
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1911287
싱가포르의 핀테크 : 시장 점유율 분석, 업계 동향과 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Singapore Fintech - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
2026년 싱가포르의 핀테크 시장 규모는 139억 7,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 2025년 120억 5,000만 달러에서 계속 성장하고 있습니다. 2031년까지의 예측으로는 292억 2,000만 달러에 이르고, 2026-2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 15.9%로 성장할 전망입니다.
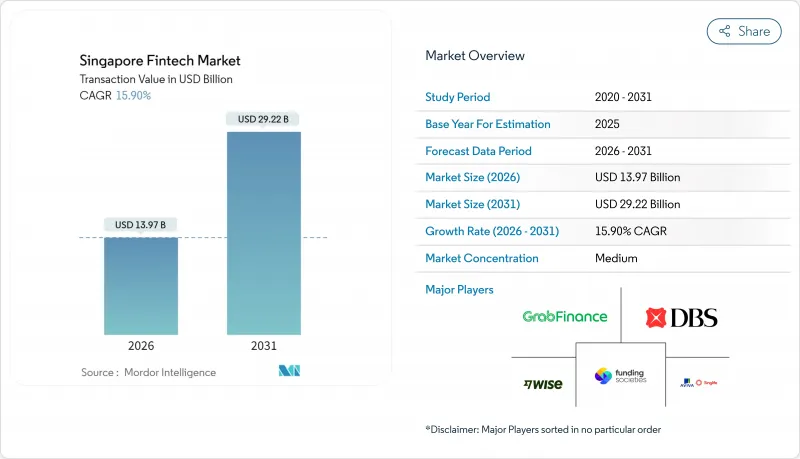
강력한 정책 지원, 깊이 있는 디지털 인프라, 지속되는 민간 자본 유입은 경쟁 강도와 규제 감독이 강화되는 상황에서도 싱가포르 핀테크 시장을 가파른 성장 궤도에 올려놓고 있습니다. 시장 모멘텀은 싱가포르 통화청(MAS)의 1억 싱가포르 달러(7,700만 달러) 규모 FSTI 3.0 프로그램이 반영된 것으로, 양자 보안 사이버 보안 및 AI 기반 위험 모델을 공동 투자하여 초기 도입 기업에 지속적인 기술 우위를 제공합니다. 추가적인 상승 요인은 2026년까지 가동 예정인 5개국 간 즉시 결제 회랑인 '프로젝트 넥서스'로, 결제 주기를 단축하고 국경 간 무역 서비스 제공업체에게 새로운 수익원을 열어줄 것입니다. 싱가포르 핀테크 시장은 또한 PayNow의 지역 연계성 확대를 통해 혜택을 보며, 이는 국경 간 전자상거래에 종사하는 중소기업(SME) 사이에서 다중 통화 지갑 수요를 가속화하고 있습니다. 동시에 암호화폐 및 후불결제(BNPL) 상품에 대한 강화된 소비자 보호 규정이 단기 수익 성장을 억제하면서, 임베디드 파이낸스(embedded finance) 및 B2B2C 유통으로의 비즈니스 모델 전환을 촉진하고 있습니다.
싱가포르의 핀테크 시장 동향 및 인사이트
실시간 결제 인프라가 결제 경제를 변화
프로젝트 넥서스는 2026년까지 싱가포르, 말레이시아, 태국, 필리핀, 인도의 결제 인프라를 연결하여 노스트로 계좌의 필요성을 없애고 결제 기간을 T+2에서 실시간으로 단축할 예정입니다. 이 전환으로 약 1,200억 달러의 묶인 유동성이 해방되고 국경 간 거래 수수료가 감소하여 상인과 중소기업에 즉각적인 비용 절감 효과를 가져올 것입니다. 초기 통합 핀테크 기업들은 실시간 결제로 선적 단계별 운전자본 상품이 활성화되는 B2B 무역 금융 시장에서 점유율을 확보할 것입니다. PayNow의 PromptPay 및 DuitNow와의 양자 연결은 2024년 250만 건 이상의 거래를 처리하며 즉각적인 지역 결제에 대한 고객 수요를 입증했습니다. 결제망이 통합됨에 따라 전통적 은행들은 레거시 API를 전면 개편하지 않으면 고수익 거래 채널을 민첩한 신생 기업에 내줄 위험에 직면합니다. 이 새로운 인프라가 소액 결제와 소액 보험도 지원함으로써 동남아시아 전역에서 활용 가능한 사례가 확대되고 있습니다.
