
|
시장보고서
상품코드
1911709
질소 비료 시장 : 시장 점유율 분석, 산업 동향 및 통계, 성장 예측(2026-2031년)Nitrogenous Fertilizers - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
질소 비료 시장 규모는 2026년에는 1,845억 8,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2025년 1,744억 달러에서 계속 성장하고 있습니다.
2031년 2,451억 3,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 추정되며, 2026-2031년 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 5.84%로 성장할 것으로 전망됩니다.

이 성장은 세계의 식량 수요 증가, 농업 기술 진보 및 영양 관리의 혁신에 기인합니다. 보조금과 정책 조치를 통한 정부의 지원은 여전히 중요한 요소입니다. 예를 들어, 유럽 위원회는 공급망의 혼란 속에서 비료의 가용성, 합리적인 가격, 지속가능성을 확보하기 위해 2024년 말까지 요소와 암모니아의 관세를 중단했습니다. 지역별로는 아시아태평양이 광범위한 농업 활동, 강력한 정부 지원, 정밀 농업 기술의 보급 확대에 의해 시장을 견인하고 있습니다. 경쟁 구도에는 세계 기업과 지역 기업이 공존하고, 세계 기업은 생산 능력 확대, 원료 다양화, 저탄소 기술 도입에 주력하고 있습니다. 한편, 지역 제조업체 및 전문 공급업체는 지역 밀착형 유통망, 맞춤형 제품 제공, 농업 기술 플랫폼과의 협력을 통해 시장 점유율을 확대하고 있습니다. 질소 비료 시장은 기술 주도형 및 지역 적응형 산업으로 진화하고 있으며, 밸류체인 전체에서 혁신과 전략적 성장의 큰 기회를 제공합니다.
세계의 질소 비료 시장 동향 및 인사이트
주식 작물 수요 증가
세계 인구가 증가함에 따라 식량 수요가 급증하고 제한된 농지에서 높은 수율을 확보하는 농업 시스템에 대한 압력이 증가하고 있습니다. 2050년까지 세계 인구가 97억 명에 달할 것으로 예상되는 가운데, 증가하는 영양 수요를 충족시키기 위해서는 식량 생산량을 약 70% 증가시켜야 합니다. 이 수요 급증은 농업 관행을 재구축하고 기후 변화 중에서도 작물 생산량을 향상시켜 수량을 안정시키기 위해 질소 비료의 보다 한층 더 높은 활용을 촉진하고 있습니다. 특히 개발도상 지역에서 소득이 증가함에 따라 식습관이 단백질 풍부한 곡물로 이행하고 있습니다. 이로 인해 질소 비료 시용량이 더 높은 밀과 쌀과 같은 작물 재배가 강화되었습니다. 기후 변화의 격화는 안정적인 수확량의 필요성을 더욱 강조하고 생산량을 안정시키기 위한 비료의 전략적 이용을 촉진하고 있습니다. 많은 지역에서는 옥수수, 콩, 쌀을 1년 이내에 윤작하는 다작 시스템이 도입되어 1헥타르당 비료 사용량이 증가하고 있습니다. 이 추세는 경작지 확대보다 기존 농지에서 생산성 극대화에 초점을 맞추고 있음을 반영합니다.
농업 투입물에 대한 지속적인 정부 지원
세계 각국 정부는 농촌 지역의 안정성 및 식량 안보에서 저렴한 식물 영양소의 중요성을 인식하고 있습니다. 많은 국가에서는 농부들이 비료를 확실하게 조달할 수 있도록 직접적인 투입 자재 보조금, 운임 환급, 저금리 대출 등의 지원 프로그램을 확충하고 있습니다. 인도는 2024-2025년도 예산에서 비료 보조금을 1조 7,500억 루피(약 210억 달러)로 증액하였고, 재정 제약 하에서도 농가의 지속적인 조달을 확보하고 있습니다. 브라질에서는 'Plano Safra 2024-2025 계획에서 비료 조달 지원을 위해 4,000억 레알(750억 달러)의 대출 범위를 설정했습니다. 이러한 노력은 민간 부문에 강한 수요를 시사하고 생산 능력, 유통 인프라, 기술 혁신에 대한 투자를 촉진하고 있습니다. 수입 의존도 감소 및 공급망 강화를 목적으로 국내 암모니아 생산을 추진하는 정부도 존재합니다. 이 정책 전환은 가격 통제를 넘어서는 비료 공급의 장기적인 탄력성 구축을 목표로 합니다.
