-1만 2,000달러가 필요하다는 것을 인식하고 있습니다. 미국 원자력 규제 위원회는 지금까지 95건의 운전 연장 인가를 승인하고 있으며, 프랑스에서는 494억 유로를 투입한 대규모 개수 프로젝트에 의해 격납 용기의 강화와 주요 기기의 교환이 진행되고 있습니다. 터빈과 노심 내부기기의 출력 향상은 통상 1기당 4-7%의 출력 증가를 가져오고, 신규 입지를 둘러싼 다툼 없이 원자력 시장을 확대하는 가장 빠른 수단이 되고 있습니다. 사업자에게는 원자로 압력 용기의 취화나 계장 기기의 진부화에 대한 대응이 여전히 요구되고 있습니다. 60년이 넘는 규제의 불확실성은 장기계획의 발판이 되지만, 많은 전력회사는 운전기간 연장을 2030년대 차세대 원자로 도입에 대한 교량으로 파악하고 있습니다.
비용 초과 및 자금 조달 과제
조지아의 보글 3-4호기 확장 프로젝트는 당초 예산의 2배 이상인 350억 달러로 부풀어 오르고 있으며 영국의 힝클리 포인트 C는 현재 430억 달러 가까이에 이르고 있습니다. 이러한 초과는 공급망 부족, 건설 중 설계 변경, 수십 년에 걸친 신규 건설의 정체로 인한 숙련 노동자의 유출로 인한 것입니다. 이러한 이유로 대출 기관은 자금을 제공 할 때 정부 보증, 규제 된 자산 담보 모델 또는 장기 전력 구매 계약을 요구합니다. 개발자들은 공사 단축을 위해 모듈화를 추진하고 있지만, 초호기가 되는 소형 모듈로(SMR)는 여전히 신뢰할 수 있는 비용 곡선을 나타내야 합니다. 정부 대출보증과 세제우대 조치는 위험을 줄이지만 민간 주도 원자력 프로젝트는 여전히 드뭅니다.
부문 분석
가압경수로는 2025년 총용량의 74.02%를 차지하여 원자력 발전 시장의 핵심 역할을 확고히 했습니다. 그러나 고속증식로는 중국의 600MWe급 CFR-600과 인도의 프로토타입로 프로그램을 견인역으로 하여 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 19.4%의 궤도를 타고 있습니다. 가스 냉각로와 용융염로의 개념은 여전히 파일럿 단계에 있지만, 고온 처리 능력은 산업용 열 수요 고객의 관심을 끌고 있습니다.
따라서 원자력 발전 시장에서는 경수로 설계가 중기적으로 점유율을 유지하는 한편, 실증용 고속로는 폐쇄형 연료 사이클의 지식 기반을 구축합니다. 규제 당국은 나트륨·납 냉각 시스템에 대한 이해를 깊게 하고 있지만, 상업화 자금 조달은 안전성과 경제성을 실증하는 조기의 성공 사례에 의존합니다. CFR-600이 성능 목표를 달성하면, 증식로 기술은 2030년대에 원자력 시장에서 상당한 점유율을 획득할 수 있습니다.
중규모 500-1,000MWe 유닛은 2025년 시점에서 설치 용량의 48.12%를 차지하며, 성숙한 송전망을 가진 국가에서 계속해서 우선 선택지가 되었습니다. 500MWe 미만의 소형로는 CAGR 19.2%로 확대될 것으로 예상되며, 이는 리스크 자본을 줄이는 모듈식 증설에 전력회사의 관심을 반영하고 있습니다. 20MWe 미만의 마이크로로는 광업 및 방위용도를 대상으로 하며 오프 그리드 환경에서 내결함성을 제공합니다.
소형 원자로의 경제성에서 공장 생산은 매우 중요합니다. 벤더 각사는 표준화를 추진하고 있으며, 10-12기의 가동 후에는 학습 곡선 효과에 의한 비용 저하가 SMR 시장 규모의 확대에 기여합니다. 한편, 1,000MWe를 넘는 대형 원자로는 코스트면에서의 역풍과 소규모국에 있어서 계통 연계 제한에 직면하고 있어 중국·인도 이외에서의 신규 수주는 억제되고 있습니다.