양자 내성 혁신 자금이 경쟁 우위를 가속화
FSTI 3.0을 통해 MAS는 양자 저항형 암호화와 AI 기반 위험 분석을 도입하는 프로젝트의 최대 50%를 공동 지원합니다. 이 보조금은 중견 핀테크 기업의 자본 지출 장벽을 낮춰 규제 의무화 이전에 사이버 보안 체계를 강화할 수 있게 합니다. 사이버 및 기술 복원력 전문가(CTREX) 패널 내 협력을 통해 마이크로소프트, 아마존, 구글 클라우드로부터의 지식 이전이 보장되며, 국내 기준을 세계의 모범 사례와 일치시킵니다. 선도 기업들은 이미 쇼어 알고리즘 공격을 견디는 양자 안전 결제 프로토콜을 테스트 중이며, 양자 암호학이 의무화될 때를 대비해 규정 준수를 위한 기반을 마련하고 있습니다. 양자 보안 키 교환을 도입한 은행들은 고가치 재무 흐름을 보호함으로써 싱가포르가 안전한 금융 호스팅 부문에서 선점 우위를 확보하도록 합니다. 장기적으로 양자 강화 최적화는 신용 위험 모델링과 포트폴리오 재조정 과정을 간소화하여 산업 생산성을 높일 수 있습니다.
고객 확보 비용이 핀테크 수익성 모델을 압박
스마트폰 보급률이 거의 보편화되면서 잠재 고객 기반이 포화 상태에 이르러, 신규 고객 확보 비용이 점점 더 높아지고 있습니다. 2024년 전자지갑 가입 인센티브 예산은 40-60% 급증하여 소규모 핀테크 기업의 투자 회수 기간을 30개월 이상으로 연장시켰다. 소비자들이 차량 호출, 음식 배달, 결제를 한데 묶은 그랩(Grab) 같은 다기능 슈퍼앱을 선호함에 따라 앱 피로도가 마케팅 비용 대비 수익률을 더욱 악화시키고 있습니다. 이러한 추세로 인해 독립형 서비스 제공업체들은 임베디드 파이낸스 파트너십으로 전환하여 서비스를 가맹점 또는 플랫폼 생태계에 통합함으로써 고객 확보 비용을 분담하고 있습니다. B2B2C 유통 방식 또한 단위 경제성을 개선합니다. 예를 들어 중소기업 소프트웨어 공급업체는 청구서 연계 신용 한도를 내장하여 마케팅 비용을 여러 수익원으로 분산시킬 수 있습니다. 따라서 높아진 고객 확보 비용은 강력한 생태계나 차별화된 지적재산권을 보유한 핀테크 기업에 유리하게 작용하는 동시에 자본이 부족한 스타트업은 통합 또는 퇴출을 유도하는 필터링 메커니즘 역할을 합니다.
부문 분석
2025년 기준 디지털 결제는 싱가포르 핀테크 시장 규모의 26.20%를 차지하며 일상 상거래의 핵심 역할을 반영했습니다. SGQR+ 상호운용성, 가맹점 소프트POS 도입, PayNow의 지역 연동으로 이 부문은 2031년까지 연평균 16.95% 성장률을 보일 전망입니다. 계좌 간 이체를 통한 카드 레일 우회 방식은 인터체인지 수수료를 절감하여 가맹점이 QR 및 즉시 결제를 우선적으로 채택하도록 유도합니다. 한편, 디지털 대출 부문의 대체 신용 평가는 결제 부문보다 성장 속도는 느리지만, 긱 노동자를 위한 신속한 소액 대출을 지속적으로 확대하고 있습니다. 인슈어테크 기업들은 차량 호출 및 배달 앱 내에 소액 보험을 내장하여 별도의 보험 계약 없이도 서비스 범위를 넓히고 있습니다. StashAway와 같은 웰스테크 플랫폼은 저비용 ETF 포트폴리오를 기반으로 규모를 확장하며, 프라이빗 뱅크의 중산층 자산 관리 시장에 도전장을 내밀고 있습니다. MAS(싱가포르 금융청)의 규제 샌드박스는 결제, 대출, 보험을 결합한 실험을 지원하여 종합적인 금융 서비스를 촉진합니다. 2030년까지 통합 플랫폼이 국내 소매 거래 가치의 40% 이상을 주도할 것으로 예상되며, 이는 결제가 광범위한 핀테크 생태계의 핵심 축으로 자리매김할 것임을 시사합니다.