환경 규제 강화
영양분의 유출 및 온실가스 배출 감축을 목적으로 한 환경 정책이 세계의 비료 사용 형태를 변용시키고 있습니다. 생태계나 수원 보호를 위해, 시용 시기, 시용량 및 제품 조성에 관한 규제 강화가 각국에서 진행되고 있습니다. 미국 등의 지역에서는 질산염의 상한 규제 및 지속가능성 기준이 보급되고 있으며, 농가는 정밀 농업 수법이나 고효율 비료의 도입을 강요받고 있습니다. 이러한 변화가 제품 개발 및 시용 기술의 혁신을 촉진하여 비료 이용과 환경 목표의 조화를 도모하고 있습니다. 규제가 강화됨에 따라 질소 비료 시장은 농학적 성능을 유지하면서 환경 부하를 줄이는 첨단 제품의 채택을 점차 반영해 나갈 것입니다. 이 전환은 생산성 및 환경 보전의 균형을 이루는 업계에서 중요한 전환점을 보여줍니다.
부문 분석
2025년 시점에서 요소는 질소 비료 시장 점유율의 43.12%를 차지하였고, 그 46%의 질소 농도와 유연한 시용 방법이 생산자에게 평가되어 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 6.78%로 추이할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다. 요소의 비용 우위성과 토양 혼화 및 시비 관개 쌍방에 대한 적응성이 대규모 곡물 생산 시스템에서의 지위를 지지하고 있습니다. 생산자는 에너지 절약 촉매 및 배출 가스 제어 장치를 통한 플랜트 업그레이드를 진행하여 경쟁력 있는 비용으로 공급 안정성을 강화하고 있습니다. CF 인더스트리즈의 도널드슨빌 확장 계획 등 지속적인 투자는 지역의 자급률과 수출 능력을 높여 질소 비료 시장에서 요소의 주도적 지위를 유지하고 있습니다.
특수 등급은 관개 원예 및 고부가가치 환금 작물로 보급이 진행되고 있어 정밀한 영양 공급이 수익 향상으로 이어지고 있습니다. 질산암모늄은 규제 및 저장 인프라가 정비된 지역에서 여전히 중요하며, 무수 암모니아는 북미 농작물에서 직접 주입 시스템에 활용되고 있습니다. 환경규제 강화에 따라 저휘발성 제품이나 피복 제품에 대한 수요는 증가할 것으로 예상되고 다양성을 더하면서 요소의 핵심 역할은 흔들리지 않습니다.
2025년 시점에서 기존 비료는 질소 비료 시장 규모의 92.12%의 점유율을 유지하였고, 예측 기간 중에는 5.86%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 확대가 예상됩니다. 이것은 세계의 제작 면적 증가와 가격 감응도의 높이가 벌크 입상 제품을 지지하는 경향과 대체로 일치하고, 전체적인 수요 동향에 따른 것입니다. 대규모의 중앙 집중식 플랜트는 규모의 경제 혜택을 받고, 단위 비용을 낮게 유지하며, 개발 도상 시장에서 경쟁력을 확보하고 있습니다. 광범위한 리셀러 네트워크와 농부의 친숙한 사용감도 광대한 경작지에서 기존 비료의 우위를 강화하고 있습니다.