원자력 시장 보고서는 원자로 유형(가압 경수 감속 냉각로, 고속 증식로 등), 원자로 규모(대형, 중형, 소형), 연료 유형(저농축 우라늄 등), 용도별(계통 연계 전력, 공업 프로세스용 열·증기 등), 최종 사용자별(전력 회사·독립계 발전 사업자, 공업·석유 화학 등), 지역별(유럽)
지역별 분석
유럽은 2025년에 있어서도 원자력 시장에서 최대의 39.35%의 점유율을 유지했으며, 이는 프랑스 국내 전력의 65%를 공급하는 56기의 원자로군에 지지되었습니다. 유럽 연합(EU)은 그린 택소노미에서 원자력 에너지를 전환 자산으로 자리매김하고 지속 가능한 자금 조달 경로를 개방하고 있습니다. 그러나 운전기간 연장비용과 후쿠시마 사고 후 안전대책 강화가 사업자의 재무를 압박하고 있으며, 2023년 독일 원자력발전소 폐쇄로 중유럽은 프랑스로부터의 수입전력 의존도가 높아졌습니다. 영국에서는 3.2기가와트의 힝클리포인트 C원자력발전소가 추진되어 6기의 유럽가압수형로(EPR)의 도입이 검토되고 있으며, 이에 따라 2050년까지 국내 원자력기술을 유지할 전망입니다.
아시아태평양은 6.6%라는 가장 빠른 CAGR을 달성하고 있으며, 중국에서 건설중인 24기의 원자로 계획과 인도의 국산 중수로(PHWR) 및 고속로 프로그램이 견인하고 있습니다. 중국은 원자력 확대를 2060년까지의 탄소 중립 공약과 정합시키고, 2030년까지 120기가와트(GW)를 목표로 하고 있습니다. 일본에서는 단계적인 재가동에 의해 가동률이 향상되고 있는 것, 국민의 회의적인 견해가 제약 요인이 되고 있습니다. 한편 한국은 28기의 원자로를 유지하고 아랍에미리트(UAE)에 APR-1,400 유닛을 수출하고 있습니다. 베트남이나 인도네시아 등 신흥 경제국에서는 실현 가능성 조사가 진행되고 있지만, 원자력 시장 진입에는 자금 조달과 규제 정비가 여전히 장벽이 되고 있습니다.
북미에서는 운전 연장과 선택적 신규 건설이 주류입니다. 미국에서는 총 발전량의 20%, 무탄소 전력의 50%를 원자력에 의존하고 있습니다. 운전연장에 의해 노후화 플랜트를 유지하면서 연방세액공제와 대출보증으로 아이다호주와 와이오밍주에서 소형모듈로(SMR) 프로젝트를 추진하고 있습니다. 캐나다에서는 CANDU로의 개수를 진행해, 2024년에는 달링턴 2호기로부터 881MWe를 추가했습니다. 원격지의 북극권 커뮤니티와 중유 채굴 현장을 위한 소형 모듈로 실증도 추진 중입니다. 멕시코는 라구나 베르데 2기의 운전을 계속하는 한편, 신규 건설의 전망은 서 있지 않습니다. 이 지역 전체에서 첨단로의 도입 경로는 고농축 우라늄(HALEU)공급과 간소화된 라이선싱 절차에 달려 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 애널리스트 지원(3개월간)
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 깨끗한 베이스로드 전력에 대한 수요 증가
- 수명 연장 및 출력 향상 프로그램
- 선진 소형 모듈로(SMR)의 상업화
- 산업 탈탄소화 프로세스 - 열 수요
- 원자력 유래 수소·암모니아 사업
- 원자력 발전에 의한 데이터센터 및 선박 용도의 출현
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 비용 초과 및 자금 조달상의 과제
- 저비용 재생에너지와의 경쟁
- 고농축 우라늄 연료 공급 병목
- 수출관리 및 확산감시
- 공급망 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술 전망
- Porter's Five Forces
- 공급기업의 협상력
- 구매자의 협상력
- 신규 참가업체의 위협
- 대체품의 위협
- 경쟁의 격렬함
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 반응로 유형별
- 가압 경수로(PWR)
- 가압 중수로(PHWR)
- 비등로(BWR)
- 흑연감속 가스냉각로(GCR)
- 고온 가스 냉각로(HTGR)
- 경수로 냉각 및 흑연 감속로(LWGR)
- 고속 증식로(FBR)
- 기타
- 원자로 규모별
- 대형(1,000MWe 이상)
- 중형(500-1,000MWe)
- 소형(500MWe 미만; 소형 모듈형 원자로(SMR) 및 마이크로 원자로 포함)
- 연료 유형별
- 저농축 우라늄(U-235 5% 미만)
- 고농축 저농축 우라늄(LEU)(U-235 5-20%)
- 혼합 산화물(MOX)
- 토륨 기반 연료
- 용도별
- 계통 연계 발전
- 독립형 및 원격 지역 전력 공급
- 산업 공정 열 및 증기
- 담수화 및 지역 난방
- 방위 및 군사 기지
- 최종 사용자 섹터별
- 유틸리티 및 독립 발전 사업자(IPP)
- 산업 및 석유화학
- 광업 및 원격 운영
- 정부 및 방위
- 연구 기관
- 지역별
- 북미
- 미국
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 유럽
- 영국
- 프랑스
- 스웨덴
- 스페인
- 우크라이나
- 러시아
- 기타 유럽
- 아시아태평양
- 중국
- 인도
- 일본
- 한국
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 남미
- 브라질
- 아르헨티나
- 기타 남미
- 중동 및 아프리카
- 아랍에미리트(UAE)
- 남아프리카
- 이집트
- 기타 중동 및 아프리카
- 북미
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 움직임(M&A, 합작 사업, 자금 조달, 전력 구입 계약)
- 시장 점유율 분석(주요 기업의 시장 순위·점유율)
- 기업 프로파일
- Electricite de France SA(EDF)
- Rosatom State Atomic Energy Corporation
- China National Nuclear Corporation(CNNC)
- Westinghouse Electric Company LLC
- GE-Hitachi Nuclear Energy
- Framatome SA
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
- Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power/KEPCO E&C
- BWX Technologies Inc.
- Bechtel Corporation
- Doosan Enerbility Co. Ltd
- Fluor Corporation(NuScale)