디지털 지갑 제공업체들이 신용 한도와 보험 부가 서비스를 확장하며 전통적 부문 경계를 모호하게 함에 따라 경쟁이 심화됩니다. 슈퍼앱은 자체 소비 데이터를 활용해 신용 평가를 정교화하는 한편, 기존 업체들은 상점 결제 흐름 내 관련성을 유지하기 위해 API를 개방합니다. 따라서 싱가포르 핀테크 시장은 판매 시점을 장악하고 고빈도 결제 사용 사례에 고마진 부가 서비스를 겹쳐 제공할 수 있는 업체들에게 계속해서 보상을 제공합니다. 토큰화된 예금과 네트워크 토큰화에 대한 규제 지원은 보안성과 상호결제 경제성을 더욱 향상시킵니다. 실시간 결제 인프라가 성숙해짐에 따라 결제 수익은 거래당 수수료보다 부가가치 데이터 분석, 로열티 프로그램, 결제 서비스에서 점차 창출될 것입니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 3개월간의 애널리스트 지원
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건과 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
제2장 조사 방법
제3장 주요 요약
제4장 시장 상황
- 시장 개요
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 실시간 결제 시스템의 급속한 도입(PayNow, Project Nexus)
- MAS 보조금으로 촉진되는 AI 및 양자 준비형 핀테크 혁신
- 다중 통화 지갑을 촉진하는 국경 간 전자상거래
- 디지털 전용 은행 라이선스로 개척되는 새로운 틈새 시장
- ESG 및 그린 파이낸스의 의무화가 새로운 핀테크 수익원을 창출
- 소기업 신용 공백으로 인한 대체 대출 플랫폼 성장
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 치열한 앱 경쟁 속 높은 고객 확보 비용
- 암호화 자산 및 BNPL(후불 서비스)에 관한 금융 관리국(MAS)의 소비자 보호 규제 강화
- AI/사이버 보안 부문의 인력 부족으로 인한 운영 비용(OPEX) 증가
- 상호운용성 및 기존 핵심 은행 시스템 통합 장애
- 가치/공급망 분석
- 규제 상황
- 기술의 전망
- Porter's Five Forces
- 신규 참가업체 위협
- 공급기업 협상력
- 구매자 협상력
- 대체품 위협
- 경쟁 기업간 경쟁 관계
제5장 시장 규모와 성장 예측
- 서비스 제안별
- 디지털 결제
- 디지털 대출 및 자금 조달
- 디지털 투자
- 인슈어테크
- 네오뱅킹
- 최종 사용자별
- 소매
- 기업
- 사용자 인터페이스별
- 모바일 애플리케이션
- Web/브라우저
- POS/IoT 디바이스
- 지역별
- 중부 지역
- 동부 지역
- 북부 지역
- 북동부 지역
- 서부 지역
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 시장 집중도
- 전략적 동향
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 프로파일
- Grab Financial Group
- DBS Bank
- OCBC Bank
- UOB Bank
- PayPal Singapore
- Wise
- Stripe Singapore
- Adyen Singapore
- Nium
- Thunes
- FOMO Pay
- Funding Societies
- Validus
- StashAway
- Endowus
- Singlife with Aviva
- Bolttech
- GXS Bank
- Trust Bank
- ANEXT Bank
- Revolut Singapore
제7장 시장 기회와 장래의 전망
HBR 26.01.29Singapore fintech market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 13.97 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 12.05 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 29.22 billion, growing at 15.9% CAGR over 2026-2031.