특수 비료는 보다 소규모의 부문이며, 양분 이용 효율을 높이고 환경 손실을 최소화하는 서방형 및 지효성 기술이 주도하고 있습니다. 비료 관개 및 수경 재배 시스템에 사용되는 액체 용액은 수자원 제약 지역에서의 적용 유연성을 확대합니다. 수용성 등급은 정밀한 영양 관리를 요구하는 온실 재배를 위해 설계되었습니다. 고가격대이지만, 특히 보호재배 및 집약적인 과수와 야채 생산에 있어서 초기 비용을 웃도는 수익이 예상되는 분야에서는 특수 형태의 채용이 진행되어 질소 비료 시장에 점증적인 성장을 가져올 것으로 기대됩니다.
질소 비료 시장 보고서는 제품별(질산암모늄, 무수암모니아, 기타), 형태별(기존, 특수품), 적용 방법별(펠티게이션, 잎면 살포, 토양 시용), 작물 유형별(밭작물, 원예작물, 기타), 지역별(아시아태평양, 유럽, 중동 및 아프리카, 북미, 남미)로 분석되고 있습니다. 시장 예측은 금액(달러)과 수량(메트릭톤)으로 제시됩니다.
지역별 분석
아시아태평양은 2025년 질소 비료 시장 규모에서 35.42%의 수익을 차지했으며, 광대한 농지, 높은 작부 밀도, 지원적인 보조금 제도를 반영하고 있습니다. 중국의 식량 안보에 중점을 두고 인도의 소규모 농가에서 현대화는 견조한 기반 수요를 보장합니다. 다작 시스템 및 고수량 하이브리드 품종의 채용 확대에 따라 지속적인 질소 투입이 필요합니다. 또한 많은 지역 기업에서 국내 생산 능력이 수입 의존도를 억제하고 있습니다. 신흥 동남아시아 국가에서는 확대되는 도시 수요에 대응하기 위해 팜유, 쌀, 야채 재배가 강화되어 점진적인 성장을 이루고 있습니다.
중동 지역은 풍부한 가스 원료와 아시아 및 아프리카를 연결하는 해운로에 대한 근접성을 살려 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 6.94%로 가장 빠른 성장이 전망됩니다. ADNOC, SABIC, Fertiglobe에 의한 청색 및 녹색 암모니아 플랜트에 대한 대규모 투자는 국내 농업 프로젝트 및 수출 시장 모두에 공급을 목적으로 합니다. 정부 정책은 수입 의존도 감소를 위한 농업 다각화를 추진하고 질소 비료의 국내 소비를 촉진하고 있습니다. 새로운 플랜트에 탄소 포집 솔루션을 통합함으로써 이 지역은 낮은 배출 공급자로 자리매김하여 경쟁 우위를 강화하고 있습니다.
북미와 유럽은 성숙하면서도 진화를 계속하는 시장을 유지하고 있습니다. 북미 생산자들은 수출 경쟁력을 지원하는 셰일가스 경제의 혜택을 받는 반면 정밀농업 도입은 수량의 점진적인 성장을 지속하고 있습니다. 유럽에서는 엄격한 환경 정책이 생산량을 억제하는 한편, 농장에서 식탁까지의 목표에 따른 고효율 제품과 디지털 자문 서비스 수요를 환기하고 있습니다. 남미는 브라질의 프론티어 확대 및 아르헨티나의 수율 회복을 배경으로 성장을 계속하고 있으며, 아프리카는 인프라 정비, 대출 액세스, 보급 서비스의 향상에 의해 비료 보급이 진행되어 장기적인 잠재력을 가지고 있습니다.