- SKODA JS as
- Holtec International
- TerraPower LLC
- Rolls-Royce SMR Ltd
- X-Energy LLC
- General Fusion Inc.
- Ontario Power Generation
- Babcock International Group
- Bilfinger SE
- Duke Energy Corporation
- Japan Atomic Power Company
- Ansaldo Nucleare
제7장 시장 기회와 향후 전망
KTH 26.01.22The Nuclear Power market is expected to grow from 402.60 gigawatt in 2025 to 404.98 gigawatt in 2026 and is forecast to reach 417.06 gigawatt by 2031 at 0.59% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Sustained capacity additions remain modest, yet the sector is undergoing a structural transition in which lifetime-extension programs shore up existing baseload generation even as small modular reactors (SMRs) move from the development stage toward commercial roll-out. Developers are focusing on factory-built modules to mitigate construction risk, while traditional gigawatt-scale projects contend with rising capital costs, lengthy lead times, and stricter financing rules. Regional dynamics are shaped by Europe's large installed base, the Asia-Pacific's rapid build-out pace, and North America's focus on life extension. Opportunities also arise from industrial decarbonization needs, where high-temperature nuclear process heat can displace coal and natural-gas boilers in the steel, cement, and chemicals industries.
Global Nuclear Power Market Trends and Insights
Increase in Demand for Clean Baseload Power
Electric-sector decarbonization targets continue to tighten, and grid managers struggle to integrate large shares of variable renewable energy sources without eroding reliability. Governments, therefore, revisit nuclear as a 24/7 carbon-free source, especially for data-center clusters whose electricity use rises 15-20% each year. Several economies that once planned to phase out nuclear power, such as Japan and South Korea, are reversing course to safeguard energy security. Capacity-value payments and ancillary-service revenues now feature in nuclear business cases, narrowing the apparent cost gap with solar and wind. The nuclear power market thereby secures a policy floor even where spot electricity prices remain volatile. At the same time, regulators insist on stricter safety margins, which lengthen licensing reviews while also reinforcing public acceptance.
Lifetime Extension & Uprate Programs
Operators find that keeping a 40-year-old reactor running for 60 or even 80 years costs USD 500-1,000 per kW, a fraction of the USD 6,000-12,000 per kW needed for new construction. The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission has granted 95 license renewals, while France's EUR 49.4 billion grand carenage project strengthens containment structures and replaces key components. Uprating turbines and core internals typically adds 4-7% capacity per unit, making these projects the swiftest way to expand the nuclear power market without new siting battles. Operators must still address the embrittlement of reactor pressure vessels and the obsolescence of instrumentation. Uncertainty about regulations beyond 60 years weighs on longer-range planning; yet, most utilities view life extension as a bridge to advanced-reactor deployment in the 2030s.