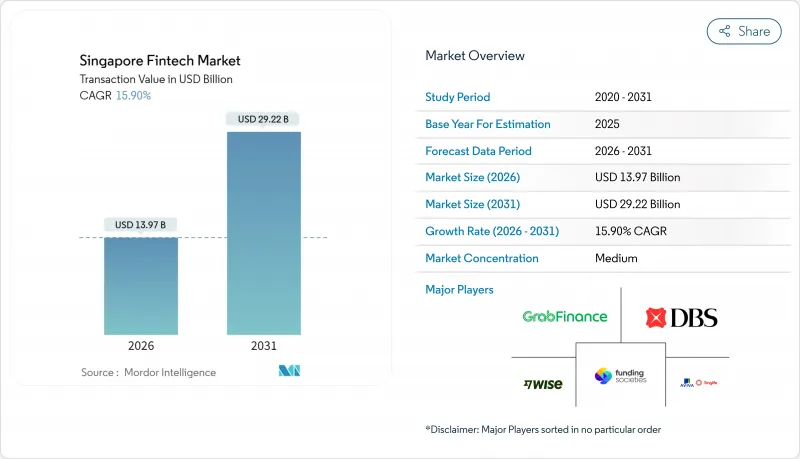
Strong policy support, deep digital infrastructure, and sustained inflows of private capital keep the Singapore fintech market on a steep expansion path, even as competitive intensity and regulatory scrutiny increase. Market momentum reflects the Monetary Authority of Singapore's (MAS) SGD 100 million (USD 77 million) FSTI 3.0 program, which co-funds quantum-safe cybersecurity and AI-driven risk models, giving early adopters a durable technology lead. Additional uplift comes from Project Nexus-the five-country instant-payment corridor that is scheduled to go live by 2026-which will compress settlement cycles and open new revenue pools for cross-border trade service providers. The Singapore fintech market also benefits from PayNow's growing regional linkages, accelerating demand for multi-currency wallets among SMEs engaged in cross-border e-commerce. At the same time, tightened consumer-protection rules for crypto and buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) products temper near-term revenue growth, prompting business-model pivots toward embedded finance and B2B2C distribution.
Singapore Fintech Market Trends and Insights
Real-Time Payment Rails Transform Settlement Economics
Project Nexus will connect payment rails in Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, the Philippines, and India by 2026, eliminating the need for nostro accounts and cutting settlement from T+2 to real-time . The shift frees up an estimated USD 120 billion in trapped liquidity and reduces cross-border transaction fees, generating immediate cost savings for merchants and SMEs. Early integrating fintech firms will gain share in B2B trade finance, where real-time settlement unlocks working-capital products tied to shipment milestones. PayNow's bilateral links with PromptPay and DuitNow processed more than 2.5 million transactions in 2024, demonstrating proven customer appetite for instant regional payments. As rails converge, traditional banks must overhaul legacy APIs or risk ceding high-margin corridors to nimble challengers. The new infrastructure also supports micropayments and micro-insurance, widening addressable use cases across Southeast Asia.
Quantum-Ready Innovation Funding Accelerates Competitive Differentiation
Through FSTI 3.0, MAS co-funds up to 50% of projects deploying quantum-resistant encryption and AI-powered risk analytics. The subsidy lowers capex barriers for mid-tier fintechs, enabling them to harden cybersecurity stacks ahead of regulatory mandates. Collaboration inside the Cyber and Technology Resilience Experts (CTREX) panel ensures knowledge transfer from Microsoft, Amazon, and Google Cloud, aligning domestic standards with global best practices. Early movers already test quantum-safe payment protocols that withstand Shor-algorithm attacks, positioning them for compliance once post-quantum cryptography becomes compulsory. Banks adopting quantum-secure key exchange safeguard high-value treasury flows, giving Singapore a first-mover lead in safe-harbor financial hosting. Over the long term, quantum-enhanced optimization may also streamline credit-risk modelling and portfolio rebalancing, boosting sector productivity.
Customer Acquisition Costs Strain Fintech Profitability Models
Nearly universal smartphone ownership produces a saturated addressable base, making marginal customer wins increasingly expensive. Incentive budgets for e-wallet sign-ups ballooned by 40-60% in 2024, pushing payback periods for small fintechs beyond 30 months. App fatigue further erodes return on marketing spend because consumers prefer multifunction super-apps such as Grab, which bundle ride-hailing, food delivery, and payments. The trend forces standalone providers to pivot toward embedded-finance partnerships, integrating services into merchant or platform ecosystems to share acquisition costs. B2B2C distribution also improves unit economics; SME software vendors, for example, can embed invoicing-linked credit lines, spreading marketing costs across multiple revenue streams. Elevated acquisition costs therefore act as a filtering mechanism, rewarding fintechs with strong ecosystems or differentiated IP, while pushing under-capitalized startups to consolidate or exit.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cross-Border E-Commerce Growth Drives Multi-Currency Innovation
- Digital Banking Licenses Create Niche Market Opportunities
- Regulatory Tightening Constrains High-Growth Fintech Segments
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2025, digital payments accounted for 26.20% of the Singapore fintech market size, reflecting their central role in day-to-day commerce. The segment is on track to expand at a 16.95% CAGR through 2031, propelled by SGQR+ interoperability, merchant SoftPOS adoption, and PayNow's regional links. Card-rail bypass via account-to-account transfers reduces interchange fees, encouraging merchants to prioritize QR and instant payments. Meanwhile, alternative credit scoring in digital lending continues to unlock quick-turnaround microloans for gig workers, albeit at a slower growth than payments. Insurtech firms embed bite-sized coverage within ride-hailing and delivery apps, widening reach without requiring stand-alone policy purchases. Wealth-tech platforms such as StashAway scale on low-cost ETF portfolios, challenging private banks for mass-affluent assets. MAS's regulatory sandbox supports experiments that bundle payments, lending, and insurance, fostering holistic financial offerings. By 2030, integrated platforms are expected to direct more than 40% of domestic retail transaction value, cementing payments as the linchpin of broader fintech ecosystems.