기타 혜택 :
- 엑셀 형식 시장 예측(ME) 시트
- 애널리스트에 의한 3개월간의 지원
자주 묻는 질문
목차
제1장 서론
- 조사의 전제조건 및 시장 정의
- 조사 범위
- 조사 방법
제2장 보고서 제공
제3장 주요 요약 및 주요 조사 결과
제4장 주요 업계 동향
- 주요 작물류의 작부 면적
- 밭작물
- 원예작물
- 평균 시비량
- 주요 영양소
- 밭작물
- 원예작물
- 주요 영양소
- 관개 설비가 정비된 농지
- 규제 프레임워크
- 밸류체인 및 유통 채널 분석
- 시장 성장 촉진요인
- 주식 작물 수요 증가
- 농업 투입물에 대한 정부의 지속적인 지원
- 암모니아 공급원의 다양화
- 요소 생산 능력 최적화
- 그린암모니아 파일럿 프로젝트 가속
- 질소 이용을 위한 디지털 자문 플랫폼의 도입
- 시장 성장 억제요인
- 천연가스 가격의 변동성
- 환경 규제 강화
- 비료 무역의 물류상 병목
- 생물학적 질소 고정 기술의 대체 수단의 출현
제5장 시장 규모 및 성장 예측(금액 및 수량)
- 제품별
- 질산암모늄
- 무수 암모니아
- 요소
- 기타
- 형태별
- 기존
- 특수
- CRF
- 액체 비료
- SRF
- 수용성
- 시비 방법별
- 시비 관개
- 잎면 살포
- 토양
- 작물 유형별
- 밭작물
- 원예작물
- 잔디 및 관상용 식물
- 지역별
- 아시아태평양
- 호주
- 방글라데시
- 중국
- 인도
- 인도네시아
- 일본
- 파키스탄
- 필리핀
- 태국
- 베트남
- 기타 아시아태평양
- 유럽
- 프랑스
- 독일
- 이탈리아
- 네덜란드
- 러시아
- 스페인
- 우크라이나
- 영국
- 기타 유럽
- 중동
- 튀르키예
- 사우디아라비아
- 기타 중동
- 아프리카
- 남아프리카
- 나이지리아
- 기타 아프리카
- 북미
- 캐나다
- 멕시코
- 미국
- 기타 북미
- 남미
- 아르헨티나
- 브라질
- 기타 남미
- 아시아태평양
제6장 경쟁 구도
- 주요 전략적 움직임 s
- 시장 점유율 분석
- 기업 개요
- 기업 프로파일
- Nutrien Ltd.
- Yara International ASA
- CF Industries Holdings, Inc.
- SABIC Agri-Nutrients Company(Saudi Basic Industries Corporation)
- Koch Fertilizer, LLC(Koch Industries, Inc.)
- EuroChem Group AG
- OCI NV
- Coromandel International Limited(Murugappa Group)
- Indian Farmers Fertiliser Co-operative Limited
- Grupa Azoty SA
- Petronas Chemicals Group Berhad(Petroliam Nasional Berhad)
- Abu Qir Fertilizers and Chemical Industries Company
- PT Pupuk Indonesia(Persero)
제7장 CEO에 대한 주요 전략적 질문
AJYNitrogenous fertilizers market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 184.58 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 174.4 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 245.13 billion, growing at 5.84% CAGR over 2026-2031.
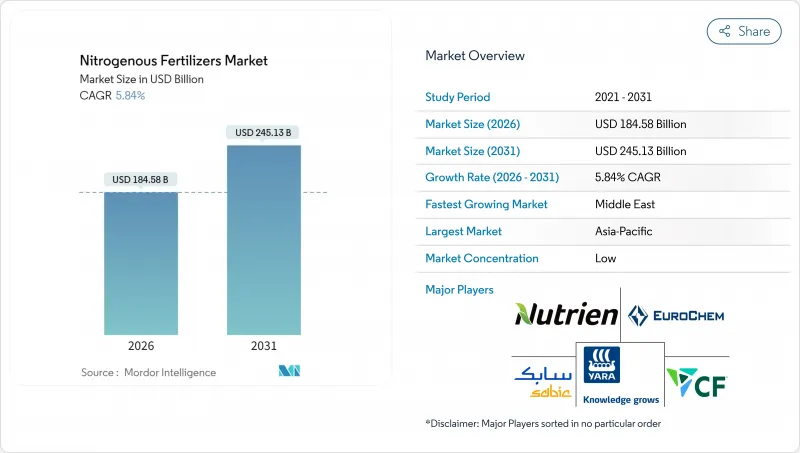
This growth is attributed to rising global food demand, advancements in farming practices, and innovations in nutrient management. Government support through subsidies and policy measures remains a critical factor. For instance, the European Commission has suspended tariffs on urea and ammonia until the end of 2024 to ensure the availability, affordability, and sustainability of fertilizers amid supply chain disruptions. Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the market due to its extensive agricultural activity, robust government support, and increasing adoption of precision farming technologies. The competitive landscape comprises both global and regional players, while global companies are focusing on capacity expansion, feedstock diversification, and the adoption of low-carbon technologies. Meanwhile, regional producers and specialty suppliers are gaining market share through localized distribution, customized product offerings, and collaborations with agricultural technology platforms. The nitrogenous fertilizers market is evolving into a technology-driven and regionally adaptive industry, offering significant opportunities for innovation and strategic growth across the value chain.