Cost Overruns & Financing Challenges
The Vogtle 3-4 expansion in Georgia has more than doubled its initial budget to USD 35 billion, and Hinkley Point C in the United Kingdom now stands at nearly USD 43 billion. Such overruns stem from supply-chain gaps, design changes during construction, and the loss of skilled labor after decades of limited new build. Lenders, therefore, demand sovereign guarantees, regulated asset-based models, or long-term power-purchase agreements before committing funds. Developers pursue modularization to compress schedules; yet, first-of-a-kind SMRs must still demonstrate credible cost curves. Government loan guarantees and tax incentives mitigate risk, but merchant nuclear projects remain rare.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Commercialization of Advanced SMRs
- Industrial Decarbonization Process-Heat Demand
- Competition from Low-Cost Renewables
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Pressurized light-water reactors accounted for 74.02% of total capacity in 2025, solidifying their role as the backbone of the nuclear power market. Fast breeder reactors, however, are on track for a 19.4% CAGR through 2031, propelled by China's 600 MWe CFR-600 and India's prototype reactor programs. Although gas-cooled and molten-salt concepts remain at the pilot stage, their high-temperature capabilities attract industrial heat clients.
The nuclear power market, therefore, sees light-water designs maintaining share in the medium term, while demonstration fast reactors build the knowledge base for closed-fuel cycles. Regulators gain familiarity with sodium and lead-coolant systems, but commercial financing hinges on early successes that demonstrate safety and economic viability. Should the CFR-600 hit performance milestones, breeder technologies may capture a meaningful nuclear power market share in the 2030s.
Medium-scale 500-1,000 MWe units held 48.12% of the installed capacity in 2025 and remain the preferred option for countries with mature grids. Small reactors under 500 MWe are forecast to expand at a 19.2% CAGR, reflecting utility interest in modular additions that lower capital at-risk. Micro-reactors with a capacity below 20 MWe target mining and defense applications, offering off-grid resilience.
Factory production is crucial to the economics of small reactors. Vendors pursue standardization so that the nuclear power market size for SMRs benefits from learning-curve cost declines after 10-12 units are in operation. Meanwhile, large reactors exceeding 1,000 MWe face cost headwinds and grid integration limits in smaller countries, curbing new orders outside China and India.
The Nuclear Power Market Report is Segmented by Reactor Type (Pressurized Light-Water Moderated and Cooled Reactor, Fast Breeder Reactor, and More), Reactor Size (Large, Medium, and Small), Fuel Type (Low-Enriched Uranium, and More), Application (Grid-Connected Power, Industrial Process Heat and Steam, and More), End-User (Utilities and IPPs, Industrial and Petro-Chemical, and More), and Geography (Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More).
Geography Analysis
Europe retained the largest 39.35% share of the nuclear power market in 2025, buoyed by France's 56-reactor fleet, which supplies 65% of the country's electricity. The European Union includes nuclear energy as a transitional asset under its green taxonomy, unlocking sustainable finance channels. Yet lifetime-extension costs and post-Fukushima upgrades strain operator balance sheets, and Germany's 2023 shutdown leaves Central Europe more reliant on French exports. The United Kingdom advances the 3.2 GW Hinkley Point C and explores a fleet of six EPRs that will sustain domestic nuclear skills through 2050.
Asia-Pacific delivers the fastest 6.6% CAGR, led by China's pipeline of 24 reactors under construction and India's indigenous PHWR and fast-reactor programs. China aligns its nuclear growth with its 2060 carbon neutrality pledge and targets 120 GW by 2030. Japan's gradual restarts lift capacity factors but remain constrained by public skepticism, while South Korea maintains a 28-reactor fleet and exports APR-1400 units to the United Arab Emirates. Emerging economies, such as Vietnam and Indonesia, conduct feasibility studies; however, financing and regulatory readiness remain hurdles before they can join the nuclear power market.
North America opts for life extension and selective new build. The United States relies on nuclear power for 20% of its total generation and 50% of its carbon-free power. License renewals keep aging plants online, while federal tax credits and loan guarantees encourage SMR projects in Idaho and Wyoming. Canada refurbishes its CANDU fleet, adding 881 MWe from Darlington unit 2 in 2024, and advances SMR demonstrations for remote Arctic communities and heavy-oil sites. Mexico retains its two-unit Laguna Verde plant with no new build on the horizon. Across the region, deployment pathways for advanced reactors hinge on HALEU supply and streamlined licensing.
- Electricite de France SA (EDF)
- Rosatom State Atomic Energy Corporation
- China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC)
- Westinghouse Electric Company LLC
- GE-Hitachi Nuclear Energy
- Framatome SA
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
- Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power / KEPCO E&C
- BWX Technologies Inc.