Competition intensifies as digital-wallet providers extend credit lines and insurance add-ons, blurring traditional segment boundaries. Super-apps leverage first-party consumption data to refine underwriting, while incumbents open APIs to retain relevance within merchant checkout flows. The Singapore fintech market, therefore, continues to reward providers that control the point of sale and can layer higher-margin, add-on services onto high-frequency payment use cases. Regulatory support for tokenized deposits and network tokenization further improves security and interchange economics. As real-time rails mature, payments revenue will increasingly derive from value-added data analytics, loyalty, and payment services rather than per-transaction fees.
The Singapore Fintech Market Report is Segmented by Service Proposition (Digital Payments, Digital Lending & Financing, Digital Investments, Insurtech, Neobanking), End-User (Retail, Businesses), User Interface (Mobile Applications, Web/Browser, POS/IoT Devices), and Geography (Central Region, East Region, North Region, North-East Region, West Region). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Grab Financial Group
- DBS Bank
- OCBC Bank
- UOB Bank
- PayPal Singapore
- Wise
- Stripe Singapore
- Adyen Singapore
- Nium
- Thunes
- FOMO Pay
- Funding Societies
- Validus
- StashAway
- Endowus
- Singlife with Aviva
- Bolttech
- GXS Bank
- Trust Bank
- ANEXT Bank
- Revolut Singapore
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid real-time payment rail adoption (PayNow, Project Nexus)
- 4.2.2 MAS grants spurring AI & quantum-ready fintech innovation
- 4.2.3 Cross-border e-commerce fueling multi-currency wallets
- 4.2.4 Digital-only banking licences opening new niches
- 4.2.5 ESG & green-finance mandates creating new fintech revenue pools
- 4.2.6 SME credit gap boosting alternative lending platforms
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High customer-acquisition costs amid intense app competition
- 4.3.2 Tightened MAS consumer-protection rules on crypto & BNPL
- 4.3.3 Talent shortages in AI / cybersecurity raising OPEX
- 4.3.4 Interoperability & legacy core-bank integration hurdles
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Service Proposition
- 5.1.1 Digital Payments
- 5.1.2 Digital Lending & Financing
- 5.1.3 Digital Investments
- 5.1.4 Insurtech
- 5.1.5 Neobanking
- 5.2 By End-User
- 5.2.1 Retail
- 5.2.2 Businesses
- 5.3 By User Interface
- 5.3.1 Mobile Applications
- 5.3.2 Web / Browser
- 5.3.3 POS / IoT Devices
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 Central Region
- 5.4.2 East Region
- 5.4.3 North Region
- 5.4.4 North-East Region
- 5.4.5 West Region
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Grab Financial Group
- 6.4.2 DBS Bank
- 6.4.3 OCBC Bank
- 6.4.4 UOB Bank
- 6.4.5 PayPal Singapore
- 6.4.6 Wise
- 6.4.7 Stripe Singapore
- 6.4.8 Adyen Singapore
- 6.4.9 Nium
- 6.4.10 Thunes
- 6.4.11 FOMO Pay
- 6.4.12 Funding Societies
- 6.4.13 Validus
- 6.4.14 StashAway
- 6.4.15 Endowus
- 6.4.16 Singlife with Aviva
- 6.4.17 Bolttech
- 6.4.18 GXS Bank
- 6.4.19 Trust Bank
- 6.4.20 ANEXT Bank
- 6.4.21 Revolut Singapore
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 Embedded finance in non-financial super-apps
- 7.2 Green fintech solutions for carbon-credit trading


