Global Nitrogenous Fertilizers Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand for Staple Crops
Global population growth is intensifying the demand for food, placing mounting pressure on agricultural systems to deliver higher yields from limited land. As the world's population is projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, food production must increase by approximately 70% to meet the growing nutritional needs of this population. This surge in demand is reshaping farming practices, encouraging greater use of nitrogenous fertilizers to boost crop output and stabilize yields amid climate variability. Rising incomes, particularly in developing regions, are shifting dietary preferences toward protein-rich grains, prompting the intensified cultivation of crops like wheat and rice, which require higher nitrogen fertilizer application rates. Climate variability further underscores the need for consistent yields, encouraging the strategic use of fertilizers to stabilize output. In many regions, multiple-cropping systems, which involve rotating maize, soybeans, and rice within a single year, are increasing fertilizer use per hectare. This trend reflects a focus on maximizing productivity on existing farmland rather than expanding acreage.
Sustained Government Support for Agricultural Inputs
Governments worldwide recognize the importance of affordable plant nutrients for rural stability and food security. Many have expanded support programs, including direct input grants, freight rebates, and low-interest loans, to ensure reliable access to fertilizers for farmers. India has increased its fertilizer subsidy budget to INR 1.75 trillion (approximately USD 21 billion) for the fiscal year 2024-25, ensuring continued access for farmers despite fiscal constraints. Brazil's Plano Safra 2024-25 earmarked BRL 400 billion (USD 75 billion) in credit to support fertilizer procurement. These initiatives signal strong demand to the private sector, encouraging investment in production capacity, distribution infrastructure, and innovation. Some governments are promoting domestic ammonia production to reduce their dependency on imports and strengthen their supply chains. This policy shift aims to build long-term resilience in them to fertilizer availability beyond price controls.
Tightening Environmental Regulations
Environmental policies aimed at reducing nutrient runoff and greenhouse gas emissions are reshaping global fertilizer usage. Governments are implementing stricter regulations on application timing, dosage, and product formulations to protect ecosystems and water sources. In regions like the United States, nitrate caps and sustainability benchmarks are becoming increasingly common, prompting farmers to adopt precision methods and more efficient fertilizers. These changes are driving innovation in product development and application technologies, aligning fertilizer use with environmental goals. As regulations tighten, the nitrogenous fertilizers market will increasingly reflect the adoption of advanced products that deliver agronomic performance with reduced environmental impact. This transition represents a significant shift for the industry, striking a balance between productivity and environmental stewardship.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Diversification of Ammonia Supply Sources
- Optimization of Urea Production Capacity
- Emergence of Biological Nitrogen-Fixation Alternatives
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Urea accounted for 43.12% of the nitrogenous fertilizers market share in 2025, with the segment projected to post a 6.78% CAGR to 2031 as growers value its 46% nitrogen concentration and flexible application. Urea's cost advantage and compatibility with both soil incorporation and fertigation underpin its position across large-scale grain systems. Producers are upgrading plants with energy-saving catalysts and emission control units, reinforcing supply security at competitive costs. Continuous investment, such as CF Industries' Donaldsonville expansion, enhances regional self-sufficiency and export capability, sustaining urea's leadership in the nitrogen fertilizer market.