- Bechtel Corporation
- Doosan Enerbility Co. Ltd
- Fluor Corporation (NuScale)
- SKODA JS a.s.
- Holtec International
- TerraPower LLC
- Rolls-Royce SMR Ltd
- X-Energy LLC
- General Fusion Inc.
- Ontario Power Generation
- Babcock International Group
- Bilfinger SE
- Duke Energy Corporation
- Japan Atomic Power Company
- Ansaldo Nucleare
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increase in demand for clean baseload power
- 4.2.2 Lifetime extension & uprate programs
- 4.2.3 Commercialization of advanced SMRs
- 4.2.4 Industrial decarbonization process-heat demand
- 4.2.5 Nuclear-produced hydrogen & ammonia initiatives
- 4.2.6 Emergence of nuclear-powered data-center & marine applications
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Cost overruns & financing challenges
- 4.3.2 Competition from low-cost renewables
- 4.3.3 HALEU fuel-supply bottlenecks
- 4.3.4 Export-control & proliferation scrutiny
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porters Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Reactor Type
- 5.1.1 Pressurized Light-Water Moderated and Cooled Reactor (PWR)
- 5.1.2 Pressurized Heavy-Water Moderated and Cooled Reactor (PHWR)
- 5.1.3 Boiling Light-Water Cooled and Moderated Reactor (BWR)
- 5.1.4 Gas Cooled, Graphite Moderated Reactor (GCR)
- 5.1.5 High-Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactor (HTGR)
- 5.1.6 Light-Water Cooled, Graphite Moderated Reactor (LWGR)
- 5.1.7 Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR)
- 5.1.8 Others
- 5.2 By Reactor Size
- 5.2.1 Large (Above 1,000 MWe)
- 5.2.2 Medium (500 to 1,000 MWe)
- 5.2.3 Small (Below 500 Mwe; includes SMRs and Micro-reactors)
- 5.3 By Fuel Type
- 5.3.1 Low-Enriched Uranium (Below 5% U-235)
- 5.3.2 High-Assay LEU (5 to 20% U-235)
- 5.3.3 Mixed Oxide (MOX)
- 5.3.4 Thorium-based Fuels
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Grid-Connected Power
- 5.4.2 Off-grid/Remote Electrification
- 5.4.3 Industrial Process Heat and Steam
- 5.4.4 Desalination and District Heating
- 5.4.5 Defense and Military Bases
- 5.5 By End-User Sector
- 5.5.1 Utilities and IPPs
- 5.5.2 Industrial and Petro-chemical
- 5.5.3 Mining and Remote Operations
- 5.5.4 Government/Defense
- 5.5.5 Research Institutions
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.2 France
- 5.6.2.3 Sweden
- 5.6.2.4 Spain
- 5.6.2.5 Ukraine
- 5.6.2.6 Russia
- 5.6.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 India
- 5.6.3.3 Japan
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Argentina
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.2 South Africa
- 5.6.5.3 Egypt
- 5.6.5.4 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, JVs, Funding, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Electricite de France SA (EDF)
- 6.4.2 Rosatom State Atomic Energy Corporation
- 6.4.3 China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC)
- 6.4.4 Westinghouse Electric Company LLC
- 6.4.5 GE-Hitachi Nuclear Energy
- 6.4.6 Framatome SA
- 6.4.7 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
- 6.4.8 Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power / KEPCO E&C
- 6.4.9 BWX Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.10 Bechtel Corporation
- 6.4.11 Doosan Enerbility Co. Ltd
- 6.4.12 Fluor Corporation (NuScale)
- 6.4.13 SKODA JS a.s.
- 6.4.14 Holtec International
- 6.4.15 TerraPower LLC
- 6.4.16 Rolls-Royce SMR Ltd
- 6.4.17 X-Energy LLC
- 6.4.18 General Fusion Inc.
- 6.4.19 Ontario Power Generation
- 6.4.20 Babcock International Group
- 6.4.21 Bilfinger SE
- 6.4.22 Duke Energy Corporation
- 6.4.23 Japan Atomic Power Company
- 6.4.24 Ansaldo Nucleare
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment
- 7.2 Advanced Small Modular Reactors
- 7.3 Floating Nuclear Plants
- 7.4 Nuclear Hydrogen & Ammonia Production
- 7.5 Data-Center & Marine Micro-reactors
- 7.6 Lifetime Extension Services Market
- 7.7 Decommissioning & Waste-Management Services


