Specialty grades are gaining traction in irrigated horticulture and high-value cash crops, where precise nutrient delivery translates into revenue gains. Ammonium nitrate remains relevant in geographies with established regulations and storage infrastructure, while anhydrous ammonia serves direct injection systems in North American row crops. As environmental scrutiny rises, demand for low-volatility or coated products is set to escalate, adding diversity without displacing urea's central role.
Conventional fertilizers retained a 92.12% share of the nitrogenous fertilizers market size in 2025, expanding at a 5.86% CAGR during the forecast period, broadly in line with overall demand, as global acreage growth and price sensitivity favor bulk granular products. Large centralized plants benefit from economies of scale, which keep unit costs low and ensure competitiveness in developing markets. Widespread dealer networks and farmer familiarity also reinforce the dominance of conventional forms in broad-acre cropping sectors.
Specialty fertilizers represent a smaller segment, led by controlled-release and slow-release technologies that enhance nutrient-use efficiency and minimize environmental losses. Liquid solutions used in fertigation and hydroponic systems broaden application flexibility in water-constrained regions. Water-soluble grades cater to greenhouse operations seeking precise nutrient regimes. Though premium-priced, specialty forms achieve strong adoption where returns justify higher upfront costs, particularly in protected cropping and intensive fruit and vegetable production, promising incremental gains for the nitrogen fertilizer market.
The Nitrogen Fertilizers Market Report is Segmented by Product (Ammonium Nitrate, Anhydrous Ammonia, and Others), Form (Conventional, Specialty), Application Mode (Fertigation, Foliar, and Soil), Crop Type (Field Crops, Horticultural Crops, and Others), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, Europe, Middle East, Africa, North America, and South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Metric Tons).
Geography Analysis
The Asia-Pacific region captured 35.42% of the revenue in 2025 of the nitrogenous fertilizers market size, reflecting its vast agricultural land, high cropping intensity, and supportive subsidy frameworks. China's emphasis on food security and India's modernization of smallholder farming guarantee robust baseline demand. Rising adoption of multiple-cropping systems and higher-yielding hybrids requires sustained nitrogen input, and domestic production capacity limits import exposure for many regional players. Emerging Southeast Asian economies are experiencing incremental growth as they intensify palm, rice, and vegetable cultivation to meet the needs of expanding urban centers.
The Middle East delivers the fastest growth at 6.94% CAGR through 2031, leveraging abundant gas feedstock and proximity to shipping lanes that connect Asia and Africa. Large-scale investments in blue and green ammonia plants by ADNOC, SABIC, and Fertiglobe aim to supply both domestic agricultural projects and export markets. Government policies favor agricultural diversification to reduce import dependence, boosting internal consumption of nitrogen fertilizers. Integration of carbon capture solutions in new plants positions the region as a low-emission supplier, strengthening its competitive edge.
North America and Europe maintain mature yet evolving markets. North American producers benefit from shale gas economics that support export competitiveness, while adoption of precision agriculture sustains incremental volume growth. Europe's stringent environmental policy constrains tonnage but spurs demand for enhanced-efficiency products and digital advisory services that align with Farm to Fork objectives. South America grows on the back of Brazilian frontier expansion and Argentine yield recovery, whereas Africa represents long-run potential as infrastructure, credit access, and extension services improve fertilizer penetration.
- Nutrien Ltd.
- Yara International ASA
- CF Industries Holdings, Inc.
- SABIC Agri-Nutrients Company (Saudi Basic Industries Corporation)
- Koch Fertilizer, LLC (Koch Industries, Inc.)
- EuroChem Group AG
- OCI N.V.
- Coromandel International Limited (Murugappa Group)
- Indian Farmers Fertiliser Co-operative Limited
- Grupa Azoty S.A.
- Petronas Chemicals Group Berhad (Petroliam Nasional Berhad)
- Abu Qir Fertilizers and Chemical Industries Company
- PT Pupuk Indonesia (Persero)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
- 1.3 Research Methodology
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY AND KEY FINDINGS
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Acreage of Major Crop Types
- 4.1.1 Field Crops
- 4.1.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2 Average Nutrient Application Rates
- 4.2.1 Primary Nutrients
- 4.2.1.1 Field Crops
- 4.2.1.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2.1 Primary Nutrients
- 4.3 Agricultural Land Equipped For Irrigation
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.6 Market Drivers
- 4.6.1 Rising Demand for Staple Crops
- 4.6.2 Sustained Government Support for Agricultural Inputs
- 4.6.3 Diversification of Ammonia Supply Sources
- 4.6.4 Optimization of Urea Production Capacity
- 4.6.5 Acceleration of Green Ammonia Pilot Projects
- 4.6.6 Adoption of Digital Advisory Platforms for Nitrogen Use
- 4.7 Market Restraints
- 4.7.1 Volatility in Natural Gas Prices
- 4.7.2 Tightening Environmental Regulations
- 4.7.3 Logistical Bottlenecks in Fertilizer Trade
- 4.7.4 Emergence of Biological Nitrogen-Fixation Alternatives
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE AND VOLUME)
- 5.1 Product
- 5.1.1 Ammonium Nitrate
- 5.1.2 Anhydrous Ammonia
- 5.1.3 Urea
- 5.1.4 Others
- 5.2 Form
- 5.2.1 Conventional
- 5.2.2 Speciality
- 5.2.2.1 CRF
- 5.2.2.2 Liquid Fertilizer
- 5.2.2.3 SRF
- 5.2.2.4 Water Soluble
- 5.3 Application Mode
- 5.3.1 Fertigation
- 5.3.2 Foliar
- 5.3.3 Soil
- 5.4 Crop Type
- 5.4.1 Field Crops
- 5.4.2 Horticultural Crops
- 5.4.3 Turf & Ornamental
- 5.5 Region
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 Australia
- 5.5.1.2 Bangladesh
- 5.5.1.3 China
- 5.5.1.4 India
- 5.5.1.5 Indonesia
- 5.5.1.6 Japan
- 5.5.1.7 Pakistan
- 5.5.1.8 Philippines
- 5.5.1.9 Thailand
- 5.5.1.10 Vietnam
- 5.5.1.11 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 France
- 5.5.2.2 Germany
- 5.5.2.3 Italy
- 5.5.2.4 Netherlands
- 5.5.2.5 Russia
- 5.5.2.6 Spain
- 5.5.2.7 Ukraine
- 5.5.2.8 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.9 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Middle East
- 5.5.3.1 Turkey
- 5.5.3.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.3.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.4 Africa
- 5.5.4.1 South Africa
- 5.5.4.2 Nigeria
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.5 North America
- 5.5.5.1 Canada
- 5.5.5.2 Mexico
- 5.5.5.3 United States
- 5.5.5.4 Rest of North America
- 5.5.6 South America
- 5.5.6.1 Argentina
- 5.5.6.2 Brazil
- 5.5.6.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Nutrien Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Yara International ASA
- 6.4.3 CF Industries Holdings, Inc.
- 6.4.4 SABIC Agri-Nutrients Company (Saudi Basic Industries Corporation)
- 6.4.5 Koch Fertilizer, LLC (Koch Industries, Inc.)
- 6.4.6 EuroChem Group AG
- 6.4.7 OCI N.V.
- 6.4.8 Coromandel International Limited (Murugappa Group)
- 6.4.9 Indian Farmers Fertiliser Co-operative Limited
- 6.4.10 Grupa Azoty S.A.
- 6.4.11 Petronas Chemicals Group Berhad (Petroliam Nasional Berhad)
- 6.4.12 Abu Qir Fertilizers and Chemical Industries Company
- 6.4.13 PT Pupuk Indonesia (Persero)


















